Switched Communication Networks
- Switched Communication Networks
- long distance transmission: intermediate switching nodes의 네트워크에서 이루어짐
- nodes: content of data가 아니라 switching / routing과 관련
- end devices: stations (computers, terminals, phones)
- communications network: collection of nodes and connections (link)
- data: node와 node 사이의 swtiching으로 routing 됨 - Nodes: 다른 node들에만 연결 or station과 다른 node들에 연결
- node-to-station links: dedicated to point-to-point links
- node-to-node links: multiplexed
- network: partially connected (mesh: fully connected)
몇몇 중복 path => reliability 제공
- switching technologies: circuit switching, packet switching
- Simple Switching Networks
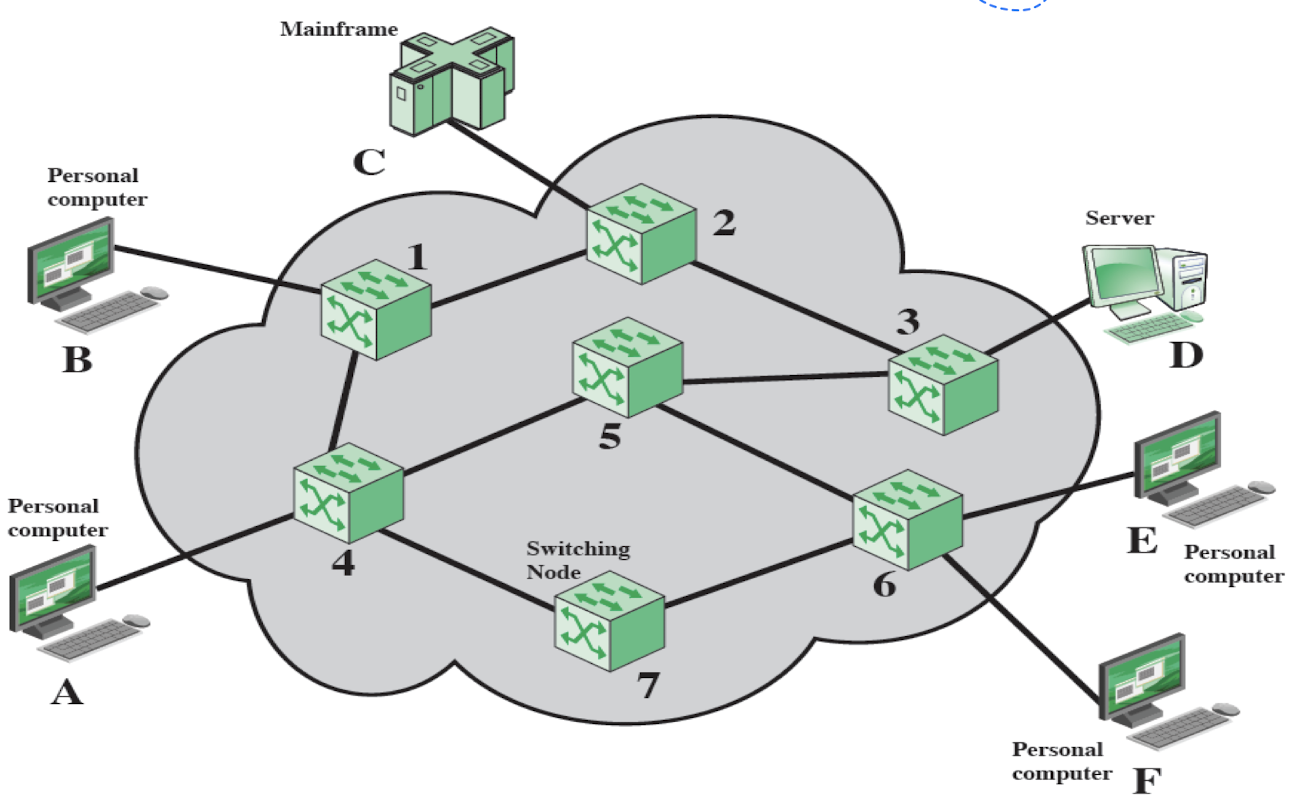
5,7: node-to-node links
1,4,3,6: node-to-station links
Circuit Switching Networks
Dedicated Communication Path between two stations
- path: connected sequence of links between nodes
Phases: circuit establishment, data transfer, circuit disconnect
Swtiching capacity(connection 요구 처리 위해)와 Reserve channel capacity(용량 부여, 자원 할당) 필요 => establish connection
- Applications
- channecl capacity는 connection 유지 기간 동안 계속 헌신. 데이터가 없으면 capacity 낭비됨
=> Inefficient
- set up (connection) takes time
- 한 번 connect되면, transfer는 transparent
- voice traffic (phone)을 위해 개발됨: 자원들은 particular call에 헌신. data rate는 고정.
