Matrix
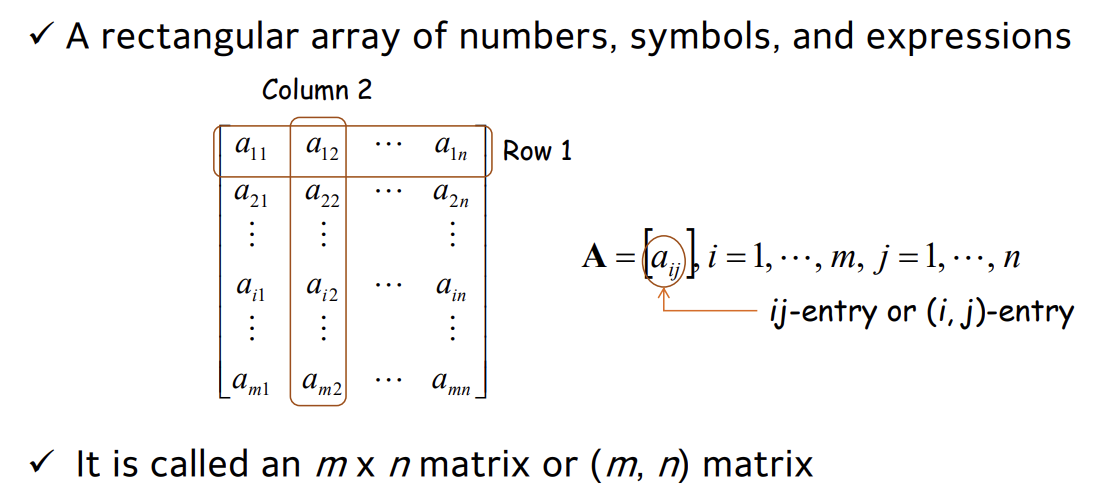
A nxm 일 때 n = Row, m = Column
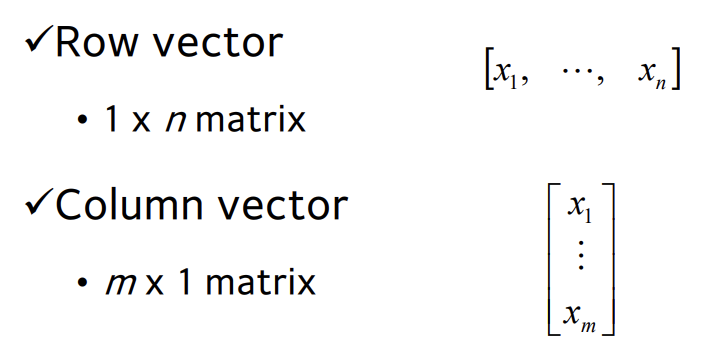
Square matrix
A matrix for which horizontal and vertical dimensions are the same: A n x n
- A matrix with n columns and n rows is called nth order square matrix
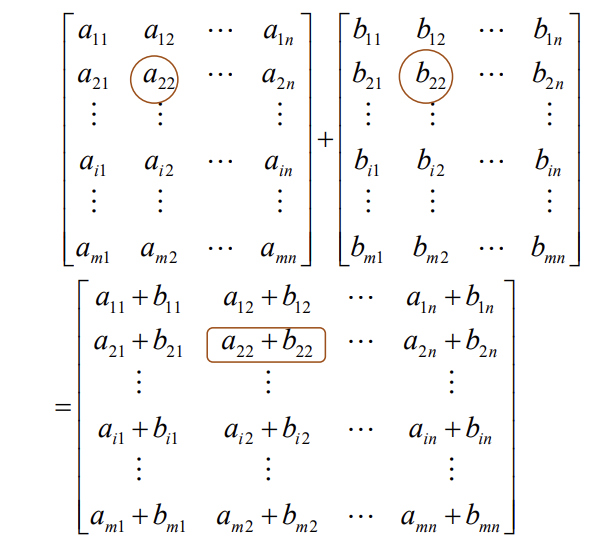
matrix addition
matrix multiplication
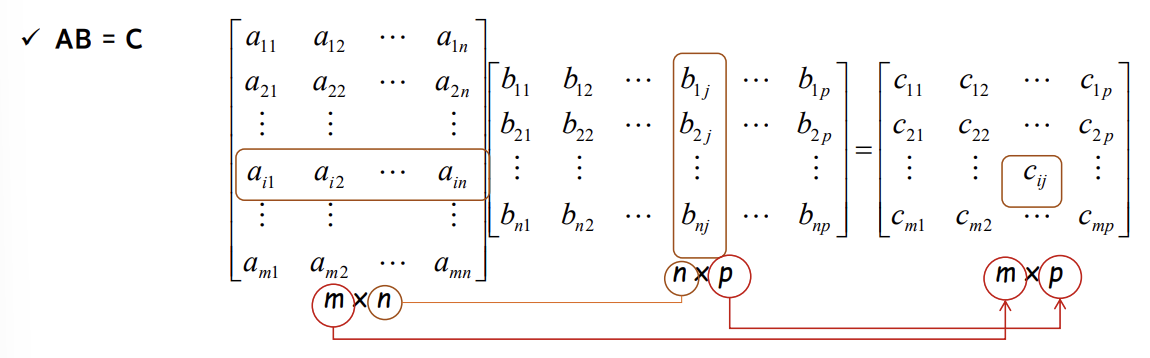
더하는거나 곱하는거나 일단 두 연산을 할 수 있는지? 를 확인해야함.
