1. 코드 분석
1. tlpi-dist/files/t_stat.c
1. 코드
#include <sys/sysmacros.h>
#if defined(_AIX)
#define _BSD
#endif
#if defined(__sgi) || defined(__sun)
#include <sys/mkdev.h>
#endif
#if defined(__hpux)
#include <sys/mknod.h>
#endif
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include "file_perms.h"
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
displayStatInfo(const struct stat *sb)
{
printf("File type: ");
switch (sb->st_mode & S_IFMT) {
case S_IFREG: printf("regular file\n"); break;
case S_IFDIR: printf("directory\n"); break;
case S_IFCHR: printf("character device\n"); break;
case S_IFBLK: printf("block device\n"); break;
case S_IFLNK: printf("symbolic (soft) link\n"); break;
case S_IFIFO: printf("FIFO or pipe\n"); break;
case S_IFSOCK: printf("socket\n"); break;
default: printf("unknown file type?\n"); break;
}
printf("Device containing i-node: major=%ld minor=%ld\n",
(long) major(sb->st_dev), (long) minor(sb->st_dev));
printf("I-node number: %ld\n", (long) sb->st_ino);
printf("Mode: %lo (%s)\n",
(unsigned long) sb->st_mode, filePermStr(sb->st_mode, 0));
if (sb->st_mode & (S_ISUID | S_ISGID | S_ISVTX))
printf(" special bits set: %s%s%s\n",
(sb->st_mode & S_ISUID) ? "set-UID " : "",
(sb->st_mode & S_ISGID) ? "set-GID " : "",
(sb->st_mode & S_ISVTX) ? "sticky " : "");
printf("Number of (hard) links: %ld\n", (long) sb->st_nlink);
printf("Ownership: UID=%ld GID=%ld\n",
(long) sb->st_uid, (long) sb->st_gid);
if (S_ISCHR(sb->st_mode) || S_ISBLK(sb->st_mode))
printf("Device number (st_rdev): major=%ld; minor=%ld\n",
(long) major(sb->st_rdev), (long) minor(sb->st_rdev));
printf("File size: %lld bytes\n", (long long) sb->st_size);
printf("Optimal I/O block size: %ld bytes\n", (long) sb->st_blksize);
