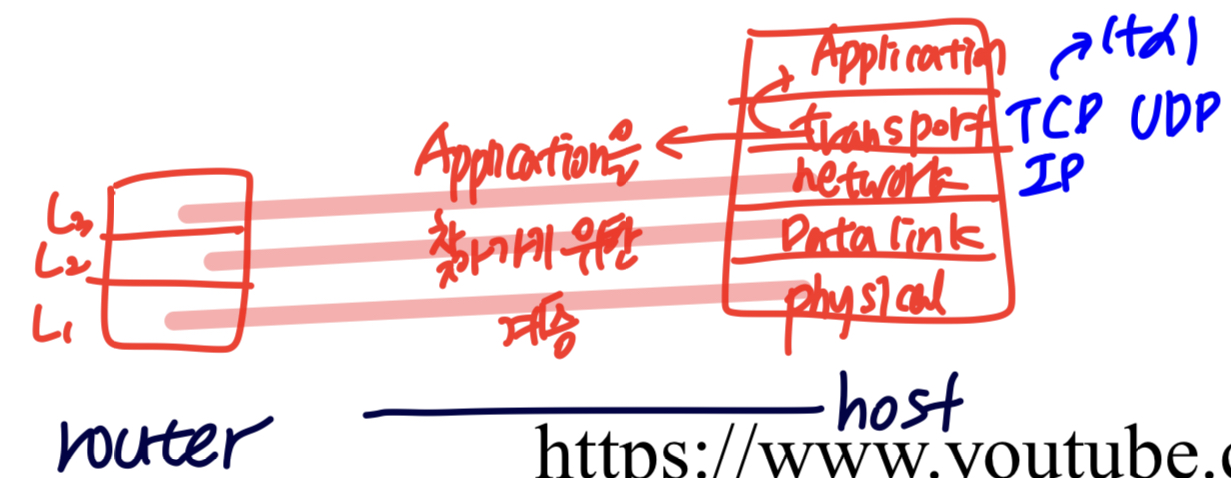
이 교재에서 다룰 핵심 내용
1. Data Communications
- 데이터를 Internet Device로 주고 받는 것
- Deals with the
transmisisonof signals in a reliable andefficient
- 헷갈릴 수 있는 용어
- transmit: 상태의 변화(bit → signal)
- transfer: 문서 이동처럼 SW의 이동
- transport: 보이는 것의 이동
reliable: 사고가 났어도 사고가 나지 않은 것처럼 전송함efficient: loss X, delay X, throughput ↑- signal transmission, transmission media, data link control, and
multiplexing
- multiplexing: 다양한 user의 data들이 하나의 케이블로 들어감
- FDMA(frequency)
- TDMA(time)
- CDMA(encoding 후 보내는 경우)
- OFDMA
- CSMA
2. Networking
- 서버나 친구에게 내 idea를 전달하기 위해 기기들을 연결해주는 요소
- 1)end user가 갖고 있는 장비, 2)중간의 network 장비, 3)그 사이를 연결하는 media의 집합
- Deals with the technology and architecture of the communications networks used to interconnect communicating devices
- architecture: network가 어떻게 구성되어 있는가? ex. local하게 있는가(한정된 범위에 node들이 존재, 짧은 링크)
- LANs / WANs 로 구분됨
3. Protocols
- Define the set of rules for peer layer communication
- peer layer끼리 통신함
Communication Models
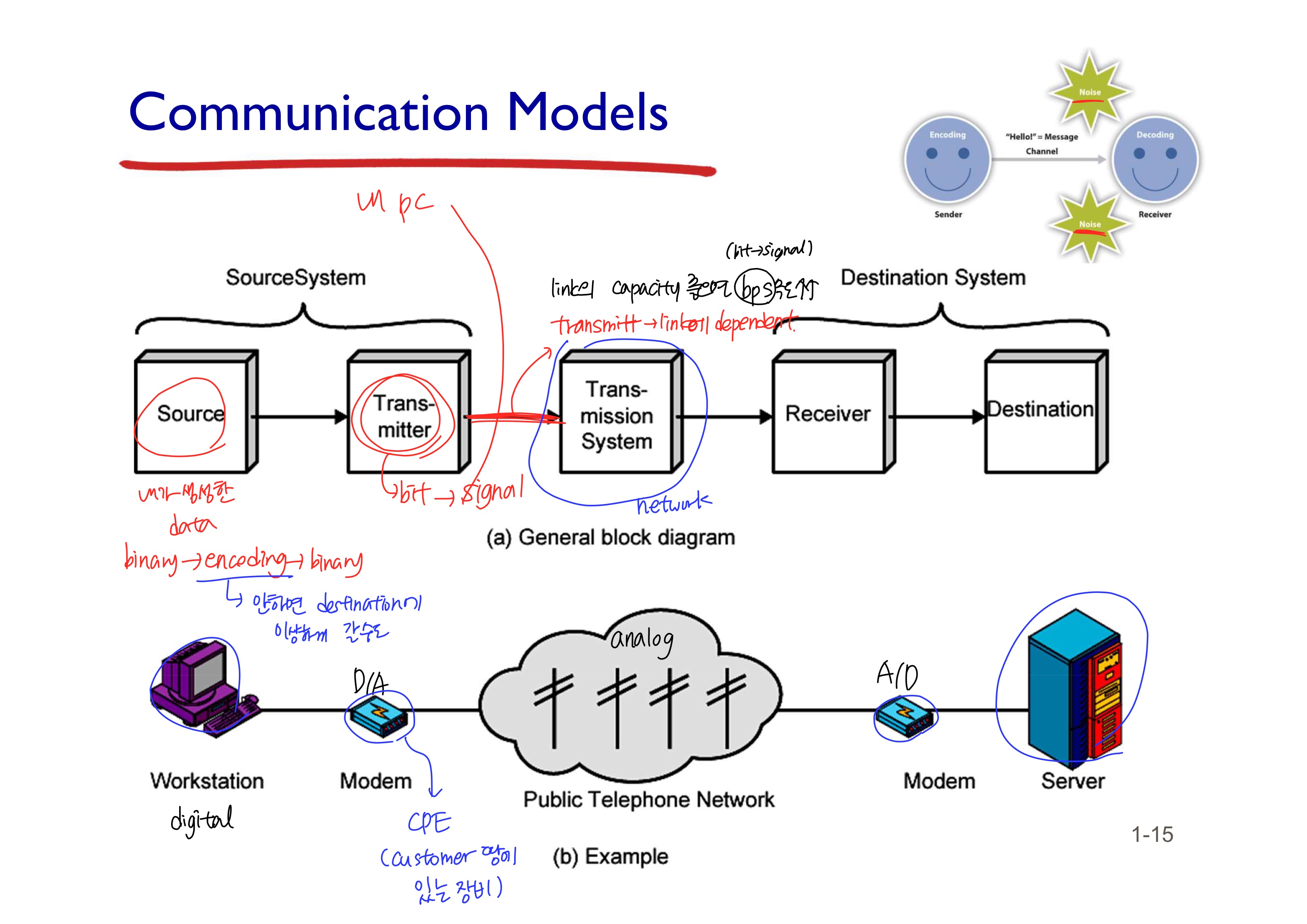
Transmitter: bit를 signal로 바꿈Transmission System: 바뀐 signal을 Receiver에게 전송함
Communication Tasks
