
Analog Signal
Periodic Signal
- 같은 패턴이 주기적으로 반복된다.
- Sine wave
- 진폭, 주파수(f, [Hz]), 주기(T, [s])
- f = 1/T and T = 1/f
- 주파수가 크면 직진성 좋고(벽에 부딪혀),
주파수가 낮으면 회전성이 좋다(벽을 막 뚫어)
-
단위
Unit Equivalent Unit Equivalent s 1 s Hz 1 Hz ms 10-3 s kHz 103 Hz μs 10-6 s MHz 106 Hz ns 10-9 s GHz 109 Hz ps 10-12 s THz 1012 Hz -
Fast means high frequency,
Slow means low frequency
- 위상(Phase)
degree : 0 ~ 360
radian : 0 ~ 2π
- 파장(wavelength)
: length of a period
= propagation speed * period
= propagation speed / frequency
- propagation speed(c) : 전파 속도. 거의 광속(3 * 108 m/s)
- Time domain과 Frequency domain
: x축이 각각 time과 frequency인 그림.
- 대역폭 (Bandwidth)
: range of frequencies contained in a composite signal
= difference between the highest frequency and the lowest frequency
Aperiodic composite signal
- AM radio
- FM radio
Digital Signal
- Signals that contains bit information (0, 1) using amplitude, frequency and phase
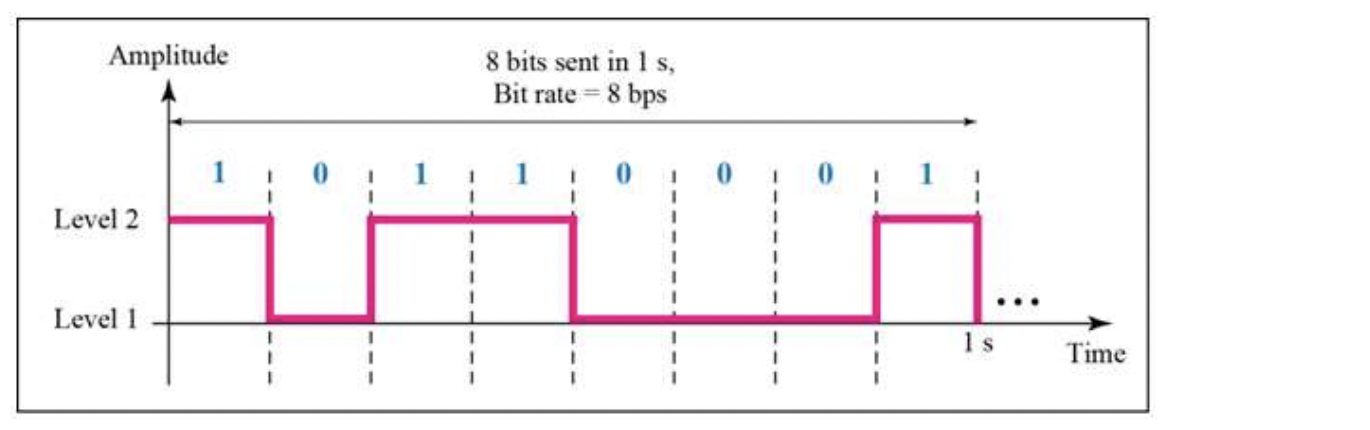
- 0 : level 1, 1 : level 2로 했을 때,
8 bits sent 1s
=> bit rate = 8 bps (bit per seconds)
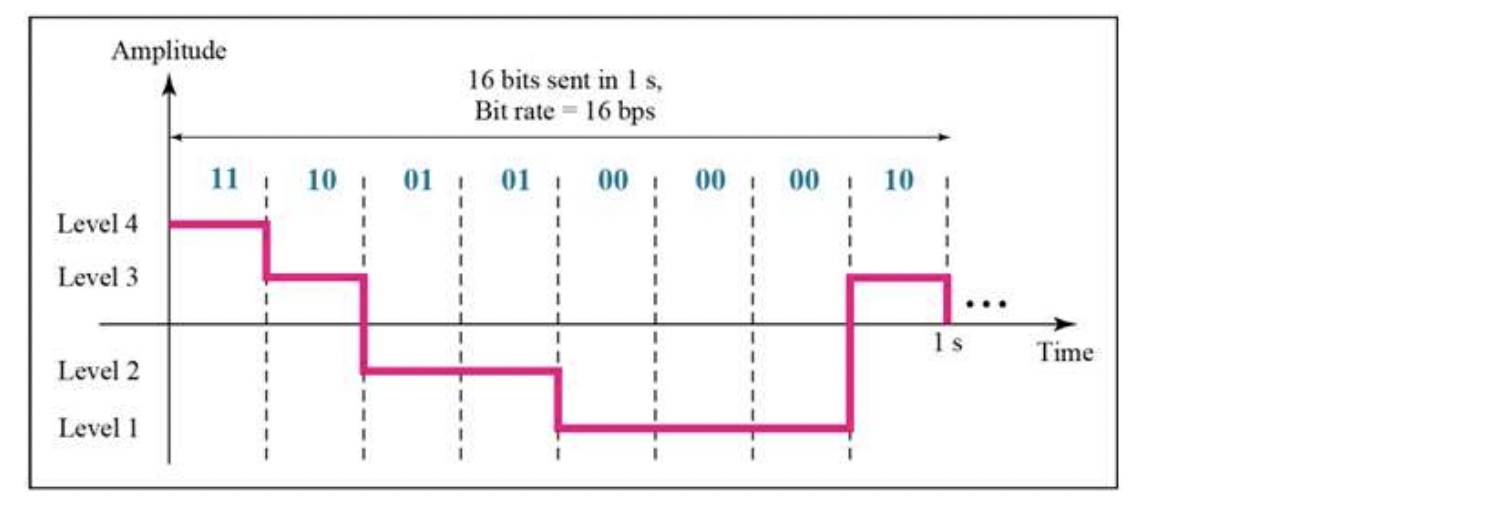
- 이걸 16bits sent 1s로 바꾸려면,
level을 4개로 만든다
00 : level 1, 01 : level 2, 10 : level 3, 11 : level4
그럼 한 칸에 bit 2개씩 보내니까
16bits sent 1s
=> bit rate = 16 bps
Q. 만약 level이 8개라면, level 하나당 몇 개의 bit가 필요할까?
