오늘 수강한 강의 - 알고리즘(31 ~ 50)
검색 알고리즘 31 ~ 32
[1] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 사용자가 입력한 숫자를 검색하는 모듈을 다음 요건에 따라 만들어 보자

lineMod 모듈
def searchNumberByLineAlgorithm(ns, sn): searchResultIdx = -1 print('Numbers: {}'.format(ns)) print('Search Numbers: {}'.format(sn))n = 0 while True: if n == len(ns): print('search FAIL!') breakif ns[n] == sn: searchResultIdx = n print('search SUCCESS!') print('search result INDEX: {}'.format(searchResultIdx)) breakn += 1return searchResultIdx
ex.py
import lineMod import randomif __name__ == '__main__': rNums = random.sample(range(1, 21), 10) searchNum = int(input('input search number: ')) resultIdx = lineMod.searchNumberByLineAlgorithm(rNums, searchNum)if resultIdx == -1: print('No results found') print('search result index: {}'.format(resultIdx))else: print('>>> Search Results <<<') print('search result index: {}'.format(resultIdx)) print('search result number: {}'.format(rNums[resultIdx]))
[2] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 사용자가 입력한 숫자를 검색하는 모듈을 다음 요건에 따라 만들어 보자

binaryMod 모듈
def searchNumberByBinaryAlgorightm(ns, sn): searchResultIdx = -1 staIdx = 0 endIdx = len(ns) - 1 midIdx = (staIdx + endIdx) // 2 midVal = ns[midIdx] print('staIdx: {}, endIdx: {}'.format(staIdx, endIdx)) print('midIdx: {}, midVal: {}'.format(midIdx, midVal))while sn >= ns[0] and sn <= ns[len(ns) - 1]: if sn == ns[len(ns) - 1]: searchResultIdx = len(ns) - 1 breakif staIdx + 1 == endIdx: if ns[staIdx] != sn and ns[endIdx] != sn: breakif sn > midVal: staIdx = midIdx midIdx = (staIdx + endIdx) // 2 midVal = ns[midIdx] print('+staIdx: {}, endIdx: {}'.format(staIdx, endIdx)) print('+midIdx: {}, midVal: {}'.format(midIdx, midVal))elif sn < midVal: endIdx = midIdx midIdx = (staIdx + endIdx) // 2 midVal = ns[midIdx] print('-staIdx: {}, endIdx: {}'.format(staIdx, endIdx)) print('-midIdx: {}, midVal: {}'.format(midIdx, midVal))elif sn == midVal: searchResultIdx = midIdx breakreturn searchResultIdx
ex.py
import binaryModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = [1, 2, 4, 6, 7, 8, 10, 11, 13, 15, 16, 17, 20, 21, 23, 24, 27, 28] searchNum = int(input('input search number: '))resultIdx = binaryMod.searchNumberByBinaryAlgorightm(nums, searchNum) print('nums: {}'.format(nums))if resultIdx == -1: print('No results found.') print('search result index: {}'.format(resultIdx))else: print('>>> Search Results <<<') print('search result index: {}'.format(resultIdx)) print('search result number: {}'.format(nums[resultIdx]))
순위 알고리즘 33 ~ 34
[1] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 아이템의 순위를 출력하고, 순위에 따라 아이템을 정렬하는 모듈 (리스트는 50부터 100까지의 난수 20개)
rankMod 모듈
