Guided media: wired / Unguided media: wireless
Design factors
- bandwidth: bandwidth ⬆ data rate ⬆
- transmission impairments: attenuation, attenuation distortion, delay distortion, noise
- interface: interference from competing signals in overlapping frequency bands can distort or wipe out a signal
- number of receivers: shared link -> each attachment introduces some attenuation and distortion, limiting distance and/or data rate
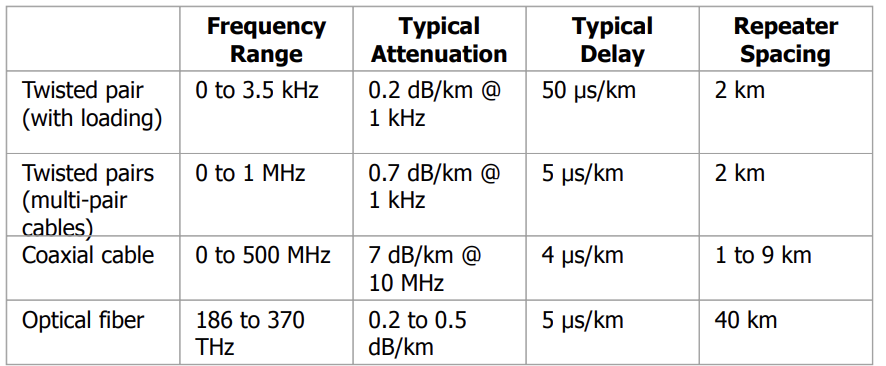
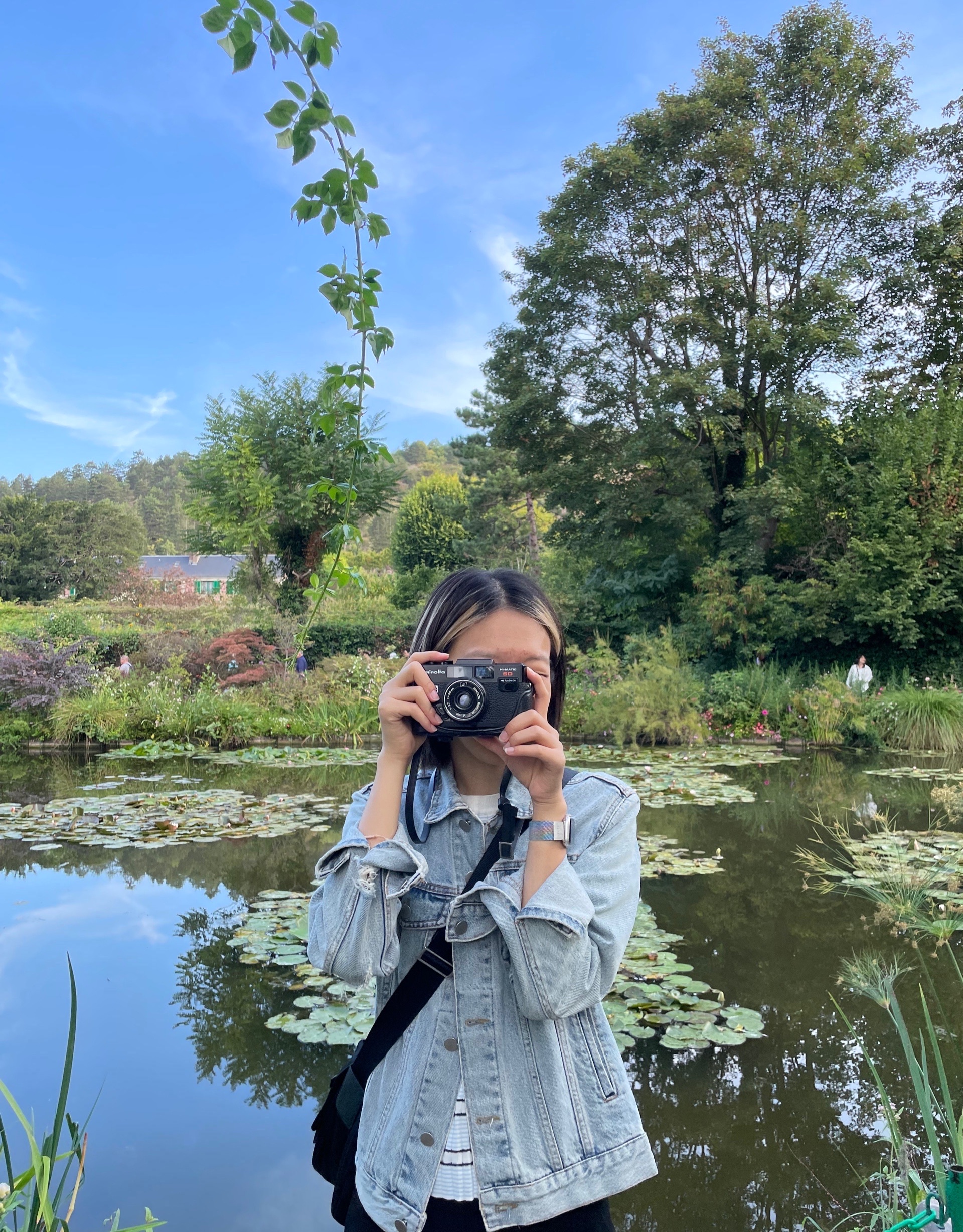
typical delay (propagation delay) => 유선 케이블의 경우, 모든 매체에서 tprop은 5 usec/km로 동일 (빛의 속도의 2/3)
Twisted Pair
값 ⬇. most widely used.
