4-1. 들어가며
학습 목표
- 탠서 개념 학습
- 텐서 데이터 타입 학습
- 텐서 연산 수행
4-2. 텐서(Tensor)
텐서(Tensor)?
-
데이터를 담기 위한 컨테이너
-
다차원 배열 or 리스트와 유사
-
수치형 데이터 저장
-
동적 크기
-
용어
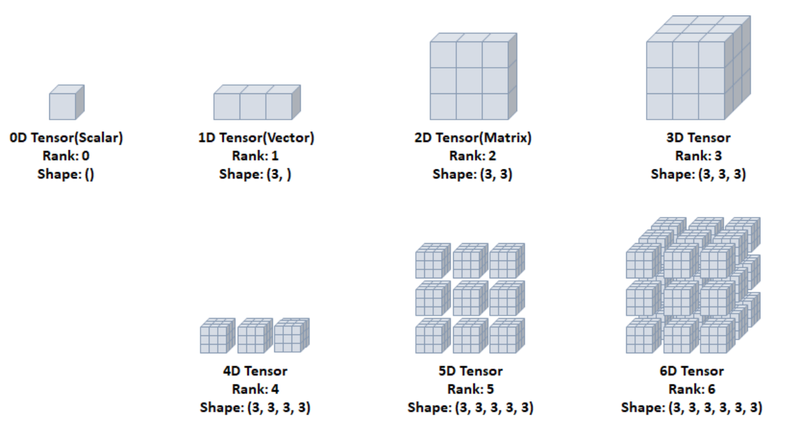
- Rank : 축(차원) 개수
- Shape: 형상(=각 축 요소 개수)
- Type: 데이터 타입
텐서 사용 방법
- TensorFlow import
import tensorflow as tf0D Tensor(Scalar)
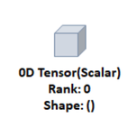
- 0차원 텐서
- 1개의 숫자를 담고 있는 텐서
- = scalar
- 축 및 형상 없음
tf.constant(): 상수 텐서- 텐서를 만들고
tf.rank()적용 : 축 개수(shape=() 부분으로 해석)
t0 = tf.constant(1)
print(t0)
print(tf.rank(t0))
1D Tensor(Vector)
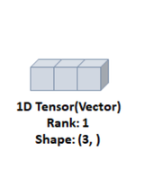
- 1차원 텐서
- 리스트와 유사
- = Vector
- 1개의 축 존재
t1 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
print(t1)
print(tf.rank(t1))
2D Tensor(Matrix)
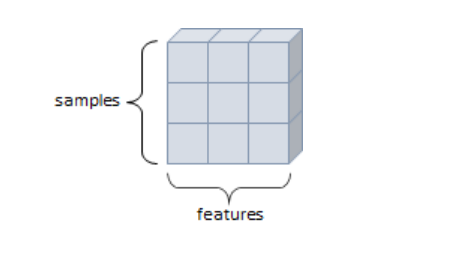
- 2차원 텐서
- 행렬
- 2개의 축
- 일반적 수치, 통계 데이터셋 해당
- samples, features 구조
t2 = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
print(t2)
print(tf.rank(t2))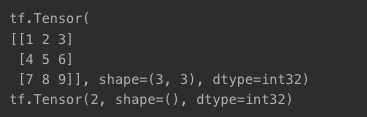
3D Tensor
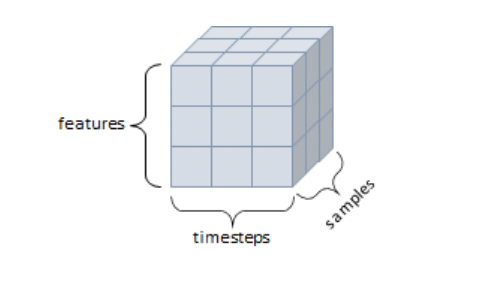
- 3차원 텐서
- 큐브 같은 형태
- 3개의 축
- 시퀀스 데이터(연속), 시계열 데이터(시간 축 포함)
- samples, timesteps, features 구조
- ex) 주식 가격, 시간에 따른 질병 발병 데이터 등
t3 = tf.constant([[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]],
[[10, 11, 12], [13, 14, 15], [16, 17, 18]],
[[19, 20, 21], [22, 23, 24], [25, 26, 27]]])
print(t3)
print(tf.rank(t3))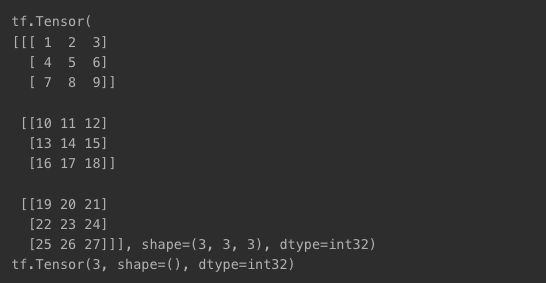
