😊들어가면서😊
빈 스코프에 대해서 알아보자.
오늘은 9강을 마저 듣고. HTTP 통신 책을 공부할 생각이다.
내가 행복했으면 좋겠다.🍀 🎯 목표
📌 빈 스코프란
📌 📌 빈 스코프란?
- 스프링 빈이 존재하는 범위를 말한다.
지금까지는 스프링 빈이 스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 함께 생성되어서 스프링 컨테이너가
종료될 때까지 유지되는 것을 보았는데 이는 "싱글톤 스코프"의 특성이다.📒 빈 스코프의 종류
✔️ 싱글톤
기본 스코프, 스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 종료까지 유지되는 가장 넓은 범위의 스코프이다.
✔️ 프로토 타입
스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈의 생성과 의존관계 주입까지만 관여하고 더는 관리하지 않는 매우 짧은 범위의 스코프이다.
➡️ 빈 생성 , 의존관계 주입, 초기화까지만 보장!
✔️ 웹 관련 스코프
스프링 웹과 관련한 기능이 들어가야 사용할 수 있다.
request: 웹(고객) 요청이 들어오고 나갈때 까지 유지되는 스코프이다.
session: 웹 세션이 생성되고 종료될 때 까지 유지되는 스코프이다.
application: 웹의 서블릿 컨텍스트와 같은 범위로 유지되는 스코프이다.
📒 빈 스코프 지정 방법
- 빈위에
@Scope( )를 통해 적으면 된다.
1. 컴포넌트 스캔 자동 등록
@Scope("prototype")
@Component
public class HelloBean {}2. 수동 등록 방법
@Scope("prototype")
@Bean
PrototypeBean HelloBean() {
return new HelloBean(); //수동 빈 등록 방법이라서 생성자 사용
}📌 싱글톤 빈 스코프
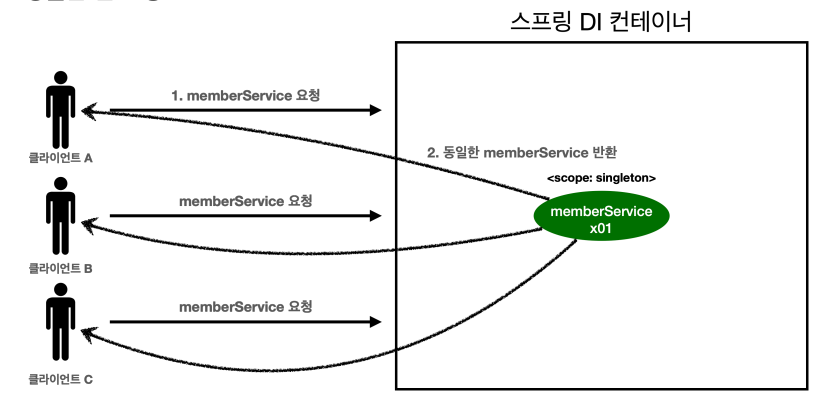
📒 싱글톤 빈 요청
- 싱글톤 스코프의 빈을 조회 ➡️ 항상 같은 인스턴스의 스프링 빈 반환
- 싱글톤 스코프의 빈을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 관리하고 있던 스프링 빈을 반환한다.
- 이후에도 동일한 스프링 빈을 반환한다.