printf("512B blocks allocated: %lld\n", (long long) sb->st_blocks);
printf("Last file access: %s", ctime(&sb->st_atime));
printf("Last file modification: %s", ctime(&sb->st_mtime));
printf("Last status change: %s", ctime(&sb->st_ctime));
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
struct stat sb;
Boolean statLink;
int fname;
statLink = (argc > 1) && strcmp(argv[1], "-l") == 0;
fname = statLink ? 2 : 1;
if (fname >= argc || (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0))
usageErr("%s [-l] file\n"
" -l = use lstat() instead of stat()\n", argv[0]);
if (statLink) {
if (lstat(argv[fname], &sb) == -1)
errExit("lstat");
} else {
if (stat(argv[fname], &sb) == -1)
errExit("stat");
}
displayStatInfo(&sb);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
2. 동작 모습
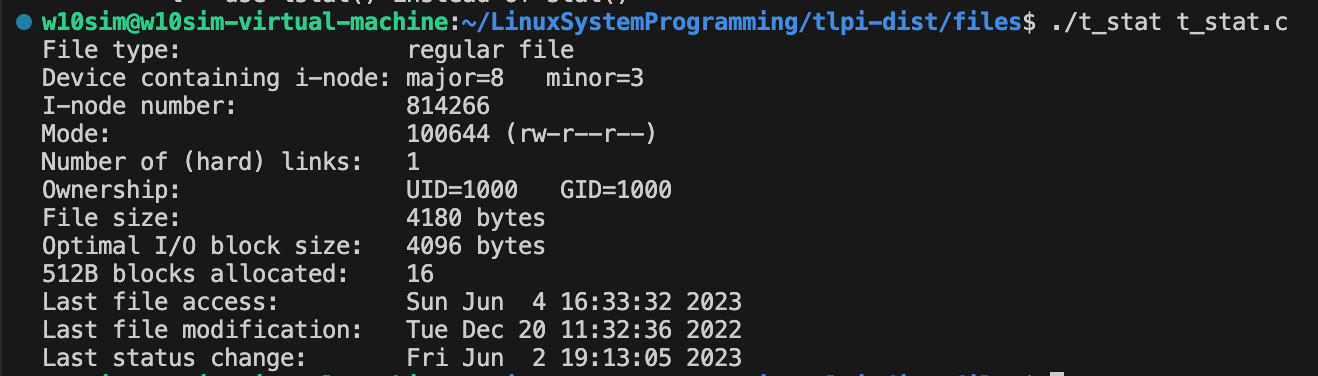
3. 디버깅 및 분석
2. tlpi-dist/files/t_chown.c
1. 코드
#include <pwd.h>
#include <grp.h>
#include "ugid_functions.h"
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
uid_t uid;
gid_t gid;
int j;
Boolean errFnd;
if (argc < 3 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s owner group [file...]\n"
" owner or group can be '-', "
"meaning leave unchanged\n", argv[0]);
if (strcmp(argv[1], "-") == 0) {
uid = -1;
} else {
uid = userIdFromName(argv[1]);
if (uid == -1)
fatal("No such user (%s)", argv[1]);
}
if (strcmp(argv[2], "-") == 0) {
gid = -1;
} else {
gid = groupIdFromName(argv[2]);
if (gid == -1)
fatal("No group user (%s)", argv[2]);
}
errFnd = FALSE;
for (j = 3; j < argc; j++) {
if (chown(argv[j], uid, gid) == -1) {
errMsg("chown: %s", argv[j]);
errFnd = TRUE;
}
}
exit(errFnd ? EXIT_FAILURE : EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
