C++ Knowledge
Template
- Data Type마다 Class Type을 다르게 설정하는 게 번거로움
- 컴파일러가 자동으로 Multuple Versions of Class Type 생성해 주도록 하는 것
- Formal Parameter: 모양을 잡아 주는 역할
- ex)
template<class ItemType>
- Actual Parameter: 실제값을 가진 매개 변수
- ex)
StackType<float> numStack;
Using Template
- Seperated Compilation
- 하나의 .exe 파일에 여러 개의 .obj가 존재할 경우 각각의 .obj 파일은 따로따로 compile
- 하나의 .cpp 파일을 수정할 경우 전체 파일을 compile하는 것이 아닌 해당 파일만 다시 compile
- template은 하나의 틀의 불과
- class 변수를 선언하면 해당 Data Type에 맞는 코드를 똑같이 재구성
- template 안에 class와 operation의 정의가 함께 존재해야 함
- Application Level과 Implecation Level을 하나의 파일 안에 구현
Address & Pointer
Recall Array
- C++: Array에 값을 삽입할 때 range를 검사하지 않음
- ex)
int a[10]; a[500] = 2;
- Error가 발생할 때도 있고 그렇지 않을 때도 있음
- 범위를 넘는 배열을 연산하고자 하면 Error 발생
- char형 Array의 경우 String이 끝났다는 표시인 null character ('\n') 삽입
- length에는 null character가 포함되지 않음
- 실제로는 메모리 공간 차지
Address and Pointer
- Address: 변수가 저장돼 있는 주소를 참조하는 Operator &
- Pointer: 주소를 저장하기 위한 변수 *
- notice)
int* x; int* y; == int *x, *y; != int* x, y;
- Reference: Pointer 변수 선언 이외에 *가 사용되는 경우
- Pointer가 가리키고 있는 주소에 저장된 값
- Pointer끼리 대입 연산 (=) 가능
- Null Pointer: 아무것도 가르키지 않는 Pointer
- 편의상 0으로 표시
- 실제로는 가리키는 값이 없기 때문에 연산에 사용하지 않음
Allocation of Memory
Static Allocation
- Building Time: Compile Time
- 메모리를 할당하는 주소가 고정적
- Lifetime: 프로그램 시작 ~ 종료
- ex)
void f() { int x; static int y;}
- f()를 여러번 실행해도 y가 저장되는 메모리 주소는 고정적
Dynamic Allocation
- Building Time: Run Time
- 메모리를 할당하는 주소가 유동적
- Lifetime: 라인이 실행되는 순간 (new) ~ 메모리 해제 (delete)
- ex)
void f() { int x; static int y;}
