Flux 패턴이란?
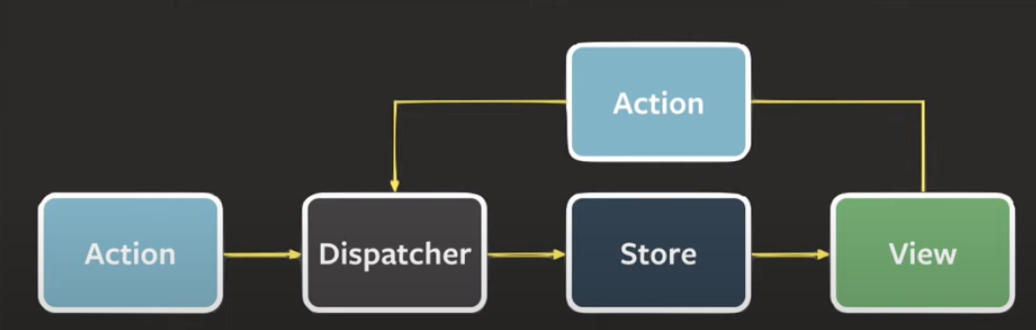
- View의 역할이 단순한 서버 사이드의 MVC 패턴과 달리, 프론트에서의 MVC 패턴은 View의 역할이 복잡하고 심지어는 View가 Model을 바꿔야 하는 일이 발생함.
- 이를 해결하고자 Controller가 View와 Model의 중간에서 중개자 역할을 담당. 여기에서도 Controller가 지나치게 비대해지는 문제 발생.
- 이를 해결하고자 나온 것이 Flux 패턴. View가 직접 Model(Store)를 조작하지 않고, Action을 통해 간접적으로 동작할 수 있게 함.
- 위 사진에서 볼 수 있듯이 흐름이 단방향으로만 흐르게 만드는 것이 flux 패턴의 핵심.
각 항목의 역할
Action
- 상태 변경을 위한 정보를 담고 있는 객체
- 종류를 나타내는 type, 변경해야 할 데이터를 담고 있는 payload라는 property들로 구성된다.
Dispatcher
- dispath: 목적에 맞게 전송한다라는 뜻
- Action을 전달받아 Action의 타입에 따라 Store의 변화를 일으킨다.
Store
View
Redux 라이브러리 뜯어보기
- flux 패턴으로 제작된 대표적인 라이브러리 redux의 코드를 살펴보도록 하자.
function createStore(reducer, preloadedState, enhancer) {
var currentReducer = reducer;
var currentState = preloadedState;
var currentListeners = [];
var nextListeners = currentListeners;
var isDispatching = false;
function getState() {
return currentState;
}
function subscribe(listener) {
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error('Cannot subscribe when the reducer is executing.');
}
var isSubscribed = true;
nextListeners.push(listener);
return function unsubscribe() {
if (!isSubscribed) {
return;
}
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error('Cannot unsubscribe when the reducer is executing.');
}
isSubscribed = false;
var index = nextListeners.indexOf(listener);
nextListeners.splice(index, 1);
currentListeners = null;
};
}
function dispatch(action) {
if (isDispatching) {
throw new Error('The reducer is already executing.');
}
try {
isDispatching = true;
currentState = currentReducer(currentState, action);
} finally {
isDispatching = false;
}
var listeners = (currentListeners = nextListeners);
for (var i = 0; i < listeners.length; i++) {
var listener = listeners[i];
listener();
}
return action;
}
return {
dispatch: dispatch,
subscribe: subscribe,
getState: getState,
};
}
const initialState = { count: 0 };
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return state;
}
}
- 위 코드는 실제 redux의 createStore.js에서 가져온 스토어 생성 함수이다. 가볍게 쓸 목적이기 때문에 복잡한 검증 로직은 제외하고 가져왔다.
- 위 코드를 실행하는 코드는 아래와 같다.
const initialState = { count: 0 };
function counterReducer(state = initialState, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return state;
}
}
const store = createStore(counterReducer);
const store = createStore(counterReducer);
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log('Current state:', store.getState());
});
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
store.dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' });
- store의 subscribe method를 호출하여 store의 변화를 감지하게 한다.
- dispatch method에 상태 변화(action)을 전달한다.
- dispatch가 일어나면 subscribe 되었던 listener(여기에서는 console.log… 부분) 들이 실행 된다.
- 위 코드에서 보면 createStore에 Observer Pattern이 사용되었음을 확인할 수 있다.
Observer Pattern
- 옵저버 패턴은 구독과 발행의 개념으로 표현된다.
function Click() {
this.handlers = [];
}
Click.prototype = {
subscribe: function (fn) {
this.handlers.push(fn);
},
unsubscribe: function (fn) {
this.handlers = this.handlers.filter(function (item) {
if (item !== fn) {
return item;
}
});
},
fire: function (o, thisObj) {
var scope = thisObj || window;
this.handlers.forEach(function (item) {
item.call(scope, o);
});
},
};
function run() {
var clickHandler = function (item) {
console.log('fired: ' + item);
};
var click = new Click();
click.subscribe(clickHandler);
click.fire('event #1');
click.unsubscribe(clickHandler);
click.fire('event #2');
click.subscribe(clickHandler);
click.fire('event #3');
}
run();
- subscribe 함수를 실행하면 해당 프로퍼티를 handler에 담아둔다.
- unsubscribe 함수를 실행하면 해당 프로퍼티에 해당하는 handler를 삭제할 수 있다.
- fire 함수를 실행하면 handler 안에 들어있는 함수들이 실행된다.
참고 자료

