human pose에 비해 동물에 대한 연구, 특히 생성쪽,는 찾기 쉽지 않습니다. 아마 데이터 부족이 큰 문제일 것이고, 그리고 아직 그런 연구나 상품에 대한 니즈가 많지 않아서도 주요 원인이지 않을까 싶습니다. 하지만, 글쎄요? 이후에 가상 펫이 생기거나 게임에서 동물이 아닌 다른 (괴)생명체의 모션이 필요할 때가 되면 분명 큰 역할을 할 것이라고 생각합니다. 어쩌면 저자들이 선구안을 가진 것이라고 저는 생각합니다.
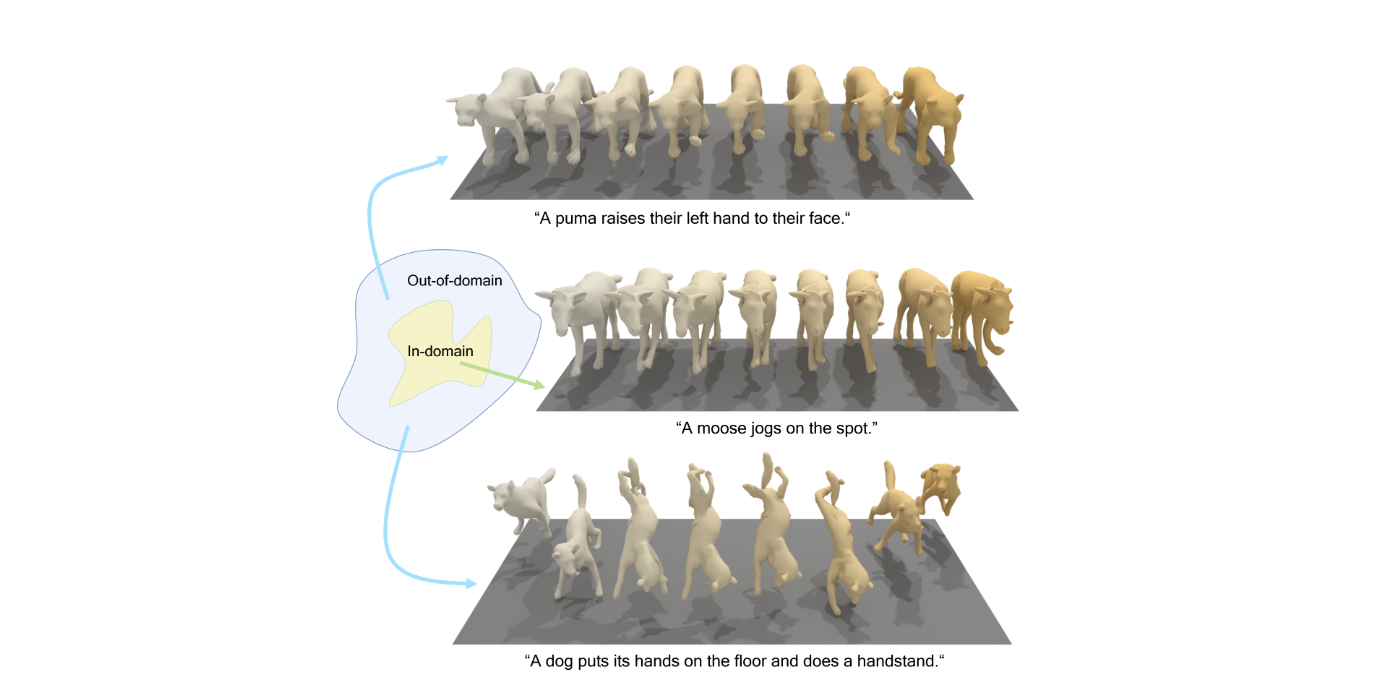
또 하나, 놀랐던 것은 동물이 하지 않을만한 행동까지도 고려했다는 것입니다. 예를 들어, 펀치를 하는 강아지는 실제 강아지들의 행동이 아니지만, 에니메이션을 보면 그 이상의 행동을 하지 않나요? 그래서 저자들의 연구에는 그런 행동들이 포함되어 있습니다. 예를 들어,"박수치는 고양이"같은 행동이요. 존경합니다... 이런 생각까지 하시다니...