- f()를 실행할 때마다 x가 저장되는 메모리 주소가 바뀜
- new Operation
- Pointer에게 제공해야 할 주소에 메모리를 할당하는 연산자
- 할당된 메모리에 저장되는 변수는 이름 없음 (Anonymous Variable)
- 필요한 연산을 가지고 메모리를 해제하는 delete 연산 필요
- 배열 a가 동적 할당일 때
delete a;는 배열의 첫 요소만 삭제
delete[] a로 배열 메모리 해제
Stack
Stack
- Homogeneous Item이 순서를 갖고 쌓이는 것
- 한쪽 방향으로만 추가와 제거 가능
- LIFO: Last in, First out
Stack ADT Operation
StackTypeStatic.h
#include "ItemType.h"
class FullStack {
};
class EmptyStack {
};
class StackType {
public:
StackType();
void MakeEmpty();
void Push(ItemType item);
void Pop();
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
ItemType Top();
private:
int top;
ItemType items[MAX_ITEMS];
};
StackTypeStatic.cpp
#include "StackTypeStatic.h"
StackType::StackType() {
top = -1;
}
void StackType::MakeEmpty() {
top = -1;
}
bool StackType::IsFull() const {
return (top == MAX_ITEMS - 1);
}
bool StackType::IsEmpty() const {
return (top == -1);
}
void StackType::Push(ItemType item) {
if (IsFull()) {
throw FullStack();
}
else {
top++;
items[top] = item;
}
}
void StackType::Pop() {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw EmptyStack();
}
else {
top--;
}
}
ItemType StackType::Top() {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw EmptyStack();
}
else {
return items[top];
}
}
StackTypeDynamic.h
#include "ItemType.h"
class FullStack {
};
class EmptyStack {
};
template <class ItemType>
class StackType {
public:
StackType();
StackType(int max);
~StackType();
void MakeEmpty();
void Push(ItemType item);
void Pop();
