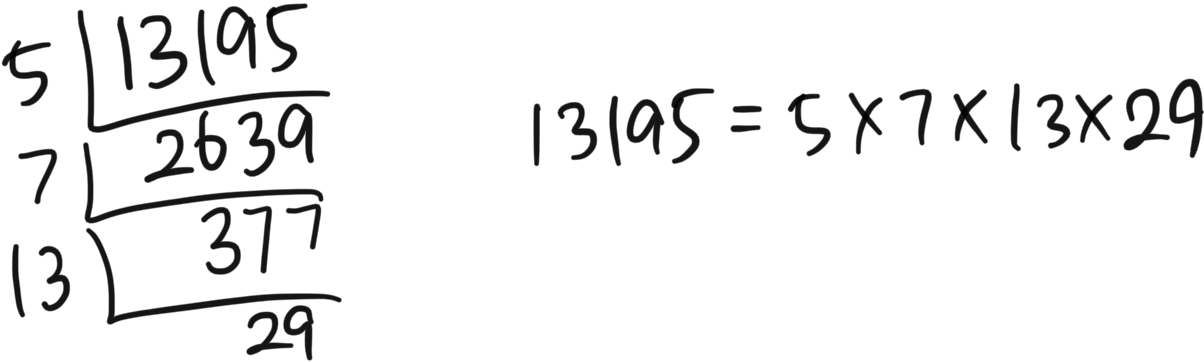Programming Lang.
문제 20.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = "Programming";
String str2 = "Programming";
String str3 = new String("Programming");
System.out.println(str1==str2);
System.out.println(str1==str3);
System.out.println(str1.equals(str3));
System.out.println(str2.equals(str3));
}
}✏️
true
false
true
true
문제 21.
class SuperObject {
public void draw() {
System.out.println("A");
draw();
}
public void paint() {
System.out.print('B');
draw();
}
}
class SubObject extends SuperObject {
public void paint() {
super.paint();
System.out.print('C');
draw();
}
public void draw() {
System.out.print('D');
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperObject a = new SubObject();
a.paint();
a.draw();
}
}✏️ BDCDD
문제 22.
class Connection {
private static Connection _inst = null;
private int count = 0;
public static Connection get() {
if(_inst == null) {
_inst = new Connection();
return _inst;
}
return _inst;
}
public void count() { count++; }
public int getCount() { return count; }
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection conn1 = Connection.get();
conn1.count();
Connection conn2 = Connection.get();
conn2.count();
Connection conn3 = Connection.get();
conn3.count();
conn1.count();
System.out.print(conn1.getCount());
}
}✏️ 4
count = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1
문제 23.
class P {
public int calc(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
return calc(n - 1) + calc(n - 2);
}
}
class C extends P {
public int calc(int n) {
if (n <= 1) return n;
return calc(n - 1) + calc(n - 3);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
P obj = new C();
System.out.print(obj.calc(7));
}
}✏️ 2
calc(7-1) + calc(7-3)
= calc(6-1) + calc(6-3) + calc(4-1) + calc(4-3)
= calc(5-1) + calc(5-3) + calc(3-1) + calc(3-3) + calc(3-1) + calc(3-3) + calc(1)
= calc(4-1) + calc(4-3) + calc(2-1) + calc(2-3) + calc(2-1) + calc(2-3) + calc(0) + calc(2-1) + calc(2-3) + calc(0) + 1
= calc(3-1) + calc(3-3) + calc(1) + calc(1) + calc(-1) + calc(1) + calc(-1) + 0 + calc(1) + calc(-1) + 0 + 1
= calc(2-1) + calc(2-3) + calc(0) + 1 + 1 + -1 + 1 + -1 + 0 + 1 + -1 + 0 + 1
= calc(1) + calc(-1) + 0 + 2
= 2
문제 24.
class firstArea {
int x, y;
public firstArea(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void print() {
System.out.println(x+y);
}
}
class secondArea extends firstArea {
int bb = 3;
public secondArea(int i) {
super(i, i+1);
}
public void print() {
System.out.println(bb*bb);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
firstArea st = new secondArea(10);
st.print();
}
}✏️ 9
super(10, 11)→ x = 10, y= 11
bb*bb= 3 * 3
문제 25.
a, b를 입력 시
x, y = input("x, y의 값을 공백으로 구분하여 입력 : ").split(' ')
print("x의 값 :", x)
print("y의 값 :", y)✏️
x, y의 값을 공백으로 구분하여 입력 : a b
x의 값 : a
y의 값 : b
문제 26.
a = "engineer information programming"
b = a[:3]
c = a[4:6]
d = a[29:]
e = b + c + d
print(e)✏️ engneing
b = eng
c = ne
d = ing
문제 27.
str = 'Sinagong'
n = len(str)
st = list()
for k in range(n):
st.append(str[k])
for k in range(n-1, -1, -1):
print(st[k], end = '')✏️ gnoganiS
n = 8
st = ['S', 'i', 'n', 'a', 'g', 'o', 'n', 'g']
range(start, stop[, step])
문제 28.