A. 3개겠지
- bit rate
1Kbps = 1000bps
1Mbps = 1000Kbps
1Gbps = 1000Mbps
Q. 1초에 100페이지를 다운받아야 한다. 한 페이지에 20줄, 한 줄에 80 characters, 한 character는 1 byte(8 bits). bit rate?
A. 80 * 24 * 100 bytes/s
=> 1.536Mbps
Q. 1920x1080 pixels per screen. 30frames per second. 1pixel uses 24bits. bit rate?
A. 1920 * 1080 * 24 * 30 bps
Transmission of Digital Signals
- media에서 digital signal을 어떻게 전송할까?
- digital signal is a composite analog signal with infinite bandwidth
Baseband Transmission(기저대역 전송)
- send signal "as it is"
- 이렇게 보내려면 infinite bandwith가 필요하다. realistic 하진 않다.
- 실제로는 어려우니까, 적당히 영역(f1 ~ f2)로 자른다.
- The more bandwidth we use, we get an approximate signal that is closer to the original
Approximation of Digital Signals
- 뭔가 이해하기 어려운데.. ppt 읽어보면 느낌 온다
- digital signal을 그래프로 보면 완전 네모낳게 생긴 애들이다.
0과 1에 따라 딱딱 나눠져있는. - 이걸 analog로 표현하려면 infinite한 bandwidth가 있어야 가능하다.
- 그게 불가능하니까, 곡선 형태인 analog 그래프를 네모인 digital로 approximation한다.
- 이를 위해 N bit를 1초에 보내려면, 최소 N/2 Hz 만큼의 bandwidth가 필요하다
- 만약 더 큰 bandwidth를 쓴다면 더 좋은 approximation이 가능하다
즉, 주파수 영역을 많이 사용할수록, 모양이 더 네모에 가까워진다.
그럼 왜곡 생길 때 복원하기도 더 쉬워진다. (better accuracy)
- Basically, bandwidth needed for baseband transmission is proportional to transfer rate
transfer rate는 bit rate를 말하는 것 같다.
