Kaniko를 이용한 Image Build & Push Pipeline 구축에서 이어서 진행한다
https://velog.io/@lijahong/0%EB%B6%80%ED%84%B0-%EC%8B%9C%EC%9E%91%ED%95%98%EB%8A%94-TEKTON-%EA%B3%B5%EB%B6%80-CICD-Pipeline-%EA%B5%AC%EC%B6%95-Kaniko%EB%A5%BC-%EC%9D%B4%EC%9A%A9%ED%95%9C-Image-Build-Push
1. Manifest File
Cluster에 배포할 때, 우리는 Kubectl 명령어 Script와 Github Private Repo에 넣어둔 매니페스트 파일을 이용해 배포할 것이다
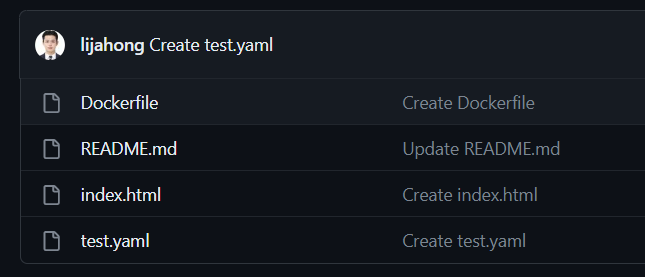
- Github Private Repo에 매니페스트 파일을 Push 하자
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: tektontestpod
namespace: hongspace
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hong
template:
metadata:
name: hongpod
labels:
app: hong
spec:
containers:
- name: hongcontainer
image: lijahong/tektontest:1.0
ports:
- containerPort: 80
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: svc-lb-hong
namespace: hongspace
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: hong
- 매니페스트 파일 내용은 위와 같다
- Build한 Image를 이용한 Deployment와 LoadBalancer Type Service를 배포할 것 이다
2. Service Account RBAC
ClusterRole
RBAC 설정 이유
Kubernetes-actions Task 실행 시 ServiceAccount를 지정하지 않으면, 자동으로 default Namespace의 default ServiceAccount를 가지고 명령을 실행한다
우리는 별도의 ServiceAccount로 명령을 실행하고 싶으므로, 해당 SA에 권한을 부여해야 한다
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
namespace: '*'
name: role-for-tektondeploy
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["*"]
- Cluster에 대한 모든 작업이 가능하도록 ClusterRole을 생성하자
만약 특정 Namespace에 대한 작업만 허용하고자 하면, ClusterRole이 아닌 Role을 생성하면 된다
ClusterRoleBinding
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: rolebind-for-deploy
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: build-bot
namespace: hongspace
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: role-for-tektondeploy
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
- 이전에 생성한 ServiceAccount인 build-bot과 위에서 생성한 ClusterRole을 Binding 하자
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: build-bot
namespace: hongspace
secrets:
- name: docker-credential
- name: github-secret
- ServiceAccount에는 GitHub 인증을 위한 Secret과 DockerHub 인증을 위한 Secret을 할당해야 한다
3. ImagePullSecret
Kubectl 명령으로 Private Registry의 Image를 Pull 할 때, ImagePullSecret 정보를 보고, Container Image Registry 에 인증 요청을 한다
- ImagePullSecret 없이 Private Registry에 접근하고 싶으면, Kubernetes Node에 Credential을 추가해야 한다
ImagePullSecret은 Pod 매니페스트 파일에 직접 명시하거나, 명령 실행에 사용하는 SA에 할당하는 방법이 있다
- 우리는 Kubectl 명령은 build-bot SA로 내리지만, Pod 생성은 default SA를 사용한다
- 앞에서 생성한 DockerHub 인증 정보를 담은 Secret을 hongspace의 default SA의 imagePullSecret으로 할당해주자
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: tektontest
namespace: hongspace
spec:
replicas: 5
selector:
matchLabels:
app: hong
template:
metadata:
name: hongpod
labels:
app: hong
spec:
containers:
- name: hongcontainer
image: lijahong/tektontest:1.0
ports:
- containerPort: 80
imagePullSecrets:
- name: docker-config-secret
- 만약 매니페스트 파일에 직접 명시하고자 한다면, 위와 같이 매니페스트 파일에 imagePullSecret을 추가하면 된다
- 허나, 매번 매니페스트 파일에 명시하는 것은 불편하다. 따라서 default SA에 imagePullSecret을 할당해주자
namespace hongspace의 default ServiceAccount에 ImagePullSecret 할당하기
- 모든 Namespace에는 기본적으로 default ServiceAccount가 존재한다. 해당 Namespace에서 작업을 실행할 때, 작업 실행에 사용할 ServiceAccount를 따로 지정하지 않는다면, 해당 Namespace의 default ServiceAccount를 이용하여 작업을 실행한다
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 auth]$ k get sa -n hongspace
NAME SECRETS AGE
build-bot 2 25m
default 0 7d4h
- default ServiceAccount를 확인하자
kubectl patch serviceaccount -n hongspace default -p '{"imagePullSecrets": [{"name": "docker-config-secret"}]}'
- 위에서 생성한 Docker 인증 정보가 담긴 Secret을 default SA에게 할당하자
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 auth]$ k describe sa -n hongspace default
Name: default
Namespace: hongspace
Labels: <none>
Annotations: <none>
Image pull secrets: docker-credential
Mountable secrets: <none>
Tokens: <none>
Events: <none>
4. Pipeline 구축
Task
Kubernetes-actions Task는 Kubectl이 동작할 수 있는 이미지를 통해 Kubectl 명령어를 사용할 수 있게 해준다
참조 : https://hub.tekton.dev/tekton/task/kubernetes-actions
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: Task
metadata:
name: kubernetes-actions
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/version: "0.2"
annotations:
tekton.dev/pipelines.minVersion: "0.17.0"
tekton.dev/categories: Kubernetes
tekton.dev/tags: CLI, kubectl
tekton.dev/displayName: "kubernetes actions"
tekton.dev/platforms: "linux/amd64"
spec:
description: >-
This task is the generic kubectl CLI task which can be used
to run all kinds of k8s commands
workspaces:
- name: manifest-dir
optional: true
- name: kubeconfig-dir
optional: true
results:
- name: output-result
description: some result can be emitted if someone wants to.