def rankAlgorithm(ns): ranks = [0 for i in range(len(ns))]for idx, n1 in enumerate(ns): for n2 in ns: if n1 < n2: ranks[idx] += 1print('nums: {}'.format(ns)) print('ranks: {}'.format(ranks))for i , n in enumerate(ns): print('num: {} \t rank: {}'.format(n, ranks[i] + 1))sortedNums = [0 for n in range(len(ns))]for idx, rank in enumerate(ranks): sortedNums[rank] = ns[idx]return sortedNums
ex.py
import random import rankModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = random.sample(range(50, 101), 20) sNums = rankMod.rankAlgorithm(nums) print('sNums: {}'.format(sNums))
[2] 알파벳 문자들과 정수들에 대한 순위를 정하는 프로그램 (알파벳은 아스키코드 값을 이용)
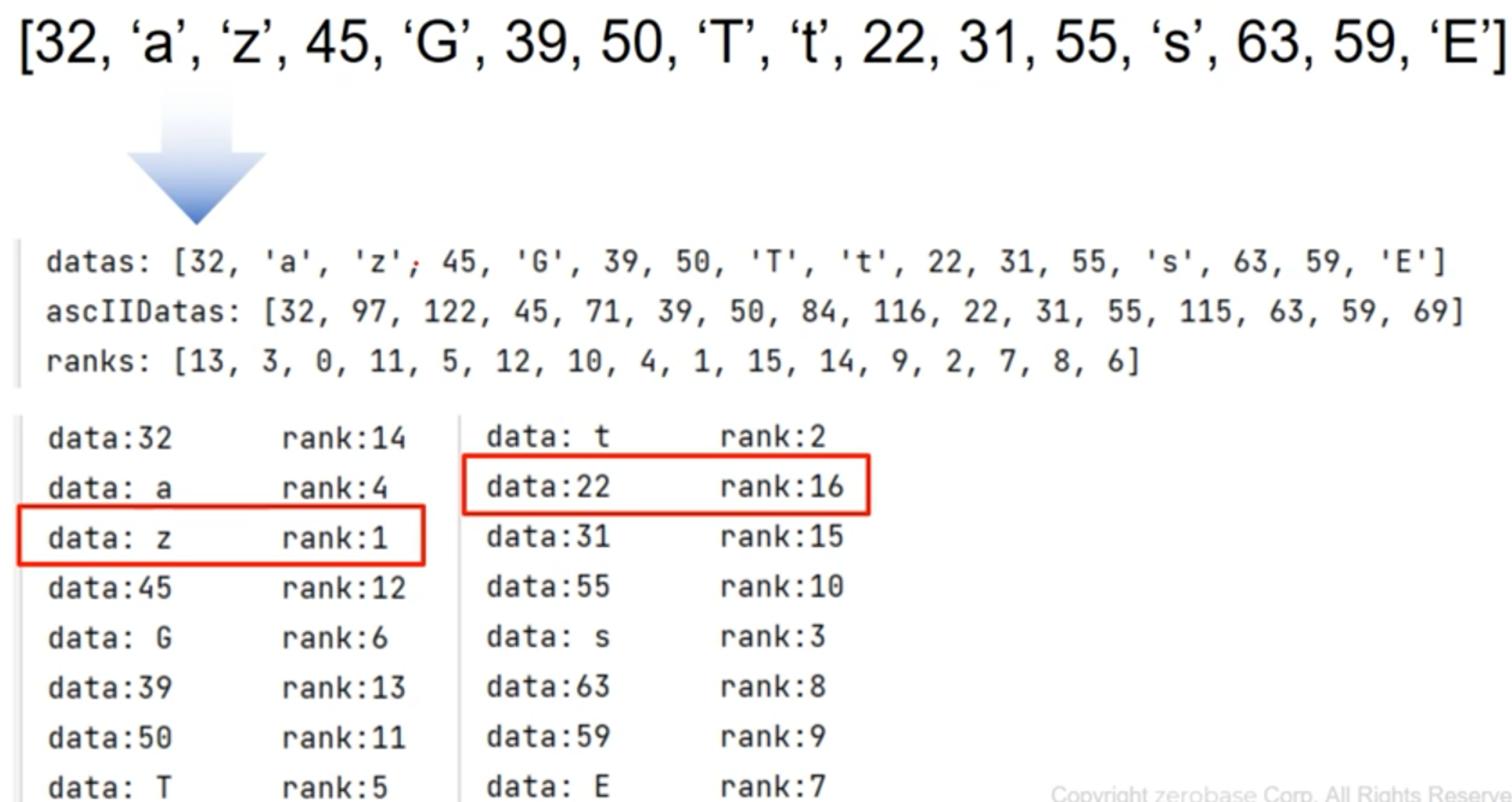
datas = [32, 'a', 'z', 45, 'G', 39, 50, 'T', 't', 22, 31, 55, 's', 63, 59, 'E'] print('datas: {}'.format(datas))ascIIDatas = [] for data in datas: if str(data).isalpha(): ascIIDatas.append(ord(data)) continue ascIIDatas.append(data) print('ascIIDatas: {}'.format(ascIIDatas))ranks = [0 for i in range(len(ascIIDatas))] print('ranks before: {}'.format(ranks))for idx, data1 in enumerate(ascIIDatas): for data2 in ascIIDatas: if data1 < data2: ranks[idx] += 1 print('ranks after: {}'.format(ranks))for i, d in enumerate(datas): print(f'data:{d:>2} \t rank:{ranks[i] + 1}')
35 ~ 38 정렬 알고리즘
[1] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트를 버블정렬 알고리즘을 이용해서 오름차순과 내림차순으로 정렬하는 모듈

bubbleMod 모듈
import copydef sortByBubbleAlgorithm(ns, asc=True): c_ns = copy.copy(ns) length = len(c_ns) - 1 for i in range(length): for j in range(length - i):if asc: if c_ns[j] > c_ns[j+1]: c_ns[j], c_ns[j+1] = c_ns[j+1], c_ns[j] else: if c_ns[j] < c_ns[j+1]: c_ns[j], c_ns[j+1] = c_ns[j+1], c_ns[j]print('ns: {}'.format(c_ns)) print()return c_ns
ex.py
import random import bubbleModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = random.sample(range(1, 20), 10) print('not sorted nums: {}'.format(nums))result = bubbleMod.sortByBubbleAlgorithm(nums) print('sorted nums by ASC: {}'.format(result)) result = bubbleMod.sortByBubbleAlgorithm(nums, asc=False) print('sorted nums by DESC: {}'.format(result))
[2] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트를 삽입정렬 알고리즘을 이용해서 오름차순과 내림차순으로 정렬하는 모듈
insertMod 모듈
import copydef sortInsertAlgorithm(ns, asc=True): c_ns = copy.copy(ns)for i1 in range(1, len(c_ns)): i2 = i1 - 1 c_Num = c_ns[i1]if asc: # 오름차순 while c_ns[i2] > c_Num and i2 >= 0: c_ns[i2 + 1] = c_ns[i2] i2 -= 1else: # 내림차순 while c_ns[i2] < c_Num and i2 >= 0: c_ns[i2 + 1] = c_ns[i2] i2 -= 1c_ns[i2 + 1] = c_Num print('c_ns: {}'.format(c_ns))return c_ns
ex.py
import random import insertModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = random.sample(range(1, 20), 10)print('not sorted nums:\n{}'.format(nums)) result = insertMod.sortInsertAlgorithm(nums) print('sorted nums by ASC:\n{}'.format(result))print('not sorted nums:\n{}'.format(nums)) result = insertMod.sortInsertAlgorithm(nums, asc=False) print('sorted nums by DESC:\n{}'.format(result))