- Telecommunications Components
- Subscribers: 네트워크 연결 장비 ex) telephone
- Subscriber line: local loop / subscriber loop. subscriber와 network 사이의 link. typical media (twisted-pair wire. FTTH). few km up to few tens of km
- Exchanges: switching centers. end office-supports subscribers
- Trunks: carrier systems. branches between exchanges. multiplexed (하나의 라인이 수천/수만개 운반)
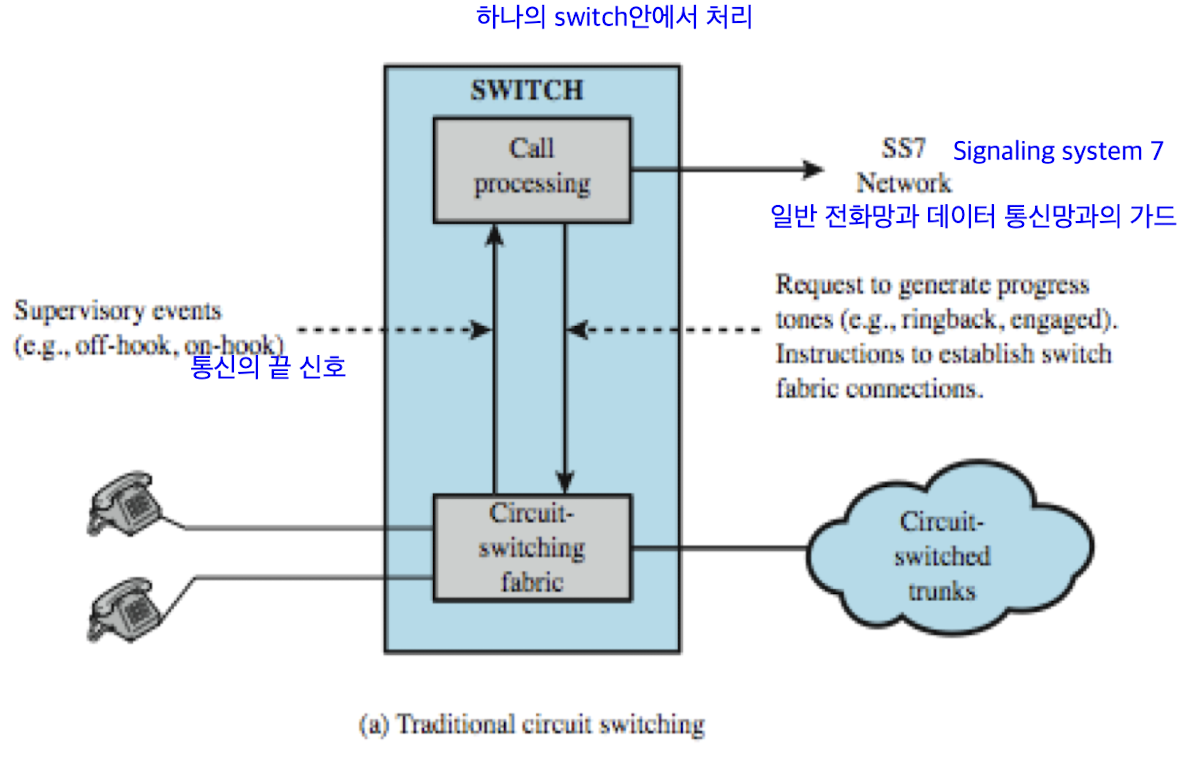
Softswitch Architecture
-
Traditional Circuit Switching
-
Softswitch
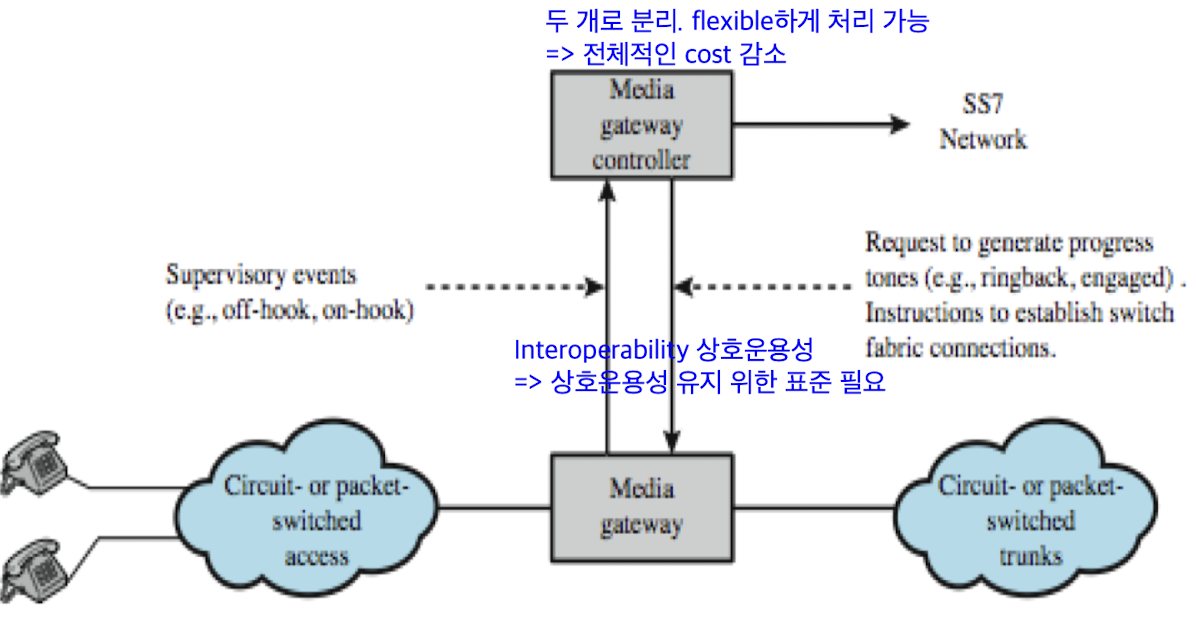
- circuit-switching technology의 최신 트렌드
- 전화 switch로 변환해주는 special sw
- 비용 저렴. 기능 많음
- digitized voice bits을 packet 단위로 전송
- 하나의 장치가 아니라 두 가지 function 분리해서 처리- Media Gateway: physical switching function (routing)
- Media Gateway Controller: call processing logic (복잡)
Packet Switching Networks
Designed for Data
-
Operation
- data: small packets으로 전송. (1000 octets). 긴 메시지는 패킷으로 분리됨. 각 패킷은 user data(part of a larger message), control info(routing, addressing) 포함
- Store-and-forward: packet을 받으면 buffered(stored briefly)되어 next node에 전달 -
