Linked List
Node
A Single Node
- .info: 실제 사용자의 데이터
- .next: 다음 노드를 가리키는 포인터
- node: 데이터 구조 중 한 요소
- 특정 노드 관점에서 보면 자신의 뒷 요소밖에 모름
- 사용자가 변수를 선언하는 시점에도 몇 개가 필요한지 모를 때 사용
- 새 요소를 만들 때마다 heap 공간에 메모리를 동적으로 할당받음
- delete 메소드를 통해 garbage 데이터 처리 필요
Destructor
- 노드를 요소로 갖는 Local Variable의 topPtr에는 첫 노드의 주소 저장
- 함수가 종료되면 Local variable 삭제
- 삭제된 Local Variable의 top Ptr가 가리키던 노드들은 Garbage
- Local Variable 삭제 전에 노드 메모리 해제가 필요함
Unsorted List
Application Level
- Transformer
- MakeEmpty
- InsertItem
- DeleteItem
- Observe+
- IsFull
- LengthIs
- RetriveItem
- Iterators
Insert Method
- 새 아이템을 가르킬 location pointer 생성

- location에 동적 메모리를 할당해 새 아이템이 들어갈 장소 마련

- location에 새 아이템 넣기

- 새 아이템의 .next 가 현재 list의 끝 노드를 가리키도록 설정

- 현재 list의 끝은 새 아이템까지 추가된 리스트를 가리키도록 설정

DeleteItem Method
- 리스트를 순회하면서 삭제할 아이템을 찾는 location 생성한 뒤 리스트의 맨 끝부터 시작
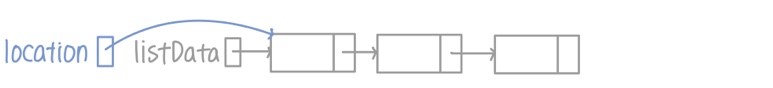
- 삭제할 아이템을 찾으면 그 아이템을 가리킬 tempLocation pointer 설정

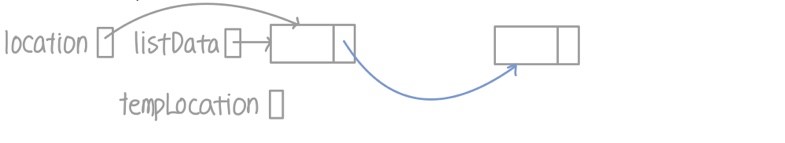
- 만약 아이템이 처음에 있을 때

- tempLocation이 삭제할 아이템인 location이 가리키는 노드를 가리키도록 설정
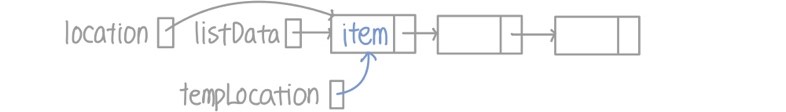
- 리스트의 끝인 listData는 곧 삭제될 아이템의 .next인 다음 노드를 가리키도록 설정
- 만약 아이템이 중간에 있을 때
- 순회하는 포인터인 location이 나타내는 노드의 다음 노드가 삭제할 아이템일 때까지 순회

