1. 차원
-
우리가 numpy를 통해 만들었던 array에 대해서 살펴보자.
-
image.shape을 했을 때, (1,)/(1,2)/(1,2,3)의 출력값을 본다면 순서대로 1차원, 2차원, 3차원이라고 생각한다. 이는 데이터 형태의 맥락에서 본 차원이다.```
-
df를 봤을 때, x축에 각각의 관측치가 3개 있고 y축에도 관측치가 3개가 있다. 그렇다면 (3,3)의 shape를 띄고 있을 텐데, 데이터 공간의 맥락에서 본다면 이는 9차원을 지닌다고 할 수 있다.
-
즉, 관측치(독립적인)가 하나의 축을 만든다고 생각하면 이해가 쉽다.
-
실습 1.
# 데이터 준비 (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.mnist.load_data() print(x_train.shape, y_train.shape) print(x_test.shape, y_test.shape) <출력> (60000, 28, 28) (60000,) (10000, 28, 28) (10000,) -> 데이터 형태 : 3차원이다. -> 데이터 공간 : x, y 축 모두 28개의 관측치로 이뤄졌다. 즉, 784차원이다. # 데이터 확인 print('정답 :', y_train[10]) plt.figure(figsize=(3,3)) plt.imshow(x_train[10], cmap='gray') # 이미지 출력할 때 plt.imshow사용 plt.show() <출력> 정답 : 3
2. 다 차원의 데이터 딥러닝 과정
- 다 차원의 관측치를 2차원의 df의 형태로 변환시킨다.
- y_train, y_test의 값에 대해서 one-hot 인코딩시킨다.
실습 2.
# 데이터를 준비한다 (x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist.load_data() # 표로 만들기 x_train = x_train.reshape(60000, 784) x_test = x_test.reshape(10000, 784) # 원핫인코딩 y_train = pd.get_dummies(y_train) y_test = pd. get_dummies(y_test) print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape) print(y_train.shape, y_test.shape) <출력> (60000, 784) (10000, 784) (60000, 10) (10000, 10) # 모델을 준비한다. x = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[784]) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.6)(h) # 0.5이면 392개를 0으로 만들겠다임, 즉 방해하겠다는 거임. 왜? 성능이 너무 좋아서, 과적합을 방지하려고 하는 행위 h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(64, activation='swish')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) # scale이 뒤죽박죽일 때 사용, 이상치가 많다면 standard를 별로 없다면 MinMax(Normalization)를 사용한다. h = tf.keras.layers.Activation(activation = 'swish')(h) # hidden에서는 특징을 간략하게 만드는 1) dropout 시키고 2) hidden layer 수 정하고 3) normalization하고 4) activation 하는게 더 좋다. y = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation= tf.keras.activations.softmax)(h) model = tf.keras.Model(x, y) model.compile(loss= categorical_crossentropy, metrics = accuracy) model.summary()
3. 기능(flatten, sparse_, model.fit(validation), 학습 과정 시각화)
- 1) flatten은 input에서 x의 shape=[784] 이렇게 사용했는데, shape=[28,28]이렇게 사용해도 알아서 펴주는 기능이다.
- 2) sparse_는 model.compile에서 loss와 metrics에서 추가로 입력해주며, 원핫인코딩을 알아서 해주는 기능이다.
- 유의점은 y의 관측치가 아이리스의 '품명'이 아닌 number로 labeling 되어 있는 경우에만 사용할 수 있는 방법이다.
- 3) validation은 모델 학습과 같이 실행시키는데 학습 도중에 오버피팅을 모니터링 하는데 사용된다.
- val_loss가 늘어나면 오버피팅이구나 판단한다.
- val_loss가 떨어지면 학습되고 있구나 판단한다.
- validation = 0.2이면, 60000개의 데이터에서 20%를 벨리데이션에 사용하고 남은 80%를 학습에 사용한다.