2. 동작 모습

3. 디버깅 및 분석
3. tlpi-dist/dirs_links/list_files.c
1. 코드
#if defined(__APPLE__)
#include <sys/types.h>
#endif
#include <dirent.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
listFiles(const char *dirpath)
{
DIR *dirp;
struct dirent *dp;
Boolean isCurrent;
isCurrent = strcmp(dirpath, ".") == 0;
dirp = opendir(dirpath);
if (dirp == NULL) {
errMsg("opendir failed on '%s'", dirpath);
return;
}
for (;;) {
errno = 0;
dp = readdir(dirp);
if (dp == NULL)
break;
if (strcmp(dp->d_name, ".") == 0 || strcmp(dp->d_name, "..") == 0)
continue;
if (!isCurrent)
printf("%s/", dirpath);
printf("%s\n", dp->d_name);
}
if (errno != 0)
errExit("readdir");
if (closedir(dirp) == -1)
errMsg("closedir");
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc > 1 && strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s [dir-path...]\n", argv[0]);
if (argc == 1)
listFiles(".");
else
for (argv++; *argv; argv++)
listFiles(*argv);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
2. 동작 모습
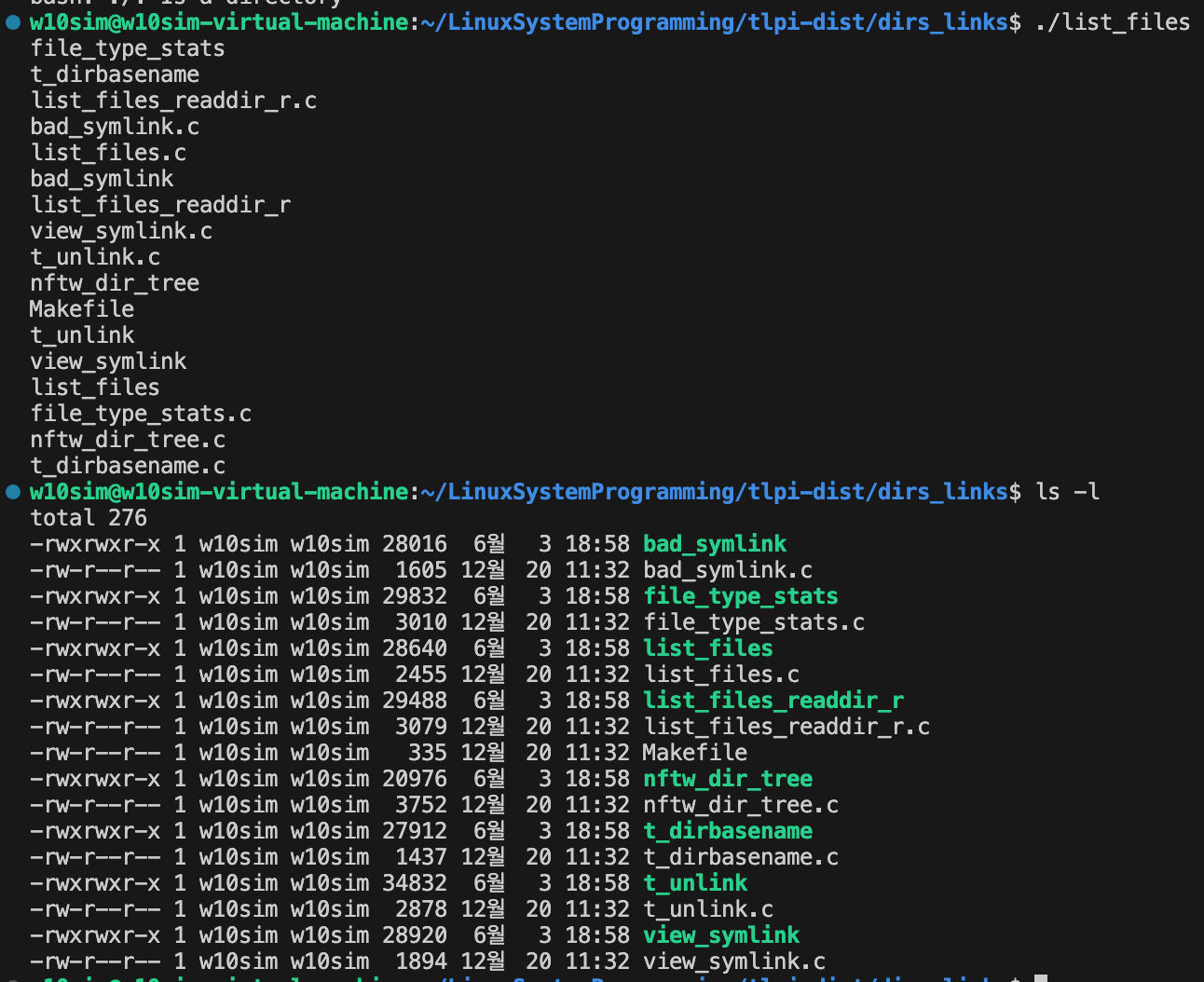
3. 디버깅 및 분석
4. tlpi-dist/inotify/demo_inotify.c
1. 코드
#include <sys/inotify.h>
#include <limits.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
static void
displayInotifyEvent(struct inotify_event *i)
{
printf(" wd =%2d; ", i->wd);
if (i->cookie > 0)
printf("cookie =%4d; ", i->cookie);
printf("mask = ");
if (i->mask & IN_ACCESS) printf("IN_ACCESS ");
if (i->mask & IN_ATTRIB) printf("IN_ATTRIB ");
if (i->mask & IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE) printf("IN_CLOSE_NOWRITE ");
if (i->mask & IN_CLOSE_WRITE) printf("IN_CLOSE_WRITE ");
if (i->mask & IN_CREATE) printf("IN_CREATE ");
if (i->mask & IN_DELETE) printf("IN_DELETE ");