물론 현재 project page가서 보면 결과가 아주 자연스럽지는 않습니다. 그래도 이런 연구들이 점차 많아지면서 가까운 미래에는 사람이외에 동물이나 그 이상의 것들의 모션도 높은 퀄리티를 보여줄 것이라고 기대합니다!!
https://zshyang.github.io/omgpt-website/
https://arxiv.org/html/2311.18303
Introduction
우선, 동물의 모션을 생성하는데에는 다음과 같은 문제들이 있다는 것을 지적합니다.
- 데이터 부족
- 인간과의 관절 수 및 정의 다름
- 동물 종류에 따른 골격 상이
- 동물의 현실적 모션과 우리가 생각하는 모션은 다름
- 강아지가 박수치는 것을 상상할 수 는 있으나, 실제로 강아지가 박수를 치는 경우는 드뭄
위와 같은 문제를 해결하기 위해서 저자들은 솔루션을 제시합니다.
- 강아지가 박수치는 것을 상상할 수 는 있으나, 실제로 강아지가 박수를 치는 경우는 드뭄
- 인간 모션 도메인의 지식(Knowledge)을 이전(transfer)하여 동물 모션 생성이 더 풍부하게
- transformer기반의 Motion Encoder를 통해 서로 다른 골격 모션을 기본 관절의 latent space로 투영하여 두 도메인간의 변환 가능
- 공통된 text 공간에 두 motion을 둬서 human motion modality, language space와 animal motion modality를 연결 (CLIP similarity loss 사용)
- 세가지 loss: atent consistency, CLIP similarity, end-effector loss
- AnimalML3D 제작(DeformingThings4D 데이터셋 중 animal mesh사용)
Method
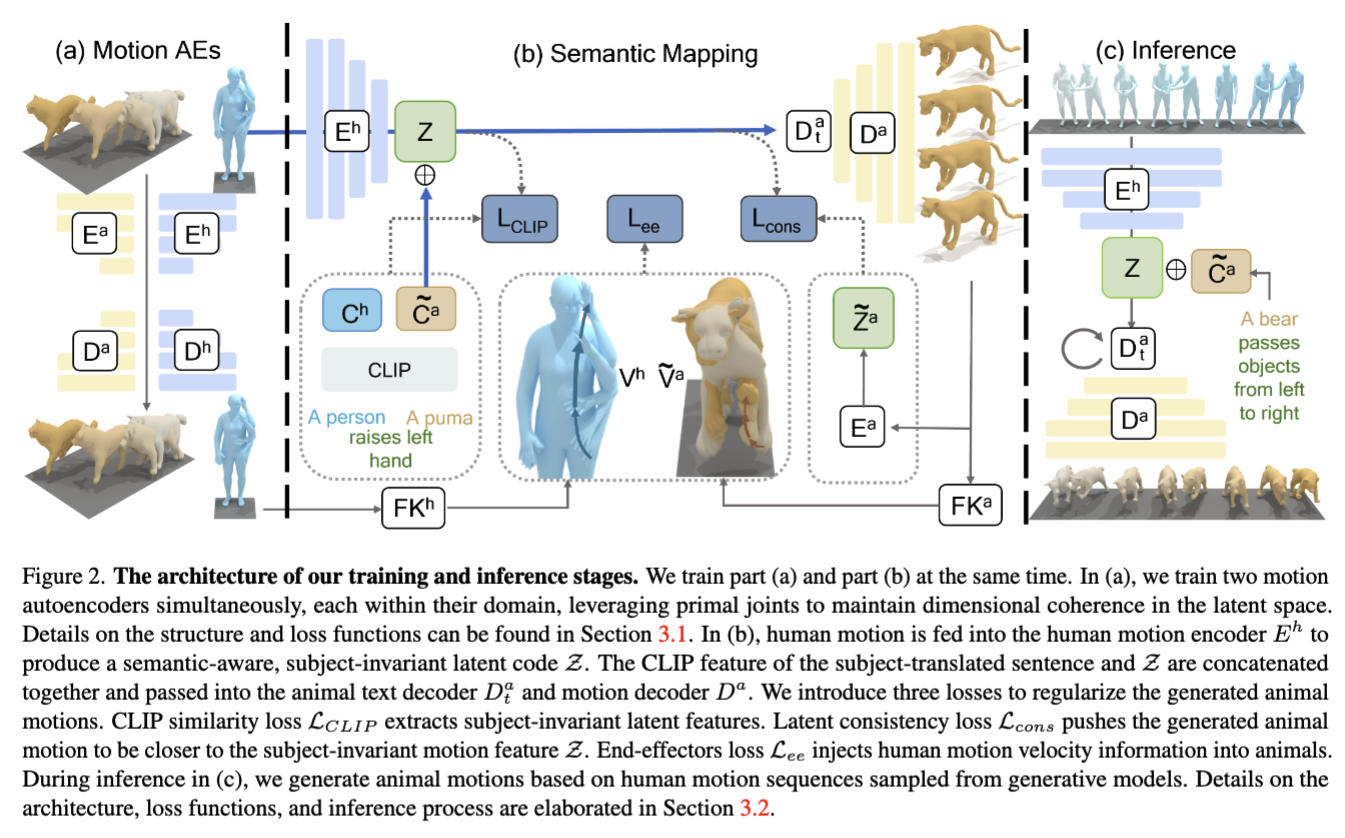
Integrating Joint and Text Awareness in Motion Autoencoders
Motion Representation
- 정적 요소(static feature) : 우리가 알고 있는 3D 위치