- To send data at N bps, we need at least N/2 bandwidth
If we have a bandwidth f, maximum transfer rate is 2f
Q. baseband transmission을 이용해서 1Mbps로 보내려고 한다. What is the required bandwidth?
A. 500kHz
Q. bandwidth 100kHz. What is the maximum bit rate of this channel?
A. 200Kbps
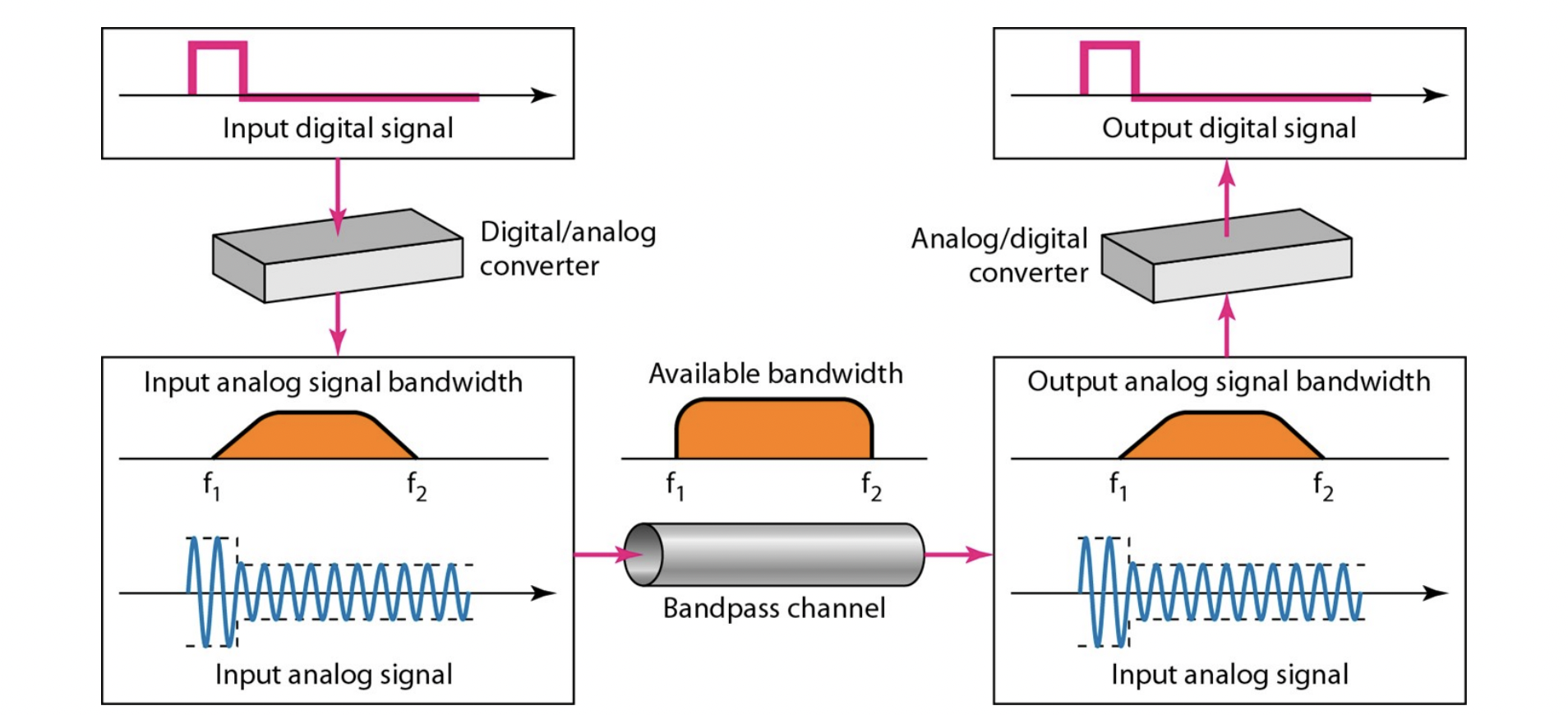
Modulation
- Band-pass channel
: f1부터 f2까지의 주파수를 통과시킨다
-
band-pass channel을 통해 신호를 전송시키려면, 우리는 신호를 modulate해야 한다
-
Modulate digital signals into analog signals
Transmission Impairment
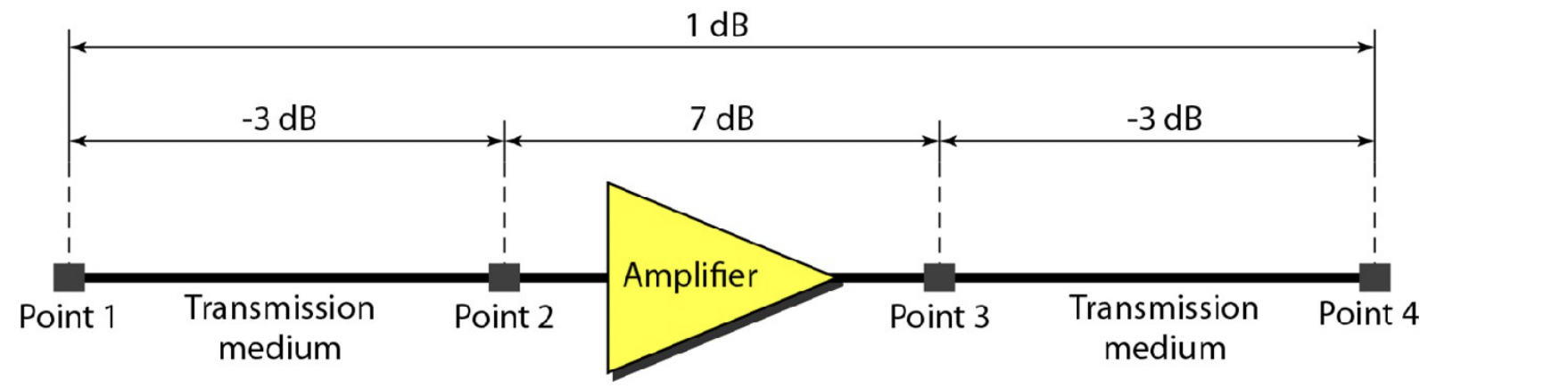
Attenuation 신호 감쇄
- 진폭 크기가 줄어든다
- Amplifier(증폭기)를 이용해서 진폭을 키워준다
- 문제는, noise도 같이 증폭되기 때문에 완벽하게 해결되는 것은 아니다
Decibel(dB)
- Units for signal strength
dB = 10log$$_{10}$$(P2/P1)- 기본적으로 두 신호 세기의 비율을 나타낸다.
Q. Suppose a signal travels through a transmission media and its power is reduced to one half. This means tha P2 = 0.5P1. In this case, the attenuation can be calculated as :
A.
= -3dB
-
3dB만큼 감소(a loss of 3dB = -3dB)하는 것은 power의 절반을 loss하는 것과 동일하다.
2배 -> P2/P1 = 2 -> 3dB
4배 -> P2/P1 = 4 -> 6dB
5dB?
10배 -> 10dB -> 이거 절반 -> 7dB -