[3] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트를 선택정렬 알고리즘을 이용해서 오름차순과 내림차순으로 정렬하는 모듈
selectMod 모듈
import copydef sortSelectAlgorithm(ns, asc=True): c_ns = copy.copy(ns)for i in range(len(c_ns) - 1): minIdx = ifor j in range(i + 1, len(c_ns)): if asc: #오름차순 if c_ns[minIdx] > c_ns[j]: minIdx = j else: #내림차순 if c_ns[minIdx] < c_ns[j]: minIdx = jc_ns[i], c_ns[minIdx] = c_ns[minIdx], c_ns[i] print('nums: {}'.format(c_ns))return c_ns
ex.py
import random import selectModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = random.sample(range(1, 21), 10)print('not sorted nums:\t {}'.format(nums)) result = selectMod.sortSelectAlgorithm(nums) print('sorted nums by ASC:\t {}'.format(result))print('not sorted nums:\t {}'.format(nums)) result = selectMod.sortSelectAlgorithm(nums, asc=False) print('sorted nums by DESC:\t {}'.format(result))
[4] 숫자로 이루어진 리스트를 병합정렬 알고리즘을 이용해서 오름차순과 내림차순으로 정렬하는 모듈

mergeAlgorithm 모듈
def mSort(ns, asc=True): if len(ns) < 2: return nsmidIdx = len(ns) // 2 leftNums = mSort(ns[0: midIdx], asc=asc) rightNums = mSort(ns[midIdx:len(ns)], asc=asc)mergedNums = [] leftIdx = 0; rightIdx = 0 while leftIdx < len(leftNums) and rightIdx < len(rightNums): if asc: if leftNums[leftIdx] < rightNums[rightIdx]: mergedNums.append(leftNums[leftIdx]) leftIdx += 1 else: mergedNums.append(rightNums[rightIdx]) rightIdx += 1 else: if leftNums[leftIdx] > rightNums[rightIdx]: mergedNums.append(leftNums[leftIdx]) leftIdx += 1 else: mergedNums.append(rightNums[rightIdx]) rightIdx += 1mergedNums += leftNums[leftIdx:] mergedNums += rightNums[rightIdx:]print('mergedNums: {}'.format(mergedNums)) return mergedNums
ex.py
import random import mergeAlgorithmrNums = random.sample(range(1, 101), 20) print('rNums: {}'.format(rNums)) print('mergeAlgorithm.mSort(rNums): {}'.format(mergeAlgorithm.mSort(rNums))) print('mergeAlgorithm.mSort(rNums): {}'.format(mergeAlgorithm.mSort(rNums, asc=False)))
39 ~ 40 최댓값 알고리즘
[1] 최댓값 알고리즘을 이용해서 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 최댓값과 최댓값의 개수를 찾는 모듈 (리스트는 1부터 50까지의 난수 30개를 이용하되, 중복이 허용)
maxMod 모듈
class MaxAlgorithm: def __init__(self, ns): self.nums = ns self.maxNum = 0 self.maxNumCnt = 0def setMaxNum(self): self.maxNum = 0 for n in self.nums: if self.maxNum < n: self.maxNum = ndef getMaxNum(self): self.setMaxNum() return self.maxNumdef setMaxNumCnt(self): self.setMaxNum() for n in self.nums: if self.maxNum == n: self.maxNum += 1def getMaxNumCnt(self): self.setMaxNumCnt() return self.maxNumCnt
ex.py
import random import maxModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = [] for n in range(30): nums.append(random.randint(1, 50))print('nums: \n {}'.format(nums)) ma = maxMod.MaxAlgorithm(nums) print('max num: {}'.format(ma.getMaxNum())) print('max num cnt: {}'.format(ma.getMaxNumCnt()))