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
ItemType Top();
private:
int top;
int maxStack;
ItemType* items;
};
template <class ItemType>
StackType<ItemType>::StackType() {
maxStack = 500;
top = -1;
items = new ItemType[maxStack];
}
template<class ItemType>
StackType<ItemType>::StackType(int max) {
maxStack = max;
top = -1;
items = new ItemType[maxStack];
}
template<class ItemType>
void StackType<ItemType>::MakeEmpty() {
top = -1;
delete[] items;
}
template<class ItemType>
bool StackType<ItemType>::IsEmpty() const {
return (top == -1);
}
template<class ItemType>
bool StackType<ItemType>::IsFull() const {
return (top == maxStack - 1);
}
template<class ItemType>
void StackType<ItemType>::Push(ItemType item) {
if (IsFull()) {
throw FullStack();
}
else {
top++;
items[top] = item;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
void StackType<ItemType>::Pop() {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw EmptyStack();
}
else {
top--;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
ItemType StackType<ItemType>::Top() {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw EmptyStack();
}
else {
return items[top];
}
}
template<class ItemType>
StackType<ItemType>::~StackType() {
delete[] items;
}
Queue
Queue
- Homogeneous한 item들이 순서를 갖고 쌓이는 것
- 양쪽 방향으로 추가와 제거 가능
- FIFO: First in, first out
Enqueue Method
- Function: Queue의 rear로 새 아이템 추가
- Precondition: Queue의 상태가 full이 아니어야 함
- Postcondition: 새 아이템은 Queue의 rear에 위치
Dequeue Method
- Function: Queue의 front에 있는 아이템 반환