- 아이템을 찾았다면 삭제할 노드를 나타내는 tempLocation이 location의 다음 노드를 가리키도록 설정
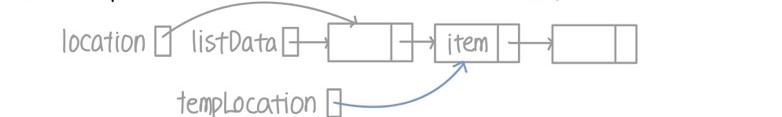
- listData 노드의 next가 삭제할 노드의 다음인 tempLocation이 나타내는 노드의 다음을 가리키도록 설정
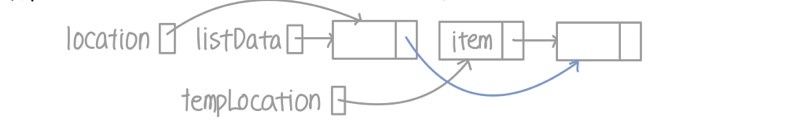
- 아이템을 모두 찾은 뒤 tempLocation 동적 할당 메모리 해제
Unsorted Linked List with C++
- UnsortedLinkedlist.cpp
#include <cstddef>
#include <new>
template <class ItemType>
struct NodeType;
template<class ItemType>
class UnsortedType {
public:
UnsortedType();
~UnsortedType();
void MakeEmpty();
void InsertItem(ItemType item);
void DeleteItem(ItemType item);
bool IsFull();
int LengthIs();
void RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found);
void ResetList();
void GetNextItem(ItemType& item);
private:
int length;
NodeType<ItemType>* listData;
NodeType<ItemType>* currentPos;
};
template<class ItemType>
struct NodeType {
ItemType info;
NodeType<ItemType>* next;
};
template<class ItemType>
UnsortedType<ItemType>::UnsortedType() {
length = 0;
listData = NULL;
}
template<class ItemType>
UnsortedType<ItemType>::~UnsortedType() {
MakeEmpty();
}
template<class ItemType>
void UnsortedType<ItemType>::MakeEmpty() {
NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr;
while (listData != NULL) {
tempPtr = listData;
listData = listData->next;
delete tempPtr;
}
length = 0;
}
template<class ItemType>
bool UnsortedType<ItemType>::IsFull() {
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
try {
location = new NodeType<ItemType>;
delete location;
return false;
}
catch (std::bad_alloc exception) {
return true;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
int UnsortedType<ItemType>::LengthIs() {
return length;
}
template<class ItemType>
void UnsortedType<ItemType>::InsertItem(ItemType item) {
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
location = new NodeType<ItemType>;
location->info = item;
location->next = listData;
listData = location;
length++;
}
template<class ItemType>
void UnsortedType<ItemType>::DeleteItem(ItemType item) {
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
NodeType<ItemType>* tempLocation;
location = listData;
if (location->info == item) {
tempLocation = location;
listData = location->next;
}
else {
while ((location->next)->info != item)
location = location->next;
tempLocation = location->next;
location->next = (location->next)->next;
}
delete tempLocation;
length--;
}
template<class ItemType>
void UnsortedType<ItemType>::ResetList() {
currentPos = NULL;
}
template<class ItemType>
void UnsortedType<ItemType>::GetNextItem(ItemType& item) {
if (currentPos == NULL) {
currentPos = listData;
}
else {
currentPos = currentPos->next;
}
item = currentPos->info;
}
template<class ItemType>
void UnsortedType<ItemType>::RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found) {