4D Tensor
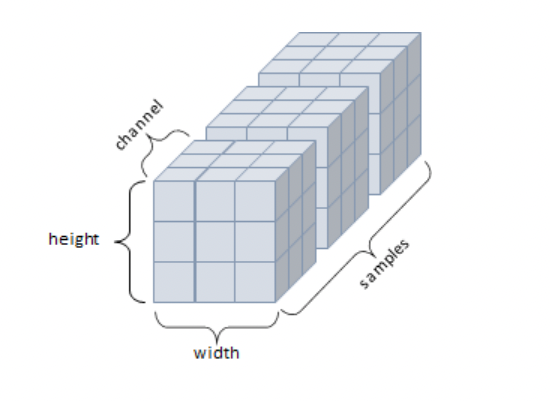
- 4차원 텐서
- 4개의 축
- 컬러 이미지(흑백의 경우 3D 텐서)
- samples, height, width, channel 구조
5D Tensor
- 5차원 텐서
- 5개의 축
- 비디오 데이터
- samples, frames, height, width, channel 구조
6D Tensor

- 6차원 텐서
- 6개의 축
- (3x3x3)이 다시 3x3x3으로 구성됨
...
4-3. 텐서 타입 및 변환
텐서 생성
- 상수값 2인 텐서 생성
- 타입 : int32
i = tf.constant(2)
print(i)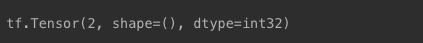
- 상수값 2.0
- 타입 : float32
f = tf.constant(2.)
print(f)
- 문자열
- 타입 : string
s = tf.constant('Suan')
print(s)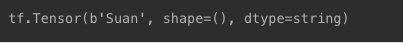
- 타입 지정도 가능
f16 = tf.constant(2., dtype=tf.float16)
print(f16)
i8 = tf.constant(2, dtype=tf.int8)
print(i8)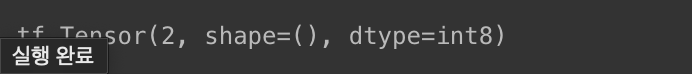
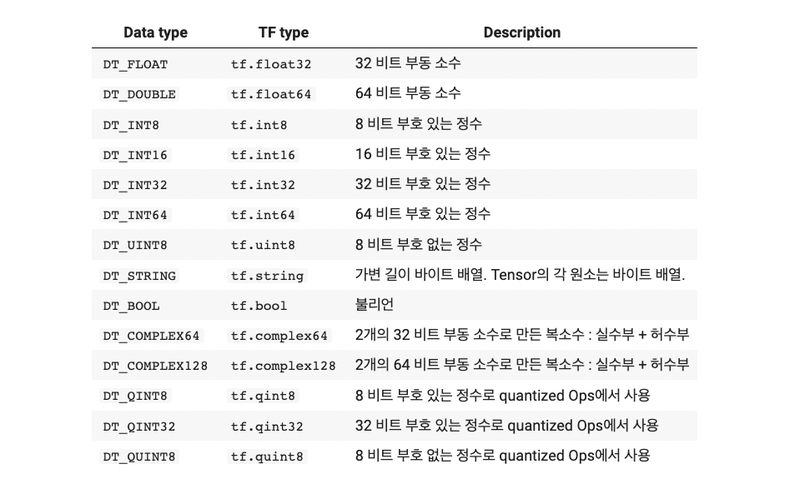
텐서 타입
- 기본 데이터 타입 : 정수형(int32), 실수형(float32), 문자열(string)
텐서 타입 변환: tf.cast
- 16비트 실수형 -> 32비트 실수형
f32 = tf.cast(f16, tf.float32)
print(f32) 
- 8비트 정수형 -> 32비트 정수형
i32 = tf.cast(i8, tf.int32)
print(i32)
텐서 형상 변환 : tf.reshape
- 원소 유지하며 텐서 구조만 바꿈
x = tf.constant([[1], [2], [3]])
print(x)
print(x.shape)
y = tf.reshape(x, [1, 3])
print(y)
print(y.shape)
텐서 전치 : tf.transpose
- 텐서를 전치해서 형상을 바꿈
print(y)
print(tf.transpose(y))
print(y.shape)
차원 압축 : tf.squeeze
- 텐서에서 크기가 1인 차원 제거
print(x)
print(tf.squeeze(x))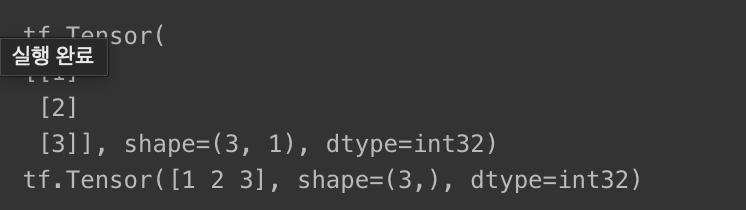
차원 추가 : tf.expand_dims
- 텐서의 차원 추가
- axis : 차원 확장 텐서 축을 지정해주는 역할
print(y)