- Precondition: Queue의 상태가 Empty가 아니어야 함
- Postcondition: front에 있던 아이템이 사라진 Queue 상태
Problem
- 두 개의 포인터인 rear와 front 모두 증가하는 방향으로 움직여 Boundary에 다다르게 됨
- 수정할 때마다 뒤로 가니까 데이터 할당 범위 초과
- 해결책 1: Dequeue할 때 front를 증가하지 않고 Queue 전체를 앞당기는 방법

- Operation이 비싸서 비효율적인 방법
- 해결책 2: Circular Queue
- front 앞이 비어 있기 때문에 끝에 다다르면 앞으로 되돌리기

- rear = (rear + 1) % maxQue
- Queue가 Full일 때
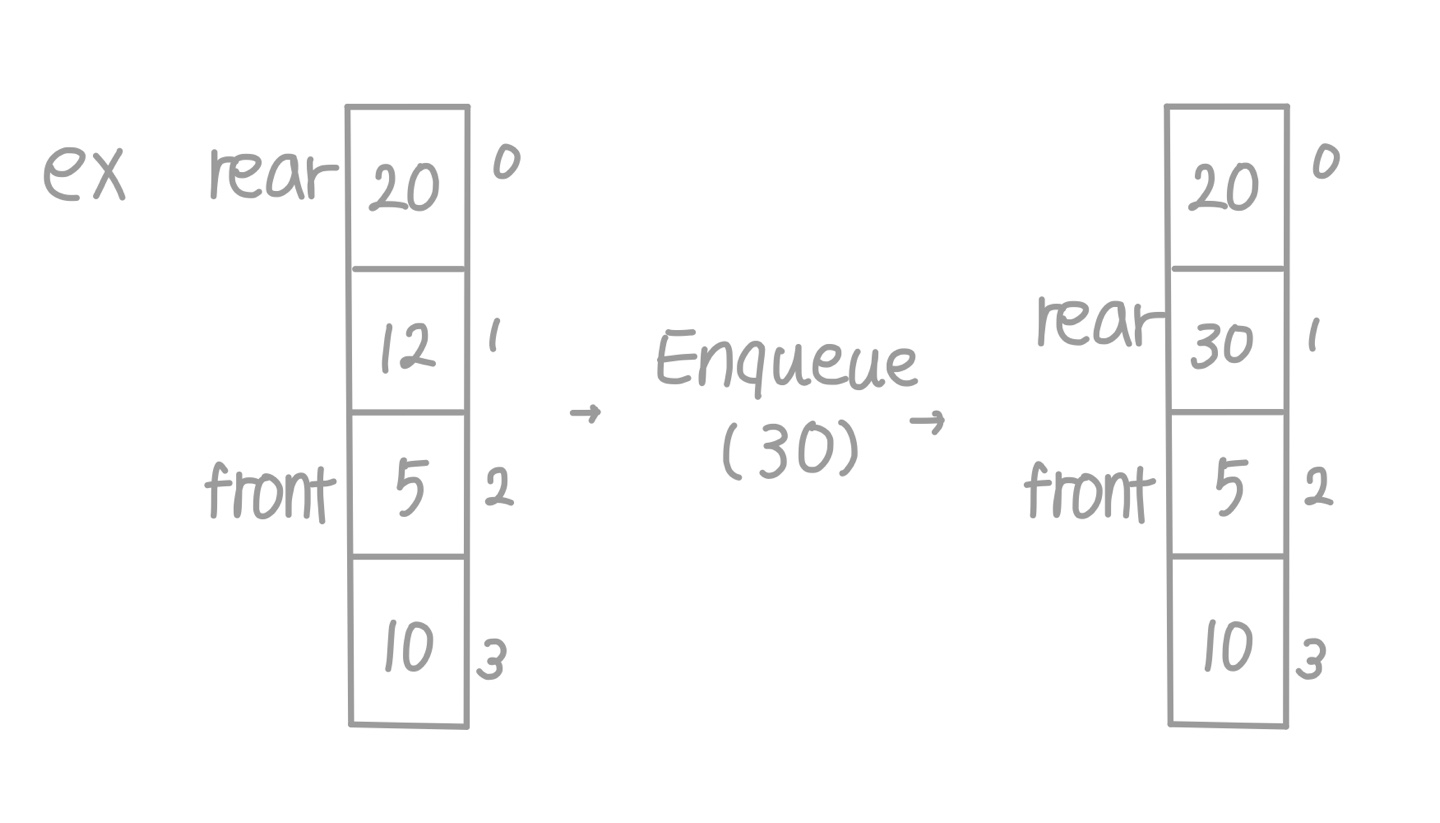
- rear + 1 = front
- Queue가 Empty일 때
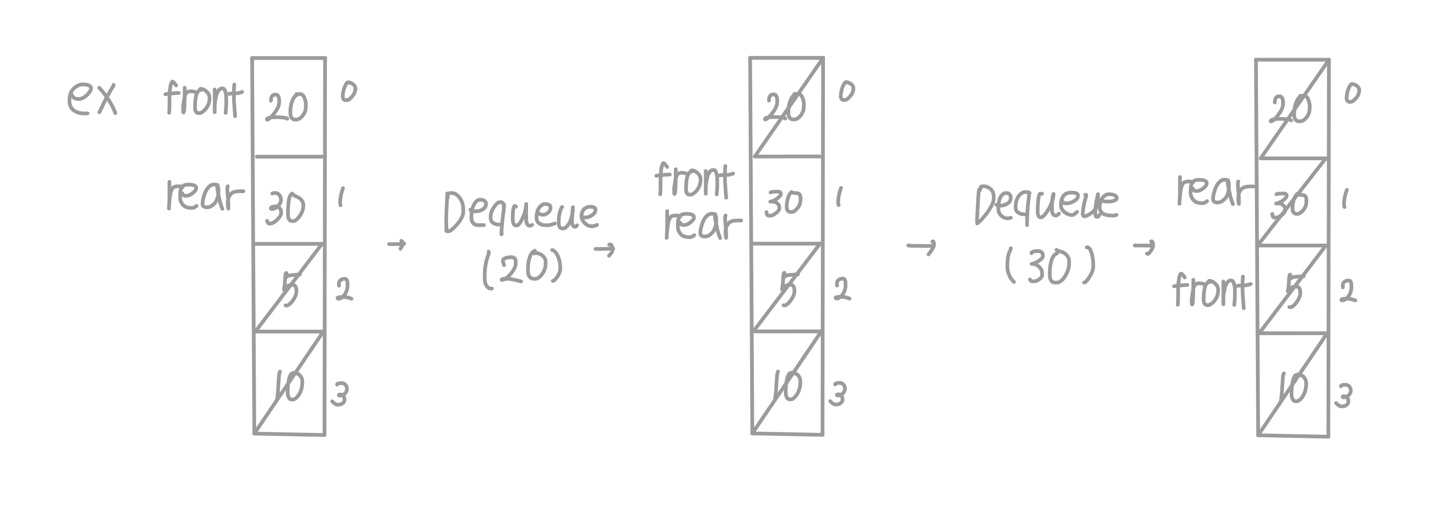
- rear + 1 = front
- Full과 Empty 상태를 구분할 수 없음
- Reserved cell
- 못 쓰는 공간, 낭비되는 메모리
- 실제 front의 하나 앞 포인팅
- Queue가 Full인 경우 (reserved cell)
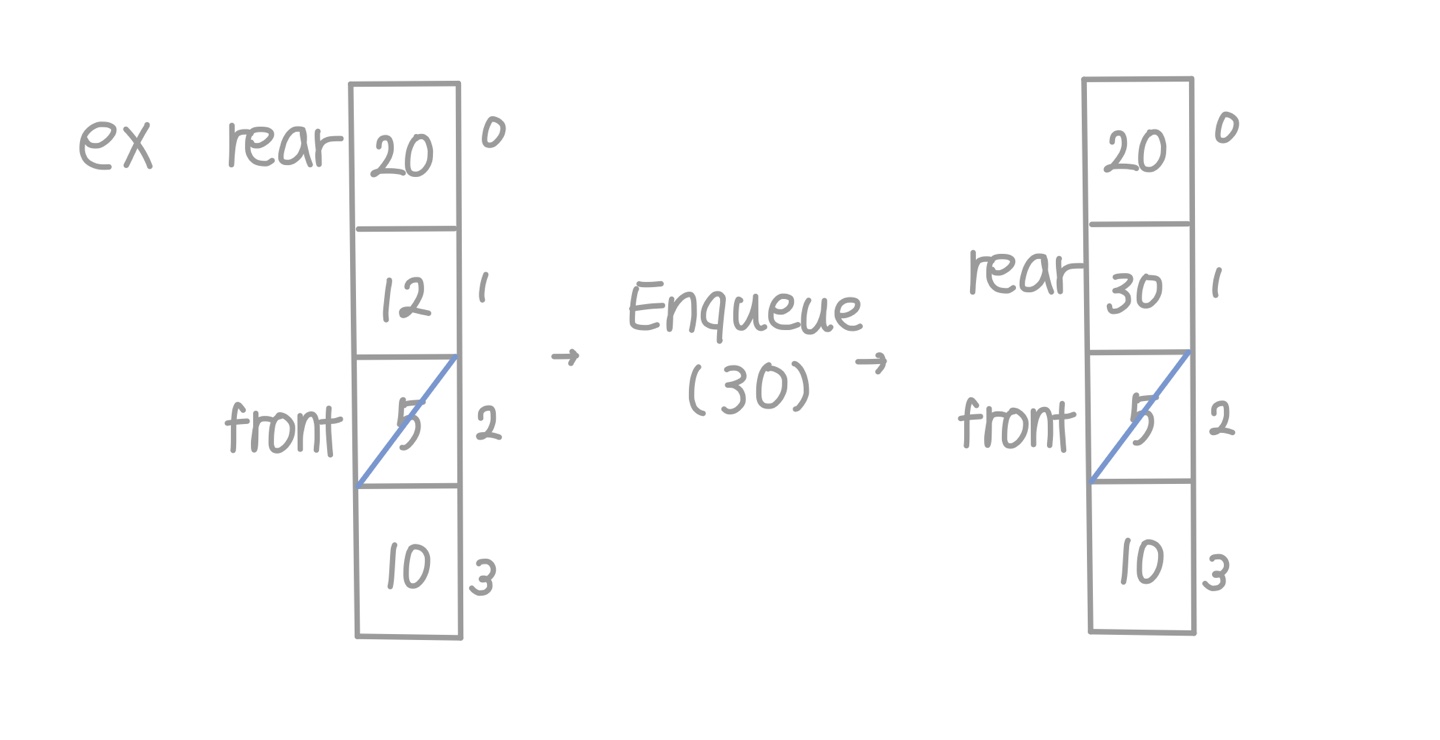
- rear + 1 = front
- Queue가 Empty인 경우 (reserved cell)
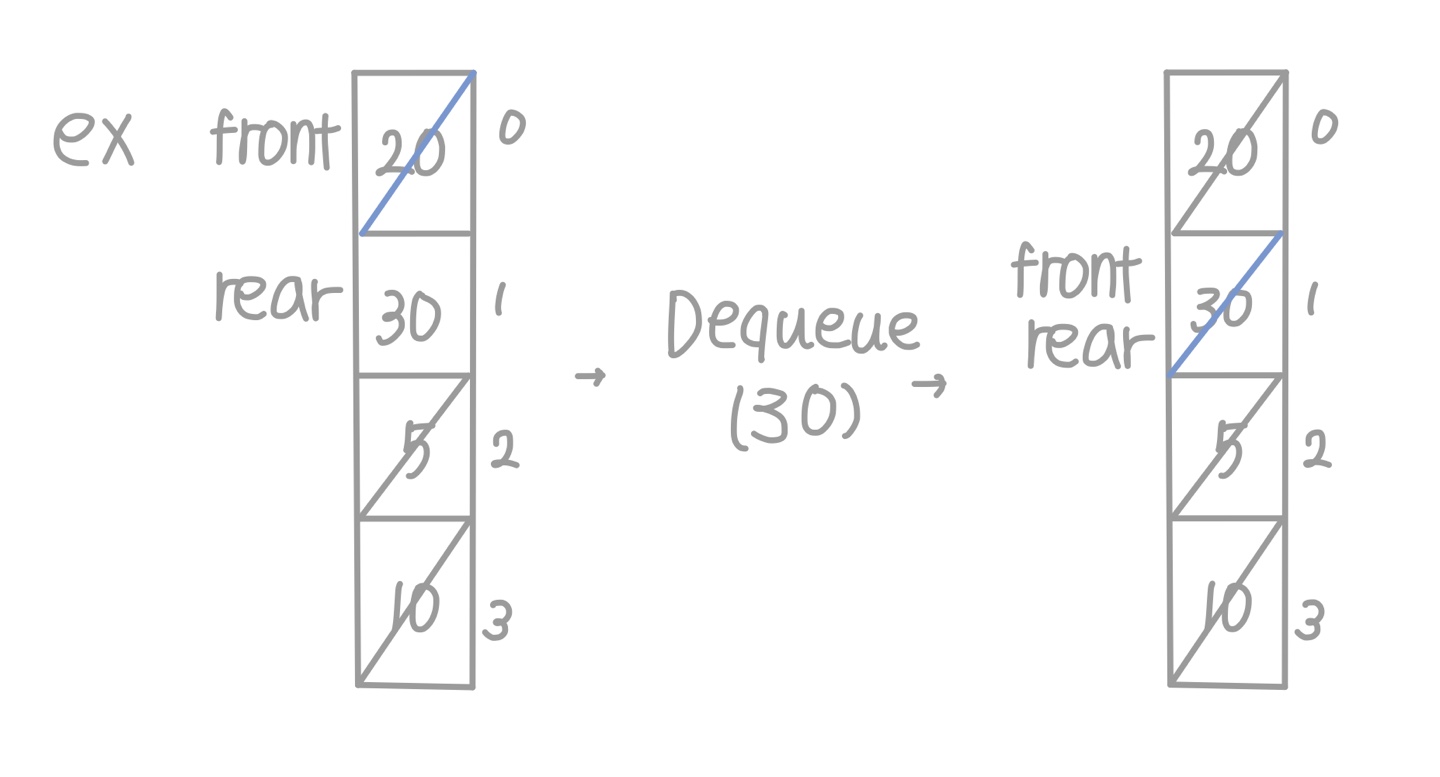
- rear == front
- Initialize front and rear
- Original cell: front = 0, rear = -1
- Reserved cell: front = -1, rear = -1
Queue ADT Operation
- Transformer
- MakeEmpty
- Enqueue
- Dequeue
- Observe
QueueTypeInt.h
#include "ItemType.h"
typedef int ItemType;
class FullQueue {
};
class EmptyQueue {
};
class QueType {
public:
QueType();
QueType(int max);
void MakeEmpty();
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
void Enqueue(ItemType item);
void Dequeue(ItemType& item);
private:
int front;
int rear;
int maxQue;
ItemType* items;
};
QueueTypeInt.cpp
#include "QueueTypeInt.h"
QueType::QueType() {
maxQue = 500;
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
items = new ItemType[maxQue];
}
QueType::QueType(int max) {
maxQue = max;