NodeType<ItemType>* location = listData;
bool moreToSearch = (location != NULL);
found = false;
while (moreToSearch && !found) {
if (location->info == item) {
found = true;
item = location->info;
}
else {
location = location->next;
moreToSearch = (location != NULL);
}
}
}
- Big O Comparision
| Operation | Array Implementaion | Linked-list Implementation |
|---|
| Constructor | O(1) | O(1) |
| MakeEmpty | O(1) | O(N) |
| InsertItem | O(1) | O(1) |
| DeleteItem | O(N) | O(N) |
| IsFull | O(1) | O(1) |
| LengthIs | O(1) | O(1) |
| RetrieveItem | O(N) | O(N) |
| ResetList | O(1) | O(1) |
| GetNextItem | O(1) | O(1) |
| Destructor | O(1) | O(N) |
Unsorted Linked List with JAVA
public class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public LinkedList() {
head = null;
}
public void addFirst(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
}
public void addLast(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null) {
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
current = current.next;
}
current.next = newNode;
}
public void delete(int data) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.data == data) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null) {
if (current.next.data == data) {
current.next = current.next.next;
return;
}
current = current.next;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
}
Unsorted Linked List with Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def add_first(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
def add_last(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None:
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next is not None:
current = current.next
current.next = new_node
def delete(self, data):
if self.head is None:
return
if self.head.data == data:
self.head = self.head.next
return
current = self.head
while current.next is not None:
if current.next.data == data:
current.next = current.next.next
return
current = current.next
def print_list(self):
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
Sorted List
Application Level
- Transformer
- MakeEmpty
- InsertItem
- DeleteItem
- Observe+
- IsFull
- LengthIs
- RetriveItem
- Iterators
Insert Method
- 새 요소를 넣어야 할 위치 찾기
- 새 요소 뒷 순서를 하나씩 뒷 index로 밀어서 자리 생성
- 빈 공간에 요소 삽입
- 길이 증가
- location Pointer 하나만 사용하는 경우
- 각 노드는 자신의 다음 노드만 알고 있음
- 새로운 item을 추가하면 item 전에 오는 노드의 next가 item을 가리킬 수 있도록 해야 함
- 따라서 location이 아닌 (location->next)->info로 검색
- 만약 item이 마지막에 들어가는 경우 참조 오류 발생
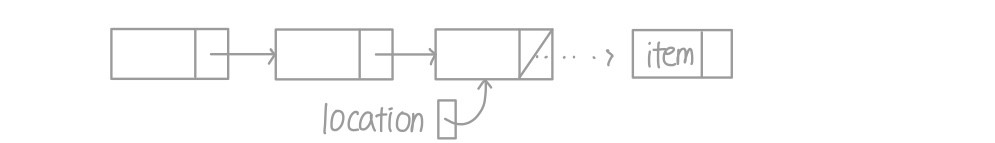
- location->next 는 NULL 값이라 item 추가 불가능
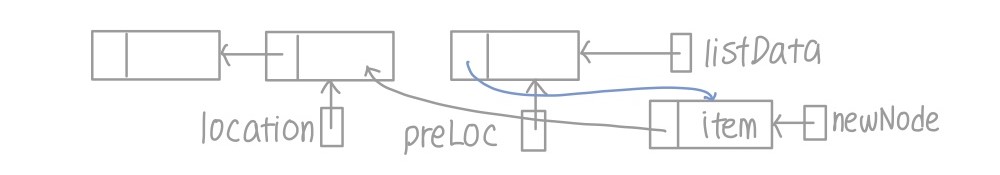
- item이 들어가기 바로 전 위치를 가리키는 preLoc Pointer 추가
- 순회하는 pointer location, 새로 추가할 노드 pointer인 newNode, item의 위치를 찾았는지 말해 주는 moreToSearch, item이 들어가는 바로 직전 위치를 말해 주는 preLoc pointer 생성

