1. Tree
자료구조 Tree는 나무의 형태를 띈 계층적 자료구조다.
하나의 데이터 아래 여러 개의 데이터가 존재하는 비선형 구조다.
아래로만 뻗어나가기 때문에 사이클이 존재하지 않는다.
1. 트리의 구조
트리는 Root라는 하나의 꼭짓점 데이터를 시작으로 여러 개의 데이터를 간선으로 연결한다.
각 데이터를 노드라 하며, 간선으로 연결되면 부모/자식 관계가 된다.
자식이 없는 노드는 Leaf Node(리프 노드) 가 된다.
2. 트리의 구현
트리는 javascript의 class로 구현 할 수 있다.
class Tree {
// 트리의 생성자(구조)
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.children = [];
}
// 트리의 삽입 메서드
insertNode(value) {
const childNode = new Tree(value); // 자식도 결국 서브트리의 node기 때문에 tree로 선언해줌.
this.children.push(childNode);
}
// 트리 안에 해당 값이 포함되어 있는지 확인하는 메서드
contains(value) {
if (this.value === value) {
return true;
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.children.length; i += 1) {
if (this.children[i].contains(value)) { // 재귀를 이용해 탐색을 진행함.
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}3. 이진 트리
이진 트리는 자식 노드가 최대 두 개인 노드로 구성된 트리다.
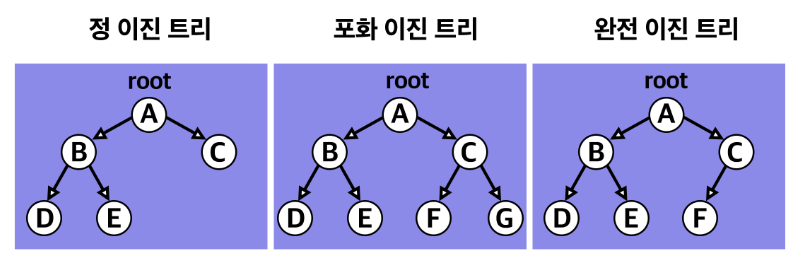
이진 트리는 자료의 삽입 삭제 방법에 따라 위 3개로 나뉘어진다.
4. 이진 탐색 트리
이진 탐색을 적용한 이진 트리다.
이진 탐색?
- 이진 탐색 알고리즘은 정렬된 데이터 중에서 특정한 값을 찾기 위한 탐색 알고리즘중 하나다.
- 배열을 오름차순으로 정렬 후 중간값부터 시작하여 찾고자 하는 값의 탐색 범위를 제한하는 알고리즘이다.
이진 트리의 특징은 트리 안에 찾고자 하는 값이 없더라도 최대 트리의 높이만큼 탐색이 진행된다.
5. 트리 순회
- 전위 순회 : 루트에서 시작해 왼쪽의 노드를 전부 탐색한다. 이후 오른쪽으로 넘어간다.
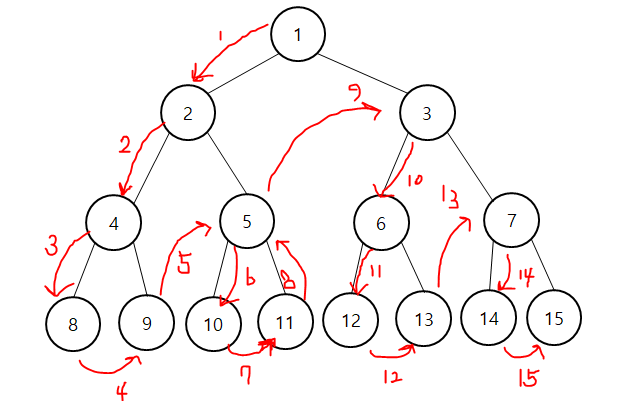
Root -> Left -> Right
- 중위 순회 : 왼쪽에서 시작해 부모를 거쳐 오른쪽으로 넘어간다.
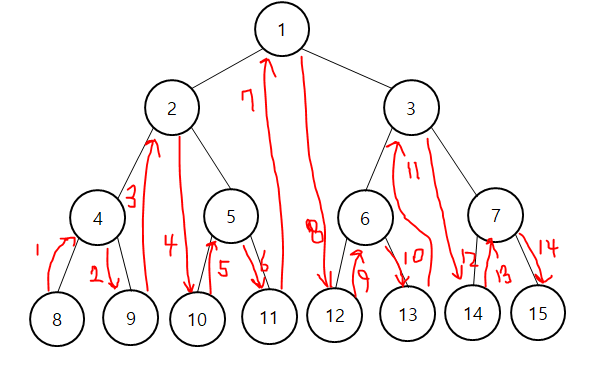
Left -> Root -> Right
- 후위 순회 : 왼쪽 자식 노드에서 시작해 오른쪽 노드를 거쳐 부모 노드로 넘어간다.
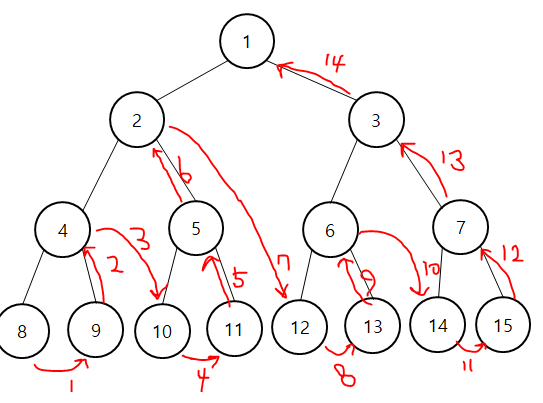
Left -> Right -> Root
6. 이진 탐색 트리 구현
class BinarySearchTree {
constructor(value) {
this.value = value;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
insert(value) {
if (value < this.value) {
if (this.left === null) {
this.left = new BinarySearchTree(value);
}
else {
this.left.insert(value);
}
}
else if (value > this.value) {
if (this.right === null) {
this.right = new BinarySearchTree(value);
}
else {
this.right.insert(value);
}
} else {
}
}
contains(value) {
if (value === this.value) {
return true;
}
if (value < this.value) {
return !!(this.left && this.left.contains(value));
}
if (value > this.value) {
return !!(this.right && this.right.contains(value));
}
}
preorder(callback) {
callback(this.value);
if (this.left) {
this.left.preorder(callback);
}
if (this.right) {
this.right.preorder(callback);
}
}
inorder(callback) {
if (this.left) {
this.left.inorder(callback);
}
callback(this.value);
if (this.right) {
this.right.inorder(callback);
}
}
postorder(callback) {
if (this.left) {
this.left.postorder(callback);
}
if (this.right) {
this.right.postorder(callback);
}
callback(this.value);
}
}