곱하는 위치는 중요.
A(BC) = (AB)C
A(B + C) = AB + AC
IA = A = AI
는 성립하지만, AB != BA 임.
Diagonal Matrix
우선 n X n square matrix 이어야 한다.
d ij 에서 i!=j 면 zero value.
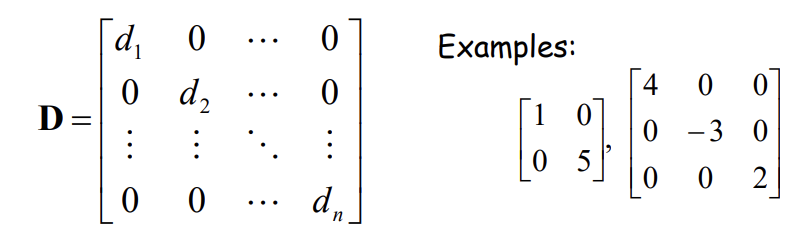
d1, d2 ... dn 이 0이어도 diagonal matrix이다.
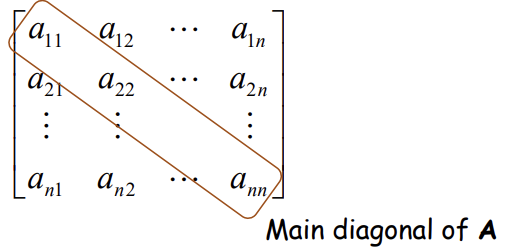
trace of Matrix
Sum of entries on the main diagonal of a square matrix A
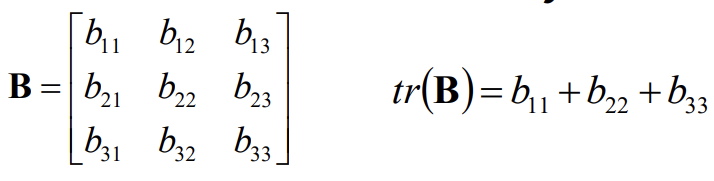
Nilpotent Matrix
If A^k = 0, when k is a positive number and A is a square but not zero matrix
-
The matrix A is nilpotent matrix
-
The smallest number k is the
nilpotencyof the matrix A -
Zero matrix는 Nilpotent Matrix라고 부르지 않는다
When the nth order square matrix A is a nilpotent matrix and k is a nilpotency
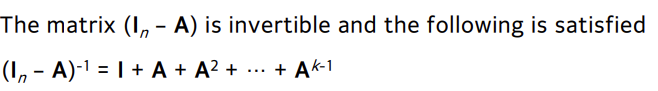
properties of trace of a matrix
Following equations are satisfied for matrices A and B
- A and B: square matrices with the same dimension

Identity Matrix
All diagonal entries of an n x n diagonal matrix is 1, then the matrix is called the identity matrix or the unit matrix

Zero Matrix
An m x n matrix consisting of all 0s
aij = 0 for i = 1, …, n and j = 1, …, m, A is called a zero matrix
Additive Inverse
- A + (-A) = 0
- The matrix –A is called the
additive inverseof the matrix A
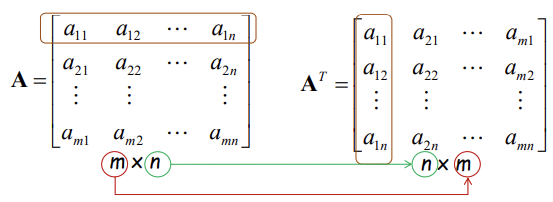
Transpose Matrix
For a m x n matrix A = [aij] and a n x m matrix B = [bij], if bij = aji, the matrix B is called the transpose of the matrix A and is written A^T
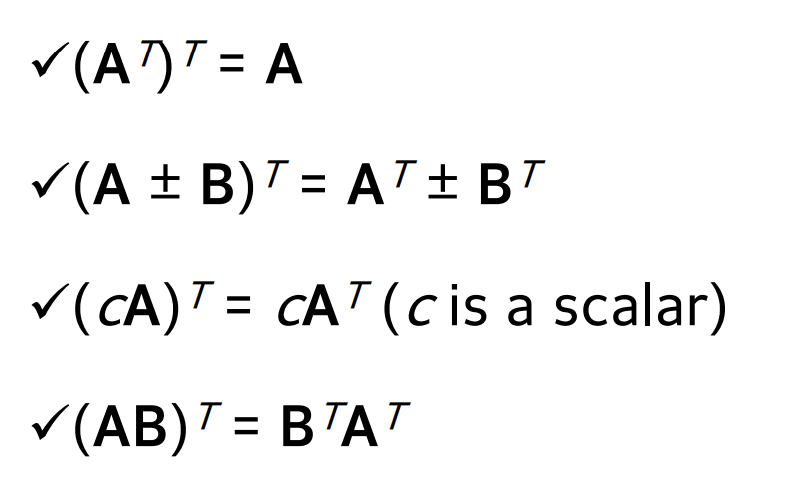
Symmetric Matrix
✓An n x n matrix A is called symmetric if A = A^T
✓In other words, aij = aji for all indices i and j in a matrix A = [aij]
Skewed - symmetric matrix
✓An n x n matrix A is called skew-symmetric if A = -A^T
✓In other words, aij = -aji for all indices i and j in a matrix A =[aij] and all diagonal entries of the matrix A are zero
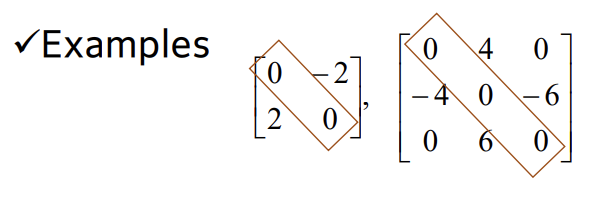
파이썬을 이용한 행렬 합 예제.