예제코드
public class SingletonTest {
@Test
void singletonBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean1 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
System.out.println("singletonBean1 = " + singletonBean1);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
assertThat(singletonBean1).isSameAs(singletonBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("singleton") // 디폴트이긴 함
static class SingletonBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("SingletonBean.init");
}
@PreDestroy
private void destroy() {
System.out.println("SingletonBean.destroy");
}
}
}
💻 실행화면
@PostConstruct,@PreDestroy애노테이션을 통해 초기화와 소멸 메소드를 지정해줌
✔️ 초기화와 소멸 메소드가 정상 실행된 것을 확인 할 수 있음.- 싱글톤 프로토 타입으로 동일한 객체가 반환되는 것을 확인할수 있음
SingletonBean.init
singletonBean1 = hellospring.demo.scope.SingletonTest$SingletonBean@6f53b8a
singletonBean2 = hellospring.demo.scope.SingletonTest$SingletonBean@6f53b8a
SingletonBean.destroy📌 프로토타입 스코프
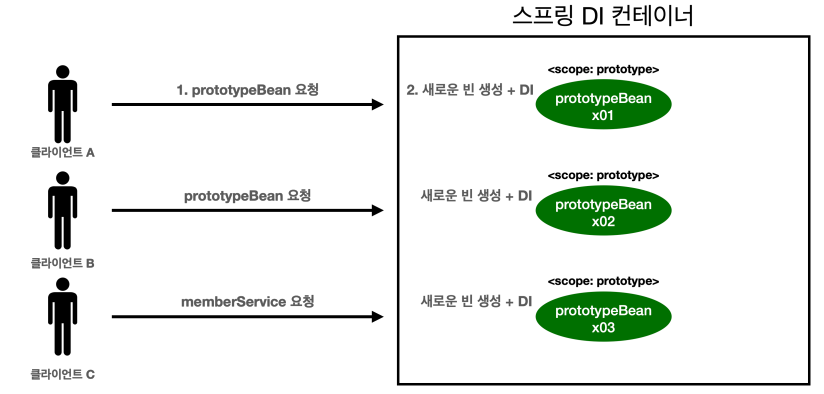
- 프로토타입 스코프의 빈을 조회 ➡️ 항상 새로운 인스턴스를 생성해서 반환
📒 프로토타입 빈 요청
- 클라이언트가 프로토타입의 스코프 빈을 요청했을 때❗프로토 타입 빈을 생성하고, 필요한 의존관계를 주입하고, 초기화 메시지
- 스프링 컨테이너는 생성한 프로토타입 빈을 클라이언트에 반환한다.
- 이후에 스프링 컨테이너에 같은 요청이 오면 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈을 생성헤서 반환한다.
⭐ 정리
스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈에 대해서 다음을 처리한다.
- 프로토타입 빈 생성
- 의존관계 주입
- 초기화처리
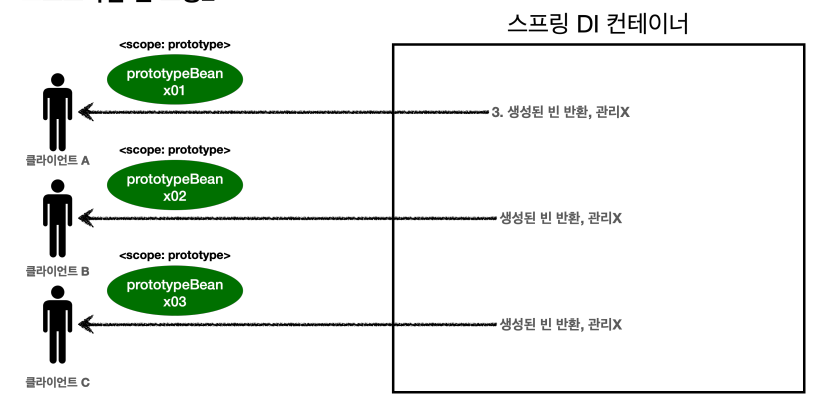
→ 스프링 컨테이너는 생성된 프로토타입 빈을 관리하지 않는다.
→ 프로토타입 빈을 관리할 책임은 프로토타입 빈을 받은 클라이언트에 있다.
👉 그래서 @PreDestroy같은 종료 메서드가 호출되지 않는다.
예제코드
public class PrototypeTest {
@Test
void prototypeBaenFing() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean1");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("find prototypeBean2");
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println("prototypeBean1 = " + prototypeBean1);
System.out.println("prototypeBean2 = " + prototypeBean2);
assertThat(prototypeBean1).isNotSameAs(prototypeBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init");
}
@PreDestroy
private void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy");
}
}
}💻 실행결과
- 클라이언트가 호출했을 때 빈이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
→PrototypeBean.init - 서로 다른 스프링 빈 호출
- 종료메서드는 호출되지 않는다.
find prototypeBean1
PrototypeBean.init
find prototypeBean2
PrototypeBean.init
prototypeBean1 = hellospring.demo.scope.PrototypeTest$PrototypeBean@4d1bf319
prototypeBean2 = hellospring.demo.scope.PrototypeTest$PrototypeBean@6f53b8a📒 예제코드 정리
-
싱글톤 빈은 스프링 컨테이너 생성 시점에 초기화 메서드가 실행 되지만, 프로토타입 스코프의 빈은 스프링 컨테이너에서 빈을 조회할 때 생성되고, 초기화 메서드도 실행된다.