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
items = new ItemType[maxQue];
}
void QueType::MakeEmpty() {
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
delete[] items;
}
bool QueType::IsEmpty() const {
return (front == rear);
}
bool QueType::IsFull() const {
return (rear + 1) % maxQue == front;
}
void QueType::Enqueue(ItemType item) {
if (IsFull()) {
throw FullQueue();
}
else {
rear = (rear + 1) & maxQue;
items[rear] = item;
}
}
void QueType::Dequeue(ItemType& item) {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw EmptyQueue();
}
else {
front = (front + 1) % maxQue;
item = items[front];
}
}
QueueType.h (template)
#include "ItemType.h"
class FullQueue {
};
class EmptyQueue {
};
template<class ItemType>
class QueType {
public:
QueType();
QueType(int max);
void MakeEmpty();
bool IsEmpty() const;
bool IsFull() const;
void Enqueue(ItemType item);
void Dequeue(ItemType& item);
private:
int front;
int rear;
int maxQue;
ItemType* items;
};
template<class ItemType>
QueType<ItemType>::QueType() {
maxQue = 500;
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
items = new ItemType[maxQue];
}
template<class ItemType>
QueType<ItemType>::QueType(int max) {
maxQue = max;
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
items = new ItemType[maxQue];
}
template<class ItemType>
void QueType<ItemType>::MakeEmpty() {
front = maxQue - 1;
rear = maxQue - 1;
delete[] items;
}
template<class ItemType>
bool QueType<ItemType>::IsEmpty() const {
return (front == rear);
}