- 동적 요소(dynamic feature)
- global rotation
- global translation
- joint rotation (부모 joint에 상대적인)
- 동적 요소
- global translation을 차원 vector에 zero padding gn concat
- t시점의 poses 의 시퀀스
Joint-aware Motion Autoencoder
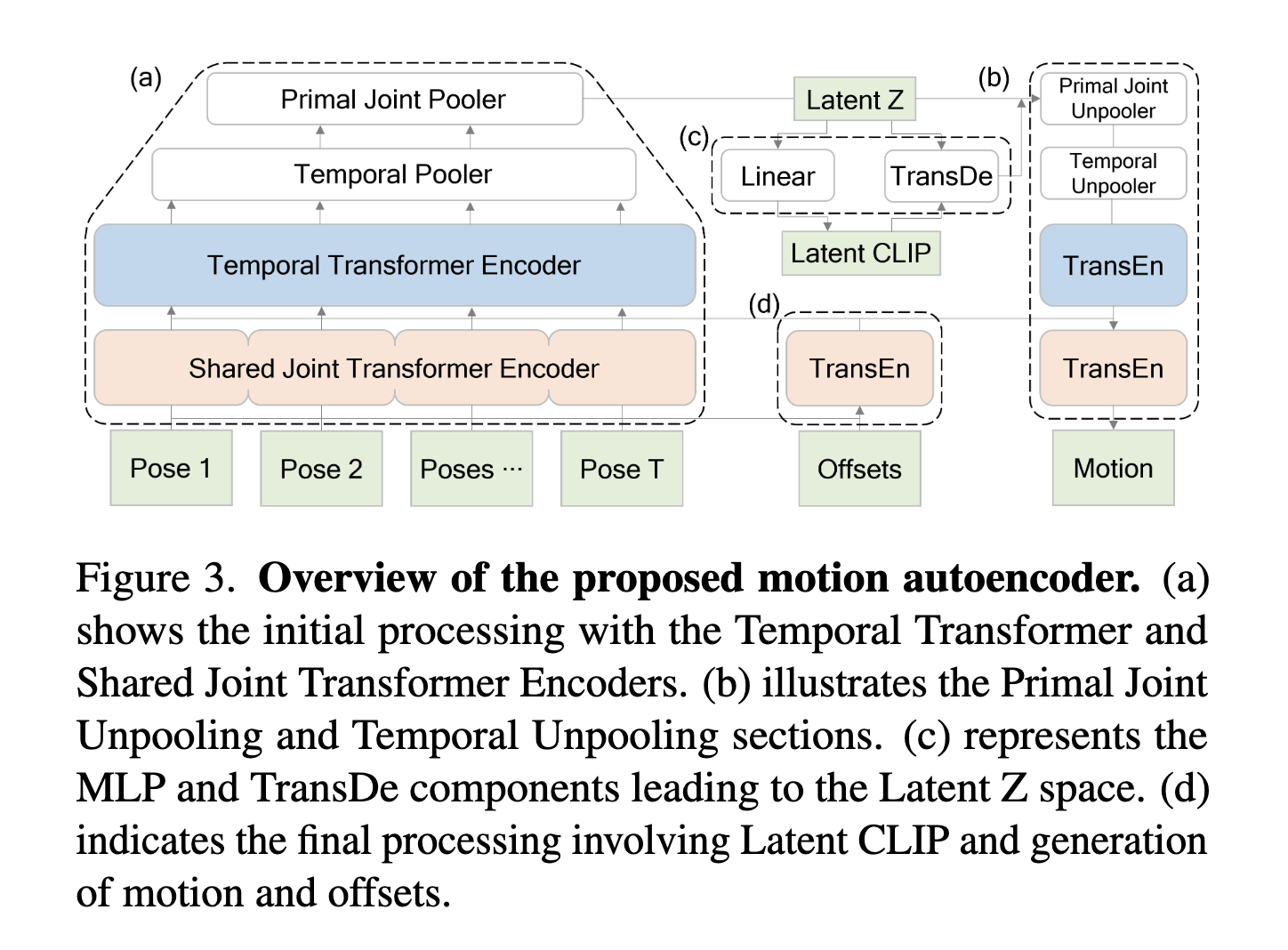
- 각 포즈에서 joint-level의 feature를 추론하는 transformer encoder
- 입력: 와 zero padding 적용된 의 concat
- 과정:
- Shared Joint Transformer Encoder: 각 포즈에 대해 feature 추출
- 같은 구조 offset에 대해서도 feature 추출
- Temporal Transformer Encoder: 시간적 특징 추출
- 1D pooling: temporal dimension reduction
- Primal Joint Pooling:서로 다른 골격 그래프에서 기본 관절을 균일하게 추출하여 잠재 특징 𝑍 생성
- : temporal 다운샘플링 비율
- : Primal Joint 개수
- temporal unpooling: Z를 𝑙 배만큼 복제
- joint unpooling: primal 관절이 아닌 위치에 0을 패딩
- 2개의 transformer encoder: 초기 인코딩 단계와 유사하게 temporal and joint dimensions에서 추가적인 정제(refinement)
- Shared Joint Transformer Encoder: 각 포즈에 대해 feature 추출
- 출력:
Text-aware Motion Autoencoder
- autoencoder에 text 정보를 넣어주기 위해 Cross-modal encoding과 decoding 방식을 개발
- latent vector 를 CLIP feature domain으로 인코딩