- 순회하는 location을 시작점인 listData에 두고 moreToSearch라면 계속 방문하며 아이템을 넣을 위치 찾기
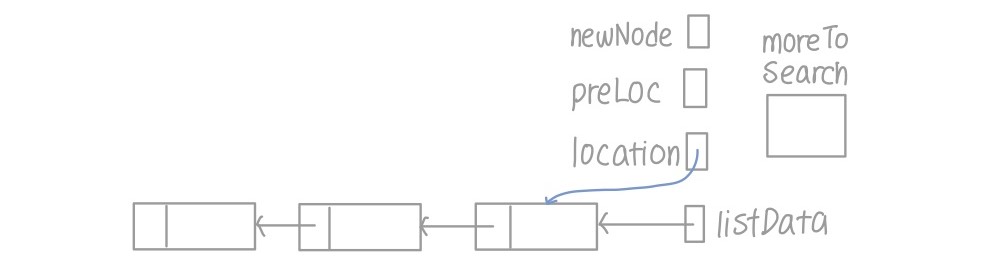
- 새로 넣을 노드를 나타내는 newNode에 노드 하나 동적 할당

- 노드 정보 넣어 주기

- 아이템 넣을 위치 찾기
- 아이템이 location의 데이터보다 작은 경우
- preLoc을 location으로 하나 이동
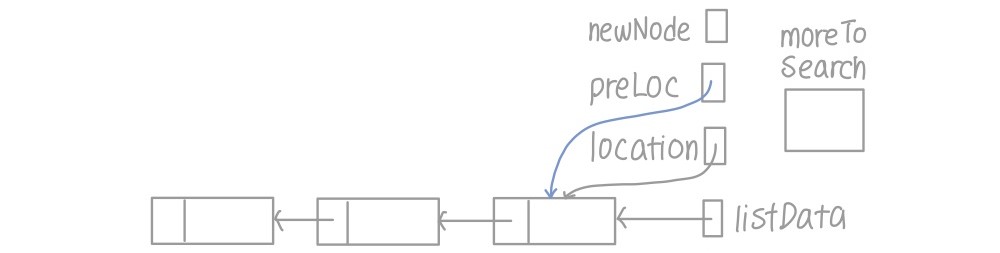
- location을 location의 next가 나타내는 노드로 하나 이동
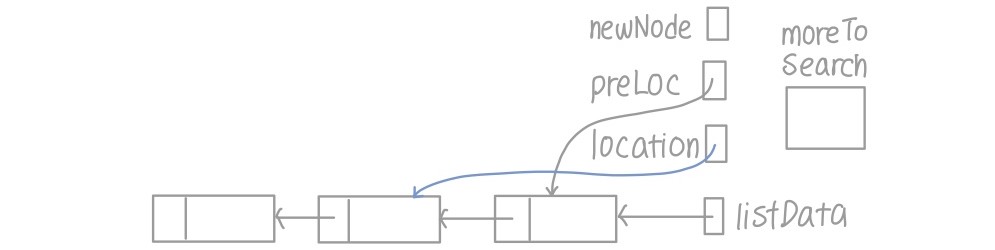
- moreToSearch가 location이 NULL인지 검사 (맨 끝에 들어가는 경우를 대비해)
- 아이템이 location의 데이터보다 큰 경우
- 아이템 넣을 위치를 찾았을 때
- 아이템이 첫 순서에 들어가는 경우
- 새 노드의 next가 현재까지의 리스트를 가리키게 함
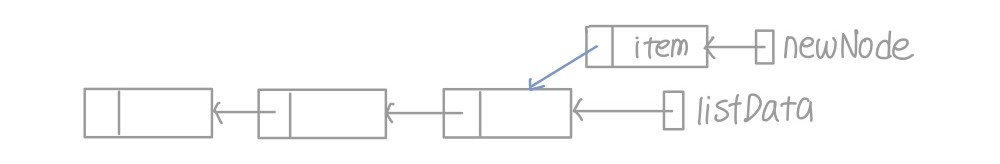
- 리스트의 끝인 listData를 새로운 노드인 newNode로 바꿔 줌
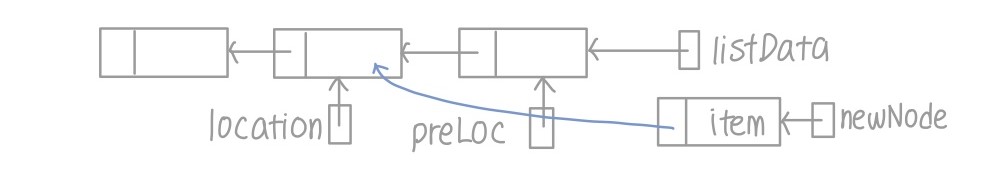
- 아이템이 중간 위치에 들어가는 경우
- location과 preLoc 사이에 newNode가 존재해야 함
- newNode의 다음 아이템을 location으로 지정

- preLoc의 다음 아이템을 newNode로 지정
Delete Item
- 리스트를 순회하면서 삭제할 아이템을 찾는 location 생성한 뒤 리스트의 맨 끝부터 시작

- 삭제할 아이템을 찾으면 그 아이템을 가리킬 tempLocation pointer 설정

- 만약 아이템이 처음에 있을 때

- tempLocation이 삭제할 아이템인 location이 가리키는 노드를 가리키도록 설정

- 리스트의 끝인 listData는 곧 삭제될 아이템의 .next인 다음 노드를 가리키도록 설정
- 만약 아이템이 중간에 있을 때
- 순회하는 포인터인 location이 나타내는 노드의 다음 노드가 삭제할 아이템일 때까지 순회