[2] 학급 전체 학생의 시험 점수에 대한 평균과 최댓값을 구하고 평균과 최댓값의 편차를 출력하는 프로그램

mod 모듈
def getAvg(ns): total = 0 for n in ns: total += n return total / len(ns)def getMax(ns): maxN = ns[0] for n in ns: if maxN < n: maxN = n return maxNdef getDeviation(n1, n2): return round(abs(n1 - n2), 2)
ex.py
import modscores = [100, 64, 94, 66, 75, 58, 99, 76, 96, 74, 54, 73, 88, 70, 68, 50, 95, 89, 69, 98]scores_avg = mod.getAvg(scores) scores_max = mod.getMax(scores) deviation = mod.getDeviation(scores_avg, scores_max)print('score_avg: {}'.format(scores_avg)) print('score_max: {}'.format(scores_max)) print('deviation: {}'.format(deviation))
41 ~ 42 최솟값 알고리즘
[1] 최솟값 알고리즘을 이용해서 숫자로 이루어진 리스트에서 최솟값과 최솟값의 개수를 찾는 모듈 (리스트는 1부터 50까지의 난수 30개를 이용하되, 중복이 허용)
minMod 모듈
class MinAlgorithm: def __init__(self, ns): self.nums = ns self.minNum = 0 self.minNumCnt = 0def setMinNum(self): self.minNum = 51 for n in self.nums: if self.minNum > n: self.minNum = ndef getMinNum(self): self.setMinNum() return self.minNumdef setMinNumCnt(self): self.setMinNum() for n in self.nums: if self.minNum == n: self.minNum += 1def getMinNumCnt(self): self.setMinNumCnt() return self.minNumCnt
ex.py
import random import minModif __name__ == '__main__': nums = [] for n in range(30): nums.append(random.randint(1, 50))print('nums: \n {}'.format(nums)) ma = minMod.MinAlgorithm(nums) print('min num: {}'.format(ma.getMinNum())) print('min num cnt: {}'.format(ma.getMinNumCnt()))
[2] 학급 전체 학생의 시험 점수에 대한 평균과 최솟값을 구하고 평균과 최솟값의 편차를 출력하는 프로그램

mod 모듈
def getAvg(ns): total = 0 for n in ns: total += n return total / len(ns)def getMin(ns): minN = ns[0] for n in ns: if minN > n: minN = n return minNdef getDeviation(n1, n2): return round(abs(n1 - n2), 2)
ex.py
import modscores = [100, 64, 94, 66, 75, 58, 99, 76, 96, 74, 54, 73, 88, 70, 68, 50, 95, 89, 69, 98]scores_avg = mod.getAvg(scores) scores_min = mod.getMin(scores) deviation = mod.getDeviation(scores_avg, scores_min)print('score_avg: {}'.format(scores_avg)) print('score_min: {}'.format(scores_min)) print('deviation: {}'.format(deviation))
<class를 이용>
mod2 모듈
class ScoreManagement: def __init__(self, ss): self.scores = ss self.score_tot = 0 self.score_avg = 0 self.score_min = 0 self.score_max = 0def getMinScore(self): if self.scores == None or len(self.scores) == 0: return None self.score_min = self.scores[0] for score in self.scores: if self.score_min > score: self.score_min = score return self.score_mindef getMaxScore(self): if self.scores == None or len(self.scores) == 0: return None self.score_max = self.scores[0] for score in self.scores: if self.score_max < score: self.score_max = score return self.score_maxdef getTotScore(self): if self.scores == None or len(self.scores) == 