[정보통신공학] 2. Protocol Architecture, TCP/IP, and Internet-Based Applications
Information Communications
Protocal Architecture
- 필요성
- source must activate communicationss path or inform network of destination
- source must make sure that destination is prepared to receive data 데이터 받을 준비 되어있는지 확인
- file transfer application on source must confirm file management program at destination is prepared to accept and store file 받고 저장 준비
- format tranlation function need to be performed if the formats on systems are different 양방향 포맷 변경 가능
Layered Structure
layered structure of hw and sw: 시스템 사이에서의 데이터 교환 지원
logic -> subtask modules로 분리
모듈은 vertical stack으로 구성: relies on next lower layer for primitive functions. provides services to the next higher layer. changes in one layer should not require changes in other layers
ex) TCP/IP protocol suite and OSI model
N+1 / N / N-1
모든 계층화 구조에서 전부 적용. 자신의 계층에서 역할 수행 후, higehr 계층으로 전달. 하위 계층에서 수행한 일에 자신의 일을 더해서 상위 계층으로 전달
Protocol: set of rules or conventions that allow peer layer communication
- syntax: format of data blocks
- semantics: control information for coordination and error handling
- timing: spped matching and sequencing 데이터 보낸 순서 == 받는 순서
컴퓨터들이 네트워크에 의해 연결. application들이 상호 간의 data를 네트워크를 통해 다른 컴퓨터에게 전달하는 환경 가정
Simple Protocol Architecture
: relatively independent layers
-
Network Access Layer
: concerned with the exchange of data between computer(end system) and network (위: 컴퓨터 // 아래: 네트워크)
- destination address provision: 목적지 주소 제공
- invoking specific services like priority: 데이터 우선순위 제공
- access to & routing data across a network for two end systems attached to the same network: 같은 네트워크 접속되어있는 두 개의 컴퓨터 사이에 routing, data accessNetwork Access Layer에 사용되는 sw는 네트워크 타입에 따라 달라진다. LAN, WAN, WIFI 등 어떤 네트워크에 따라 달라지는가는 모두 이 계층에서 해결
higher layers는 어떤 네트워크인지 신경 안 써도 됨. same higher layer sw는 특정 네트워크 관계 없이 사용 가능
-
Transport Layer
: provides reliable data transfer (오류X. 보낸 순서대로 도착)
concerned with providing reliable delivery of data
common layer shared by all applications
essentially independent of the nature of the applications (다양한 application이 하나의 transport layer에 연결. -> application에 독립적) -
Application Layer
: contains logic to support applications (사용자 인터페이스 제공)
contains the logic needed to supprot user applications, separate module is needed for each type of application