a = [[1, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 1, 0]]
tot, totsu = 0, 0
for i in a:
for j in i:
tot += j
totsu = totsu + len(i)
print(totsu, tot)✏️ 9 5
i = [1, 1, 0, 1, 0]: tot = 1 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 1 = 3, totsu = 0 + 5 = 5
i = [1, 0, 1, 0]: tot = 3 + 1 + 0 + 1 + 0 = 5, totsu = 5 + 4 = 9
문제 29.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int ary[][] = new int[3][5];
int n = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
ary[i][j] = j * 3 + i + 1;
System.out.print(ary[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}✏️
1 4 7 10 13
2 5 8 11 14
3 6 9 12 15
ary[0][0]=0 * 3 + 0 + 1 = 1
ary[0][1]=1 * 3 + 0 + 1 = 4
ary[0][2]=2 * 3 + 0 + 1 = 7
ary[0][3]=3 * 3 + 0 + 1 = 10
ary[0][4]=4 * 3 + 0 + 1 = 13
ary[1][0]=0 * 3 + 1 + 1 = 2
ary[1][1]=1 * 3 + 1 + 1 = 5
ary[1][2]=2 * 3 + 1 + 1 = 8
ary[1][3]=3 * 3 + 1 + 1 = 11
ary[1][4]=4 * 3 + 1 + 1 = 14
ary[2][0]=0 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 3
ary[2][1]=1 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 6
ary[2][2]=2 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 10
ary[2][3]=3 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 12
ary[2][4]=4 * 3 + 2 + 1 = 15
문제 30.
입력한 값이 5일 경우,
#include <stdio.h>
int func(int a) {
if (a <= 1) return 1;
return a * func(a - 1);
}
int main() {
int a;
scanf("%d", &a);
printf("%d", func(a));
}✏️ 120
5 * func(4)= ...5 * 4 * 3 * 2 * 1
문제 31.
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 10
int isWhat[MAX_SIZE];
int point = -1;
int isEmpty() {
if (point == -1) return 1;
return 0;
}
int isFull() {
if (point == 10) return 1;
return 0;
}
void into(int num) {
if (isFull() == 1) printf("Full");
else isWhat[++point] = num;
}
int take() {
if (isEmpty() == 1) printf("Empty");
else return isWhat[point--];
return 0;
}
void main() {
into(5); into(2);
while (!isEmpty()) {
printf("%d", take());
into(4); into(1); printf("%d", take());
into(3); printf("%d", take()); printf("%d", take());
into(6); printf("%d", take()); printf("%d", take());
}
}✏️ 213465
into(5):isFull() == 0→else isWhat[0] = 5into(2):isFull() == 0→else isWhat[1] = 2printf("%d", take());:isEmpty() == 0→else return→take()=isWhat[point--], ∴isWhat[1]= 2 출력, (point = 0)into(4):isFull() == 0→else isWhat[1] = 4into(1):isFull() == 0→else isWhat[2] = 1printf("%d", take());:isEmpty() == 0→else return→take()=isWhat[point--], ∴isWhat[2]= 1 출력, (point = 1)into(3):isFull() == 0→else isWhat[2] = 3printf("%d", take());:isEmpty() == 0→else return→take()=isWhat[point--], ∴isWhat[2]= 3 출력, (point = 1)printf("%d", take());:isEmpty() == 0→else return→take()=isWhat[point--], ∴isWhat[1], 4 출력, (point = 0)into(6):isFull() == 0→else isWhat[1] = 6printf("%d", take());:isEmpty() == 0→else return→take()=isWhat[point--], ∴isWhat[1], 6 출력, (point = 0)printf("%d", take());:isEmpty() == 0→else return→take()=isWhat[point--], ∴isWhat[0], 5 출력, (point = -1)
문제 32.
#include <stdio.h>
int isPrime(int number) {
for (int i = 2; i < number; i++)
if (number % i == 0) return 0;
return 1;
}
int main() {
int number = 13195;
int max_div = 0;
for (int i = 2; i < number; i++)
if (isPrime(i) == 1 && number % i == 0) max_div = i;
printf("%d", max_div);
}✏️ 29
isPrime(i) == 1는 i가 소수임을 의미.
number % i == 0i가 number의 약수라는 것을 의미.
∴ 소수이자 number의 약수인 수를 구하면 됨.
가장 큰 소스인 29가 최종적으로 max_div에 저장됨.
문제 33.
class Car implements Runnable {
int a;
public void run() {
try {
while(++a < 100) {
System.out.println("miles traveled : " + a);
Thread.sleep(100);
}
} catch(Exception E) { }
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String args[]) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(new Car());
t1.start();
}
}✏️
miles traveled : 1
miles traveled : 2
miles traveled : 3
miles traveled : 4
...
참고,
시나공