: two insulated copper wires. wire pair -> single communication link처럼 행동
pairs -> cable로 묶임.
twist length ⬇, 성능 ⬆ (가격 ⬆)
- applications: analog & digital 모두에게 가장 common medium
- telephone network: between house & local exchange
- within buildings
- for local area networks (LAN) - pros and cons
(+) cheap. easy to work with
(-) performance ⬇, range ⬇ - transmission characteristics
- analog transmission: amplifier(증폭기) 5-6km마다 있어야 함
- digital transmission: analog or digital signals 사용, repeaters가 2-3km마다 필요
- distance, bandwidth, data rate에 limit
- interference, noise에 민감 (susceptible)
Unshielded and Shielded TP
- Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP)
- ordinary 전화 wire
- cheapest
- flexible. easy to install, work with
- external electromagnetic 방해 잘 받음
- throughput 빠름.
- end-to-end delay - Shielded Twisted Pair (STP)
- metallic braid or sheating -> interference ⬇
- performance ⬆, data rate ⬆
- expensive
- harder to handle (thick, heavy)
- configurations: FTP(Foil twisted pair), F/UTP, S/FTP(Shielded/foil twisted pair: 페어 + wire)
Twisted Pair Categories and Classes
- Category 5e / Class D
- bandwidth ⬇
- cable type: UTP
- insertion loss ⬆
- NEXT loss ⬇
- ACR ⬇ - Category 6/ Class E
- UTP/FTP
- majority of structured cabling specified for new buildings - Category 6A / Class E_{A}
- UTP/FTP - Category 7 / Class F
- S/FTP - Category 7A / Class F_{A}
- S/FTP
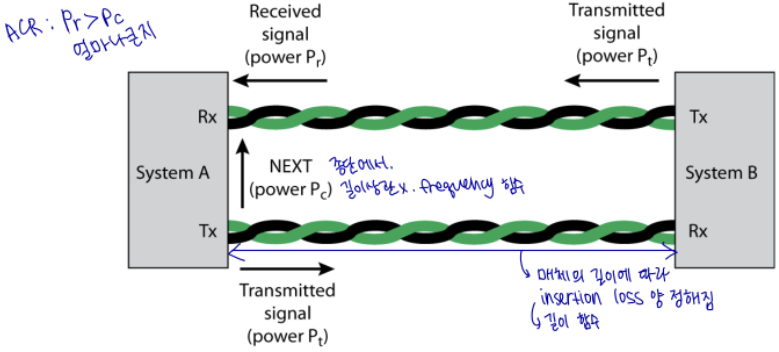
Insertion loss: 신호 감쇄량. amount of attenuation across link from transmitting systme to receiving system. 길이 함수
Near-end crosstalk (NEXT) loss: 신호 결합. picked up by the near-receive pair => 종단에서. 길이 상관 X. Frequency 함수
Attenuation-to-crosstalk ratio (ACR): received signal의 강도가 같은 pair 상의 crosstalk과 비교해서 얼마나 큰지 나타내는 숫자
ACR ⬆ 좋은 신호 (ACR 발전 시, 비트에러 줄일 수 있음)
Pr > Pc 얼마나 큰지
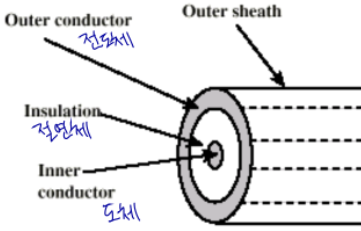
Coaxial cable
- Ethernet
- 10BASE-5: segment 길이 500m. coaxial. 10Mbps(data rate). base band(digital signal)
- 10BASE-2: segment 길이 200m -> 케이블 TV
- 10BASE-T: twisted pair (구리)
=> Optical fiber 유리
twisted pair보다는 전반적으로 우수. 광섬유보다는 떨어짐. -> 거의 광섬유로 교체. 많이 사용 X.