각각에 대응하는 layer, protocol끼리 통신 => peer layer communication
Addresssing
- Each computer on the network has a unique network address
: 네트워크 상에서 컴퓨터 A가 컴퓨터 C를 찾아가기 위한 주소- Each application has an address that is unique with that computer (SAPs)
: 컴퓨터 C를 찾아간 후, 어떤 application을 찾아가기 위한 주소
TCP/IP
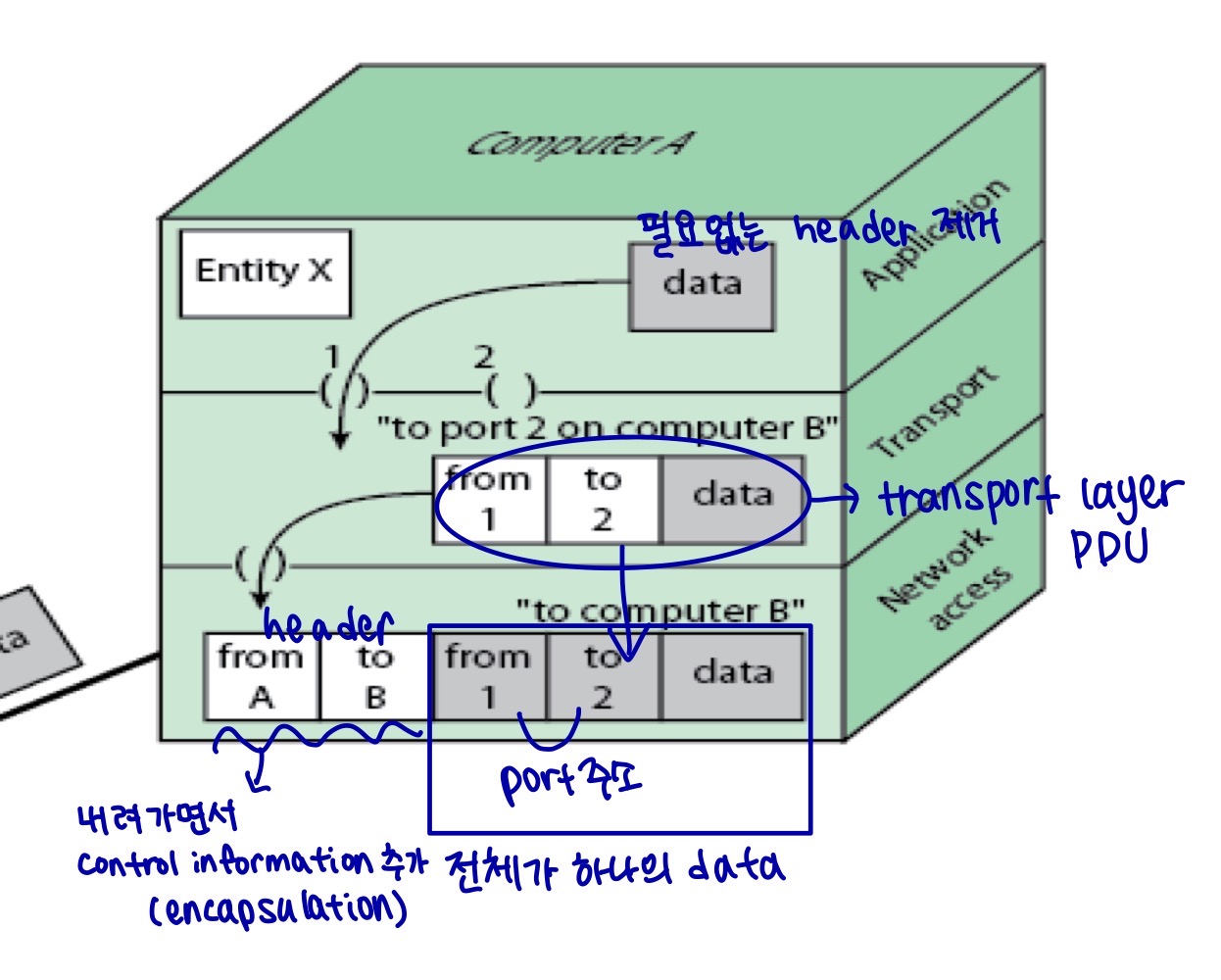
- Protocol Data Unit (PDU)
: combination of data from the next higher layer and control information
Control information -> PDU header에 들어가있음. peer transport protocol에서 사용됨
headers: source port, destination port, sequence number, error-detection code(checksum)
- Network Access Protocol
segment (transport layer pdu)를 받은 후, network access protocol은 network의 transmission을 요구해야 한다.
-> control information이 담긴 packet (network access pdu) 생성
header: source computer address, destination computer address, facilities requests (priority 포함)
TCP/IP layers
-
Application: TCP/IP 환경에 대한 접근 provides access ex) SMTP, FTP, SSH, HTTP
- contain logic to support various user applications
need a separate module for each application -
Transport: 전체 메시지의 reliable delivery
순서대로 전달ex) TCP, UDP
- host-to-host
- commonly use TCP -
Internet: routing ex) IPv4, IPv6, ICMP, OSPF, RSVP, ARP
- Internet Protocol (IP) to provide routing function
end systems, routers에 implemented
router -> connects two networks, relays data between them -
Network Access: Packet에 대한 reliable delivery 컴퓨터, 네트워크 사이의 인터페이스.
오류 없이 전달ex) Ethernet, Wifi, ATM, frame relay
- destination address provision, invoking specific services like priority, access to & routing data accross a network for two end systems attached to the same network
software used at this layer -> type of networks to be used
higher-layers network 신경 안 써도 됨
-
Physical: 전송매체 data -> signal encoding. transmission of bit stream ex) Twisted pair, optical fiber, satellite, terrestrial microwave
- characteristics of transmission medium, nature of signals, data rate
-
TCP, IP operation: tcp/ip는 router 위에 올려서 사용하지 X. 계층 늘어나니까.
PDUs in TCP/IP
- Transport layer: TCP segment
- Network Access layer: IP datagram
- Physical layer: Frame
Addressing level
- network level address
subnetwork의 host는 unique global internet address를 가져야 함
data가 proper host에 전달되도록. - process within the system
host의 process는 host별로 고유한 port주소를 가져야 함
tcp가 proper process에 전달되도록.
