Wireless LAN
Wireless LAN Configuration
- Control Module (CM)
- acts as an interface to a WLAN
- includes either bridge or router functionality to link WLAN to the backbone
- includes some sort of access control logic, such as a polling or token-passing scheme (round robin), to regulate the access from the end systems 접근제어 logic 포함 - User Module (UM) 무선구간 여러 station 제어
- controls a number of stations off a wired LAN
- may also be part of the WLAN configuration
AP: CM, UM 역할 모두 수행
Wireless LAN Requirements
- throughput: 처리율. 단위시간 당 전달되는 데이터의 양. 모든 네트워크에서 가장 중요한 성능 평가치.
* end-to-end delay, throughput: network 성능 평가
* end-to-end: tframe + tprop + tproc + tqueue delay - number of nodes: 하나의/multiple cell에 몇 개의 node 지원되는지
- connection to backbone LAN: 무선 구간을 연결하기 위해서는 유선으로 연결
- service area: 설치된 안테나의 파워에 따라 다름. 지름 100-300m 커버 일반적
- battery power consumption: station이 얼마나 오랫동안 통신가능한지. sleep mode: 사용하지 않을 때 battery save
- transmission robustness and security: transmisson 오류 없이 전달. 보안 => interference, 도청, privacy
- collocated network operation: 두 개 이상의 wireless LAN이 같은 지역에서 전달. 여러 개 무선 랜 공존할 때 발생할 수 있는 문제 커버
- license-free operation: 유선 - 돈 내고 사용(주파수에 돈 지불), 무선랜은 라이센스 프리 필요
- handoff / roaming: 한 cell 넘어 다른 cell 이동
- dynamic configuration: mac addressing, network management와 관계. deletion, addition 대처
IEEE 802.11
Architecture
-
Wi-fi alliance
: always a concern whether products from different vendors will successfully interoperate- wireless ethernet compatibility alliance
- Wi-Fi Alliance: test suite to certify interoperability for 802.11 products
- WPA 보안작업: WPA2 incorporates all of the features of IEEE 802.11i WLAN security specification
-
Wireless LAN Security
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- privacy portion of the 802.11 standard
- contain major weakness
- Wi-fi protected Access (WPA)
- WEP의 보안
- set of security mechanisms that eliminates most 802.11 security issues
- based on the current state of the 802.11i standard
- Robust Security Network (RSN)
- final form of the 802.11i standard
- wifi alliance certifies vendors in compliance with full 802.11i spec under WPA2 program
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
-
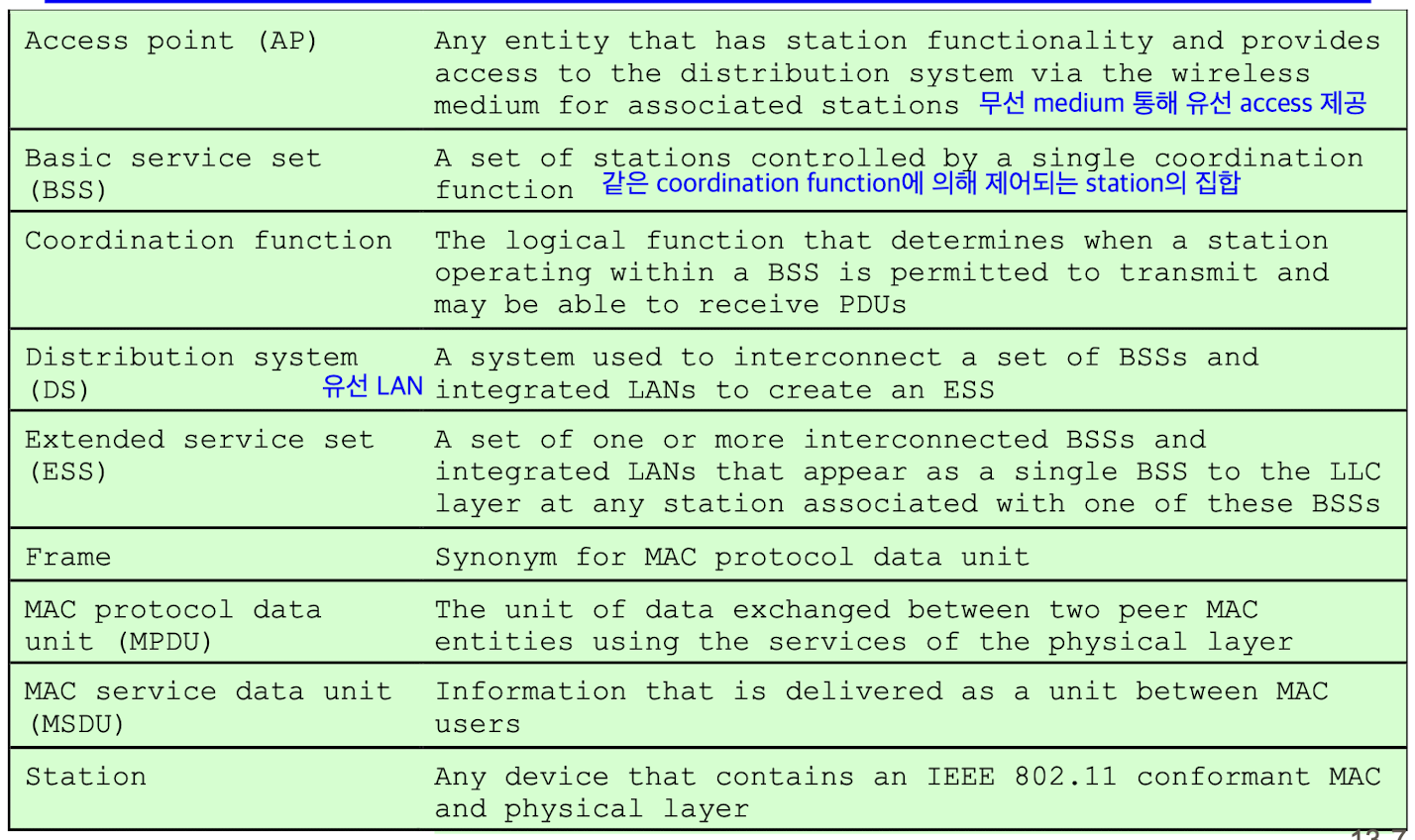
Network Components & Architecture
- smallest building block of WLAN: BSS
- consists of stations executing same MAC protocol and competing for access to the same shared wireless medium
- isolated or connect to backbone DS through AP
- AP functions: as a bridge and a relay point
- In BSS, stations do not communicate directly with one another, rather communicate through AP
- In independent BSS (IBSS), all mobile stations communicate directly with one another (AP 없이 각각의 station이 AP 기능 수행)
- Possible for two BSSs to overlap geographically
- ESS consists of two or more BSSs interconnected by DS
- appears as a single logical LAN to LLC level
- smallest building block of WLAN: BSS
Services
-
Services
- service provider: either station or DS
- station services are implemented in every 802.11 station
- DS services are provided between BSSs: implemented in AP or special-purpose device attached to DS
- service type
- 3 services: control 802.11 LAN access and confidentiality
- 6 services: support delivery of MSDUs between stationsservice provider used to support association distribution system MSDU delivery authentication station LAN access and security deauthentication station LAN access and security disassociation distribution system MSDU delivery distribution distribution system MSDU delivery integration distribution system MSDU delivery MSDU delivery station MSDU delivery Privacy station LAN access and security reassociation distribution system MSDU delivery -