- : latent encoder
- latent decoder 를 사용하여, joint-aware lant space로 디코딩
- decoder는 CLIP feature와 latent vector 를 input으로 하는 casual attention 기반 transforemer
- 는 joint-aware decoder에 입력되어 생성
- latent vector 를 CLIP feature domain으로 인코딩
Training Objectives
- the reconstruction loss (joint-aware autoencoder)
- CLIP Similarity Loss
- CLIP Forward Reconstruction Loss
- LOSS
Semantic Mappings between Motion Autoencoders
Architecture
- 2개의 autoencoder
- human-focused model
- animal-focused model
- 를 통해 와 를 latent space 로 인코딩
- human motion description에서 주어를 동물의 이름으로 변경
- CLIP을 통해 각각의 desciption을 와 로 임베딩
- 이후, 동물 디코더 와 에 입력
- 중간에 동물의 정적 요소 와 결합
- 간단히 표현해서
Training Objectives
- CLIP loss
- 저자들의 이곳에서 목표는 인간 모션 데이터에서 주어(subject)와는 별개의 독립적인 action에 대한 latent feature 를 추출하는 것.
- 예를 들어, "한 사람이 달리고 있다"에서 추출되어야하는 latent feature 는 '달리기'의 개념만 있어야하고, '한 사람'은 없어야 함.
- 따라서, Joint-aware Motion Autoencoder의 CLIP loss이외에도, 주제를 동물로 바꿔서 얻는 CLIP 특징에 대한 loss도 필요
- 저자들의 이곳에서 목표는 인간 모션 데이터에서 주어(subject)와는 별개의 독립적인 action에 대한 latent feature 를 추출하는 것.
