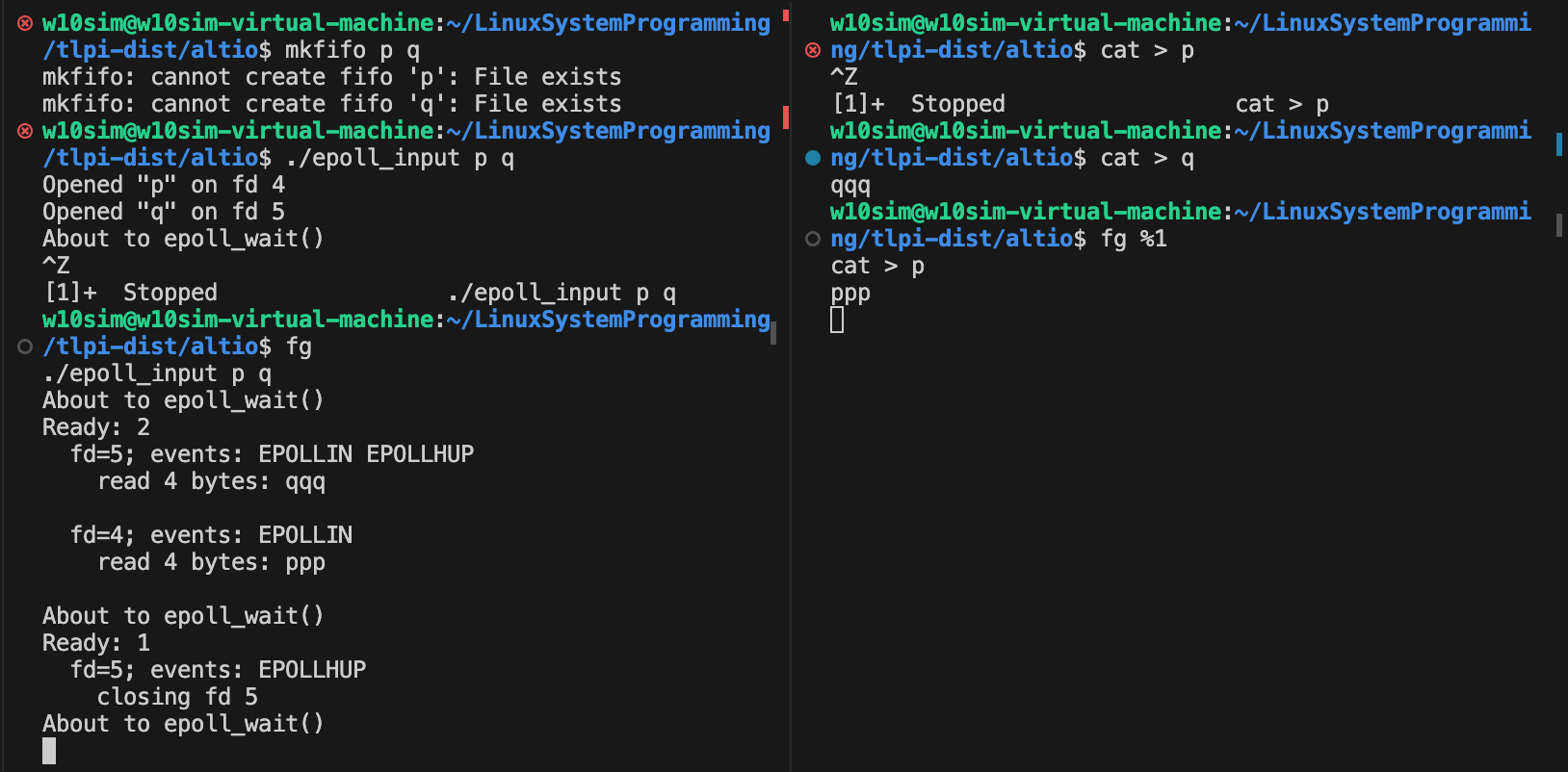
1. 코드 분석
1. tlpi-dist/altio/epoll_input.c
1. 코드
/* epoll_input.c
Example of the use of the Linux epoll API.
Usage: epoll_input file...
This program opens all of the files named in its command-line arguments
and monitors the resulting file descriptors for input events.
This program is Linux (2.6 and later) specific.
*/
#include <sys/epoll.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "tlpi_hdr.h"
#define MAX_BUF 1000 /* Maximum bytes fetched by a single read() */
#define MAX_EVENTS 5 /* Maximum number of events to be returned from
a single epoll_wait() call */
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int epfd, ready, fd, s, j, numOpenFds;
struct epoll_event ev;
struct epoll_event evlist[MAX_EVENTS];
char buf[MAX_BUF];
if (argc < 2 || strcmp(argv[1], "--help") == 0)
usageErr("%s file...\n", argv[0]);
epfd = epoll_create(argc - 1);
if (epfd == -1)
errExit("epoll_create");
/* Open each file on command line, and add it to the "interest
list" for the epoll instance */
for (j = 1; j < argc; j++) {
fd = open(argv[j], O_RDONLY);
if (fd == -1)
errExit("open");
printf("Opened \"%s\" on fd %d\n", argv[j], fd);
ev.events = EPOLLIN; /* Only interested in input events */
ev.data.fd = fd;
if (epoll_ctl(epfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &ev) == -1)
errExit("epoll_ctl");
}
numOpenFds = argc - 1;
while (numOpenFds > 0) {
/* Fetch up to MAX_EVENTS items from the ready list of the
epoll instance */
printf("About to epoll_wait()\n");
ready = epoll_wait(epfd, evlist, MAX_EVENTS, -1);
if (ready == -1) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue; /* Restart if interrupted by signal */
else
errExit("epoll_wait");
}
printf("Ready: %d\n", ready);
/* Deal with returned list of events */
for (j = 0; j < ready; j++) {
printf(" fd=%d; events: %s%s%s\n", evlist[j].data.fd,
(evlist[j].events & EPOLLIN) ? "EPOLLIN " : "",
(evlist[j].events & EPOLLHUP) ? "EPOLLHUP " : "",
(evlist[j].events & EPOLLERR) ? "EPOLLERR " : "");
if (evlist[j].events & EPOLLIN) {
s = read(evlist[j].data.fd, buf, MAX_BUF);
if (s == -1)
errExit("read");
printf(" read %d bytes: %.*s\n", s, s, buf);
} else if (evlist[j].events & (EPOLLHUP | EPOLLERR)) {
/* After the epoll_wait(), EPOLLIN and EPOLLHUP may both have
been set. But we'll only get here, and thus close the file
descriptor, if EPOLLIN was not set. This ensures that all
outstanding input (possibly more than MAX_BUF bytes) is
consumed (by further loop iterations) before the file
descriptor is closed. */
printf(" closing fd %d\n", evlist[j].data.fd);
if (close(evlist[j].data.fd) == -1)
errExit("close");
numOpenFds--;
}
}
}
printf("All file descriptors closed; bye\n");
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}