0: return None self.score_tot = 0 for score in self.scores: self.score_tot += score return self.score_totdef getAvgScore(self): if self.scores == None or len(self.scores) == 0: return None self.score_avg = round(self.getTotScore() / len(self.scores), 2) return self.score_avgdef getMaxDeviation(self): result = abs(self.getAvgScore() - self.getMaxScore()) return round(result, 2)def getMinDeviation(self): result = abs(self.getAvgScore() - self.getMinScore()) return round(result, 2)
ex.py
import mod2scores = [100, 64, 94, 66, 75, 58, 99, 76, 96, 74, 54, 73, 88, 70, 68, 50, 95, 89, 69, 98]sm = mod2.ScoreManagement(scores) print('score_avg: {}'.format(sm.getAvgScore())) print('score_min: {}'.format(sm.getMinScore())) print('score_max: {}'.format(sm.getMaxScore())) print('score_min_deviation: {}'.format(sm.getMinDeviation())) print('score_max_deviation: {}'.format(sm.getMaxDeviation()))
43 ~ 44 최빈값 알고리즘
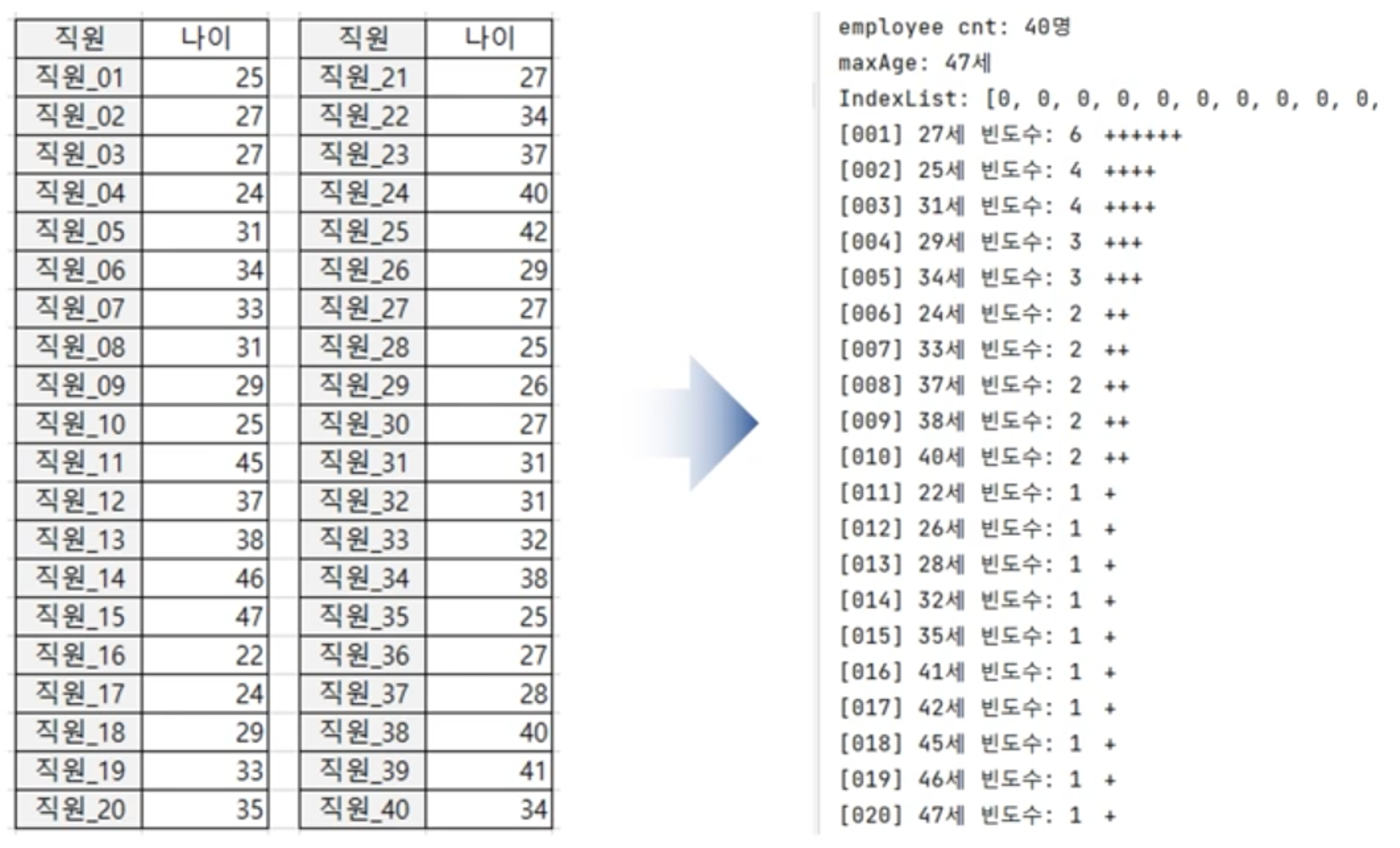
[1] 최빈값 알고리즘을 이용해서 나이 분포를 간단한 그래프로 출력하는 모듈
maxMod 모듈
class MaxAlgorithm: def __init__(self, ns): self.nums = ns self.maxNum = 0 self.maxNumIdx = 0def setMaxIdxAndNum(self): self.maxNum = 0 self.maxNumIdx = 0for i, n in enumerate(self.nums): if self.maxNum < n: self.maxNum = n self.maxNumIdx = idef getMaxNum(self): return self.maxNumdef getMaxIdx(self): return self.maxNumIdx
modeMod 모듈
import maxModclass ModeAlgorithm: def __init__(self, ns, mn): self.nums = ns self.maxNum = mn self.indexes = []def setIndexList(self): self.indexes = [0 for i in range(self.maxNum + 1)] for n in self.nums: self.indexes[n] = self.indexes[n] + 1def getIndexList(self): if sum(self.indexes) == 0: return None else: return self.indexesdef printAges(self): n = 1 while True: maxAlo = maxMod.MaxAlgorithm(self.indexes) maxAlo.setMaxIdxAndNum() maxNum = maxAlo.getMaxNum() maxNumIdx = maxAlo.getMaxIdx()if maxNum == 0: break print(f'[{n:0>3}] {maxNumIdx}세 빈도수: {maxNum}\t', end='') print('+' * maxNum) self.indexes[maxNumIdx] = 0n += 1
ex.py
import modeMod import maxModages = [25, 27, 27, 24, 31, 34, 33, 31, 29, 25, 45, 37, 38, 46, 47, 22, 24, 29, 33, 35, 27, 34, 37, 40, 42, 29, 27, 25, 26, 27, 31, 31, 32, 38, 25, 27, 28, 40, 41, 34]print('employee cnt: {}명'.format(len(ages)))maxAlo = maxMod.MaxAlgorithm(ages) maxAlo.setMaxIdxAndNum() maxAge = maxAlo.getMaxNum() print('maxAge: {}세'.format(maxAge))modAlo = modeMod.ModeAlgorithm(ages, maxAge) modAlo.setIndexList() print('IndexList: {}'.format(modAlo.getIndexList()))modAlo.printAges()
[2] 최빈도 알고리즘을 이용해서 모든 회차의 각각의 번호에 대한 빈도수를 출력하는 프로그램

mod 모듈
class LottoMode: def __init__(self, ln): self.lottoNums = ln self.modeList = [0 for n in range(1, 47)]def getLottoNumMode(self): for roundNums in self.lottoNums: for num in roundNums: self.modeList[num] = self.modeList[num] + 1 return self.modeListdef printModeList(self): if sum(self.modeList) == 0: return Nonefor i, m in enumerate(self.modeList): if i != 0: print(f'번호: {i:>2}, 빈도: {m}, {"*" * m}')