Advantages
- line efficiency ⬆️
- single node to node link는 packet들에 공유 가능
- packet들은 queue를 사용하여 빠르게 전송 - data rate conversion
- each station connects to the local node at its own speed
- nodes buffer data if data rate 달라도 해결 가능
- two stations with different data rates can exchange packets - packets: network가 바빠도 accept됨. delivery delay는 증가
- priorities 사용 가능: high-priority packet 먼저 전송
- line efficiency ⬆️
-
Switching Technique
: message length > maximum packet size => station은 message를 packet 단위로 분리
- packets는 네트워크에 한 번에 전송
- packet 처리 방식: datagram, virtual circuit
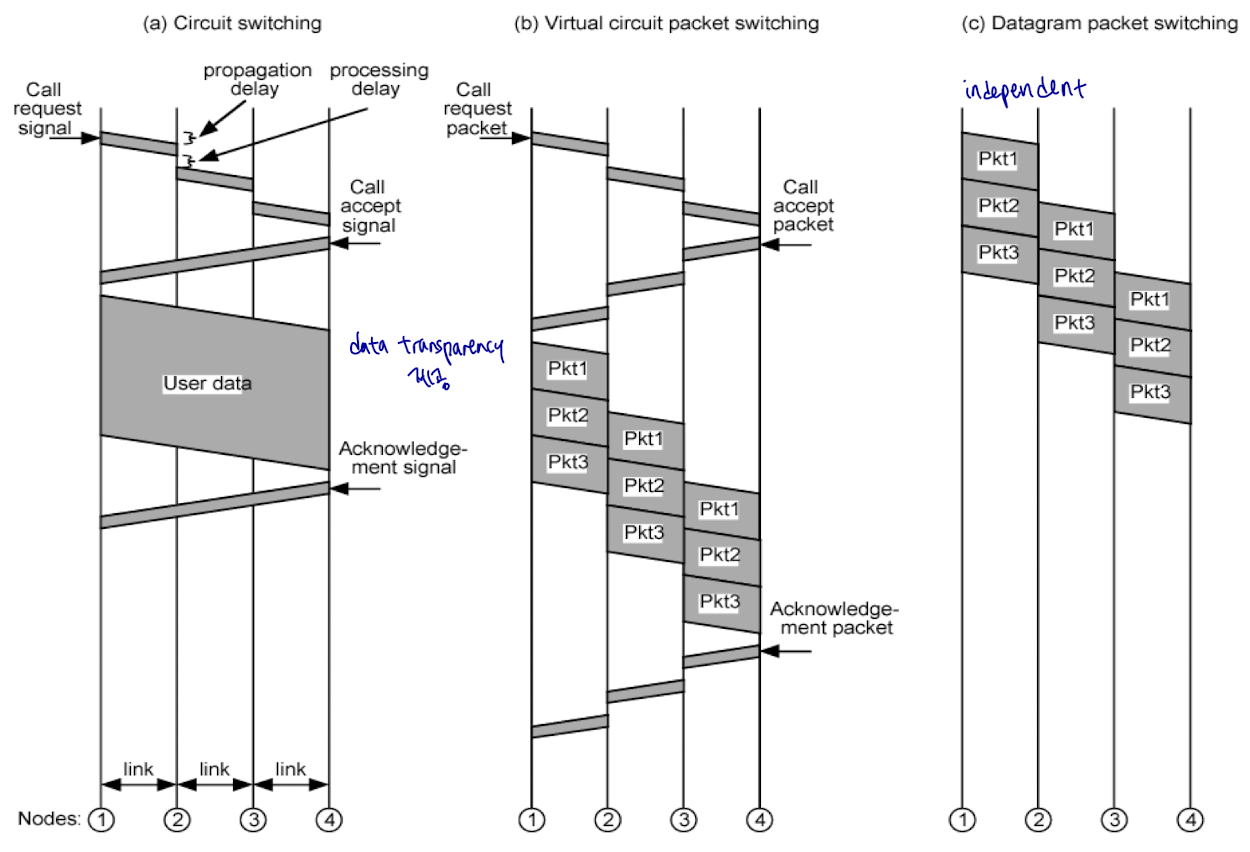
Datagram Packet Switching
- each packet: treated independently
- packets: 어느 route를 타도 됨. 순서 다르게 도착. missing 있음
- up to either exit node or receiver to re-order packets and recover from missing packets
Virtual Circuit Packet Switching
-
packet 전송 시작 전에 preplanned route 설정
-
dedicated path X, logical connection O
-
handshake: call request and call accept packets establish connection
- 각각의 packet이 자신의 길 찾아감 => destination address 필요