- Transmission system utilization
- Interfacing
- addressing과 연관
- Signal generation
- Synchronization
- Exchange management
- connection이 oriented면 상태 유지
- connection oriented: 4계층에서 패킷이 여러 라우터를 거쳐갈 때, 앞/뒤로 지나갔던 패킷을 기억하고 있는 경우
- connection이 oriented면 상태 유지
- Error detection and correction
- 2계층: network 장비들을 지나갈 때마다 수행
- 4계층: end to end
- Flow control
- not to overflow
receiver(destination) buffer - 도착지 버퍼가 넘치지 않도록 흐름을 조절하는 것
- sender doesn't send data faster than they can be process & receive at destination
- 도착지 버퍼의 상태를 컨트롤하기 위해, 전송지에서 보내는 데이터의 속도를 조절함
- link와 sender의 성능이 다 좋아도 receiver의 버퍼 성능이 떨어진다면 overflow가 발생할 수 있음 (sender가 보낸 데이터가 손실될 수 있음)
- not to overflow
- Addressing
- layer마다 다양함
- ex. 3계층의 IP
- Routing
- 패킷이 이동할 때, 어떤 라우터를 거쳐갈지 정하는 것
- Recovery
- network를 에러가 나기 전 상태로 돌려 놓는 것
- Message formatting
protocol
- Security
- Network management
Wide Area Networks (WAN)
- Span large geographical area
- 매우 넓은 지역을 관할하는 네트워크
- 내 땅이 아닌 땅을 지나가게 됨
- Rely in part on common carrier circuits
- carrier =
ISP(Internet Service Provider)
- carrier =
- Alternative technologies
- General technology
- 1-1.
