Programming Lang.
문제 34.
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
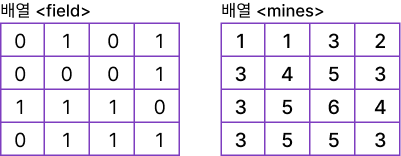
int field[4][4] = {{0,1,0,1},{0,0,0,1},{1,1,1,0},{0,1,1,1}};
int mines[4][4] = {{0,0,0,0},{0,0,0,0},{0,0,0,0},{0,0,0,0}};
int w = 4, h = 4;
for(int y=0; y<h; y++) {
for(int x=0; x<w; x++) {
if(field[y][x] == 0) continue;
for(int j=y-1; j<=y+1; j++) {
for(int i=x-1; i<=x+1; i++) {
if(chkover(w,h,j,i) == 1) {
mines[j][i] += 1;
}
}
}
}
}
}
int chkover(int w, int h, int j, int i) {
if (i >= 0 && i < w && j >= 0 && j < h) return 1;
return 0;
}✏️
문제 35.
class IntClass{
int a;
int b;
int c;
}
public class Problem {
public static void main(String[] args){
IntClass myVar = new IntClass();
myVar.a = 10;
myVar.b = 20;
prnt(myVar);
System.out.printf("a=%d, b=%d, c=%d\n", myVar. a, myVar.b, myVar.c);
}
static void prnt(IntClass myVar)
{
myVar.a += 30;
myVar.b -= 30;
if (myVar.a <= myVar.b)
myVar.c = myVar.a + myVar.b;
else
myVar.c = myVar.a - myVar.b;
}
}✏️ a=40, b=-10, c=50
myVar.a = 10 + 30 = 40
myVar.b = 20 - 30 = -10
myVar.c = myVar.a - myVar.b = 40 - (-10) = 50
문제 36.
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int numAry[] = { 0,0,0,0,3 };
int i, j;
for (j = 4; j >= 0; --j)
for (i = 4; i > j; --i)
numAry[j] += numAry[i];
for (j = 0; j < 5; ++j)
printf("%d ", numAry[j]);
}✏️ 24 12 6 3 3
j = 4,i = 4...: xj = 3,i = 4: numAry[3] = 0 + numAry[4] = 3∴ numAry[3] = 3j = 2,
i = 4: numAry[2] = 0 + numAry[4] = 3,∴ numAry[2] = 3i = 3: numAry[2] = 3 + numAry[3] = 3 + 3,∴ numAry[2] = 6j = 1,
i = 4: numAry[1] = 0 + numAry[4] = 3,∴ numAry[1] = 3i = 3: numAry[1] = 3 + numAry[3] = 3 + 3,∴ numAry[1] = 6i = 2: numAry[1] = 6 + numAry[2] = 6 + 6,∴ numAry[1] = 12j = 0,
i = 4: numAry[0] = 0 + numAry[4] = 3,∴ numAry[0] = 3i = 3: numAry[0] = 3 + numAry[3] = 3 + 3,∴ numAry[0] = 6i = 2: numAry[0] = 6 + numAry[2] = 6 + 6,∴ numAry[0] = 12i = 1: numAry[0] = 12 + numAry[1] = 12 + 12,∴ numAry[0] = 24
문제 37.
#include <stdio.h>
void prnt(int *a, int *b, int *c);
void main() {
int a = 0, b = 5, c = 0;
prnt(&a, &b, &c);
printf("a=%d, b=%d, c=%d\n", a, b, c);
}
void prnt(x, y, z)
int *x, *y, *z;
{
while (*x < *y) {
++*x;
*z = *z + *x;
prnt(x, y, z);
}
}✏️ a=5, b=5, c=15
- x=0, y=5, z=0
while (*x < *y):
*x = 0 : *z = 0 + 1 = 1
*x = 1 : *z = 1 + 2 = 3
*x = 2 : *z = 3 + 3 = 6
*x = 3 : *z = 6 + 4 = 10
*x = 4 : *z = 10 + 5 = 15- x=5, y=5, z=15
문제 38.
5을 입력했을 시 출력값을 구하시오.
a, b = 1, 1
y = a + b
n = int(input())
for k in range(3, n + 1):
c = a + b
y = y + c
a = b
b = c
print(y)✏️ 12
- y = 1 + 1 = 2, n = 5
for k in range(3, 6):
c = 1 + 1 = 2, y = 2 + 2 = 4, a = 1, b = 2
c = 1 + 2 = 3, y = 4 + 3 = 7, a = 2, b = 3
c = 2 + 3 = 5, y = 7 + 5 = 7, a = 3, b = 5
문제 39.
import java.lang.Math;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int p = 2;
int n = 3;
while (true) {
double t = Math.sqrt(n);
int m = (int)t;
for (int i = 2; i <= m; i++) {
int r = n % i;
if (r == 0)
break;
if (i == m)
p = n;
}
n++;
if (n > 100)
break;
}
System.out.printf("%d\n", p);
}
}✏️ 97
double t = 1.732051,int m = 1→ n = 4double t = 2,int m = 2
→r = 4 % 2 = 0따라서, break문으로 인해 for문을 벗어남 → n = 5double t = 2.23606...,int m = 2
→i = 2,r = 5 % 2 = 1,if (r == 0)는 만족을 못해 다음 if문으로 이동.if (i == m)는 만족함으로p = 5→ n = 6
...- n = 97일 때,
double t = 9.84885...,int m = 9
→i = ...9,r = 97 % 9 = 7,if (r == 0)는 만족을 못해 다음 if문으로 이동.if (i == m)는 만족함으로p = 97→ n = 98
...