if (i->mask & IN_DELETE_SELF) printf("IN_DELETE_SELF ");
if (i->mask & IN_IGNORED) printf("IN_IGNORED ");
if (i->mask & IN_ISDIR) printf("IN_ISDIR ");
if (i->mask & IN_MODIFY) printf("IN_MODIFY ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVE_SELF) printf("IN_MOVE_SELF ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVED_FROM) printf("IN_MOVED_FROM ");
if (i->mask & IN_MOVED_TO) printf("IN_MOVED_TO ");
if (i->mask & IN_OPEN) printf("IN_OPEN ");
if (i->mask & IN_Q_OVERFLOW) printf("IN_Q_OVERFLOW ");
if (i->mask & IN_UNMOUNT) printf("IN_UNMOUNT ");
printf("\n");
if (i->len > 0)
printf(" name = %s\n", i->name);
}
#define BUF_LEN (10 * (sizeof(struct inotify_event) + NAME_MAX + 1))
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int inotifyFd, wd, j;
char buf[BUF_LEN] __attribute__ ((aligned(8)));
ssize_t numRead;
char *p;
struct inotify_event *event;
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s pathname...\n", argv[0]);
inotifyFd = inotify_init();
if (inotifyFd == -1)
errExit("inotify_init");
for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) {
wd = inotify_add_watch(inotifyFd, argv[j], IN_ALL_EVENTS);
if (wd == -1)
errExit("inotify_add_watch");
printf("Watching %s using wd %d\n", argv[j], wd);
}
for (;;) {
numRead = read(inotifyFd, buf, BUF_LEN);
if (numRead == 0)
fatal("read() from inotify fd returned 0!");
if (numRead == -1)
errExit("read");
printf("Read %ld bytes from inotify fd\n", (long) numRead);
for (p = buf; p < buf + numRead; ) {
event = (struct inotify_event *) p;
displayInotifyEvent(event);
p += sizeof(struct inotify_event) + event->len;
}
}
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
2. 동작 모습
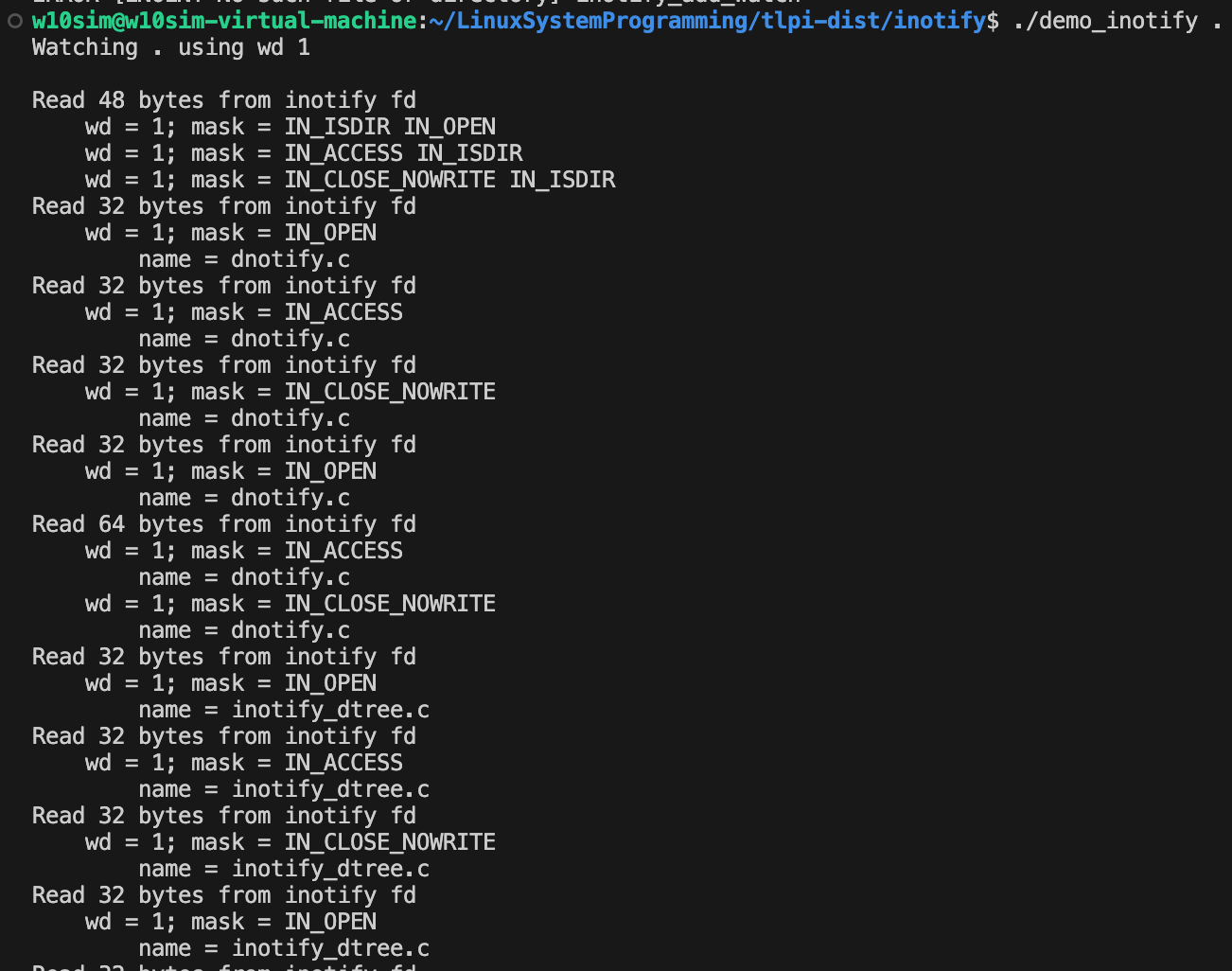
3. 디버깅 및 분석




