📊 DL 다항분류
📌 다항분류란?
- 정의
- 1개 이상의 독립변수로 레이블 내의 unique value 개수가 3개 이상인 레이블 중 하나로 분류하는 방법이다.
📌 DL 다항분류 실습
1. 라이브러리 Import
import pandas as pd import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import seaborn as sns from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from keras.utils import to_categorical from keras.models import Model from keras.layers import Input, Dense from keras.optimizers import Adam from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, classification_report, roc_curve, auc
2. 데이터 준비
data = pd.read_csv('../testdata/iris.csv') print(data.head()) print(data.shape) # Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width Species # 0 5.1 3.5 1.4 0.2 setosa # 1 4.9 3.0 1.4 0.2 setosa # 2 4.7 3.2 1.3 0.2 setosa # 3 4.6 3.1 1.5 0.2 setosa # 4 5.0 3.6 1.4 0.2 setosa # (150, 5)
3. 레이블 인코딩
encoder = LabelEncoder() data['Species'] = encoder.fit_transform(data['Species']) print(data['Species'].unique()) # [0 1 2]
4. 학습, 테스트 데이터 분리
feature = np.array(data.iloc[:, :-1]) label = np.array(data.iloc[:, -1]) x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(feature, label, test_size=0.3, stratify=label, random_state=1) print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape) # (105, 4) (45, 4) (105,) (45,) y_train = to_categorical(y_train) y_test = to_categorical(y_test)
5. Functional API 다항 분류 모델 구축
inputs = Input(shape=(4,)) net1 = Dense(units=64, activation='relu')(inputs) net2 = Dense(units=32, activation='relu')(net1) net3 = Dense(units=16, activation='relu')(net2) net4 = Dense(units=8, activation='relu')(net3) net5 = Dense(units=4, activation='relu')(net4) outputs = Dense(units=3, activation='softmax')(net5) model = Model(inputs, outputs)
6. 모델 학습 최적화 설정
model.compile(optimizer=Adam(learning_rate=0.01), loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['acc'])
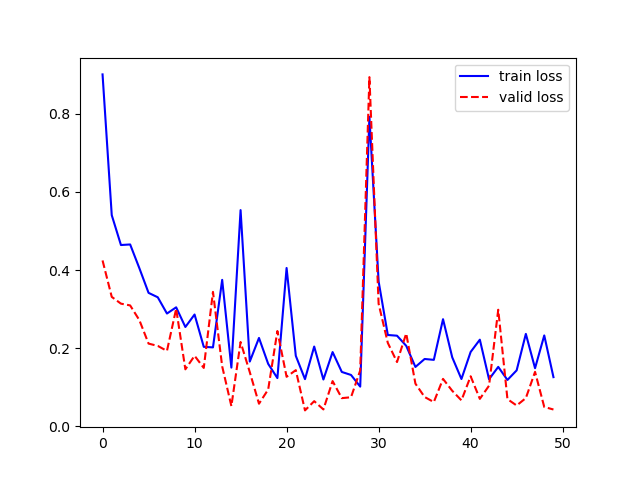
7. 모델 학습
history = model.fit( x=x_train, y=y_train, batch_size=1, epochs=50, validation_split=0.2, verbose=0 ) plt.plot(history.history['loss'], 'b-', label='train loss') plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'], 'r--', label='valid loss') plt.legend() plt.show()
8. 모델 검증
loss, acc = model.evaluate( x=x_test, y=y_test, batch_size=1, verbose=0 ) print('loss : ', loss) print('acc : ', acc) # loss : 0.05600221827626228 # acc : 0.9777777791023254
9. 모델 예측값, 실제값 비교
y_pred = model.predict(x_test) y_pred = np.where(y_pred > 0.5, 1, 0) print('예측값 : ', y_pred[:4]) print('실제값 : ', y_test[:4]) # 예측값 : [[0 0 1] # [1 0 0] # [1 0 0] # [0 0 1]] # 실제값 : [[0. 0. 1.] # [1. 0. 0.] # [1. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 1.]]
10. 분류모델 성능 평가 - 정확도
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred) print('정확도 : ', acc) # 정확도 : 0.9777777777777777
11. 분류모델 종합 성능 평가 - 정확도, 재현도, 정밀도
report = classification_report(y_test, y_pred) print(report) # precision recall f1-score support # # 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 15 # 1 1.00 0.93 0.97 15 # 2 0.94 1.00 0.97 15 # # micro avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 45 # macro avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 45 # weighted avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 45 # samples avg 0.98 0.98 0.98 45
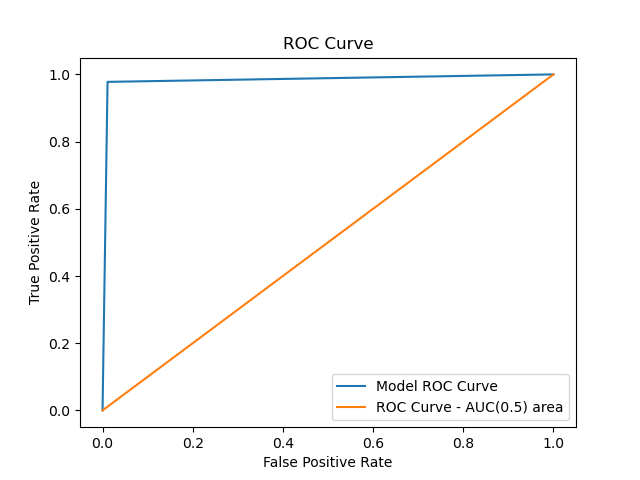
12. ROC 곡선 그리기
FPR, TPR, _ = roc_curve(y_test.flatten(), y_pred.flatten()) auc_value = auc(FPR, TPR) plt.plot(FPR, TPR, label='Model ROC Curve') plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], label='ROC Curve - AUC(0.5) area') plt.legend() plt.title('ROC Curve') plt.xlabel('False Positive Rate') plt.ylabel('True Positive Rate') plt.show()
13. AUC 면적값 추출
print('AUC 값 : ', auc_value) # AUC 값 : 0.9666666666666668