- n = 100일 때,
double t = 10,int m = 10
→i = 2, `r = 100 % 2 = 50, break문으로 인해 for문을 벗어남 → n = 101Math.sqrt(double a) :
sqrt는 Square Root를 의미하며 제곱근을 뜻한다. double형의 값의 제곱근을 반환한다.
Math.sqrt(double a) == a의 제곱근
- 인자로 a를 전달하면 a의 제곱근이 리턴
- 인자로 0을 전달하면 0이 리턴
- 인자로 음수나 NaN(Not a Number)를 전달하면 NaN이 리턴
double a = 16; double b = 121; double c = 10; System.out.println(Math.sqrt(a)); //출력 4.0 System.out.println(Math.sqrt(b)); //출력 11.0 System.out.println(Math.sqrt(c)); //출력 3.1622776601683795
Math.pow(double a, double n):pow는 power를 의미하며 거듭제곱을 뜻한다. 전달된 두개의 double형 인자를 갖고 제곱연산을 수행한다.
Math.pow(double a, double n) == a의 n승(=aⁿ, a를 n번 곱한 값을 리턴)double result = Math.pow(2, 4); System.out.println(result); //출력 16.0 double result1 = Math.pow(2.5, 3); System.out.println(result1); //출력 15.625 int resultInt = (int) Math.pow(2.5, 3); System.out.println(resultInt); //출력 15
문제 40.
class SuperObject {
public void paint() {
draw();
}
public void draw() {
draw();
System.out.println("Super Object");
}
}
class SubObject extends SuperObject {
public void paint() {
super.draw();
}
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Sub Object");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SuperObject a = new SubObject();
a.paint();
}
}✏️
Sub Object
Super Object
문제 41.
입력값 : 34 86 21 45 77 93 64 11 50 37
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int num[10];
int min = 9999;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
if (**min > num[i]**) {
min = num[i];
}
}
printf("가장 작은 값은 %d이다.", min);
}✏️ 가장 작은 값은 11이다.
문제 42.
#include <stdio.h>
#define s 6
void bubble_sort(int list[]) {
int j, k, p, tmp;
for (j = 1; j < s; j++) {
for (k = 0; k < s - j; k++) {
if (list[k] > list[k + 1]) {
tmp = list[k];
list[k] = list[k + 1];
list[k + 1] = tmp;
}
for (p = 0; p < s; p++)
printf("%d", list[p]);
printf("\n");
}
}
}
void main()
{
int list[s] = { 9, 4, 3, 6, 8, 1 };
int i;
// for (i = 0; i < s; i++)
// printf("%d", list[i]);
// printf("\n");
bubble_sort(list);
}✏️
/tmp/PbcobZuByC.o
493681
439681
436981
436891
436819
346819
346819
346819
346189
346189
346189
341689
341689
314689
134689
문제 43.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] a = new int[3][4];
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for(int j = 3; j >= 0; j--) {
a[i][j] = i + j;
System.out.printf("%d ", a[i][j]);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}✏️
3 2 1 0
4 3 2 1
5 4 3 2
문제 44.
입력값 : 10 11 12 13 14 15
#include <stdio.h>
void main() {
int i, a[5], cnt = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if (**a[i] % 2 != 0**)
cnt = cnt + 1;
}
printf("홀수의 개수 : %d개", cnt);
}✏️ 홀수의 개수 : 2개
문제 45.
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int E[ ] = { 95, 75, 85, 100, 50 };
int i = 0;
int Temp = 0;
do
{
int j = i;
do
{
if( E[i] > E[j] )
{
Temp = E[i];
E[i] = E[j];
E[j] = Temp;
}
j++;
} while (j < 5);
i++;
} while (i < 4);
for (int a = 0; a < 5; a++ )
{
System.out.printf(E[a]+"\t");
}
}
}✏️ 50 75 85 95 100
문제 46.
public class Problem {
static int Stack[] = new int[5];
static int Top = -1;
public static void main(String[] args){
push(100);
push(110);
push(120);
pop();
push(130);
push(140);
pop();
}
static void push(int i) {
Top++;
if (Top >= 5)
System.out.printf("overflow");
else
Stack[Top] = i;
}
static void pop() {
if (Top < 0)
System.out.printf("underflow");
else
System.out.printf("%d\n", Stack[Top--]);
}
}✏️
120
140