- virtual circuit: preplanned route 설정. 길 공유. identifier 필요. (destination address는 필요 X) -
packet별로 routing decisions 필요 X. virtual circuit establish 전에 only one decision 필요 => Preplanned route
E\I Datagram(IP) Virtual Circuit Datagram(UDP) O (destination station) X Virtual Circuit(TCP) O (exit node) O(ATM) -
Effect of packet size
tproc, tprop = 0
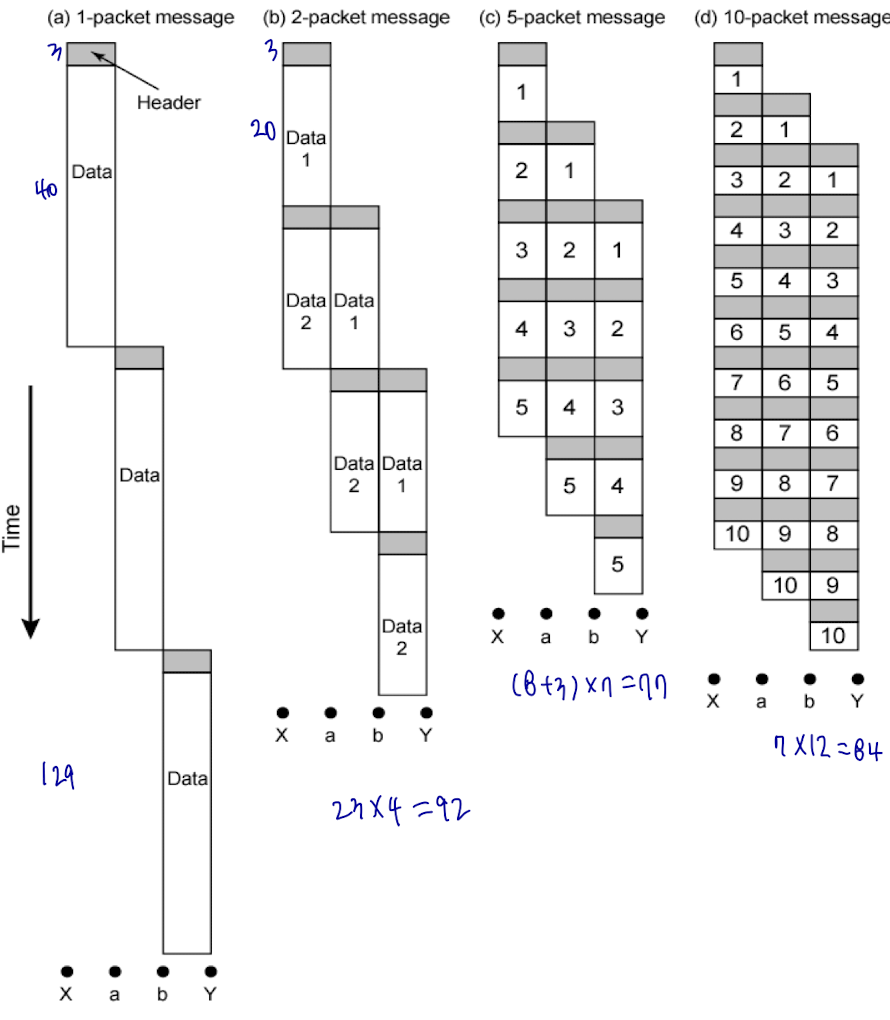
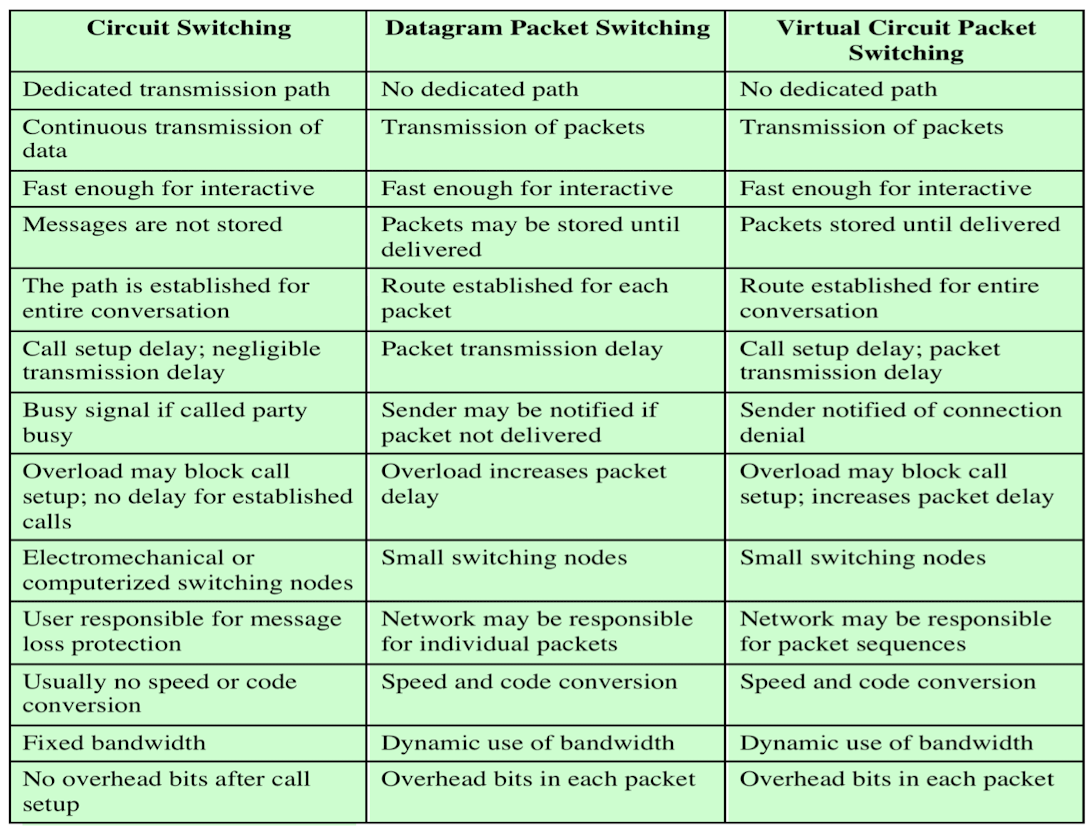
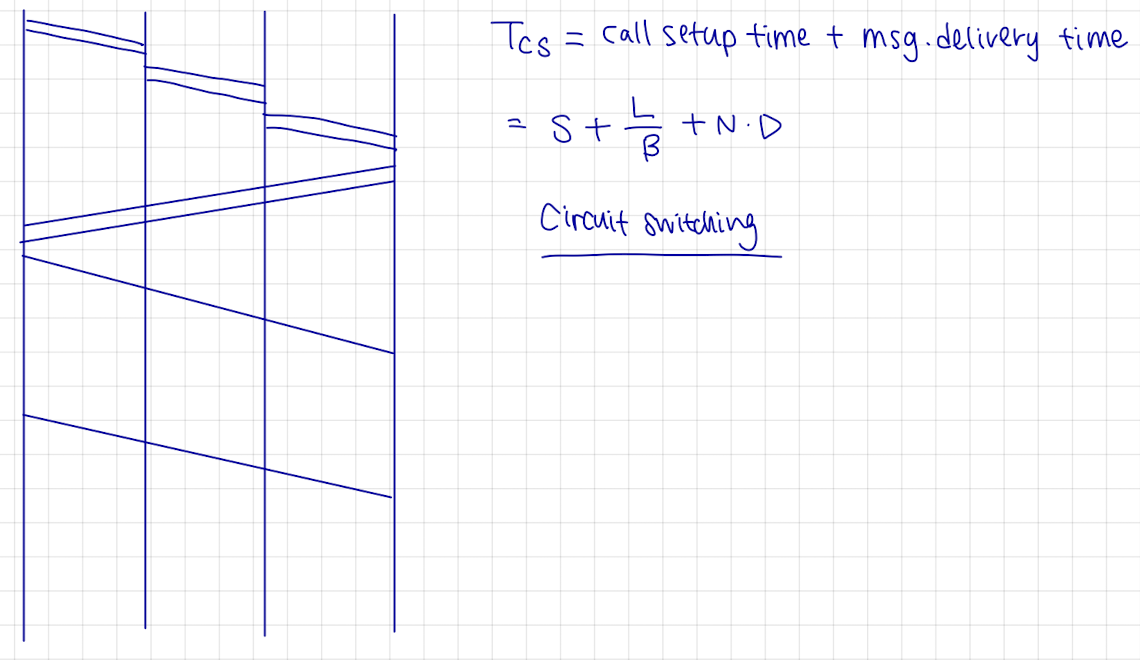
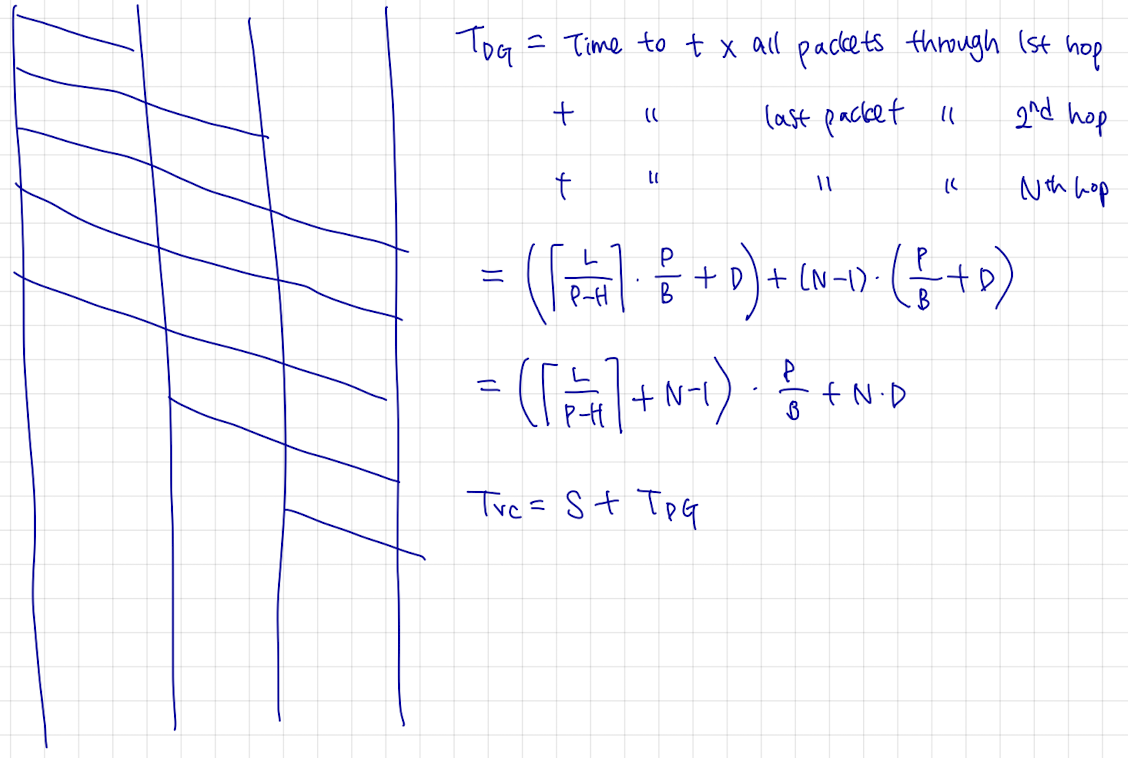
Communication Switching Techniques 비교
Example
N: # of hops between two given stations
L: message length in bits
B: data rate, in bits per second (bps), on all links
P: fixed packet size in bits
H: overhead (header) bits per packet
S: call setup time (circuit switching or virtual circuit) in sec
D: propagation delaty per hop in sec
Asynchronous Transfer Mode(ATM)
- cell: ATM에서 사용하는 packet. 53 octets. small and 고정 길이
- Connection-Oriented
- performance of a circuit-switching network and the flexibility and efficiency of a packet-switching network