params:
- name: script
description: The Kubernetes CLI script to run
type: string
default: "kubectl $@"
- name: args
description: The Kubernetes CLI arguments to run
type: array
default:
- "help"
- name: image
default: gcr.io/cloud-builders/kubectl@sha256:8ab94be8b2b4f3d117f02d868b39540fddd225447abf4014f7ba4765cb39f753
description: Kubectl wrapper image
steps:
- name: kubectl
image: $(params.image)
script: |
#!/usr/bin/env bash
[[ "$(workspaces.manifest-dir.bound)" == "true" ]] && \
cd $(workspaces.manifest-dir.path)
[[ "$(workspaces.kubeconfig-dir.bound)" == "true" ]] && \
[[ -f $(workspaces.kubeconfig-dir.path)/kubeconfig ]] && \
export KUBECONFIG=$(workspaces.kubeconfig-dir.path)/kubeconfig
$(params.script)
args:
- "$(params.args)"
코드를 살펴보자
workspaces:
- name: manifest-dir
optional: true
- name: kubeconfig-dir
optional: true
- workspace는 위와 같다
- yaml 파일이 저장된 workspace와 Kubeconfig 파일이 저장된 workspace를 Bound 할 수 있으며, 이는 선택적이다
- Kubeconfig는 다른 Cluster에 배포하고 싶을 때, 해당 Cluster의 Kubeconfig 파일이 담긴 workspace를 Bound 하면 된다
- 우리는 Tekton이 설치된 Cluster에 배포할 것이므로, Kubeconfig를 따로 Bound 하지 않아도 된다
params:
- name: script
description: The Kubernetes CLI script to run
type: string
default: "kubectl $@"
- name: args
description: The Kubernetes CLI arguments to run
type: array
default:
- "help"
- name: image
default: gcr.io/cloud-builders/kubectl@sha256:8ab94be8b2b4f3d117f02d868b39540fddd225447abf4014f7ba4765cb39f753
description: Kubectl wrapper image
- 전달 받을 파라미터는 위와 같다
- script는 kubectl 명령어이다. 기본값은 kubectl $@ 이다. 이는 매개 변수들을 개별 문자로 취급하며, 이를 이용하여 kubectl 명령어를 실행한다는 의미이다
- 예시로 script를 지정하지 않고, args로 "get", "pod"를 넘겨 주면, kubectl get pod가 자동으로 실행된다
- 반대로 $* 은 매개 변수들을 하나의 문자열로 취급하는 것이다
- args는 kubectl 명령어에 사용될 매개 변수들의 인자 값이 담긴 배열이다. 사용자가 script를 따로 정의하지 않는다면, kubectl $@을 통해 전달 받은 매개 변수들의 인자 값을 이용하여 kubectl 명령어를 실행하는데, 이때 사용된다
- image는 kubectl 명령을 내릴 수 있는 환경이 구성된 image로 용량이 크다. 따라서 처음 실행 시, 시간이 소요될 수 있다
steps:
- name: kubectl
image: $(params.image)
script: |
#!/usr/bin/env bash
[[ "$(workspaces.manifest-dir.bound)" == "true" ]] && \
cd $(workspaces.manifest-dir.path)
[[ "$(workspaces.kubeconfig-dir.bound)" == "true" ]] && \
[[ -f $(workspaces.kubeconfig-dir.path)/kubeconfig ]] && \
export KUBECONFIG=$(workspaces.kubeconfig-dir.path)/kubeconfig
$(params.script)
args:
- "$(params.args)"
- 작업은 다음과 같다. Pipeline에게 전달 받은 args 배열에 들어있는 값들을 컨테이너에게 인자 값으로 넘겨준다
- 만약 yaml 파일이 저장된 workspace가 Bound 되어 있다면, 해당 디렉토리로 이동한다
- 만약 Kubeconfig 파일이 저장된 workspace가 Bound 되어 있고, 안에 Kubeconfig 파일이 존재한다면, 해당 Kubeconfig 파일 경로를 KUBECONFIG 환경 변수로 설정한다
- Kubectl 명령어를 실행한다
Pipeline
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: Pipeline
metadata:
name: hong-cicd
namespace: hongspace
spec:
params:
- name: repo-url
type: string
- name: image-reference
type: string
- name: kubectl-args
type: array
workspaces:
- name: shared-data
tasks:
- name: fetch-source
taskRef:
name: git-clone
workspaces:
- name: output
workspace: shared-data
params:
- name: url
value: $(params.repo-url)
- name: build-push
runAfter: ["fetch-source"]
taskRef:
name: kaniko
workspaces:
- name: source
workspace: shared-data
params:
- name: IMAGE
value: $(params.image-reference)
- name: deploy
runAfter: ["build-push"]
taskRef:
name: kubernetes-actions
workspaces:
- name: manifest-dir
workspace: shared-data