실습 3-1
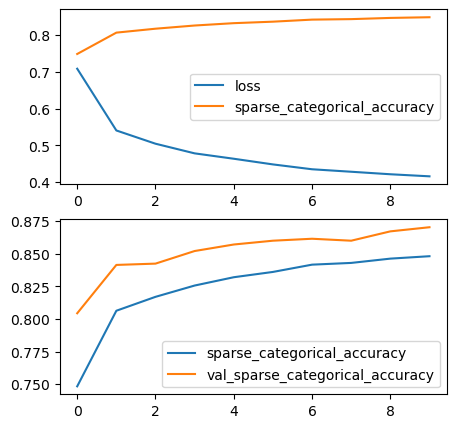
# 모델 준비 x = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[28, 28]) h = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(x) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation = tf.keras.activations.swish)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) y = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation= tf.keras.activations.softmax)(h) model = tf.keras.Model(x, y) model.compile(loss= tf.keras.losses.sparse_categorical_crossentropy, metrics = tf.keras.metrics.sparse_categorical_accuracy) # 풀어서 activation, loss와 metrics 작성해주면 다른 방법들이 어떤게 있는지 확인하면서 사용할 수 있음. 공부에 도움이 됨. 그냥 작성해줘도 됨. model.summary() <출력> Model: "model_9" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= input_10 (InputLayer) [(None, 28, 28)] 0 flatten_9 (Flatten) (None, 784) 0 dropout_14 (Dropout) (None, 784) 0 dense_23 (Dense) (None, 128) 100480 batch_normalization_14 (Ba (None, 128) 512 tchNormalization) dense_24 (Dense) (None, 10) 1290 ================================================================= Total params: 102282 (399.54 KB) Trainable params: 102026 (398.54 KB) Non-trainable params: 256 (1.00 KB) _________________________________________________________________ # 모델 학습 result = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size = 300, validation_split=0.2) <출력> Epoch 10/10 192/192 [==============================] - 3s 13ms/step - loss: 0.6932 - accuracy: 0.7483 - val_loss: 0.4857 - val_accuracy: 0.8203 # 학습 과정 확인 reslut.history 입력하면 epoch 단계마다의 loss, accuracy, val_loss, val_accuracy를 확인할 수 있다. # 학습 과정 시각화 plt.subplot(2,1,1) plt.plot(result.history['loss']) plt.plot(result.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']) plt.legend(['loss', 'sparse_categorical_accuracy']) plt.subplot(2,1,2) plt.plot(result.history['sparse_categorical_accuracy']) plt.plot(result.history['val_sparse_categorical_accuracy']) plt.legend(['sparse_categorical_accuracy', 'val_sparse_categorical_accuracy']) <출력>
실습 3-2(validation, early stop)
- val_loss가 올라가면, 즉 과적합 발생 갯수가 특정 갯수에 도달했을 때, 학습을 자동으로 종료시키는 방법이다.
# 모델 준비 x = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[32, 32, 3]) h = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(x) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(24, activation = 'swish')(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) y = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(h) model = tf.keras.Model(x, y) model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics = 'accuracy', optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0001)) model.summary() <출력> Model: "model_10" _________________________________________________________________ Layer (type) Output Shape Param # ================================================================= input_11 (InputLayer) [(None, 32, 32, 3)] 0 flatten_10 (Flatten) (None, 3072) 0 dropout_15 (Dropout) (None, 3072) 0 dense_25 (Dense) (None, 24) 73752 batch_normalization_15 (Ba (None, 24) 96 tchNormalization) dense_26 (Dense) (None, 10) 250 ================================================================= # 모델 학습 early = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping( monitor = 'val_loss', # 디폴트 값이라 안넣어줘도 됨. min_delta=0, # 얘도 디폴트 값임. patience=10, # 이 횟수 동안 개선이 없으면 끝냄. restore_best_weights=True, # False - > 맨 마지막 학습된 상태로 출력하겠다. True -> val_loss가 낮았던 모델로 출력하겠다. ) model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=150, batch_size=512, validation_split=0.2, callbacks=[early]) <출력> 쭈르륵 학습 되다가 val_loss가 올라가는 횟수가 10번이 될 때, 학습을 자동으로 멈춘다.
실습 4(skip connection)
- hidden layer에 add를 for 구문을 통해서 깊은 망 신경학습을 하는 방법이다.
# 모델 준비 x = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[32, 32, 3]) h = tf.keras.layers.Flatten()(x) h = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128)(h) h = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h) h = tf.keras.layers.Activation('swish')(h) for i in range(32): h1 = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(h) h1 = tf.keras.layers.Dense(128)(h) h1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(h1) h = tf.keras.layers.Add()([h, h1]) h = tf.keras.layers.Activation('swish')(h) y = tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')(h) model = tf.keras.Model(x, y) model.compile(loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy', metrics = 'accuracy', optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(learning_rate=0.0001)) #optimizers.SGD(learning_rate=0.001) model.summary() <출력> 32번의 깊은 망 신경 학습을 하게 된다. # 모델 학습 early = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(patience=10, restore_best_weights=True) model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=150, batch_size=512, validation_split=0.2, callbacks=[early]) <출력> Epoch 24/150 79/79 [==============================] - 10s 128ms/step - loss: 1.9701 - accuracy: 0.2805 - val_loss: 1.9204 - val_accuracy: 0.3002