-
프로토타입 빈을 2번 조회했으므로 완전히 다른 스프링 빈이 생성되고, 초기화도 2번 실행된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
-
싱글톤 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하기 때문에 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때 빈의 종료 메서드가 실행되지만,프로토타입 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 생성과 의존관계 주입 그리고 초기화 까지만 관여하고, 더는 관리하지 않는다.
-
따라서 프로토타입 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때 @PreDestroy 같은 종료 메서드가 전혀 실행되지 않는다.
➡️ 직접 종료메서드를 호출해야한다.
prototypeBean1.destroy();
prototypeBean2.destroy();🤔 문제점
프로토 타입은 자주 사용하지 않고, 싱글톤을 주로 사용하게 되는데 그러면,
싱글톤과 함께 쓰게 된다. 그럴때 발생하는 문제점이 있다. 문제점을 알아보자.🔍 프로토타입을 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용시 문제점
⚠️ 경고
싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용할 때는 의도한 대로 잘 동작하지 않는다.
상황 1. 프로토타입 빈 직접 요청
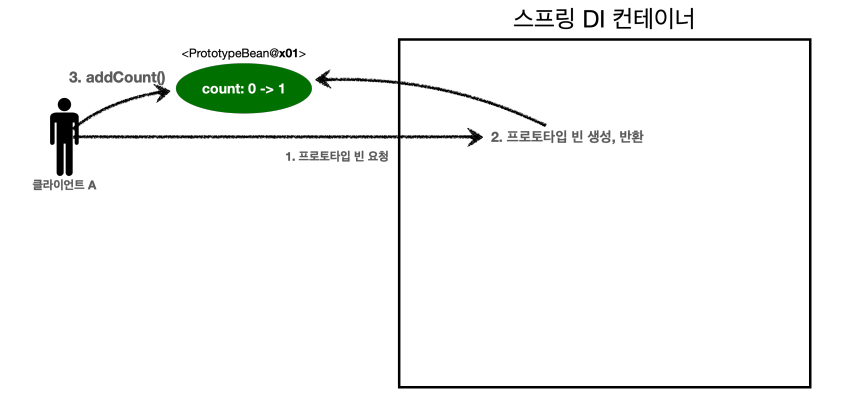
- 클라이언트A는 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 새로 생성해서 반환(x01)한다.
해당 빈의 count 필드 값은 0이다. - 클라이언트는 조회한 프로토타입 빈에 addCount() 를 호출하면서 count 필드를 +1 한다.
➡️ 결과적으로 프로토타입 빈(x01)의 count는 1이 된다.
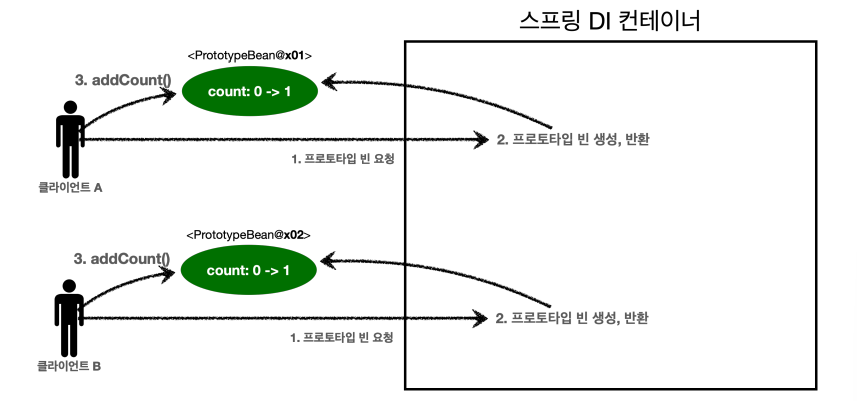
- 클라이언트B는 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 새로 생성해서 반환(x02)한다.
해당 빈의 count 필드 값은 0이다. - 클라이언트는 조회한 프로토타입 빈에 addCount() 를 호출하면서
count필드를 +1 한다.
➡️ 결과적으로 프로토타입 빈(x02)의 count는 1이 된다
- B 프로토타입 빈은 2개가 존재하고 카운트는 둘다 1,1이다.