print(tf.expand_dims(y, axis=0))
print(tf.expand_dims(y, axis=1))
print(tf.expand_dims(y, axis=2))
텐서 분리 : tf.split
- 텐서의 지정 차원 기준 -> 여러 개 텐서로 구분
# 텐서 x를 3개로 분리
print(x)
print(tf.split(x, 3))tf.Tensor(
[[1]
[2]
[3]], shape=(3, 1), dtype=int32)
[<tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 1), dtype=int32, numpy=array([[1]], dtype=int32)>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 1), dtype=int32, numpy=array([[2]], dtype=int32)>, <tf.Tensor: shape=(1, 1), dtype=int32, numpy=array([[3]], dtype=int32)>]텐서 연결 : tf.concat
- 축 axis를 기준으로 텐서 이어붙이기 가능
print(x)
print(tf.concat([x, x], axis=0))
print(tf.concat([x, x], axis=1))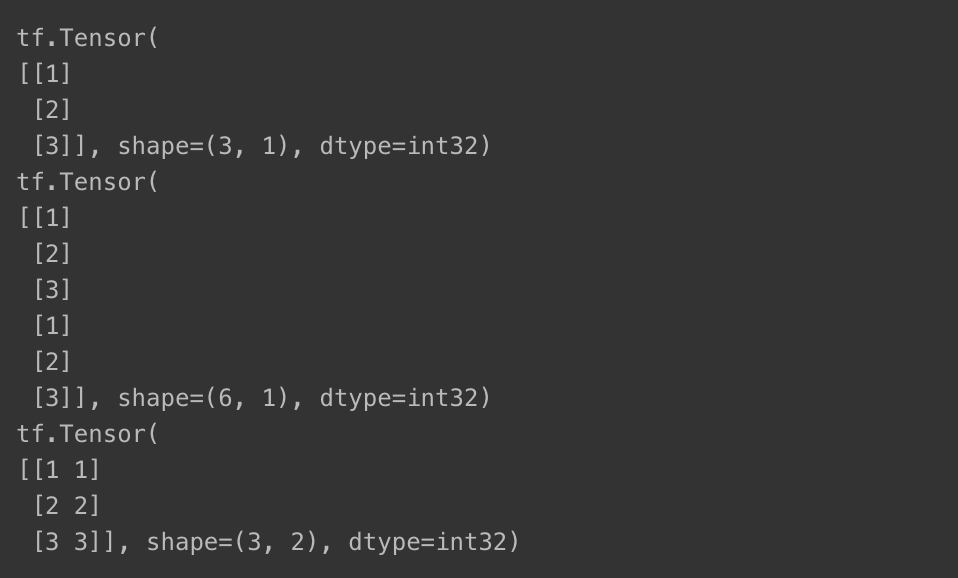
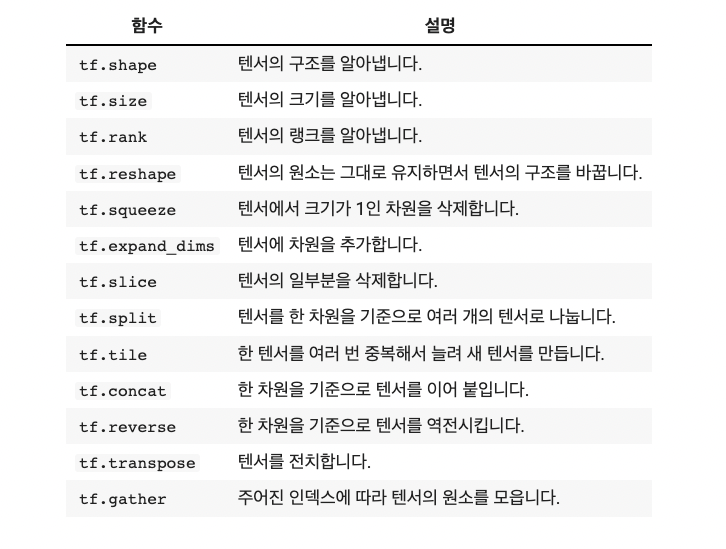
텐서 변환 함수
함수 활용해보기
tensor = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6]) # 1차원 텐서
reshaped_tensor = tf.reshape(tensor, [2, 3])
print("reshaped_tensor:", reshaped_tensor)
# tf.reduce_sum() : 합
sum_of_tensor = tf.reduce_sum(reshaped_tensor)
print("합:", sum_of_tensor)
# tf.reduce_mean() : 평균
mean_of_tensor = tf.reduce_mean(reshaped_tensor)
print("평균:", mean_of_tensor)
# tf.argmax() : 최대값의 인덱스
max_index = tf.argmax(reshaped_tensor, axis=1) # 행별 최대값 인덱스
print("행별 최대값 인덱스:", max_index)
# tf.equal() : 비교 (두 텐서가 동일한지)
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
b = tf.constant([1, 0, 3])