Circuit switching- 전화망에서 사용했음
- H/W로 dedicated circuit 잡음 = physical path
- 물 새듯 줄줄 데이터가 이동하며, packet을 언패킷하는 과정도 없음
- 통신할 때에는 교환기(스위치)가 아무 일도 하지 않음(processing X)
- buffer도 없음
- real time에 좋음
- 1-2.
Packet switching- 멀티미디어에 적합함 (Data / Virtual circuit)
- Datagram packet switching
- Virtual circuit packet switching: SW로 circuit 잡음 (중간중간 확인) / Dedicated X / path는 고정됨
- 1-1.
- Protocol(Virtual Circuit switching)
- 2-1.
Frame relay(FR) - 2-2.
Asynchronous Transfer Mode(ATM)
- 2-1.
- General technology
Circuit Switching과 Virtual circuit packet switching의 공통점
: 통신이 끝날 때까지 fixed path
1-1. Circuit Switching
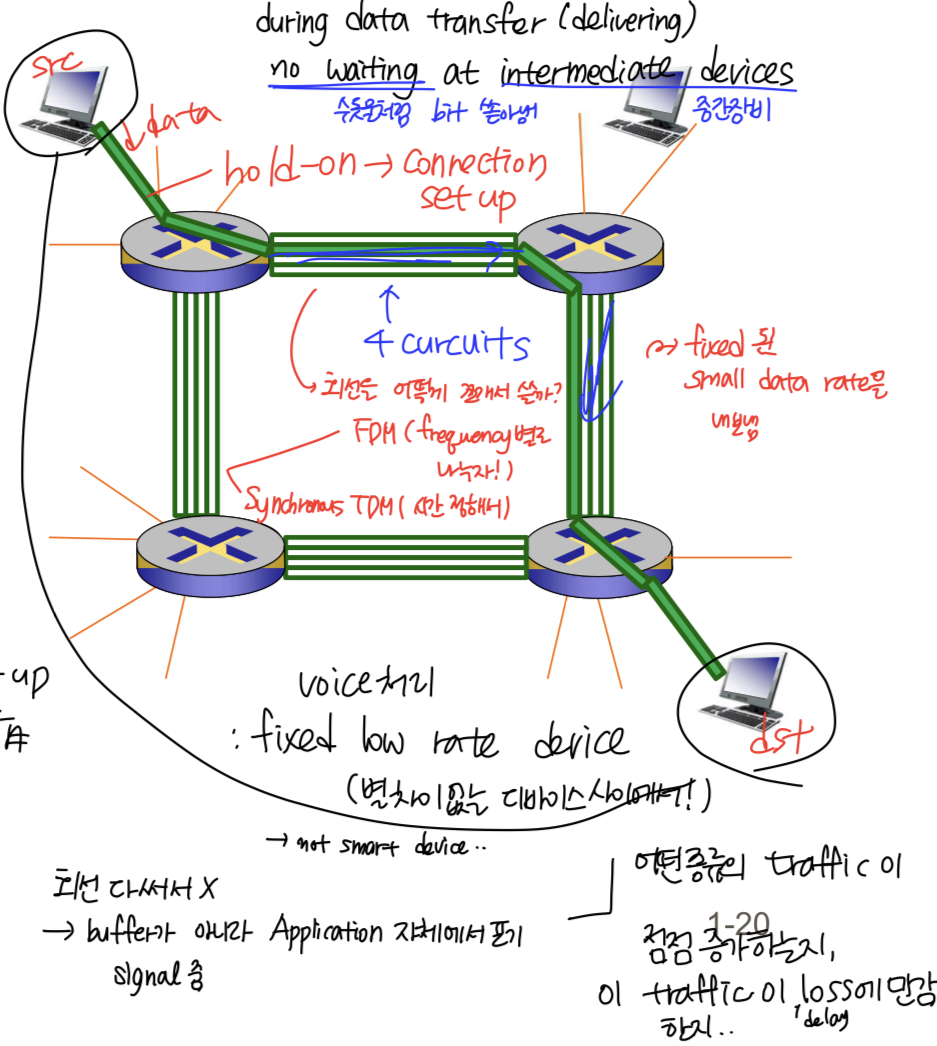
