
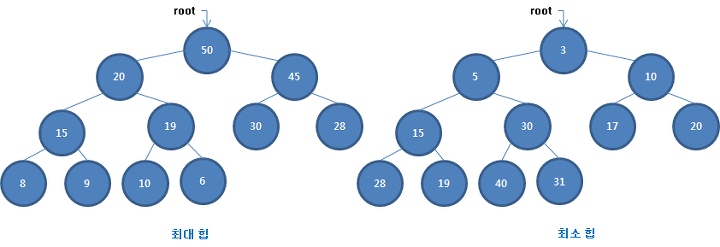
이진힙에서의 규칙은 단순하다. 노드당 자식은 항상 2개까지 둘 수 있고, 자식은 부모노드보다 작아야한다. 따라서 같은 계층의 형제노드끼리는 특별한 규칙이 없다.
힙은 주로 그래프 순회나 우선순위 큐에 사용된다.
힙 정렬
힙 정렬이 된 array에서 index가 n인 경우 해당 index의 왼쪽 자식은 2n+1, 오른쪽 자식은 2n+2의 인덱스에 할당되어 있다. 자식에서 부모를 추정할 때는 반대로 (n-1)/2를 하여 소수는 내림하면 된다.
class MaxBinnaryHeap {
constructor() {
this.values = [41, 39, 33, 18, 27, 12];
}
// 힙 정렬의 규칙에 맞게 insert한다.
insert(element) {
this.values.push(element);
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp() {
let idx = this.values.length - 1;
const element = this.values[idx];
while (idx > 0) {
const parentIdx = parseInt((idx - 1) / 2);
const parent = this.values[parentIdx];
if (element <= parent) break;
[this.values[parentIdx], this.values[idx]] = [element, parent];
idx = parentIdx;
}
}
// 최대 값을 추출하고, 힙 정렬의 규칙에 맞게 다시 정렬한다.
extractMax() {
// Edge case come back to this
const max = this.values[0];
const end = this.values.pop();
if (this.values.length > 0) {
this.values[0] = end;
this.sinkDown();
}
return max;
}
sinkDown() {
let idx = 0;
const length = this.values.length;
const element = this.values[0];
while (true) {
let leftChildIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
let rightChildIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
let leftChild, rightChild;
let swap = null;
if (leftChildIdx < length) {
leftChild = this.values[leftChildIdx];
if (leftChild > element) {
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
if (rightChildIdx < length) {
rightChild = this.values[rightChildIdx];
if (
(swap === null && rightChild > element) ||
(swap !== null && rightChild > leftChild)
) {
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
if (swap === null) break;
this.values[idx] = this.values[swap];
this.values[swap] = element;
idx = swap;
}
}
}
우선순위큐
우선순위큐는 각 요소가 그에 해당하는 우선순위를 가지는 데이터 구조다.
더 높은 우선순의를 가진 요소가 더 낮은 우선순위를 가진 요소보다 먼저 처리된다.
만약 병원에서 총을 맞은 사람은 감기환자, 찰과상 환자 등 다른 환자보다 최우선으로 진료를 받는 것으로 정했다고 하자. 병원에 감기환자 100명이 대기 중인 상태에서 총 맞은 환자가 나중에 오더라도 총 맞은 환자가 가장먼저 진료를 받게 된다. 우선순위큐도 이와 같다.
우선순위 큐는 힙과 거의 같은데, 차이점은 Node Class가 존재한다는 것이다. 왜냐하면 값과 우선순위 정보가 있어야 하기 때문이다.
class PriorityQueue {
constructor(){
this.values = [];
}
enqueue(val, priority){
let newNode = new Node(val, priority);
this.values.push(newNode);
this.bubbleUp();
}
bubbleUp(){
let idx = this.values.length - 1;
const element = this.values[idx];
while(idx > 0){
let parentIdx = Math.floor((idx - 1)/2);
let parent = this.values[parentIdx];
if(element.priority >= parent.priority) break;
this.values[parentIdx] = element;
this.values[idx] = parent;
idx = parentIdx;
}
}
dequeue(){
const min = this.values[0];
const end = this.values.pop();
if(this.values.length > 0){
this.values[0] = end;
this.sinkDown();
}
return min;
}
sinkDown(){
let idx = 0;
const length = this.values.length;
const element = this.values[0];
while(true){
let leftChildIdx = 2 * idx + 1;
let rightChildIdx = 2 * idx + 2;
let leftChild,rightChild;
let swap = null;
if(leftChildIdx < length){
leftChild = this.values[leftChildIdx];
if(leftChild.priority < element.priority) {
swap = leftChildIdx;
}
}
if(rightChildIdx < length){
rightChild = this.values[rightChildIdx];
if(
(swap === null && rightChild.priority < element.priority) ||
(swap !== null && rightChild.priority < leftChild.priority)
) {
swap = rightChildIdx;
}
}
if(swap === null) break;
this.values[idx] = this.values[swap];
this.values[swap] = element;
idx = swap;
}
}
}
class Node {
constructor(val, priority){
this.val = val;
this.priority = priority;
}
}이진힙의 bigO
Insertion - O(logN)
Removal - O(logN)
Search - O(N)
이진힙도 여타 이진 트리처럼 계층이 하나 내려갈 때마다 2배의 노드가 더 생긴다.
삽입시 만약 가장 끝에 삽입될 수 있는 경우는 바로 삽입이 되고, root까지 올려갈 경우라도 계층을 하나씩 타고 올라가서 결국 logN의 시간 복잡도를 가지게 된다. 삭제의 경우도 마찬가지다.
이진힙은 형제간의 규칙성이 없다. 따라서 계층을 내려갈 때마다 소거를 할 수 없다. 그러므로 결국 모든 노드를 탐색해야 우너하는 노드를 찾을 수 있다. 결국 시간복잡도는 N이 된다.