TCP (Transmission Control Protocol)
reliable connection
-
connection: temporary logical association between two entities in different systems
-
tcp pdu: tcp segment
- source & destination ports -> header에 포함
: identify respective users (applications)
: connection refers to pair of ports -
each entity tacks TCP segments during connection: keep tracking. flow 통제. -> reliable 전송 제공
: to regulate the flow of segments
: to recover from lost or damaged segments -
applications using TCP: http 등 대부분의 프로토콜은 tcp 사용
- simple mail transfer protocol (SMTP)
- file transfer protocol (FTP)
- telnet -
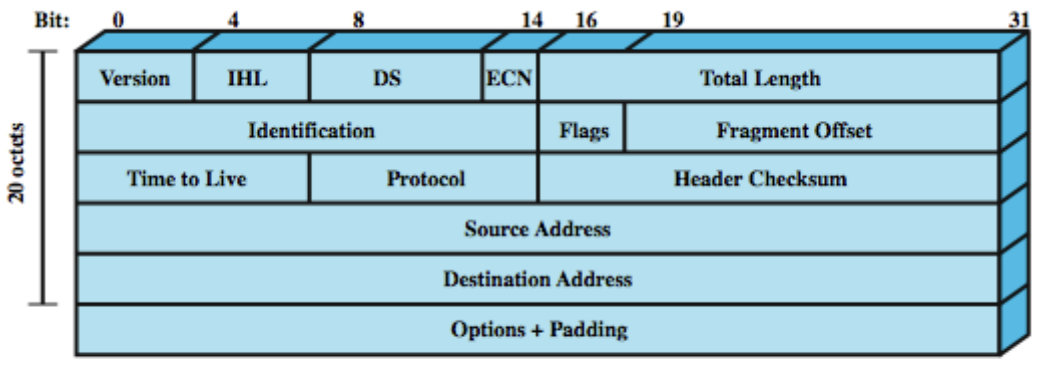
tcp header: 32 bits
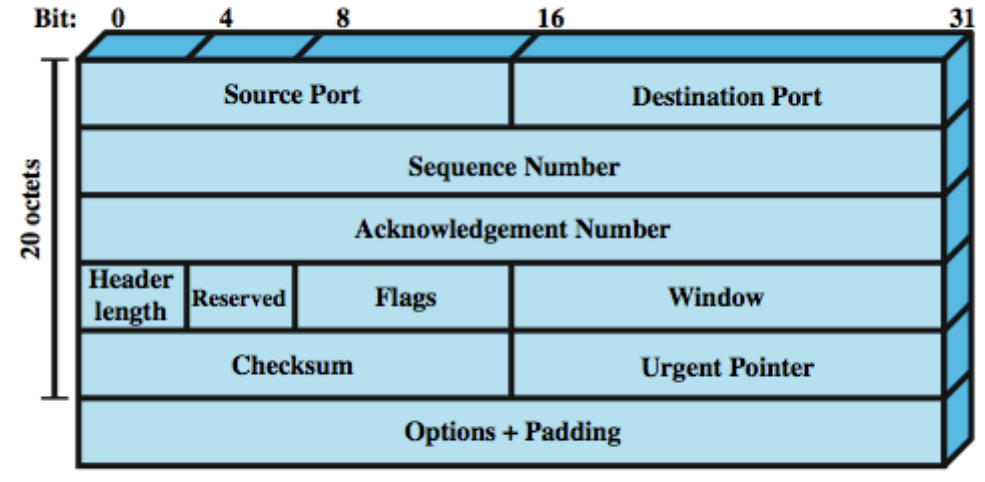
- source port, destination port: 각각 2octets -> port 주소에서 4octets
- sequence number: packet의 첫번째 data octet의 번호가 무엇인지. flow/error control에 사용octet vs byte?
-
octet: 8bit 한 묶음. 사용 코드 상관 없이 8bits
-
byte: 한 문자를 저장하기 위한 최소 비트수. ascii는 8bit 사용.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol)
delivery 보장 X, sequence 보존 X, duplication 방지 X => unreliable
BUT! minimum overhead => 전송시간 단축: UDP 주 목적
IP에 port addressing 더한 것
- applications using UDP: SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
대부분은 TCP. 망 관리만 udp로 작동.