def main():
# 파일 경로
file_path = "C:/pythontest/input.txt"
toCalculateMatrices = [] # 계산할 행렬들
matrix = [] # 행렬에 관한 총 정보
try:
with open(file_path, 'r') as file:
lines = file.readlines()
except FileNotFoundError:
print("파일을 찾을 수 없습니다.")
exit()
i = 0 # 현재 읽고 있는 줄 인덱스
while i < len(lines):
num_matrices = int(lines[i].strip()) # 행렬 개수
i += 1 # 다음 줄로 이동
for _ in range(num_matrices):
matrix_name = lines[i].strip() # 행렬 이름
i += 1
rows, cols = map(int, lines[i].strip().split()) # 행과 열 개수
i += 1
matrix_data = []
for _ in range(rows):
row_data = list(map(int, lines[i].strip().split())) # 행 데이터
matrix_data.append(row_data)
i += 1
matrix.append({
'name': matrix_name,
'rows': rows,
'cols': cols,
'data': matrix_data
})
for m in matrix:
print(f"행렬 이름: {m['name']}")
print(f"행 수: {m['rows']}")
print(f"열 수: {m['cols']}")
print("행렬 데이터:")
for row in m['data']:
print(" ".join(map(str, row)))
print()
num_op = int(lines[i].strip())
i += 1
for _ in range(num_op):
j = 0
operand = lines[i].strip() # 연산 이름
i += 1
op_matrix = int(lines[i].strip()) # 연산에 사용되는 행렬 개수
i += 1
for p in range(len(lines[i])):
if p % 2 == 0:
toCalculateMatrices.append(lines[i][p]) # 한 라인에서 짝수번재 인덱스가 행렬이니..(홀수는 공백)
i += 1
if operand == 'Add': #덧셈 연산 수행 시
operand_matrices = []
result_matrix = []
for m in matrix:
for t in toCalculateMatrices: # 모든 행렬을 담은 matrix 과 계산할 행렬을 담은 toCalculateMatrices 바교
if m['name'] == t: # 같은 걸 찾았다면 연산 수행할 operand_matrices 배열에 추가(행, 열, 데이터)
operand_matrices.append({
'rows' : m['rows'],
'cols' : m['cols'],
'data' : m['data']
})
result_matrix.append({
'rows' : operand_matrices[0]['rows'],
'cols' : operand_matrices[0]['cols'],
'data' : operand_matrices[0]['data']
})
# 결과를 담을 배열을 openand_matrices[0] 으로 초기화
# 위에서 행, 열을 받은 이유는 모든 연산이 마찬가지로 행과 열을 따져서 계산이 우선 가능한지 따져봐야하기 때문
# 계산할 행렬을 담은 배열 사이즈가 입력했던 계산할 행렬 개수와 같을 경우
if len(toCalculateMatrices) == op_matrix:
for k in range(op_matrix): # 행과 열이 다르다면 리턴
if(operand_matrices[k]['rows'] != result_matrix[0]['rows']) or (operand_matrices[k]['cols'] != result_matrix[0]['cols']):
print("Error : Size is different")
return
for k in range(1, op_matrix): #행과 열 각각 더해주기. result배열에 계속 더해짐
for row in range(operand_matrices[0]['rows']):
for col in range(operand_matrices[0]['cols']):
result_matrix[0]['data'][row][col] += operand_matrices[k]['data'][row][col]
# 파일 출력
nf = open("output.txt", 'w')
nf.write(operand + " ")
for x in toCalculateMatrices:
nf.write(x + " ")
nf.write("\n")
nf.write("행렬 합:\n")
for row in range(result_matrix[0]['rows']):
for col in range(result_matrix[0]['cols']):
nf.write(str(result_matrix[0]['data'][row][col]))
nf.write(" ")
nf.write("\n")
nf.close()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()