PSTN(Public Switch Telephone Network) for voiceDedicatedcommunications path is established for the duration of conversation- Dedicated: no sharing during communication (= data deliver, data transfer)
- 즉, 패킷이 지나가는 길 + Resource(Bandwidth)까지 정해져있음
- 실제 데이터가 나가기 전 라우팅을 하며 (physical path), 통신이 끝나기 전까지는 영원히 이 길로 이동함
- 패킷을 전송하기 전,
Connection set-up delay 존재 - 각각의 라우터에 들어오는 데이터들은 delay 없이 바로 라우팅함 (데이터 전송 전 set-up이 끝났기 때문)
1-2. Packet Switching
Datagram, Virtual Circuit Swtiching 공통의 특징
- 데이터들은
packets이라고 불리는 작은 청크(chunk)들로 쪼개져 전송됨 - 각각의 패킷들은 src부터 dst까지 존재하는 node(router)들을 개별로 거쳐감 (3계층 내용)
- 각각의 node(router)에서는 1) 전체 패킷을 받은 후 2) 잠시 저장해두었다가, 3) forwarding이 끝난 후에 4) 다음 노드로 transmit 시킴
왜 패킷으로 쪼개는가?
- Variable한 data rate application을 support 하기 위해
- reliable한 network service를 통해 효율적인 에러 recovery를 하기 위함
Datagram packet switching 특징
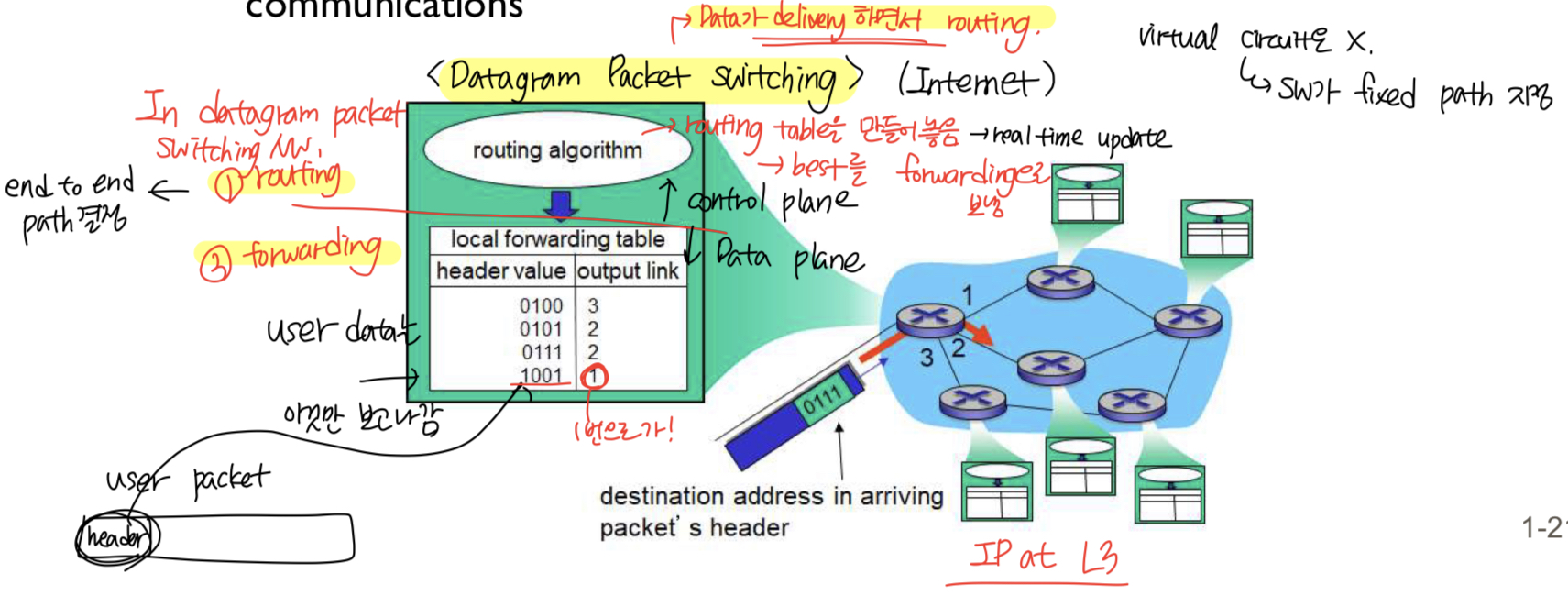
routing- routing algorithm으로, real time으로 update 되는 routing table을 만들어 놓음
- 가장 최선의 길로 forwarding
forwarding
Circuit switching vs Packet switching
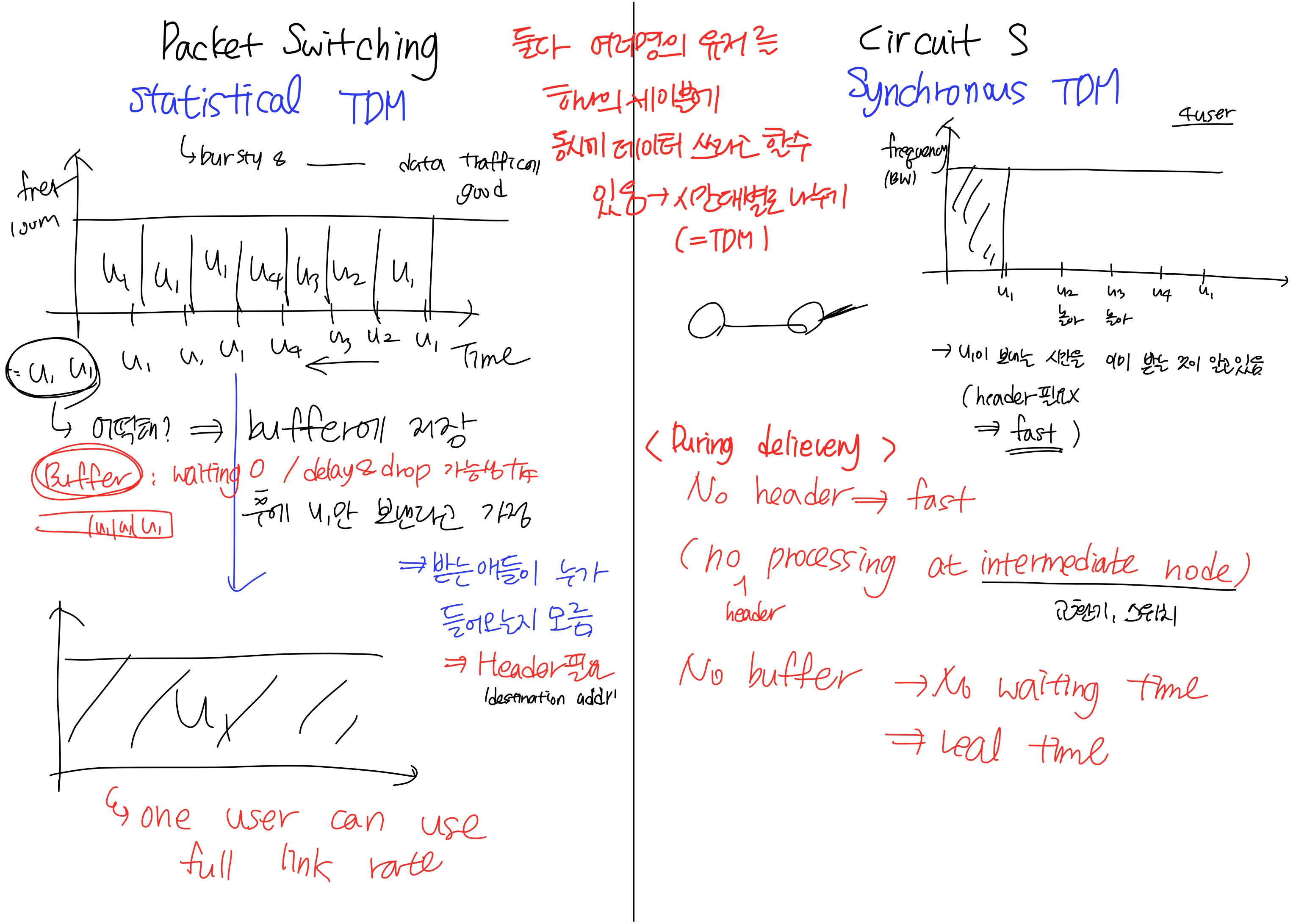
Packet switching (Datagram packet switching)
- Call set-up delay가 없음 (Virtual circuit switching도 마찬가지)
- Resource reservation이 없어 receiver가 어떤 패킷을 받을지 모르기 때문에, output buffer가 존재함
- buffer가 존재하기 때문에 '일단 받아'라는 마인드가 생겨 한 유저가 full link rate를 사용할 가능성이 있음(statistical)
- Communication 동안 다양한 유저들 사이에 Resource sharing이 일어남