해당 예제코드
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest1 {
@Test
void prototypeFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
PrototypeBean prototypeBean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean1.addCount();
assertThat(prototypeBean1.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
PrototypeBean prototypeBean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean2.addCount();
assertThat(prototypeBean2.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init" + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy");
}
}
}상황 2. 싱글 톤 빈에서 프로토타입 빈 사용
<싱글톤 빈이 의존관계 주입을 통해서 프로토타입 빈을 주입받아서 사용하는 예>
- 의존관계 자동 주입을 사용하는 싱글톤 빈
clientBean이 프로토타입 빈인prototypeBean을 가진다. - 주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토 타입 빈을 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성해서 반환한다. 이후 관리하지 않는다.
- 싱글톤 빈
clientBean은 내부 필드에 프로토타입 빈prototypeBean의 참조값을 가진다.
-
클라이언트 1이 스프링 컨테이너에
clientBean을 요청한다. -
클라이언트 1이
clientBean.logic()를 호출한다.
➡️prototypeBean의 addCount()실행
➡️ +1된 프로토타입 빈의count반환
✔️실행결과= 1 -
클라이언트 2이 스프링 컨테이너에
clientBean을 요청한다.
✔️clientBean은 싱글톤으로 스프링 컨테이너는 아까와 같은 동일한 인스턴스를 반환한다.
⭐ clientBean이 내부에 가지고 있는 프로토타입 빈은 이미 과거에 주입이 끝난 빈이다. -
클라이언트 2이
clientBean.logic()를 호출한다.
➡️prototypeBean의 addCount()실행
➡️ +1된 프로토타입 빈의count반환
✔️실행결과≠ 1
→ 실제 실행결과 = 1
해당 예제코드
@Test
void singletonClientUsePrototype(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ClientBean.class, PrototypeBean.class);
ClientBean client1 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count1 = client1.logic();
assertThat(count1).isEqualTo(1);
ClientBean client2 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count2 = client2.logic();
assertThat(count2).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
private final PrototypeBean prototypeBean;
@Autowired
ClientBean(PrototypeBean prototypeBean) {
this.prototypeBean = prototypeBean;
}
public int logic() {
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
}💻 실행화면
count1 = 1
count2 = 2📒 정리
싱글톤빈에서 등록을 할 때 의존관계를 주입한다.
✔️ 이때 프로토타입 빈이 생성이 되고, 할당이 된다.
➡️ 이후 클라이언트 1,2가 logic을 호출할 때 할당되었던 동일한 프로토타입빈을 가진다.
⭐주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 프로토타입 빈이 새로 생성이 된 것이지, 사용 할 때마다 새로 생성되는 것이 아니다!
여러 빈에서 같은 프로토타입 빈을 주입 받으면, 주입 받는 시점에 각각 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성된다. 예를 들어서 clientA, clientB가 각각 의존관계 주입을 받으면 각각 다른 인스턴스의 프로토타입 빈을 주입 받는다.
🤔 우리가 원하는 것은..?
사용할 때 마다 새로 생성해서 사용하고 싶었는데...🔨 문제 해결 - Provider
1. 스프링 컨테이너에 요청
- 싱글톤 빈이 프로토타입을 사용할 때마다 스프링 컨테이너에 새로 요청하는 것이다.
예제코드
- 실행해보면 ac.getBean() 을 통해서 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
@Autowired
ApplicationContext ac;
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean prototypeBean = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
}Dependency Lookup(DL) 의존관계 조회
- 의존관계를 외부에서 주입(DI) 받는게 아니라 이렇게 직접 필요한 의존관계를 찾는 것
➡️ 그런데 이렇게 스프링의 애플리케이션 컨텍스트 전체를 주입받게 되면,
스프링 컨테이너에 종속적인 코드가 되고,단위 테스트도 어려워진다.🤔 지금 필요한 기능은 지정한 프로토타입 빈을 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는 딱! DL 정도의 기능만 제공하는 무언가가 있으면 된다.
2. ObjectFactory, ObjectProvider 사용
⚒️ ObjectProvider는 지정한 빈을 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는 DL 서비스를 제공한다.
특징
- ObjectFactory: 기능이 단순, 별도의 라이브러리 필요 없음, 스프링에 의존
- ObjectProvider: ObjectFactory 상속, 옵션, 스트림 처리등 편의 기능이 많다.