dB를 사용하게 되면 곱을 덧셈뺄셈으로 표현할 수 있다.
dBm
- dBm is used to measure signal power in milliwatts
- dBm =
- Pm : power in milliwatt unit
- 1mW = 0dBm, 10mW = 10dBm, 100mW = 20dBm
Q. The loss in a cable is usually defined in decibels per kilometer (dB/km). 만약 -0.3dB/km의 cable의 시작에서 signal이 2mW의 power를 갖는다면, what is the power of signals at 5km?
A. 일단 5km이므로, 총 -1.5dB의 loss 발생
-1.5dB = 10log(P2/P1)
=> P2/P1 = 10-0.15 = 0.71
=> P2 = 0.71 * P1 = 0.7 * 2mW = 1.4mW
Distortion
- Signal changes its form or shape
Noise
-
Several types of noise, thermal(열) noise, induced noise(noise generated in a circuit by a varying magnetic or electrostatic field produced by another circuit), crosstalk(혼선), and impulse noise(원치 않는 거의 즉각적인 날카로운 사운드를 포함하는 노이즈 범주), may corrupt the signal
-
Signal-to-Noise Ratio(SNR)
SNR = signal power / noise power
전력의 비율을 나타낸다
단위는 W 또는 dB
Q. 신호의 세기(power)가 10mW이고, noise가 1uW이다. What are the values of SNR and SNRdB?
A. 1uW = 0.001mW
SNR = 10mW / 0.001mW = 10000
SNRdB = 10log1010000 = 40
- SNR이 너무 낮으면, signal을 복구하기가 힘들다. noise와 별 차이가 없으면, 원래 신호의 위 아래를 구분하기가 어렵다.