- applications: television. long distance telephone transmission. short distance computer system links. local area networks. 케이블 티비 외에는 거의 사용 X
- characteristics
- interference에 덜 민감. crosstalk ⬇ than twisted pair.
- analog: amplifiers needed every few kms. closer spacing for higher frequencies
- digital: repeater needed every km. closer spacing for higher data rates
Optical fiber
criticle angle보다 큰 각: 100% 반사
- benefits
- greater capacity: data rates of 100Gbps
- smaller size & lighter weight: core, claddle이 유리로 되어 있기 때문에 설치 용이.
- lower attenuation: 신호 퀄리티 good -> attenuation 작음
- electromagnetic isolation: not vulnerable to interference, impulse noise, or crosstalk. higher degree of security from 도청
- greater repeater spacing: repeater 설치 간격 넓어짐 -> 설치 적게 해도 됨 -> 가격 절약 - applications
- long-haul trunks 장거리 전화선
- metropolitan trunks
- rural exchange trunks
- subscriber loops
- LANs - optical communication: 전자가 아니라 광자(빛)이 전달됨. 들어오는 source는 electrical digital signal. 그러나 lightwave pulse로 변환해서 전송. Optical fiber 말단의 단말에서 그 빛의 pulse를 digital signal로 다시 변환 (converter)
- transmission characteristics
- total internal reflection (전반사): 적외선 ~ 가시광선
- types of light source
- LED: cheaper, greater temperature range, last longer
- ILD: more efficient. quality ⬆, data rate ⬆
- wavelength division multiplexing (WDM): 케이블을 통해 전달되는 light는 여러 개의 파장으로 구성. (여러 개의 파장은 여러 개의 frequency로 이루어져있다는 뜻) 각각의 파장이 하나의 데이터를 전송하는 데이터 채널로 사용. 100개의 채널은 100개의 파장. 각각이 10Gbps. 100개면 1000Gpbs -> 1Tbps. 하나의 데이터 채널로 1Tbps 달성은 힘들지만 10기가 짜리 백개의 채널로 1Tbps 달성은 좀 더 용이함
-optical fiber transmission modes
- step-index multimode: core 두꺼움. Q0보다 작으면 굴절, Q0보다 크면 반사. 낮은 quality 신호 전달 => 짧은 거리 LAN. high quality 부적합. (core 두께⬆, range⬆)
core 안에는 전반사가 일어나서 전달되는 데이터 채널들도 상대방이 도착하는 path가 다르기 때문에 도착하는 시간이 달라짐. 빛을 쏠 때는 날렵 pulse, 도착하는 output pulse는 강도 떨어진 빛 도착. - graded-index multimode: core의 센터로 들어오는 빛들은 느리게, 가장자리(craddle에 가까운 쪽으로 오는 것들)는 빨리 전송. 일정 거리를 가다보면 들어오는 빛들은 다시 만남 => 신호 quality 높여줌.
- single mode: core 두께 얇음. 하나의 빛만 들어갈 수 있음. 거의 input pulse가 도착 output pulse까지 유지되도록. => 가장 high quality. long distance application에 주로 사용
Data rate and bandwidth
signal의 스펙트럼: frequency의 범위
bandwidth: 주파수폭.
(Effective) bandwidth: bandwidth that contains most of the energy in signal
=> data rate에 한계 있음
data rate: bits per sec (bps)
bandwidth: cycles per sec, or Hertz
Transmission impairments
analog - degradation of signal quality
digital - bit errors
Attenuation
signal strength falls off with distance
depends on medium
frequency ⬆ attenuation ⬆
segment 길이: 500m for 10BASE-5 / 200m for 10BASE-2
Delay distortion
guided media(유선)에만 있음
propagation velocity(전송속도)는 frquency에 따라 다름
various frequency signal이 receiver에게 각기 다른 시간에 옴 => phase shifts between frequencies. (multimode fiber)
Noise
additional signals inserted between transmitter and receiver
- thermal(열): thermal agitation of electrons. uniformly distributed. white noise
- intermodulation(상호변조): sum, difference, multiples를 produce함
- crosstalk: signal from one line is picked up by another
- impulse: noncontinuous noise.
- analog data: minor annoyance
- digital data: primary source of error
