그래프 완전 탐색 기법 중 하나
깊이 우선 탐색은 그래프의 시작 노드에서 출발하여 탐색할 한 쪽 분기를 정하여 최대 깊이까지 탐색을 마친 후 다른 쪽 분기로 이동하여 다시 탐색을 수행하는 알고리즘
그래프 완전 탐색
- 재귀 함수로 구현 => DFS
- 스택 자료 구조로 이용
시간 복잡도 : O(V + E) 노드 수 : V , 에지 수 : E
깊이 우선 탐색은 실제 구현 시 재귀 함수를 이용하므로 스택 오버플로에 유의해야함
단절점 찾기, 단절선 찾기, 사이클 찾기, 위상 정렬 등이 있다.
DFS는 한 번 방문한 노드를 다시 방문하면 안되므로 노드 방문 여부를 체크할 배열이 필요하며, 그래프는 대부분 인접 리스트로 표현한다. 후입선출의 특성을 가지므로 스택을 사용하여 설명
스택보다는 스택 성질을 갖는 재귀 함수로 많이 구현하지만 강의에선 스택으로 설명했다..
-
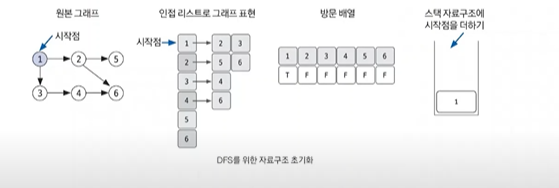
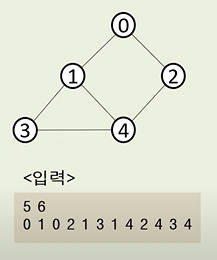
DFS를 시작할 노드를 정한 후 사용할 자료구조 초기화 하기 => 인접리스트
DFS를 위해 필요한 초기 작업은 인접 리스트로 그래프 표현하기, 방문 배열 초기화 하기, 시작 노드 스택에 삽입하기이다. 스택에 시작 노드를 1로 삽입할 때 해당 위치의 방문 배열을 체크하면 T,F,F,F,F,F가 된다
-
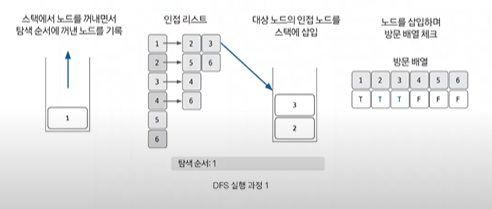
스택에서 노드를 꺼낸 후 꺼낸 노드의 인접 노드를 다시 스택에 삽입하기
pop을 수행하여 노드를 꺼낸다. 꺼낸 노드를 탐색 순서에 기입하고 인접 리스트의 인저 노드를 스택에 삽입하여 방문 배열을 체크한다. 방문 배열은 T,T,T,F,F,F가 된다
-
스택 자료구조에 값이 없을 때까지 반복
이미 다녀간 노드는 방문 배열을 바탕으로 재삽입하지 않는 것이 핵심
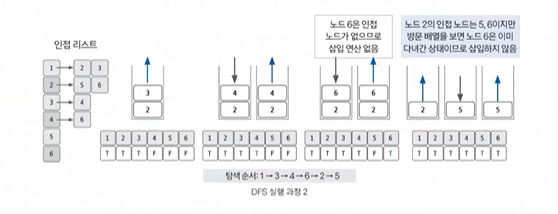
스택에 노드를 삽입할 때 방문 배열을 체크하고 스택에서 노드를 뺄 때 탐색 순서에 기록하여 인접 노드를 방문 배열과 대조하여 살펴본다
public class Main {
static final int MAX_N = 10;
static int N,E;
static int[][] Graph = new int[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 인접행렬
static boolean[] Visited = new boolean[MAX_N];
static void dfs(int node) {
Visited[node] = true;
System.out.println(node + " ");
for(int next = 0; next < N; next++) {
if(!Visited[next] && Graph[node][next] != 0)
dfs(next);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
E = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
Graph[u][v] = Graph[v][u] = 1;
}
dfs(0);
}
} // 0 1 3 4 2 // stack 사용 LIFO
public class Main {
static final int MAX_N = 10;
static int N,E;
static int[][] Graph = new int[MAX_N][MAX_N]; // 인접행렬
static void dfs(int node) { // 시작노드 입력
boolean[] visited = new boolean[MAX_N];
Stack<Integer> mystack = new Stack<>();
mystack.push(node);
while(!mystack.empty()) {
int curr = mystack.pop();
if(visited[curr]) continue;
visited[curr]=true;
System.out.println(curr+" ");
for(int next = 0; next < N; next++) {
if(!visited[next]&&Graph[curr][next]!=0)
mystack.push(next);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
E = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<E; i++) {
int u = sc.nextInt();
int v = sc.nextInt();
Graph[u][v] = Graph[v][u] = 1;
}
dfs(0);
}
} // 0 2 4 3 1Flood fill

// Flood fill (stack 사용)
public class Main {
static final int MAX_N = 10;
static int[][] D= {{-1,0},{1,0},{0,-1},{0,1}}; //상하좌우
static int N;
static int[][] Board = new int[MAX_N][MAX_N];
static class Point{
Point(int r, int c) { row = r; col = c; }
int row, col;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
N = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=0; i<N; i++)
for(int j=0; j<N; j++)
Board[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
int sRow = sc.nextInt(), sCol = sc.nextInt();
int color = sc.nextInt();
dfs(sRow,sCol,color);
for(int i=0;i<N;i++) {
for(int j=0; j<N; j++) {
System.out.print(Board[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
static void dfs(int r, int c, int color) {
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[MAX_N][MAX_N];
Stack<Point> mystack = new Stack<>();
mystack.push(new Point(r,c));
while(!mystack.empty()) {
Point curr = mystack.pop();
if(visited[curr.row][curr.col]) continue;
visited[curr.row][curr.col] = true;
Board[curr.row][curr.col] = color;
for(int i=0; i<4; i++) {
int nr = curr.row+D[i][0], nc = curr.col+D[i][1];
if(nr < 0 || nr > N-1 || nc < 0 || nc > N-1) continue;
if(visited[nr][nc]) continue;
if(Board[nr][nc]==1) continue;
mystack.push(new Point(nr,nc));
}
}
}
}