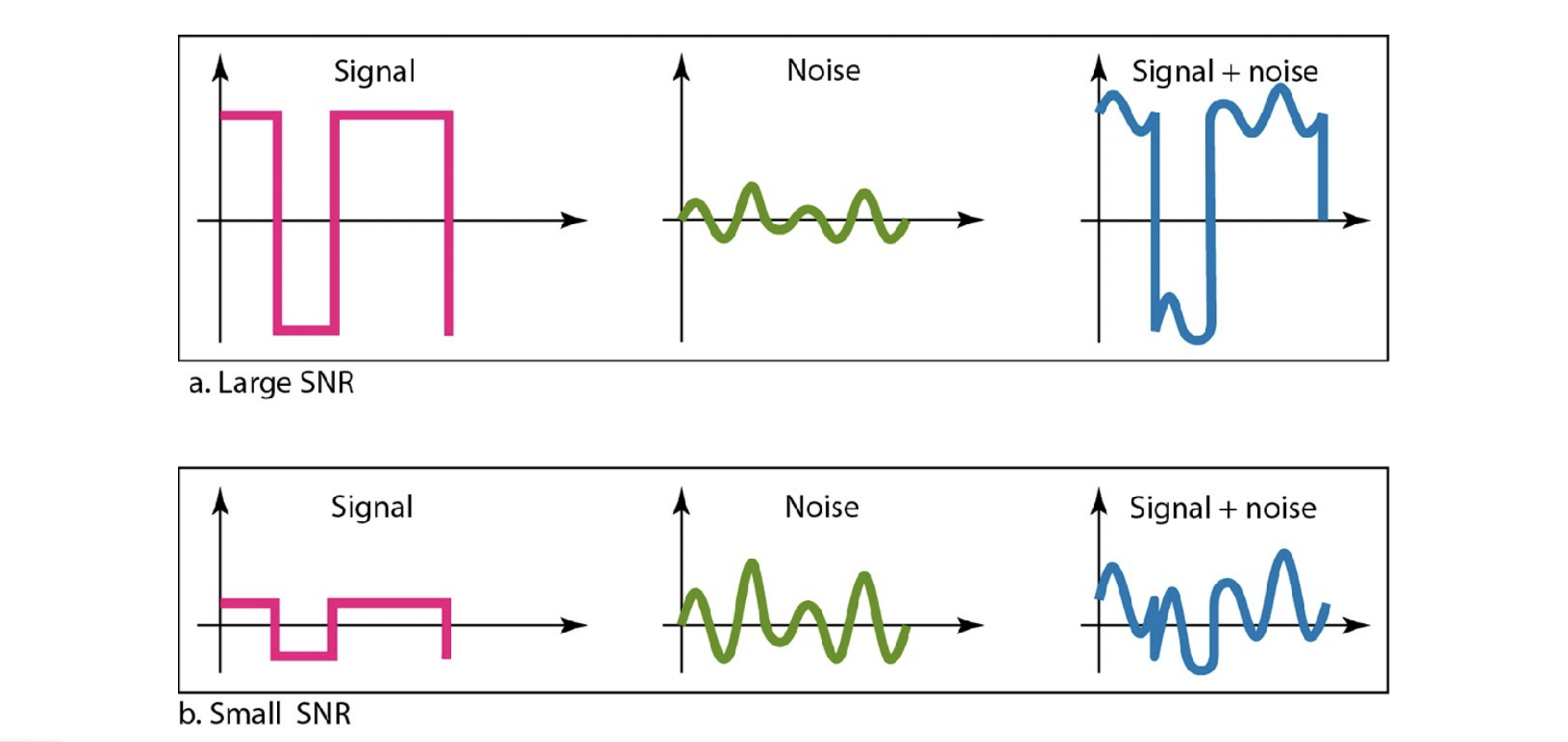
Data Rate Limits
- data transfer rate(bit rate) is dependent upon
- bandwidth
- number of signal levels
- channel quality (noise level)
Nyquist Equation
- Assuming noiseless channel(이론적),
- Data rate = 2 x B x log2L
B : bandwidth, L : number of signal levels - level을 많이 쓰게 되면 속도가 올라간다.
하지만 level을 많이 쓴다는 건 그만큼 잘게 나눈다는 뜻이고, 두 신호 사이의 차이가 적어지기 때문에 그만큼 오류가 많이 발생한다. 즉, 정확성이 떨어진다.
Q. Consider a noiseless channel with a bandwidth of 3000Hz transmitting a signal with two signal levels. What is the maximum bit rate?
A. 2 x 3000 x log22 = 6000bps
Q. 265kbps를 보내야 한다. noiseless channel이고, bandwidth는 20kHz이다. 몇 개의 signal level이 필요하냐?
A. 2 x 20 x log2L = 265
=> log2L = 6.625
=> L = 98.7 levels
근데, the number of levels는 2의 거듭제곱이어야 한다.