ex.py
import modlottoNums = [[13, 23, 15, 5, 6, 39], [36, 13, 5, 3, 30, 16], [43, 1, 15, 9, 3, 38], [32, 42, 24, 45, 8, 31], [18, 39, 41, 11, 4, 9], [12, 39, 11, 38, 32, 5], [29, 25, 13, 6, 14, 8], [21, 33, 19, 20, 42, 7], [6, 28, 3, 45, 41, 24], [42, 15, 8, 5, 35, 4], [14, 4, 35, 24, 29, 3], [15, 20, 6, 37, 34, 39], [27, 5, 32, 15, 25, 19], [45, 25, 2, 8, 30, 43], [4, 19, 33, 10, 6, 24], [25, 26, 45, 23, 24, 16], [33, 28, 45, 21, 38, 24], [4, 30, 29, 28, 32, 38], [11, 28, 12, 2, 42, 3], [40, 29, 16, 8, 9, 28], [6, 9, 37, 30, 3, 35], [29, 18, 41, 28, 38, 15], [9, 31, 13, 44, 1, 36], [36, 1, 37, 32, 15, 12], [41, 32, 16, 6, 26, 33], [12, 43, 10, 29, 39, 9], [41, 9, 23, 35, 18, 17], [35, 38, 3, 28, 36, 31], [21, 44, 4, 29, 18, 7], [20, 23, 6, 2, 34, 44]]lm = mod.LottoMode(lottoNums) mList = lm.getLottoNumMode() print('mList: {}'.format(mList)) lm.printModeList()
45 ~ 46 근삿값 알고리즘
[1] 근삿값 알고리즘을 이용해서 수심을 입력하면 수온을 출력하는 모듈

nearMod 모듈
class NearAlgorithm: def __init__(self, d): self.temps = {0: 24, 5: 22, 10: 20, 15: 16, 20: 13, 25: 10, 30: 6} self.depth = d self.nearNum = 0 self.minNum = 24def getNearNumbers(self): for n in self.temps.keys(): absNum = abs(n - self.depth) if absNum < self.minNum: self.minNum = absNum self.nearNum = nreturn self.temps[self.nearNum]
ex.py
import nearModdepth = int(float(input('input depth: '))) print('depth: {}m'.format(depth))na = nearMod.NearAlgorithm(depth) temp = na.getNearNumbers() print('water temperature: {}도'.format(temp))
[2] 사용자의 몸무게와 키를 입력하면 체질량지수(BMI)를 계산하고 근삿값 알고리즘과 BMI표를 이용해서 신체 상태를 출력하는 프로그램

nearMod 모듈
class BmiAlgorithm: def __init__(self, w, h): self.BMISection = {18.5:['저체중', '정상'], 23:['정상','과체중'], 25:['과체중', '비만']} self.userWeight = w self.userHeight = h self.userBMI = 0 self.userCondition = '' self.nearNum = 0 self.minNum = 25def calculatorBMI(self): self.userBMI = round(self.userWeight / (self.userHeight * self.userHeight), 2) print('userBMI: {}'.format(self.userBMI))def printUserCondition(self): for n in self.BMISection.keys(): absNum = abs(n - self.userBMI) if absNum < self.minNum: self.minNum = absNum self.nearNum = n print('self.nearNum: {}'.format(self.nearNum))if self.userBMI <= self.nearNum: self.userCondition = self.BMISection[self.nearNum][0] else: self.userCondition = self.BMISection[self.nearNum][1] print('self.userCondition: {}'.format(self.userCondition))
ex.py
import nearModuWeight = float(input('input weight(Kg): ')) uHeight = float(input('input height(m): '))na = nearMod.BmiAlgorithm(uWeight, uHeight) na.calculatorBMI() na.printUserCondition()
47 ~ 48 재귀 알고리즘