comparison_result = tf.equal(a, b)
print("두 텐서가 동일한지:", comparison_result)
4-4. 텐서 연산
텐서 연산

0차원 텐서 연산
- 더하기 & 빼기
print(tf.constant(2) + tf.constant(2))
print(tf.constant(2) - tf.constant(2))
print(tf.add(tf.constant(2), tf.constant(2)))
print(tf.subtract(tf.constant(2), tf.constant(2)))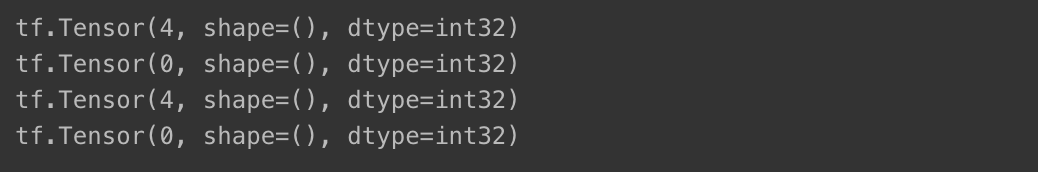
- 곱하기 & 나누기
print(tf.constant(2) * tf.constant(2))
print(tf.constant(2) / tf.constant(2))
print(tf.multiply(tf.constant(2), tf.constant(2)))
print(tf.divide(tf.constant(2), tf.constant(2)))
- 🚨 다른 타입은 연산 안됨
print(tf.constant(2) + tf.constant(2.2))InvalidArgumentError: cannot compute AddV2 as input #1(zero-based) was expected to be a int32 tensor but is a float tensor [Op:AddV2]- 타입 변환 후 사용 가능
print(tf.cast(tf.constant(2), tf.float32) + tf.constant(2.2))
1차원 이상 텐서 연산
- 연산이 되도록 형상을 맞추면 가능
1차원 텐서 연산
- 1차원 텐서 2개 생성
a = tf.constant([1,2,3])
b = tf.constant([4,5,6])
print(a)
print(b)
- 사칙연산
print(a+b)
print(a-b)
print(a*b)
print(b/a)
2차원 텐서 연산
- 2차원 텐서 생성
a = tf.constant([[1,2], [3,4]])
b = tf.constant([[5,6], [7,8]])
print(a)
print(b)
- 요소별 연산 수행
@: 행렬곱 연산
print(a + b) # element-wise addition
print(a - b) # element-wise subtraction
print(a * b) # element-wise multiplication
print(a @ b) # matrix multiplication
print(a / b) # element-wise division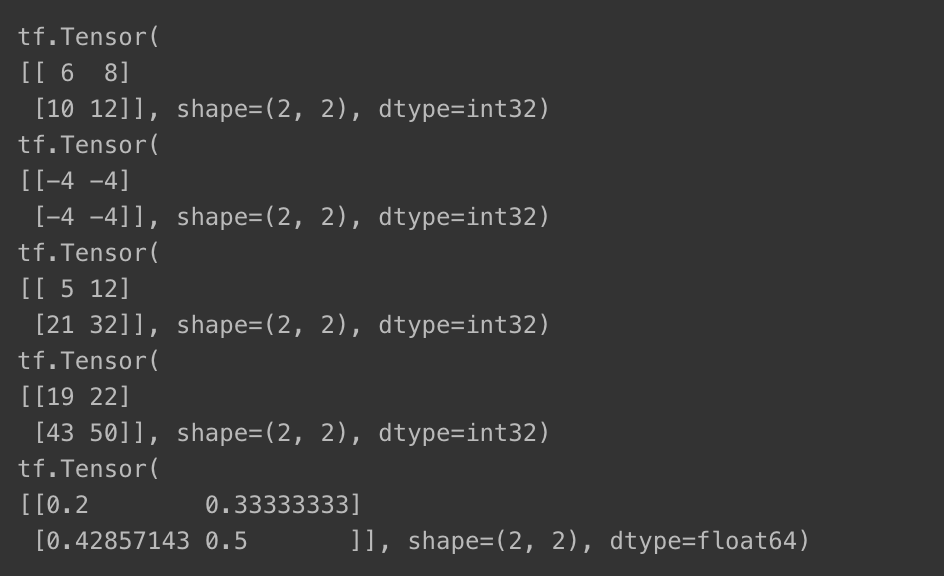
- 함수로도 연산 가능
print(tf.add(a, b))
print(tf.subtract(a, b))