따라서 답은 128 levels이고, 속도는 280kbps가 된다.
Shannon Capacity
-
Maximum bit rate in a noisy channel (최대로 낼 수 있는 전송 속도)
-
C = B x log2(1 + SNR)
C : capacity (maximum bit rate), B : bandwidth
Q. Consider an extremely noisy channel in which SNR is zero. What is the maximum bit rate for this channel
A. SNR이 0이라는건, signal = 0이거나 noise가 ∞이다.
어쨌든,
C = B x log2(1 + SNR) = B * 0 = 0.
- In other words, 이 channel을 통해 어떠한 data도 받을 수 없다.
Q. A telephone line normally has a bandwidth of 3000Hz assigned for data communications. The signal-to-noise ratio is usually 3162. The channel capacity?
A. C = B x log2(1 + SNR)
= 3000 x log2(3163)
= 3000 x 11.62
= 34,860bps
Q. Suppose SNR is 36dB, and channel bandwidth is 2MHz. The channel capacity?
A. 먼저, SNR을 dB로 주었기 때문에 dB 아닌걸로 바꿔주어야 한다
SNRdB = 10 log10SNR
=> SNR = 10SNRdB/10 = 103.6 = 3981
C = B x log2(1 + SNR)
= 2 x 106 x log23982
= 24 Mbps
-
SNR이 아주 높다면, SNR과 SNR + 1을 거의 같다고 볼 수 있다. 이 경우, theoretical channel capacity는 더 간단하게 쓸 수 있다.
-
C = B x (SNRdB / 3)
-
For the previous example,
C = 2MHz x (36/3) = 24Mbps -
SNR을 dB로 주면, 이게 더 편할 듯 싶다.
Performance
Bandwidth
- 두 가지 의미
- The size in frequency domain of a channel (Hz)
- The maximum bit rate (bps)
- 단위를 보고 구분해야 한다
Bandwidth of a line is 4kHz.
This line has 56Kbps of bandwidth
Throughput
- 실제 전송률. The actual data transfer rate (bps)
- Bandwidth보다 작거나 같다
Q. A network with bandwidth of 10Mbps can pass only an average of 12,000 frames per minute with each frame carrying an average of 10,000 bits. What is the throughput of this network?
A. Throughput = (12,000 x 10,000)/60 = 2Mbps
Delay
-
Duration between
the time the first bit of a message leaves the source
and
the time the last bit of the message is received at the destination -
Delay
= transmission delay + propagation delay + queuing delay + processing delay.
4가지의 component가 있다.- Transmission delay
Duration between
the time the first bit leaves the source
and
the time the last bit leaves the source - Propagation delay
Duration of time a bit travels from source to destination
distance / speed of travel - Queuing delay
Time waiting for other packets ahead of the packet - Processing delay
Time used by system to process the message
- Transmission delay
Q. What is the propagation time if the distance between the two points is 12,000km? Assume the propagation speed to be 2.4 x 108m/s in cable
A. 시 = 거 / 속
= 12 x 106 m / (2.4 x 108) s
= 50ms
Q. What are the propagation time and the transmission time for a 2.5KB message if the bandwidth of the network is 1Gbps? Assume that the distance between the sender and the receiver is 12,000km and that the signal travels at 2.4 x 108m/s
A. propagation time = (12,000 x 103) / (2.4 x 108) = 50ms
transmission time = 프레임의 크기 / 회선의 최대 전송 속도(bandwidth)
= (2500 x 8) / 109 = 0.020ms
- Message는 짧은데 bandwidth가 크면,
propagation time이 주요 요인이 된다.
Q. What are the propagation time and the transmission time for 5MB message if the bandwidth of the network is 1Mbps? Assume that the distance between the sender and the receiver is 12,000km and the signal travels at 2.4 x 108m/s
A. transmission time = (5,000,000 x 8) / 106 = 40s
Bandwidth-Delay Product
- channel의 부피를 의미한다.
- How much data can be fit into the channel between sender and receiver
- The number of bits that fills up the pipe
- 수도관에 들어갈 수 있는 물의 부피는 수도관의 길이(delay)와 폭(bandwidth)로 계산된다. 비슷하다.
- Volume = bandwidth x delay
bps x s = bits/s x s = bits
Q. Suppose bandwidth of a link is 10Mbps, and the delay is 50ms. What is the amount of data to fill up this channel?
A. 10Mbps x 50ms = 10 x 106 x 50 x 10-3 bits = 500 x 103 = 500Kbit