- 아이템을 찾았다면 삭제할 노드를 나타내는 tempLocation이 location의 다음 노드를 가리키도록 설정

- listData 노드의 next가 삭제할 노드의 다음인 tempLocation이 나타내는 노드의 다음을 가리키도록 설정

- 아이템을 모두 찾은 뒤 tempLocation 동적 할당 메모리 해제

Sorted Linked List with C++
- SortedLinkedList.cpp
#include <cstddef>
#include <new>
#include "ItemType.h"
#define MAX_ITEMS 100
template<class ItemType>
class SortedType {
public:
SortedType();
~SortedType();
void MakeEmpty();
void InsertItem(ItemType item);
void DeleteItem(ItemType item);
bool IsFull();
int LengthIs();
void RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found);
void ResetList();
void GetNextItem(ItemType& item);
private:
int length;
NodeType<ItemType>* listData;
NodeType<ItemType>* currentPos;
};
template<class ItemType>
struct NodeType {
ItemType info;
ItemType* next;
};
template<class ItemType>
SortedType<ItemType>::SortedType() {
length = 0;
listData = NULL;
}
template<class ItemType>
SortedType<ItemType>::~SortedType() {
MakeEmpty();
}
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::MakeEmpty() {
NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr;
while (listData != NULL) {
tempPtr = listData;
listData = listData->next;
delete tempPtr;
}
length = 0;
}
template<class ItemType>
bool SortedType<ItemType>::IsFull() {
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
try {
location = new NodeType<ItemType>;
delete location;
return false;
}
catch (std::bad_alloc exception) {
return true;
}
}
template<class ItemType>
int SortedType<ItemType>::LengthIs() {
return length;
}
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::InsertItem(ItemType item) {
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
NodeType<ItemType>* preLoc;
NodeType<ItemType>* newNode;
location = listData;
preLoc = NULL;
bool moreToSearch = (location != NULL);
while (mroeToSearch) {
if (location->info < item) {
preLoc = location;
location = location->next;
moreToSearch = (location != NULL);
}
else
moreToSearch = false;
}
newNode = new NodeType<ItemType>;
newNode->info = item;
if (preLoc == NULL) {
newNode->next = location;
listData = newNode;
}
else {
newNode->next = location;
preLoc->next = newNode;
}
length++;
}
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::DeleteItem(ItemType item) {
NodeType<ItemType>* location;
NodeType<ItemType>* tempLocation;
location = listData;
if (location->info == item) {
tempLocaton = location;
listData = location->nextl
}
else {
while ((location->next)->infp != item)
locaiton = location->next;
tempLocation = location->next;
location->next = (location->next)->next;
}
delete tempLocation;
length--;
}
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::ResetList() {
currentPos = NULL;
}
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::GetNextItem(ItemType& item) {
if (currentPos == NULL) {
currentPos = listData;
}
else {
currentPos = currentPos->next;
}
item = currentPos->info;
}
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found) {
NodeType<ItemType>* location = listData;
bool moreToSearch = (location != NULL);
found = false;
while (moreToSearch && !found) {
if (location->info == item) {
found = true;
item = location->info;
}
else {
location = location->next;
moreToSearch = (location != NULL);
}
}
}
- Big O Comparison
| Operation | Array Implementaion | Linked-list Implementation |
|---|
| Constructor | O(1) | O(1) |
| MakeEmpty | O(1) | O(N) |
| InsertItem | O(1) | O(1) |
| DeleteItem | O(N) | O(N) |
| IsFull | O(1) | O(1) |
| LengthIs | O(1) | O(1) |
| RetrieveItem | O(N) | O(N) |
| ResetList | O(1) | O(1) |
| GetNextItem | O(1) | O(1) |
| Destructor | O(1) | O(N) |
Sorted Linked List with JAVA
public class Node {
int data;
Node next;
public Node(int data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class SortedLinkedList {
Node head;
public SortedLinkedList() {
head = null;
}
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data);
if (head == null || data < head.data) {
newNode.next = head;
head = newNode;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null && current.next.data < data) {
current = current.next;
}
newNode.next = current.next;
current.next = newNode;
}
public void delete(int data) {
if (head == null) {
return;
}
if (head.data == data) {
head = head.next;
return;
}
Node current = head;
while (current.next != null && current.next.data != data) {
current = current.next;
}
if (current.next != null) {
current.next = current.next.next;
}
}
public void printList() {
Node current = head;
while (current != null) {
System.out.print(current.data + " ");
current = current.next;
}
}
}
Sorted Linked List with Python
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SortedLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def insert(self, data):
new_node = Node(data)
if self.head is None or data < self.head.data:
new_node.next = self.head
self.head = new_node
return
current = self.head
while current.next is not None and current.next.data < data:
current = current.next
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
def delete(self, data):
if self.head is None:
return
if self.head.data == data:
self.head = self.head.next
return
current = self.head
while current.next is not None and current.next.data != data:
current = current.next
if current.next is not None:
current.next = current.next.next
def print_list(self):
current = self.head
while current is not None:
print(current.data, end=' ')
current = current.next
Array VS Linked List
Memory Comparision
- Array-based Implimentation
- item 하나가 80bytes라고 가정하면 100개의 item으로 이루어진 배열은 8000bytes
- Reserved cell 80 bytes
- front와 rear Pointer은 각각 2bytes씩 차지해서 총 4bytes
- 8084 bytes
- Linked-list Implimentation
- Node의 info는 80bytes next Pointer는 4bytes
- Node 하나 당 84bytes
- Array는 항상 일정한 수의 메모리 사용
- Linked-list는 item의 수가 많아질수록 많은 메모리 사용
- 하나의 item이 차지하는 메모리 크기가 클수록 Linked-list가 유리