- 별도의 라이브러리 필요 없음,
- 스프링에 의존
예제코드
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest1 {
@Test
void singletonClientUsePrototype(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ClientBean.class, PrototypeBean.class);
ClientBean client1 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count1 = client1.logic();
assertThat(count1).isEqualTo(1);
System.out.println("count1 = " + count1);
ClientBean client2 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count2 = client2.logic();
System.out.println("count2 = " + count2);
assertThat(count2).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
@Autowired
private ObjectProvider<PrototypeBean> prototypeBeansProvider;
//⚒️ ObjectProvider는 지정한 빈을 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는
// DL 서비스를 제공한다.
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean prototypeBean = prototypeBeansProvider.getObject();
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init : " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy");
}
}
}
💻 실행코드
- 각기 다른 PrototypeBean을 주입
ObjectProvider 의 getObject()를 호출하면 내부에서는 스프링 컨테이너를 통해 해당 빈을 찾아서 반환한다. (DL)- 스프링이 제공하는 기능을 사용하지만, 기능이 단순하므로 단위테스트를 만들거나 mock 코드를 만들기는 훨씬쉬워진다.
PrototypeBean.init :
hellospring.demo.scope.SingletonWithPrototypeTest1$PrototypeBean@6b09fb41
count1 = 1
PrototypeBean.init :
hellospring.demo.scope.SingletonWithPrototypeTest1$PrototypeBean@23202fce
count2 = 1➕ ObjectFactory vsObjectProvider
ObjectFactory 가 있었는데, 여기에 편의 기능을 추가해서 ObjectProvider 가 만들어졌다.
3. JSR-330 Provider 사용
javax.inject.Provider 라는 JSR-330자바 표준을 사용하는 방법이다.
➕ 이를 사용하기 위해서는 다음 라이브러리는 gradle에 추가해야한다.
스프링부트 3.0
javax.inject:javax.inject:1
스프링부트 3.0
jakarta.inject:jakarta.inject-api:2.0.1
스프링 부트 3.0
jakarta.inject.Provider📒 특징
- get() 메서드 하나로 기능이 매우 단순하다.
- 별도의 라이브러리가 필요하다.
- 자바 표준이므로 스프링이 아닌 다른 컨테이너에서도 사용할 수 있다.
예제코드
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest {
@Test
void singletonClientUsePrototype(){
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac =
new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(ClientBean.class, PrototypeBean.class);
ClientBean client1 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count1 = client1.logic();
assertThat(count1).isEqualTo(1);
System.out.println("count1 = " + count1);
ClientBean client2 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count2 = client2.logic();
System.out.println("count2 = " + count2);
assertThat(count2).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
@Autowired
private Provider<PrototypeBean> prototypeBeansProvider;
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean prototypeBean = prototypeBeansProvider.get();
prototypeBean.addCount();
return prototypeBean.getCount();
}
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.init : " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean.destroy");
}
}
}💻 실행화면
- 실행해보면 provider.get() 을 통해서 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
provider의get()을 호출하면 내부에서는 스프링 컨테이너를 통해 해당 빈을 찾아서 반환한다. (DL)- 자바 표준이고, 기능이 단순하므로 단위테스트를 만들거나 mock 코드를 만들기는 훨씬 쉬워진다.
Provider는 지금 딱 필요한 DL 정도의 기능만 제공한다.
PrototypeBean.init : hellospring.demo.scope.SingletonWithPrototypeTest$PrototypeBean@479cbee5
count1 = 1
PrototypeBean.init : hellospring.demo.scope.SingletonWithPrototypeTest$PrototypeBean@1c852c0f
count2 = 1🤔 프로토타입 빈을 언제 사용할까?
매번 사용할 때 마다 의존관계 주입이 완료된 새로운 객체가 필요하면 사용하면 된다. 그런데 실무에서 웹 애플리케이션을 개발해보면, 싱글톤 빈으로 대부분의 문제를 해결할 수 있기 때문에 프로토타입 빈을 직접적으로 사용하는 일은 매우 드물다.
ObjectProvider , JSR330 Provider의 사용
ObjectProvider , JSR330 Provider 등은 프로토타입 뿐만 아니라 DL이 필요한 경우에 언제든지 사용할수 있다.
- 순환 참조 경우
➕ ObjectProvider는 DL을 위한 편의 기능을 많이 제공해주고 스프링 외에 별
도의 의존관계 추가가 필요 없기 때문에 사용이 더 편리하다.
🤔마무리하면서🤔
📌 좋은 코드란?
→ 의도대로 동작하는 코드?