- Latent Consistency Loss
- framework안에서 latent feature의 정합성을 보장하기 위한 loss
- framework안에서 latent feature의 정합성을 보장하기 위한 loss
- End-Effectors Loss
- 인간에서 동물로 모션 변환 과정에서 skeleton의 end-effectors(말단)의 속도를 비교하여, kinematic 일관성 유지
- Cross-domain Motion Adaptation Loss
- entire framework
Inference
- text description을 로 변환
- 기존 인간 모션 생성 방식에서 얻은 motion을 를 통해 를 생성
- animal text decode 를 통해, 새로운 latent feature 샘플링
- 를 통해 동물 모션 생성
AnimalML3D
- 동물 언어-모션 데이터셋, 922 trainig pairs, 318 test pair data
- DeformingThings4D 확장, 31개 동물이나 humanoid 카테고리만 사용
- three descriptive captions
- 메쉬를 직접 만들어서 키포인트 결정
Experiments
- 데이터셋: AnimalML3D
- Metrics: MPJPE, FID, User Study
- Quantitative Motion Generation Comparison
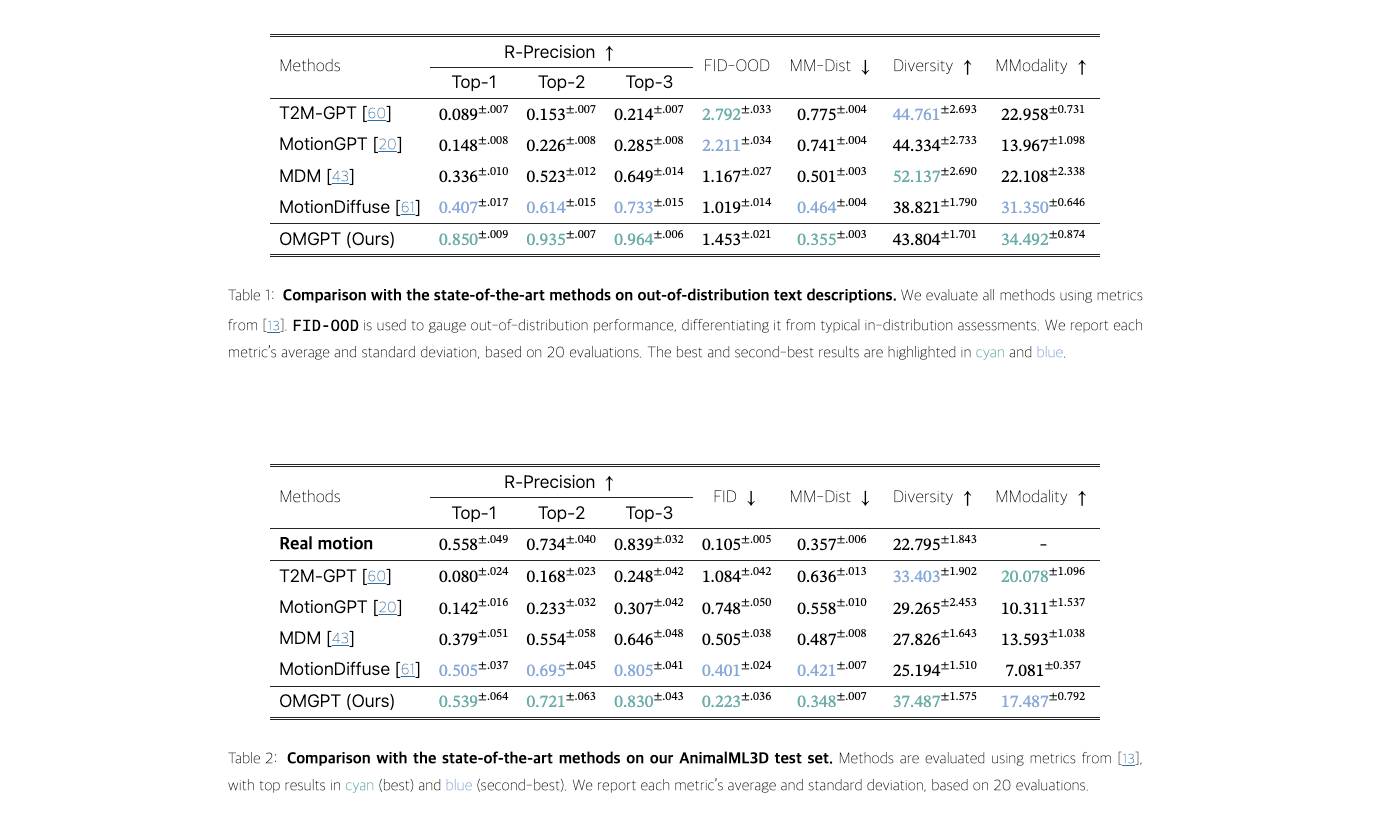
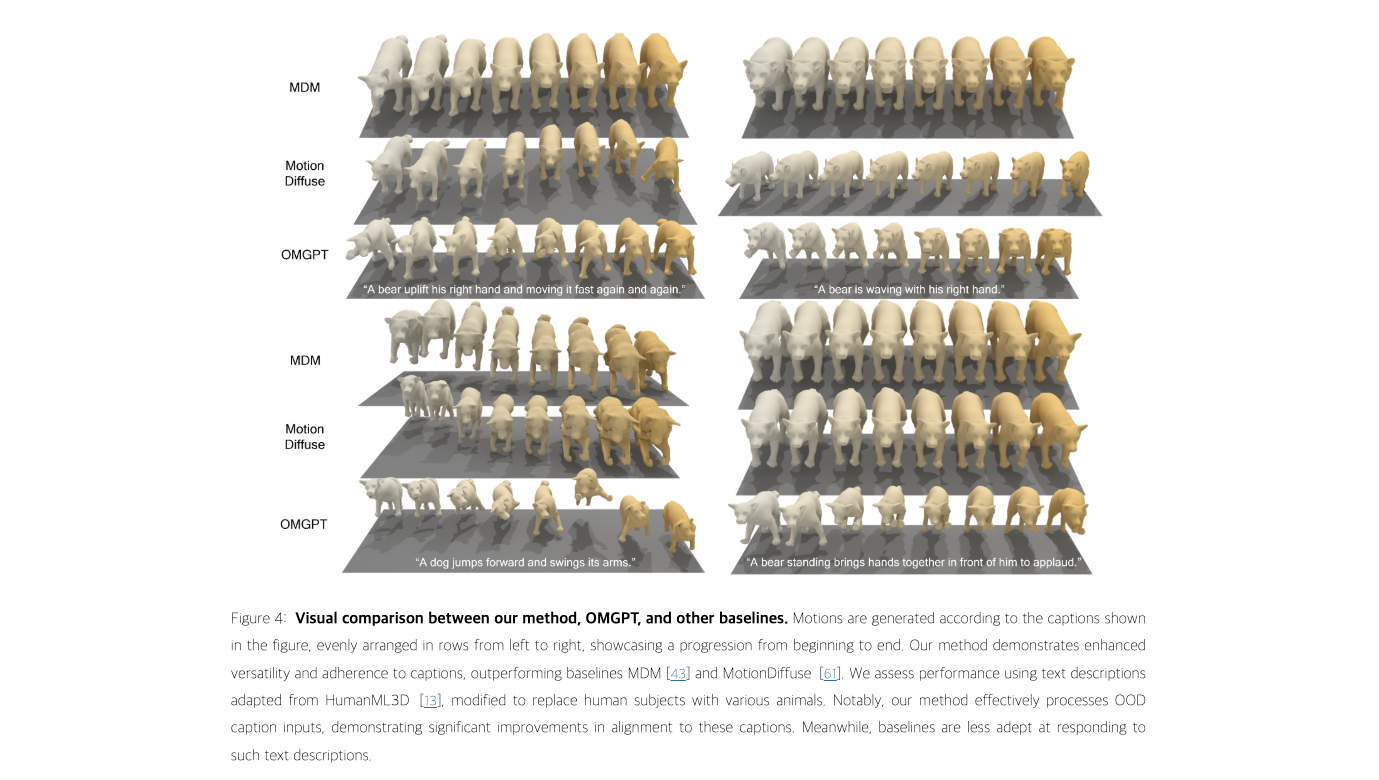
- Qualitative Motion Generation Analysis
Ablation study