- data, voice, video support
- transmission based on priority and QoS
Protocol Architecture
ATM과 Packet Switching 유사점
- transfer of data in discrete chunks
- muptiple logical connections multiplexed over single physical interface
streamlined protocol with minimal error and flow control
- reduce overhead of processing cells
- reduce # of overhead bits in each cell
- enable ATM to operate at high data rates
use of fixed-size cells -> simplifies processing at each node
data rates (phywical layer): 25.6Mbps to 622.08Mbps
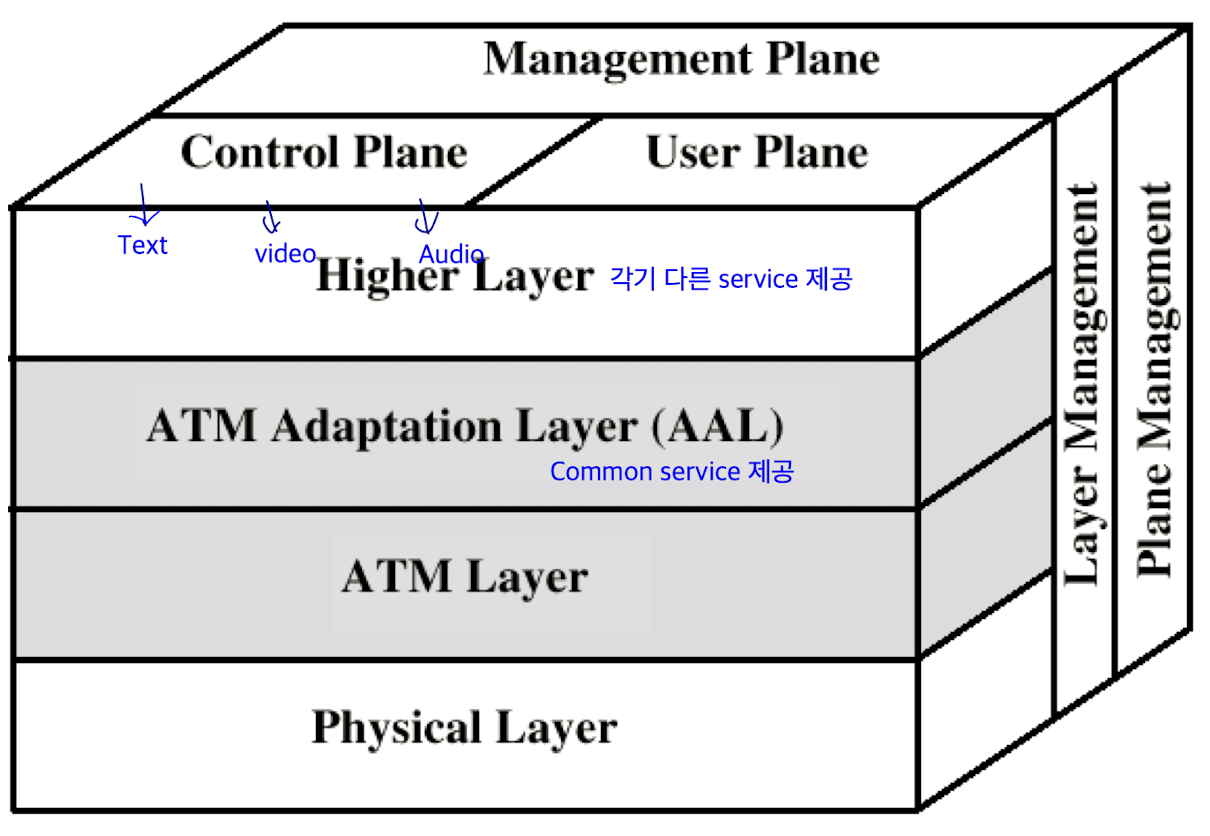
Reference Model Planes
- User plane: provides for user info transfer
- Control plane: performs call and connection control functions
- Management plane
- plane management: performs management functions related to a system. provides coordination between all the planes
- layer management: performs management functions relating to resources and parameteres in protocol entities
Logical Connections
-
Virtual Channel Connection (VCC): basic unit of switching