망관리 system (NMS): 성능 관리 위해 client와 메시지 주고 받음. 이 과정에서 tcp 사용하면 번거로움
메시지를 reliable하게 deliver하는 것보다는 빠른 전송이 필요하다면 ? => UDP 사용
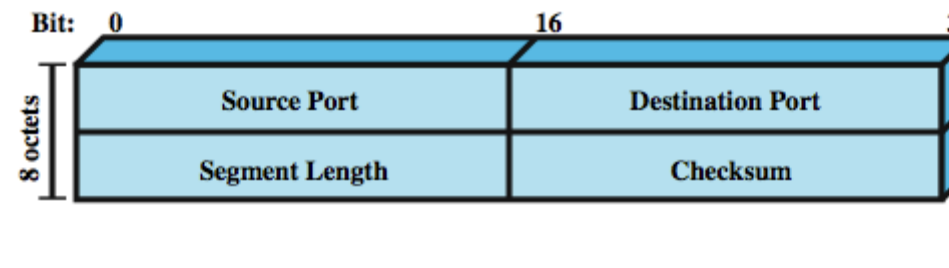
header가 8octets로 작아짐 -> 전송시간 단축
IP
IPv6
IP 전반적으로 enhancement
- accommodate higher speeds, mix of graphic & video data
- 128-bit source and destination address fields
IPv4
모든 프로토콜은 IP 위에서 작동!!
IP 위에 TCP, UDP
IP 위에서 바로 작동: ICMP(에러 핸들링), IGMP, OSPF, RSVP(예약 기반 작동)
OSI
OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) Reference Model
: a framework for defining standards for linking heterogeneous computers
- layered architecture with 7 layers
: communication functions -> 계층화된 레이어의 집합으로 partitioned
- primitive 기능 위해 하위 계층에 의존
- 상위 계층에 서비스 제공
- 특정 계층에 변화는 다른 계층의 변화에 영향 X
- layer 많음 -> 많은 기능 수행 가능. but, 많은 시간 걸림
7 layers
- application: 접근점 제공
- presentation: 시스템마다 다른 데이터 표현방식
- session: thin layer. 적은 기능 수행
- transport: reliable delivery. 전체 data. packet으로 data 잘라줌
- network: routing
- data link: reliable delivery. 하나의 packet. 네트워크로 전달되는 최종 data-> frame. header 이외에 trailer도 붙음.
- physical: 전송
outgoing: encapsulation(header 붙임). incoming: decapsulation(header 제거함)
보안 적용 시, 모든 계층에서 적용 가능. 그러나 application layer에서만 적용 시, application 단계에서의 data에만 보안 적용됨. data link layer에서 적용 시, data 전체에서 보안 적용
=> 위에서 적용할수록 보안 강도 떨어짐. 보안 적용하는 데이터 양이 작기 때문에 속도 fast, 비용 cheap
왜 OSI -> TCP/IP 전환?
: 90년대부터 전환됨.
OSI는 7계층. 고속 전송 니즈 충족 어려워짐. 대체할 수 있는 프로토콜이 TCP/IP 뿐이었음
다양한 네트워크에 interoperability 제공. ATM도 등장, 그러나 53byte cell로 다 잘라야해서 사용 어려움

primitive function에 rely, higher layer에 전달
Standardized protocol architecture
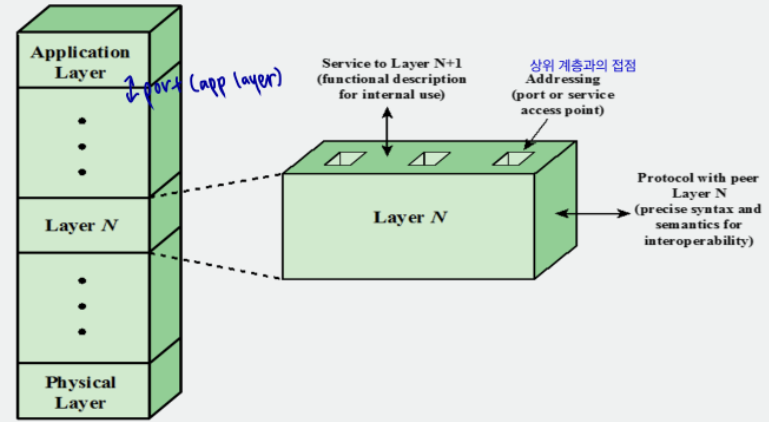
- protocol specification: same layer on two systems. 다른 operating system 포함 가능
- Format of PDUs
- Semantics of all fields
- Allowable sequence of PDUs - service definition: what services are provided
- addressing: each layer -> services to entities at the next higher layer by means of SAP (Service Access Point). 접근점.