[1] 재귀 알고리즘을 이용해서 1월부터 12월까지 전월대비 매출 증감액을 나타내는 프로그램
(A상사의 2021년 월별 매출)

sales = [12000, 13000, 12500, 11000, 10500, 98000, 91000, 91500, 10500, 11500, 12000, 12500]def salesUpAndDown(ss): if len(ss) == 1: return ssprint('sales: {}'.format(ss)) currentSales = ss.pop(0) nextSales = ss[0] increase = nextSales - currentSales if increase > 0: increase = '+' + str(increase) print('매출 증감액: {}'.format(increase))return salesUpAndDown(ss)if __name__ == '__main__': salesUpAndDown(sales)
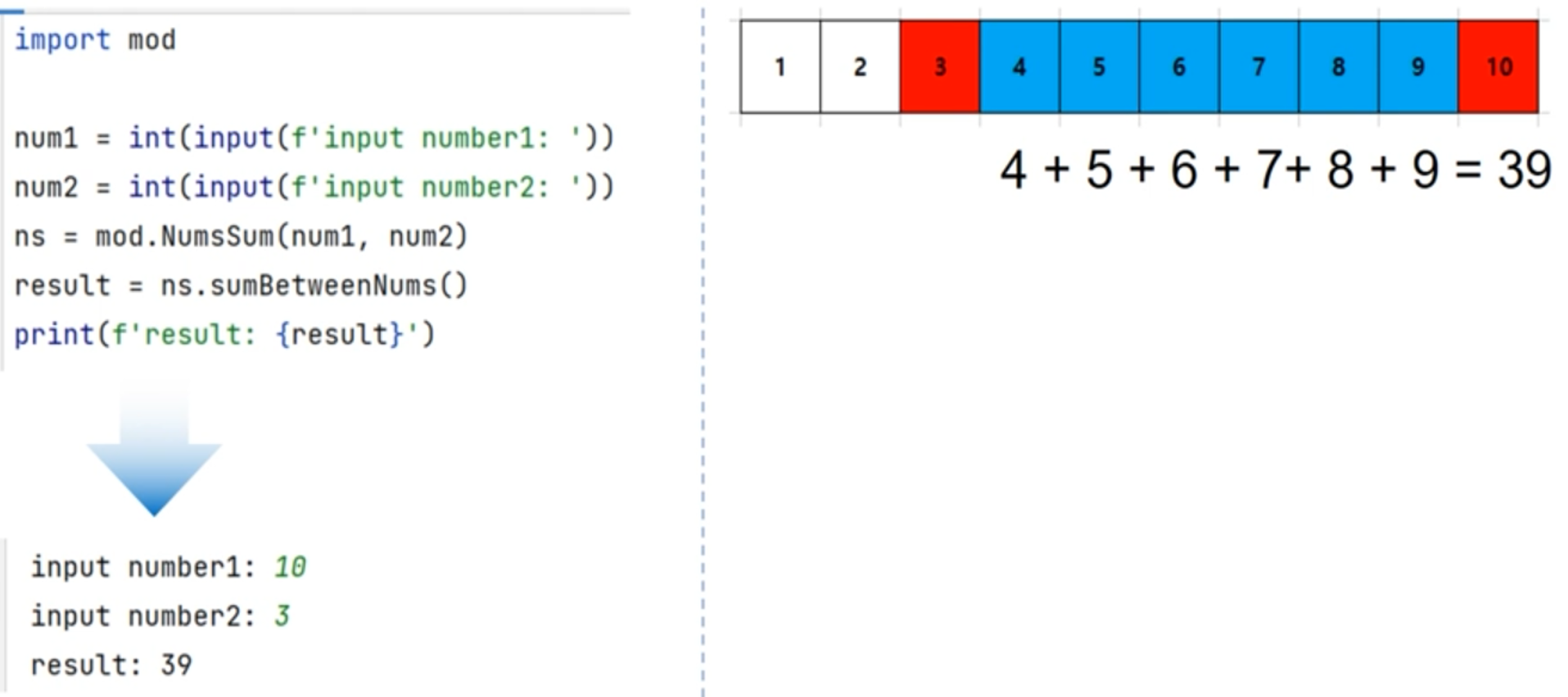
[2] 사용자가 정수 두개를 입력하면 작은 정수와 큰 정수 사이의 모든 정수의 합을 구하는 프로그램
mod 모듈
class NumsSum: def __init__(self, n1, n2): self.bigNum = 0 self.smallNum = 0 self.setN1N2(n1, n2)def setN1N2(self, n1, n2): self.bigNum = n1 self.smallNum = n2if n1 < n2: self.bigNum = n2 self.smallNum = n1def addNum(self, n): if n <= 1: return n return n + self.addNum(n-1)def sumBetweenNums(self): return self.addNum(self.bigNum - 1) - self.addNum(self.smallNum)
ex.py
import modnum1 = int(input('input number1: ')) num2 = int(input('input number2: ')) ns = mod.NumsSum(num1, num2) result = ns.sumBetweenNums() print('result: {}'.format(result))
49 ~ 50 평균 알고리즘
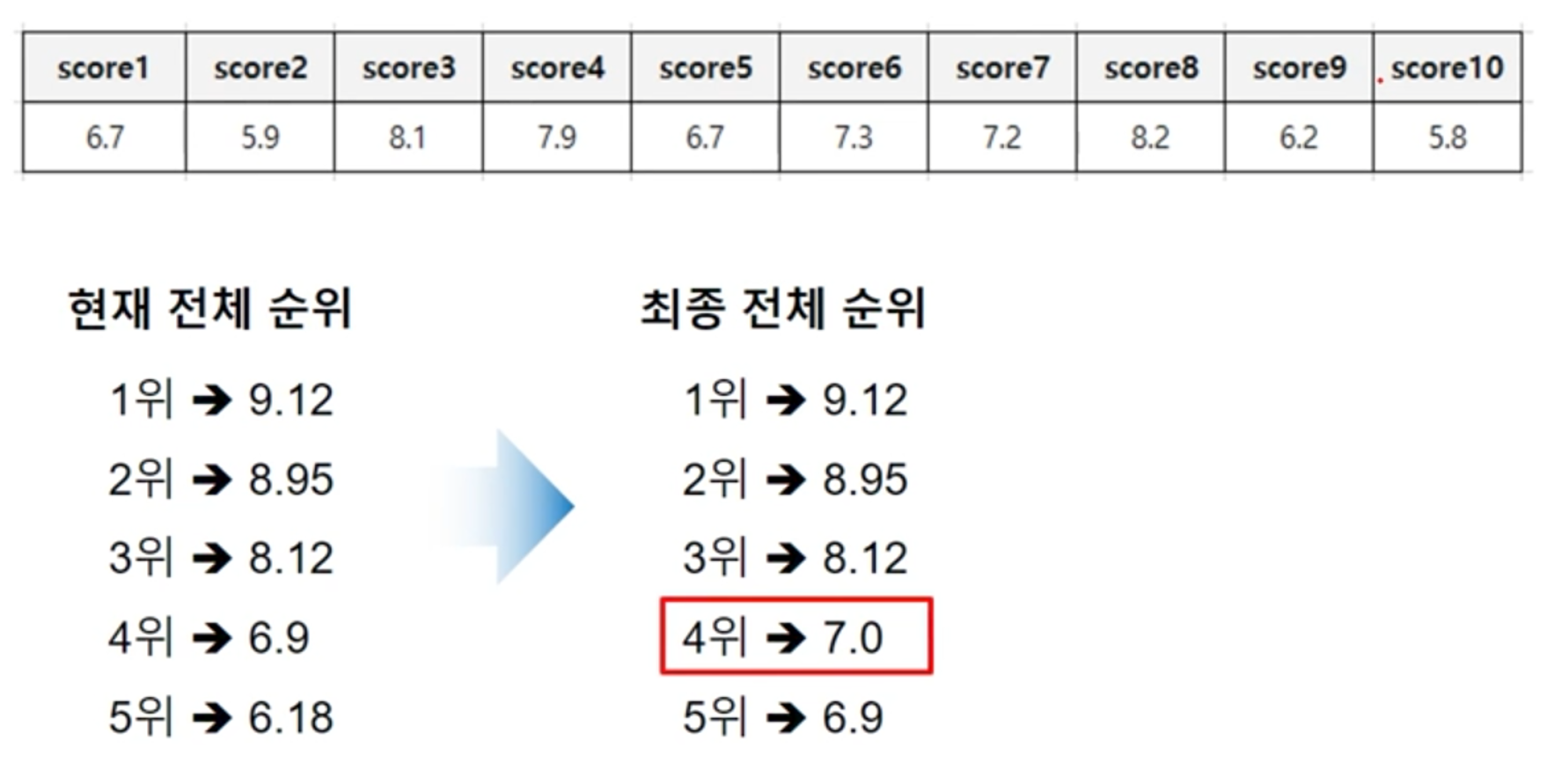
[1] 최댓값과 최솟값을 제외한 나머지 점수에 대한 평균을 구하고 순위를 정하는 알고리즘
maxAlgorithm 모듈
class MaxAlgorithm: def __init__(self, ss): self.scores = ss self.minScore = 0 self.maxIdx = 0def removeMaxScore(self): self.maxScore = self.scores[0]for i, s in enumerate(self.scores): if self.maxScore < s: self.maxScore = s self.maxIdx = iprint('self.maxScore: {}'.format(self.maxScore)) print('self.maxIdx: {}'.format(self.maxIdx))self.scores.pop(self.maxIdx) print('scores: {}'.format(self.scores))
minAlgorithm 모듈
class MinAlgorithm: def __init__(self, ss): self.scores = ss self.minScore = 0 self.minIdx = 0def removeMinScore(self): self.minScore = self.scores[0]for i, s in enumerate(self.scores): if self.minScore > s: self.minScore = s self.minIdx = iprint('self.maxScore: {}'.format(self.minScore)) print('self.maxIdx: {}'.format(self.minIdx))self.scores.pop(self.minIdx) print('scores: {}'.format(self.scores))
nearAlgorithm 모듈
class Top5Players: def __init__(self, cts, ns): self.currentScores = cts self.newScore = nsdef setAlignScore(self): nearIdx = 0 minNum = 10.0for i, s in enumerate(self.currentScores): absNum = abs(self.newScore - s) if absNum < minNum: minNum = absNum nearIdx = iif self.newScore >= self.currentScores[nearIdx]: for i in range(len(self.currentScores) - 1, nearIdx, -1): self.currentScores[i] = self.currentScores[i-1] self.currentScores[nearIdx] = self.newScoreelse: for i in range(len(self.currentScores)-1, nearIdx+1, -1): self.currentScores[i] = self.currentScores[i-1] self.currentScores[nearIdx+1] = self.newScoredef getFinalTop5Scroes(self): return self.currentScores
ex.py