- analogous to virtual circuit in X.25
- set up between two end users and a variable-rate, full-duplex flow of fixed-size cells is exchanged- user-network exchange (control signaling): user-network 사이의 interface
- network-network exchange (network management, routing): network 사이의 interface
-
Virtual Channel Connection Uses
: cell sequence integrity preserved within a VCC: cell 순서 무결성 VCC 내에서 유지- between end users
- carry end-to-end user data/control signaling between end users
- VPC provides overall capacity -> VCC organization is up to two end users, Set of VCCs does not exceed VPC capacity - between an end user and a network entity
- used for user-to-network control signaling
- user-to-network VPC can be used to aggregate traffic from end user to network exchange or server (VPC 레벨에서 말단 network로 들어오는 traffic 묶음) - between two network entities
- used for network traffic management and routing functions
- net-to-net VPC can be used to define a common route for exchange of network management information
- between end users
-
Virtual Path Connection (VPC): bundle of VCC with same end points
(advantages)
- simplified network architecture: network transport functions can be separated into those related to VCC and VPC
- increased network perfo and reliability: network deals with fewer aggregated entities
- reduced processing and short connection setup time: much of the work is done when VP is set up
- enhanced network services: user may define closed user gropus or closed networks of VC bundles
Cells
-
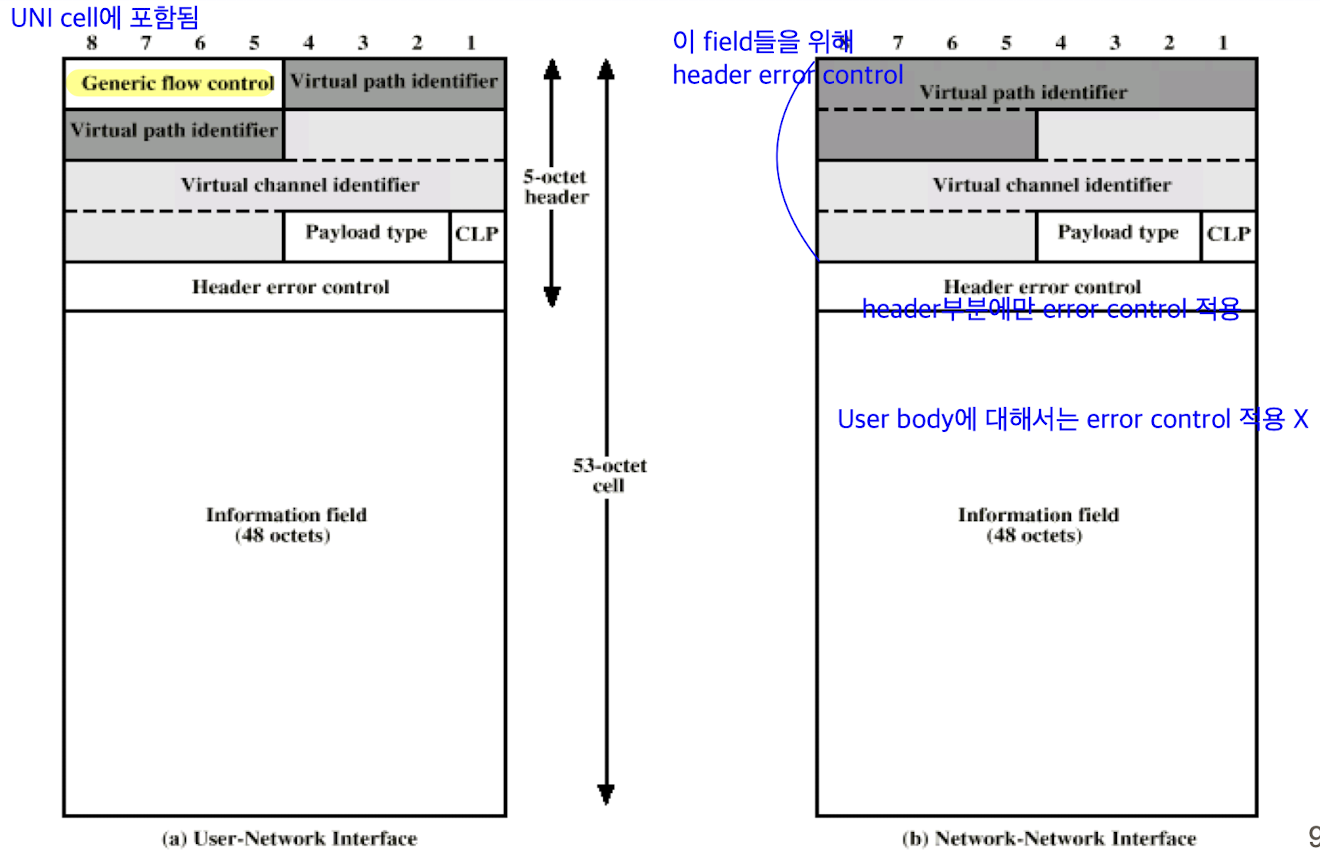
ATM cells: fixed-size cells, 총 53 octets (5 header + 48 info field)
-
Advantages
- reduce queuing delay for high-priority cells
- can be switched more efficiently
- easier to implement the switching mechanism in hardware
-
Header format
- generic flow control (GFC): only at user-network interface (UNI)
: used to control cell flow for different QoS only at UNI
: used to alleviate short-term overload conditions in network
- virtual path identifier (VPI): constitutes routing field for network
- virtual channel identifier (VCI): used for routing to and from end user