Distribution of messages within a DS
integration service distribution service enables transfer of data between a station on an IEEE 802.11 LAN and a station on an integrated IEEE 802.x LAN MPDU exchange between two stations in either different BSSs or in the same BSS required address translation and media conversion logic for the exchange of data if stations are in the same BSS, distribution service logically goes through the single AP of that BSS -
Association-related services
DS requires information about stations within the ESS that is provided by the association related services 유-무선 구간 연결.
station must be associated before DS can deliver data to or accept data from it (association 먼저 필요. 연결 정보 알고 데이터 전달)- transition types based on mobility
- no transition
: a station is either stationary or moves only within the direct communication range of a single BSS - BSS transition
: same ESS 안에서 BSS 간의 transition. delivery of data to the station requires that the addressing capability be able to recognize the new location of the station - ESS transition
: 한 ESS 안의 BSS 에서 다른 ESS 안의 BSS로 이동. 완전히 다른 동네로 이동 ex) KT -> SKT. maintenance of upper-layer connections supported by 802.11 cannot be guaranteed. disruption of service 발생 가능
- no transition
- 3 services relate to know the identity of the AP of which the message should be delivered
- association
: estabilishes initial association between station and AP - reassociation
: enables an established association to be transferred from one AP to another - disassociation
: a notification from either a station or an AP that an existing association is terminated
- association
- transition types based on mobility
Medium Access Control
- Medium Access Control
- reliable data delivery 신뢰성 있는 데이터 전송
- access control 접근 제어
- security 보안
Reliable Data Delivery
- Reliable data delivery
- 802.11 physical and MAC layers: unreliable
- noise, interference, and other propagation effects result in loss of frames
- even with error-correction codes, frames may not successfully be received - can be dealt with at a higher layer
: TCP에서 처리 가능. 상위계층에서 처리 시, delay 길어짐 - more efficeint to deal with errors at MAC level
- frame exchange protocol
- station receiving frame returns acknowledgement (ACK) frame
- if no ACK within short period of time, retransmit (two frame exchange)
- 802.11 physical and MAC layers: unreliable
- Four Frame Exchange
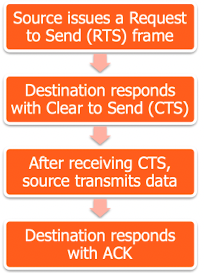
- RTS: alerts all stations within range of source that exchange is under way
- CTS: alerts all stations within range of destination
- Other stations: don't transmit to avoid collision
- RTS / CTS exchange: a required function of MAC but may be disabled
Access Control
-
MAC Algorithm
- Distributed access protocols
- distribute the decision to transmit over all nodes using a carrier sense mechanism
- useful for an ad hoc network of peer workstations ex) IBSS
- attractive in WLAN configurations that consist primarily of bursty traffic - Centralized access protocols
- involve regulation of transmission by a centralized decision maker
- natural for configurations in which a number of wireless stations are interconnected with each other and some sort of base station that attaches to a backbone wired LAN