template<class ItemType>
bool QueType<ItemType>::IsFull() const {
return (rear + 1) % maxQue == front;
}
template<class ItemType>
void QueType<ItemType>::Enqueue(ItemType item) {
if (IsFull()) {
throw FullQueue();
}
else {
rear = (rear + 1) & maxQue;
items[rear] = item;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
void QueType<ItemType>::Dequeue(ItemType& item) {
if (IsEmpty()) {
throw EmptyQueue();
}
else {
front = (front + 1) % maxQue;
item = items[front];
}
}
int length
- int length인 멤버 변수를 추가해 Queue에 몇 개가 저장돼 있는지 카운팅하는 방법
- Enqueue 시에 length++
- Dequeue 시에 length--
- length를 추가하는 일은 비용이 많이 들어 비효율적인 구현 방법
- Enqueue, Dequeue가 빈번하게 사용되는데, 사용할 때마다 length 연산 필요하기 때문
- 길이를 알고자 하는 LengthIs() 함수를 자주 사용한다면 유리한 전략
Palindromes
Palindromes
- 앞으로 읽으나 뒤로 읽으나 똑같은 것
- Stack:LIFO
- Queue: FIFO
- Stack의 pop() = Queue의 Dequeue()면 Palindromes
Palindrome.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cctype>
#include "StackTypeDynamic.h"
#include "QueueType.h"
int main() {
StackType<char> s;
QueType<char> q;
char ch, sitem, qitem;
int mismatches = 0;
std::cout << "Enter string" << std::endl;
while (std::cin.peek() != '\\n') {
std::cin >> ch;
if (isalpha(ch)) {
if(!s.IsFull()) {
s.Push(ch);
}
if (!q.IsFull()) {
q.Enqueue(ch);
}
}
}
while (!s.IsEmpty() && !q.IsEmpty()) {
sitem = s.Top();
s.Pop();
q.Dequeue(qitem);
if (sitem != qitem) {
++mismatches;
}
}
if (mismatches == 0) {
std::cout << "That is a palindrome" << std::endl;
}
else {
std::cout << "That is not a palindrome" << std::endl;
}
}