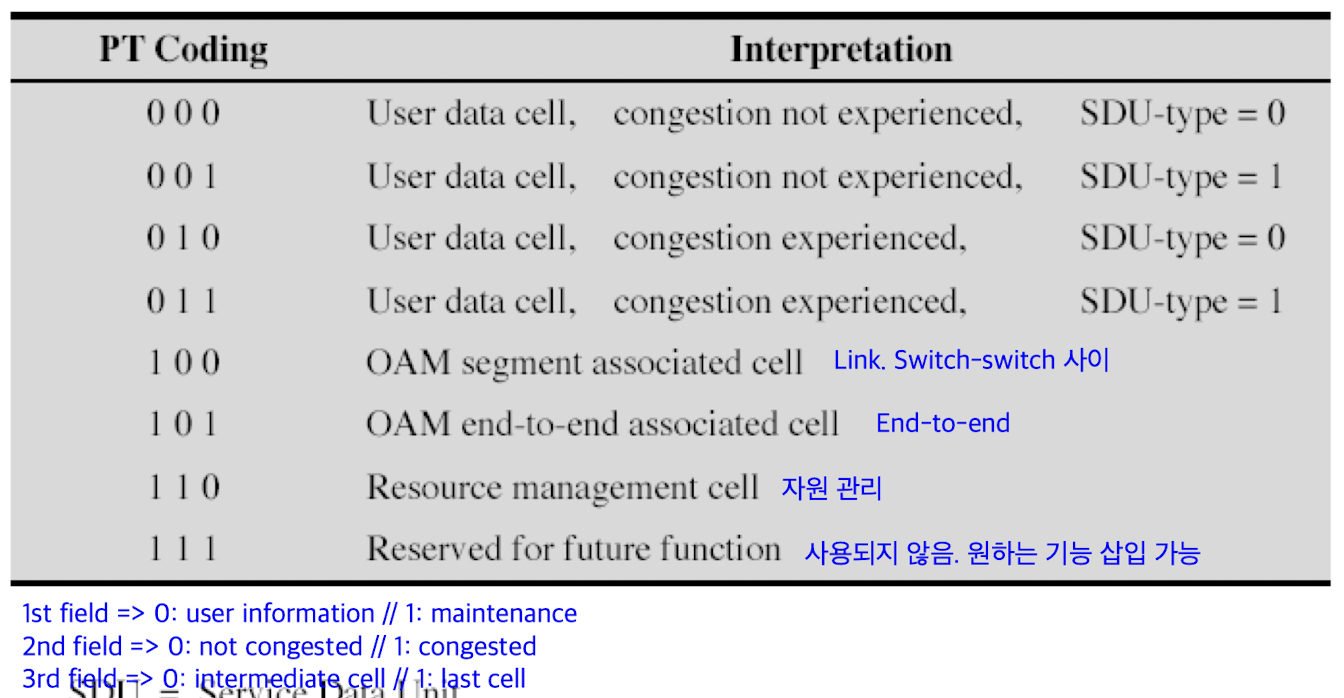
- payload type (PT): 3 bits only
: indicates type of info in info field ex) user info or network management/maintenance info
: provide inband control infoPayload Type Field Coding
-
Cell loss priority (CLP): 1 bit
: used to provide guidance to network in event of congestion (congestion의 발생을 network에 알려줌)
- 0: cell of relatively higher priority. alternative 없으면 discard 안 됨
- 1: cell is subject to discard
- cell with CLP = 1 is delivered == network is not congested
- the network sets CLP to 1 for any data cell in violation of agreement between user and network -
Header Error Contro (HEC)
- 8-bit error control field
- calculated on remaining 32 bits of header- polynomial:
- allows not only error detection but single-bit error correction because of sufficient redundancy in the code
* FCS: error detection을 위해 사용
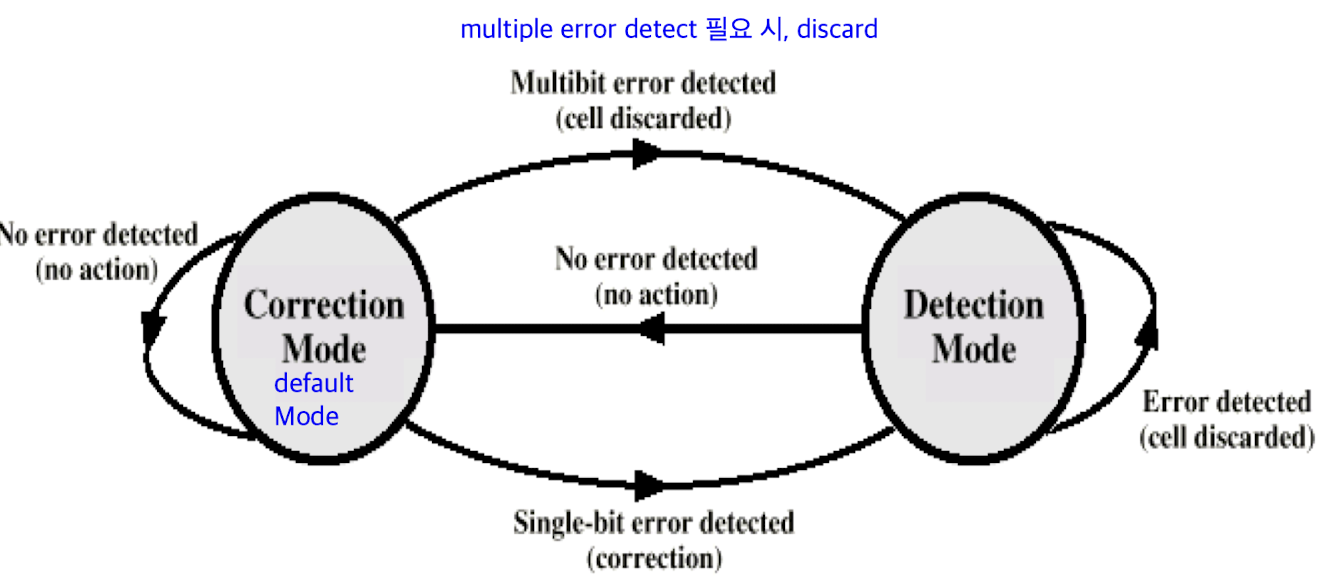
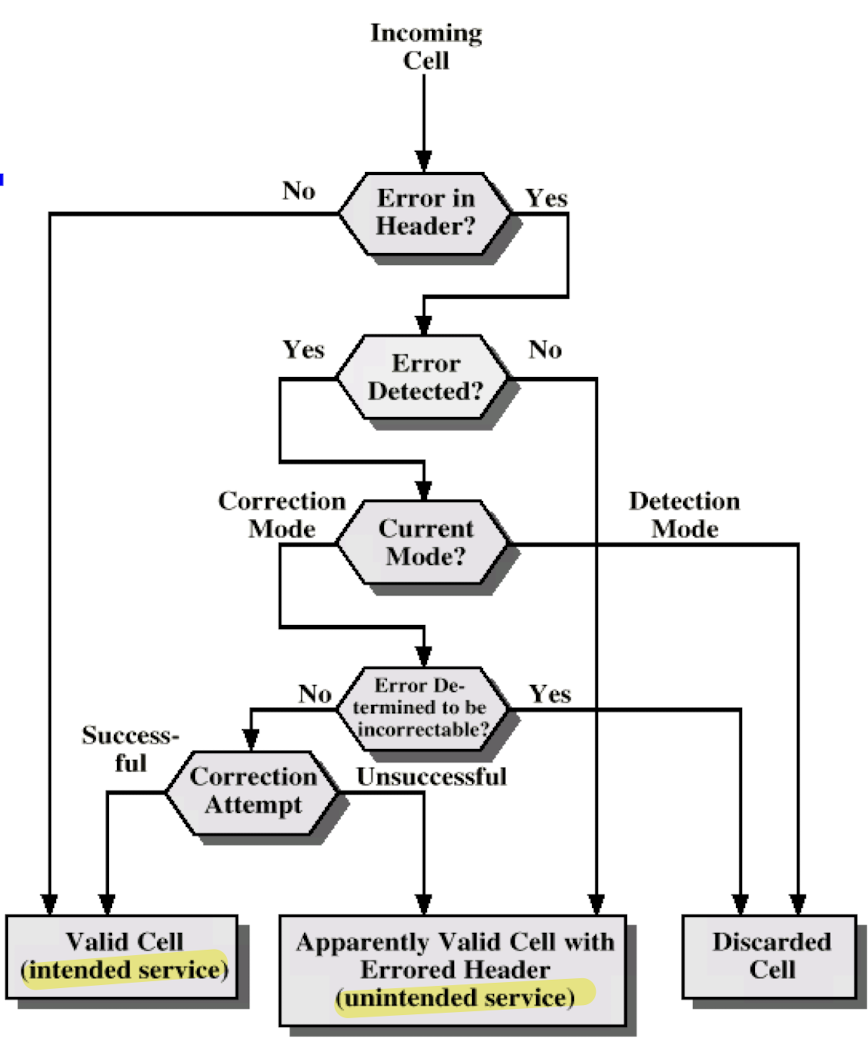
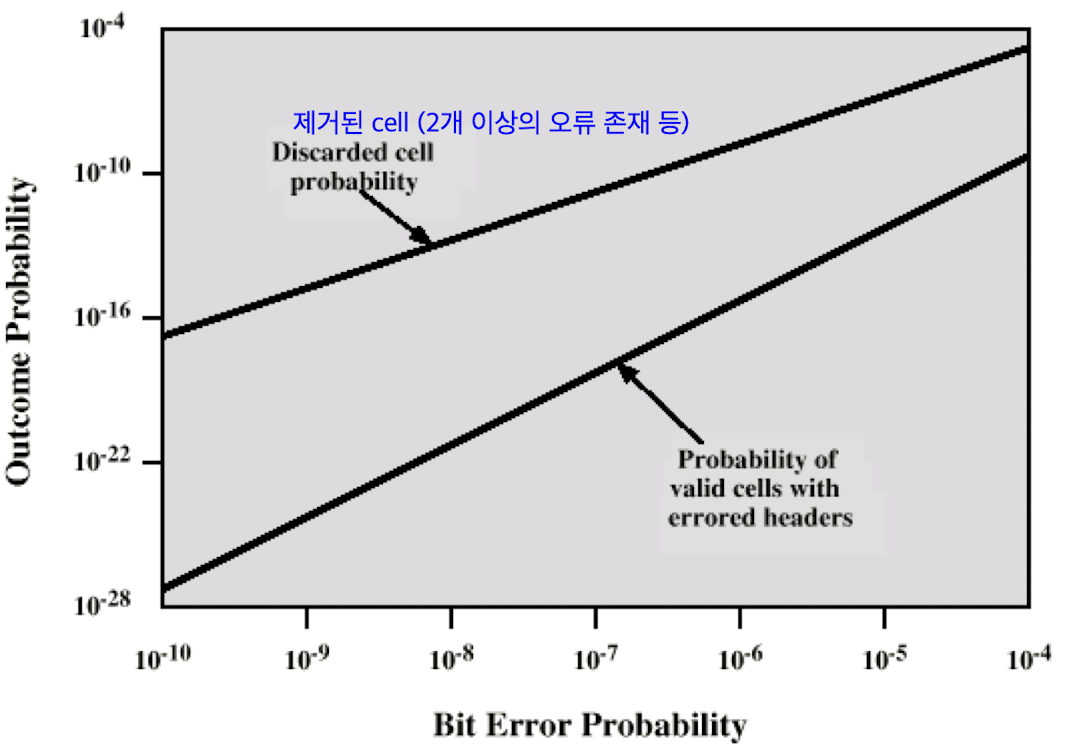 오류 생기지 않게 정규하게 cell switch 설계
오류 생기지 않게 정규하게 cell switch 설계