- useful if some of the data is time sensitive or high priority
- Distributed access protocols
-
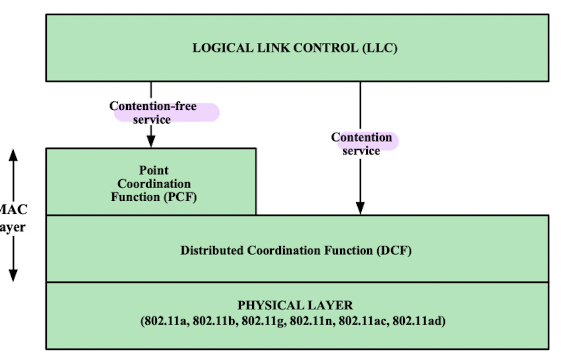
DFWMAC (Distributed Foundation Wireless MAC)
- the end result for 802.11 mac algorithm
- provides a distributed access control mechanism with an optional centralized control built on top of that- Distributed Coordination Function (DCF)
- lower sublayer of the MAC layer
- uses a contention algorithm (경쟁 알고리즘) to provide access to all traffic
- ordinary asynchronous - Point Coordination Function (PCF) - sublayer
- centralized MAC algorithm used to provide contention-free(비경쟁) service
- built on top of DCF and exploits features of DCF to assure access for its users (DCF 위에서 built. 활용)
- Distributed Coordination Function (DCF)
-
Distributed Coordination Function (DCF)
- DCF sublayer uses CSMA algorithm
- does not include a collision detection function because it is not practical on a wireless network
- includes a set of delays that amounts to a priority schemeif station has frame to send, it listens to medium
if medium is idle, station may transmit
otherwise waits until current transmission is complete -
Priority IFS Values
(Inter Frame Space)
- SIFS (short IFS)
: for all immediate response actions
- PIFS (point coordination funciton IFS)
: used by the centralized controller in PCF scheme when issuing polls (contention free)
- DIFS (distributed coordination function IFS)
: used as minimum delay for asynchronous frames contending for access
Basic Access Methods
Collision 피하기 위해 매 시점마다 체크 후 전송
- SIFS (Short Interframe Space)
- any station using SIFS to determine transmission opportunity has the highest priority
- used in the following circumstances- Acknowledgement (ACK)
- station responds with an ACK frame after waiting only for a SIFS gap - Clear to Send (CTS)
- station ensures data frame gets through by issuing RTS
- addressed station immediately respond with CTS if ready
- all other station immediately respond with CTS if ready - Poll response
- Acknowledgement (ACK)
- Point Coordination Function (PCF)
- alternative access method implemented on top of DCF
- polling by centralized polling master (point coordinator)
- uses PIFS when issuing polls
- point coordinator polls in round-robin to stations configured for polling
- when poll issued, polled station may respond using SIFS
- if point coordinator receives response, it issues another poll using PIFS
- if no response during expected turnaround time, coordinator issues poll
- coordinator could lock out asynchronous traffic by issuing polls
- have a superframe interval definedPCF Superframe Construction
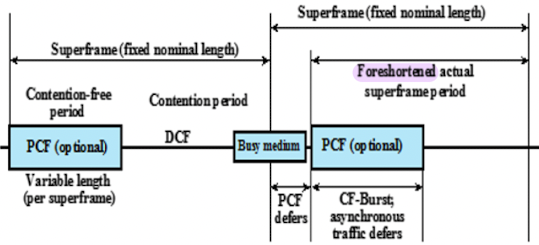 네트워크 독점 사용 방지
네트워크 독점 사용 방지
Security Considerations
- Authentication
- used to establish station identity
- wired LANs assume physical connection gives authority to use LAN
- not a valid assumption for wireless LANs
- 802.11 supports several authentication schemes
- does not mandate any particular scheme
- range from relatively insecure handshaking to public-key encryption
- 802.11 requires mutually acceptable, successful authentication before association with AP - Deauthentication
- invoked whenever an existing authentication is to be terminated 인증 종료시마다 - Privacy
- used to prevent messages being read by others
- 802.11 allows optional use of encryption(암호화) - original WEP(Wired Equivalent Privacy) security features were weak
- subsequently 802.11i and WPA (Wifi Protected Access) alternatives evolved giving better security