- NW congestion에 의해 delay나 loss가 발생할 수 있음
- Queueing delay 발생(
at output buffer of routers) Intermittent & bursty한 데이터에 좋음
Circuit switching
- Call set-up delay 존재 (data delivery 이전에 발생)
connection-oriented delivery= 데이터의 순서가 바뀌지 않음 (fixed path)- Resource Reservation regardless of demand (physical path를 잡아놓았기 때문)
- link utilization엔 좋지 않음(idle 상태인 link가 존재할 수 있음)
Real time으로 전송해야 하는 데이터에 좋음
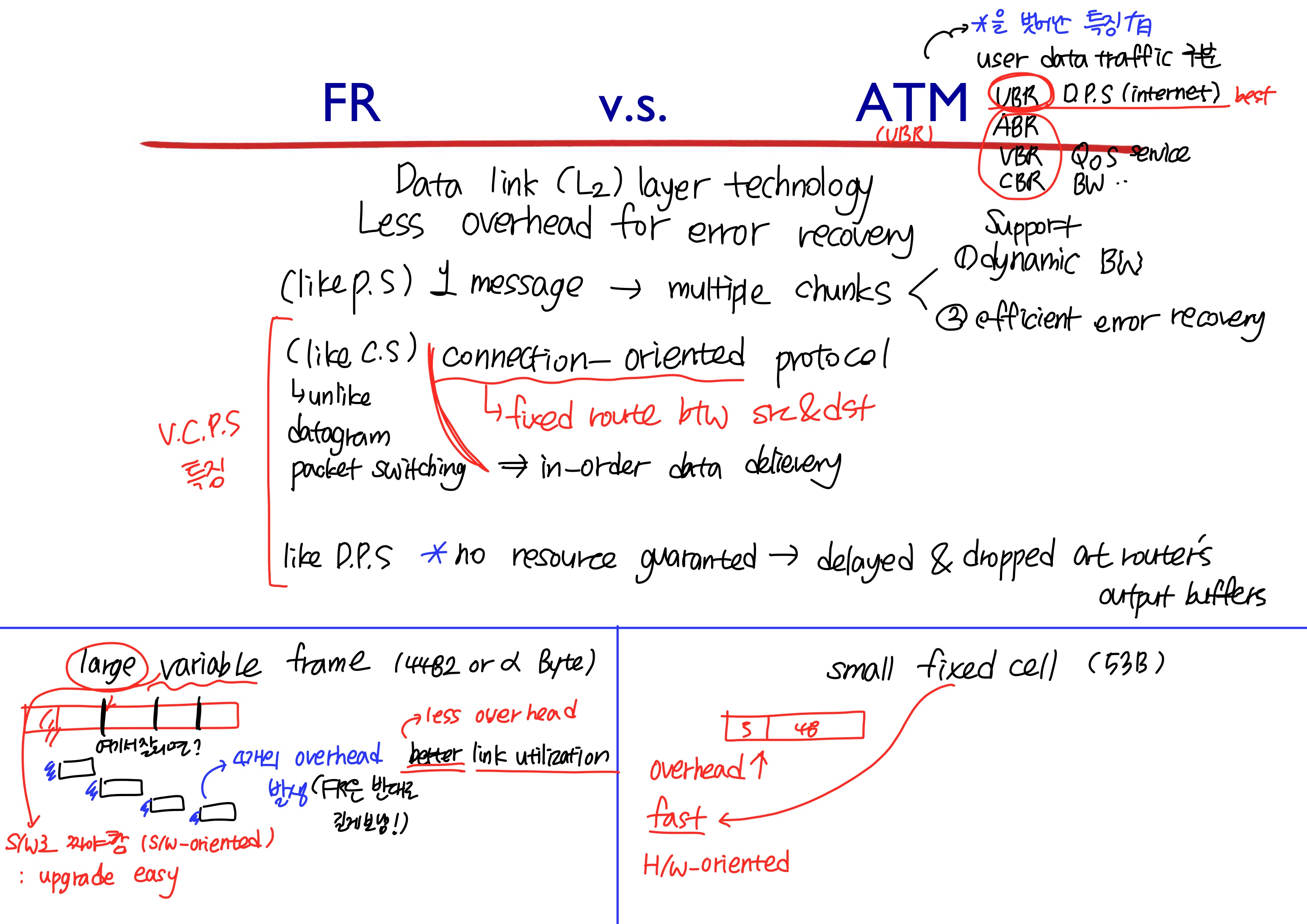
2-1. Frame Relay(FR)
Frame= packet- Developed to take advantage of high data rates and low error rates
- P.S의 에러 핸들링을 위한 오버 헤드를 없애기 위해 link recovery 알고리즘을 없앰
- 2 Mbps까지 동작함
V.C.P.S
- 가져온 C.S의 특징
- preplanned route between 2 end-node(a pair of src-dst) before data is sent
- fixed route during data delivery = in-order data delivery
- C.S와의 차이점
- S/W path (not physical path) = delayed or dropped at output buffers of routers
2-2. Asynchronous Transfer Mode(ATM)
- 고정된 길이의 packet으로 쪼갬
- 쪼개진 packet을
cell이라고 부르며, ATM 자체를cell relay라고 부르기도 함 - error control을 위한 약간의 오버헤드 발생
- FR의 evolution (10Mbps ~ Gbps까지 동작)
FR vs ATM
Local Area Networks(LAN)
- 작은 빌딩이나 캠퍼스처럼 좁은 영역을 관할하는 네트워크
- 보통 하나의 조직이 소유함 (ex. 이화 NW)
- WAN 보다 Internal data rates가 큼 (= 빠름)
- Ethernet (유선) - 802.3 / Wifi (Wireless) - 802.11
- WAN 보다 예측하기 쉬움
- 높은 BW가 가능함 (트래픽이 WAN에 비해 작기 때문에, 1명의 유저가 사용가능한 BW가 큼)
Reference
- 이화여대 이숙영 교수님 정보통신공학 강의자료