import maxAlgorithm, minAlgorithm import nearAlgorithmtop5Scores = [9.12, 8.95, 8.12, 6.90, 6.18] scores = [6.7, 5.9, 8.1, 7.9, 6.7, 7.3, 7.2, 8.2, 6.2, 5.8] print('scores: {}'.format(scores))maxA = maxAlgorithm.MaxAlgorithm(scores) maxA.removeMaxScore() minA = minAlgorithm.MinAlgorithm(scores) minA.removeMinScore()total = 0 average = 0for n in scores: total += naverage = round(total / len(scores), 2)print('total: {}'.format(round(total, 2))) print('average: {}'.format(average))tp = nearAlgorithm.Top5Players(top5Scores, average) tp.setAlignScore() top5Scores = tp.getFinalTop5Scroes() print('top5Scores: {}'.format(top5Scores))
[2] 홍길동 학생을 제외한 나머지 학생의 평균과 홍길동 학생의 점수의 차이를 출력하는 프로그램 (과목별 점수와 평균 점수를 모두 출력한다)
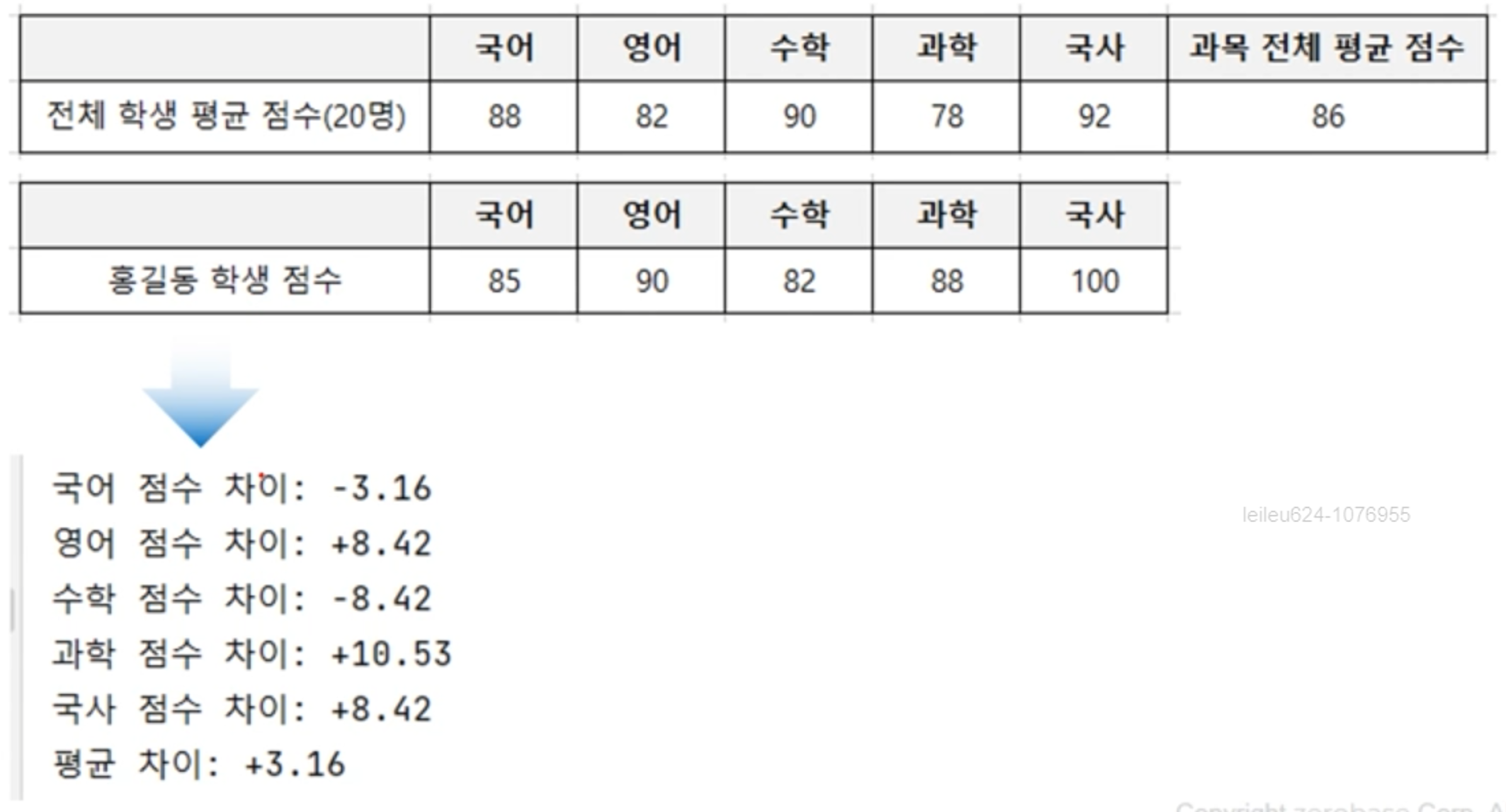
ex.py
kor_avg = 88; eng_avg = 82; mat_avg = 90 sci_avg = 78; his_avg = 92hong_kor_score = 85; hong_eng_score = 90; hong_mat_score = 82 hong_sci_score = 88; hong_his_score = 100stu19cnt_kor_total = kor_avg * 20 - hong_kor_score stu19cnt_eng_total = eng_avg * 20 - hong_eng_score stu19cnt_mat_total = mat_avg * 20 - hong_mat_score stu19cnt_sci_total = sci_avg * 20 - hong_sci_score stu19cnt_his_total = his_avg * 20 - hong_his_scorestu19cnt_kor_avg = stu19cnt_kor_total / 19 stu19cnt_eng_avg = stu19cnt_eng_total / 19 stu19cnt_mat_avg = stu19cnt_mat_total / 19 stu19cnt_sci_avg = stu19cnt_sci_total / 19 stu19cnt_his_avg = stu19cnt_his_total / 19kor_gap = hong_kor_score - stu19cnt_kor_avg eng_gap = hong_eng_score - stu19cnt_eng_avg mat_gap = hong_mat_score - stu19cnt_mat_avg sci_gap = hong_sci_score - stu19cnt_sci_avg his_gap = hong_his_score - stu19cnt_his_avgprint('국어 점수 차이: {}'.format("+" + str(round(kor_gap, 2)) if kor_gap > 0 else round(kor_gap, 2))) print('영어 점수 차이: {}'.format("+" + str(round(eng_gap, 2)) if eng_gap > 0 else round(eng_gap, 2))) print('수학 점수 차이: {}'.format("+" + str(round(mat_gap, 2)) if mat_gap > 0 else round(mat_gap, 2))) print('과학 점수 차이: {}'.format("+" + str(round(sci_gap, 2)) if sci_gap > 0 else round(sci_gap, 2))) print('국사 점수 차이: {}'.format("+" + str(round(his_gap, 2)) if his_gap > 0 else round(his_gap, 2)))stu19Cnt_total = stu19cnt_kor_avg + stu19cnt_eng_avg + stu19cnt_mat_avg + stu19cnt_sci_avg + stu19cnt_his_avg stu19Cnt_avg = stu19Cnt_total / 5 hong_total = hong_kor_score + hong_eng_score + hong_mat_score + hong_sci_score + hong_his_score hong_avg = hong_total / 5avg_gap = round(hong_avg - stu19Cnt_avg, 2) print('평균 차이: {}'.format("+" + str(round(avg_gap, 2)) if avg_gap > 0 else round(avg_gap, 2)))
재미있었던 부분
재귀 알고리즘을 이용해서 1월부터 12월까지 전월대비 매출 증감액을 나타내는 프로그램을 만들어 본 것이 가장 기억에 남고 재미있었다
어려웠던 부분
평균 알고리즘이 쉽다고 생각했는데 오늘 해본 문제풀이는 너무 길어서 중간에 내용을 놓치고 해결하는데 아주 오래걸려서 힘들었다
느낀점 및 내일 학습 계획
알고리즘 너무 어렵다 진짜
구조를 짜는 것이 익숙해져야 하는데 도저히 익숙해 지지가 않는다
기본 개념 강의을 다시 복습하고 와야하나 싶은 느낌이다
내일은 파이썬 테스트가 있다