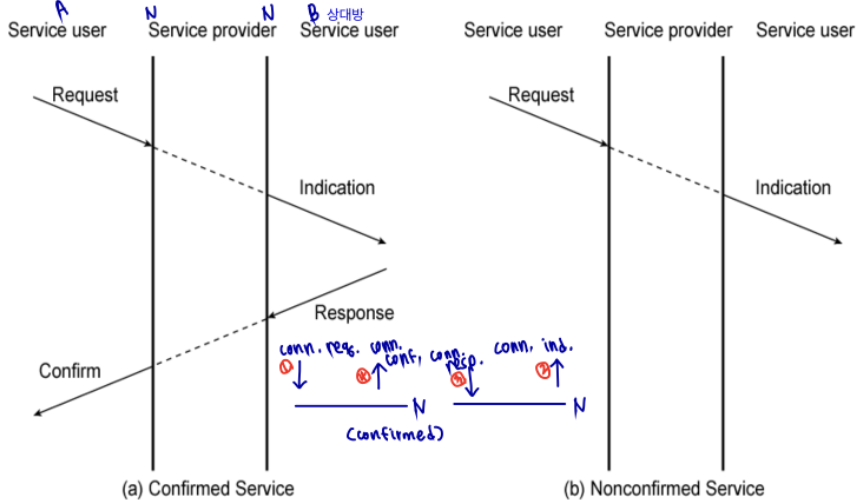
Service Primitives and Parameters
- service between adjacent layers : primitives, parameters
peer layer: protocol, adjacent layer: primitive & parameter - primitives: 수행할 함수 구체화
- parameters: pass data, control information
- request: service user에 의해. 서비스. parameter 전달
- indication: service provide에 의해. procedure가 invoke됐다는 거 나타냄. provider-initiated action (오류 발생 시, indication만)
- response: service user에 의해.
- confirm
Internet-Based Applications
- Traditional VS Multimedia Applications
increasing growth in multimedia applications
Addresses and ARP
-
Application: communicating, distributed processes
"user space". exchange messages to implement app
ex) email, file transfer, web -
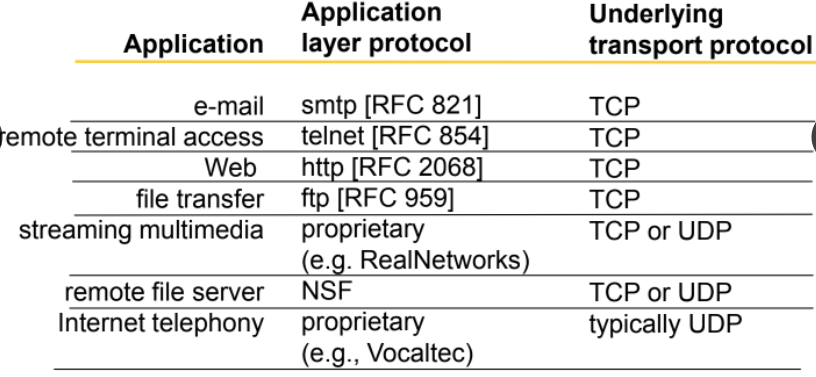
Application-layer protocols
one "piece" of an app. define messages exchange by apps and actions taken
use services provided by lower layer protocols. 최상위계층.
- LAN addresses
- 32-bit IP address: network-layer address
used to get datagram (IP pdu) to destination network
- MAC address: used to get datagram from one interface to another physically-connected interface (same network)
48 bit MAC address. LAN has unique MAC address.
- IEEE에 의해 allocation.
- MAC flat address => portability (가지고 다닐 수 있는데 주소 안 변 함)
- IP hierarchical address NOT portable
Port: TCP가 Application 찾아가기 위한 주소
IP: transport layer 아래쪽에서 사용. 서브넷을 찾아가는 주소
MAC: 호스트를 찾아가는 주소
ex) MAC address: 주민등록번호 / IP address: 우편번호
-
Routing: link layer sends datagram to B inside link-layer frame
-
ARP: Address Resolution Protocol
How to determine MAC address of B given B's IP address?
A: knows B's IP address, adn wants to learn MAC address of B
A: broadcasts ARP query packet, containing B's IP address
B: receives ARP packet, and replies to A with its MAC address
A: caches(saves) IP-to-MAC address pairs until information becomes old (time out => TTL) -
Walkthrough: routing from A to B via R