print(tf.multiply(a, b))
print(tf.matmul(a, b))
print(tf.divide(a, b))
더 다양한 계산법
reduce_max(): 텐서 값 중 최댓값 계산argmax(): 최댓값 위치 반환nn.softmax(): 텐서 값을 0과 1 사이 값으로 보여줌
c = tf.constant([[4.0, 5.0, 6.0],
[10.0, 9.0, 8.0]])
print(tf.reduce_max(c))
print(tf.argmax(c))
print(tf.nn.softmax(c))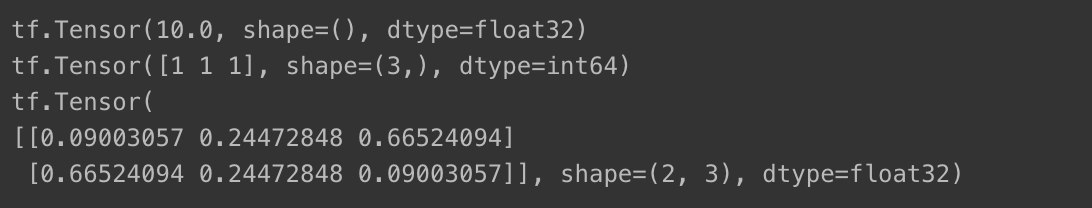
연산 활용
a = tf.constant([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]])
b = tf.constant([[7, 8, 9], [10, 11, 12]])
# 최대값과 인덱스 찾기
max_value = tf.reduce_max(a)
max_index = tf.argmax(a, axis=1)
print("\n최대값:", max_value)
print("행마다 최대값의 인덱스:\n", max_index)
# 텐서 비교
compare_result = tf.equal(a, b)
print("\n텐서 비교 결과 (a와 b):\n", compare_result)
# Broadcasting 연산
c = tf.constant([1, 2, 3])
broadcast_result = a + c
print("\nBroadcasting 연산 결과:\n", broadcast_result)
# Tensor Slicing
slice_result = a[:, 1:]
print("\nTensor Slicing 결과:\n", slice_result)
# 조건부 연산 : tf.where
condition = a > 3
where_result = tf.where(condition, a, tf.zeros_like(a))
print("\n조건부 연산 결과 (a > 3):\n", where_result)
4-4. 마치며
종합 문제
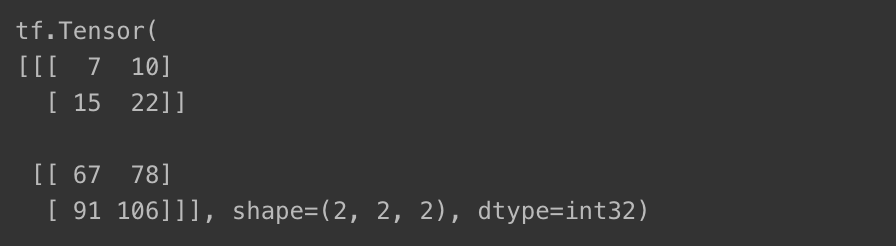
- 텐서를 각각 (2, 2, 2) 형태를 가진 3차원 텐서로 만들고, 행렬곱 연산 수행하기
a = tf.constant([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
b = tf.constant([[1., 2., 3., 4., 5., 6., 7., 8.]])
a = tf.reshape(a, [2, 2, 2])
b = tf.reshape(b, [2, 2, 2])
b = tf.cast(b, tf.int32)
print(a@b)