params:
- name: args
value: $(params.kubectl-args[*])
- Pipeline의 Deploy Task를 추가하고, 넘겨줄 workspace랑 params를 정의하자
- runAfter를 통해 Image Build & Push 작업이 완료된 후에 실행되도록 설정해야 한다
- git에서 clone한 yaml 파일이 저장된 workspace인 shared-data를 manifest-dir이란 이름으로 넘겨 주면 된다
- PipelineRun에서 넘겨준 배열 kubectl-args에 들어있는 값들을 모두 Task의 배열 args에게 넘겨 준다. 이 배열에 들어있는 값들을 컨테이너에게 인자 값으로 넘겨 주어 kubectl 명령어를 실행할 것이다
PipelineRun
apiVersion: tekton.dev/v1beta1
kind: PipelineRun
metadata:
namespace: hongspace
generateName: hong-cicd-run-
spec:
serviceAccountName: build-bot
pipelineRef:
name: hong-cicd
podTemplate:
securityContext:
fsGroup: 65532
workspaces:
- name: shared-data
volumeClaimTemplate:
spec:
accessModes:
- ReadWriteOnce
resources:
requests:
storage: 1Gi
params:
- name: repo-url
value: "https://github.com/lijahong/tektontest.git"
- name: image-reference
value: lijahong/tektontest:1.0
- name: kubectl-args
value:
- "apply"
- "-f"
- "test.yaml"
- PipelineRun에는 Kubectl 명령어 실행에 사용될 매개 변수들의 인자 값들만 정의해주면 된다
- GitHub Private Repo에서 Clone한 매니페스트 파일을 apply 할 것이므로, 위와 같이 "apply" "-f" "test.yaml"을 배열에 넣어주면 된다
- Task에서 $@을 통해 매개 변수 값들을 개별 문자로 취급하기에 써줘야 한다
5. 결과 확인
작업 결과 확인
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 auth]$ tkn pr list -n hongspace
NAME STARTED DURATION STATUS
hong-cicd-run-fpq6m 1 hour ago 41s Succeeded
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 auth]$ tkn pr logs -n hongspace hong-cicd-run-fpq6m
.
.
[fetch-source : clone] + '[' false '=' true ]
[fetch-source : clone] + '[' false '=' true ]
[fetch-source : clone] + '[' false '=' true ]
[fetch-source : clone] + CHECKOUT_DIR=/workspace/output/
[fetch-source : clone] + '[' true '=' true ]
[fetch-source : clone] + cleandir
[fetch-source : clone] + '[' -d /workspace/output/ ]
[fetch-source : clone] + rm -rf /workspace/output//lost+found
[fetch-source : clone] + rm -rf '/workspace/output//.[!.]*'
[fetch-source : clone] + rm -rf '/workspace/output//..?*'
[fetch-source : clone] + test -z
[fetch-source : clone] + test -z
[fetch-source : clone] + test -z
[fetch-source : clone] + /ko-app/git-init '-url=https://github.com/lijahong/tektontest.git' '-revision=' '-refspec=' '-path=/workspace/output/' '-sslVerify=true' '-submodules=true' '-depth=1' '-sparseCheckoutDirectories='
.
.
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0001] Retrieving image manifest nginx:1.21.1
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0001] Retrieving image nginx:1.21.1 from registry index.docker.io
.
.
.
/usr/share/nginx/html/index.html requires it.
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0007] COPY ./index.html /usr/share/nginx/html/index.html
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0007] Taking snapshot of files...
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0007] EXPOSE 80
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0007] cmd: EXPOSE
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0007] Adding exposed port: 80/tcp
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0007] Pushing image to lijahong/tektontest:1.0
[build-push : build-and-push] INFO[0010] Pushed image to 1 destinations
[build-push : write-url] lijahong/tektontest:1.0
[deploy : kubectl] deployment.apps/tektontestpod unchanged
- PipelineRun 실행 결과와 log를 확인하자. 잘 실행 되었다
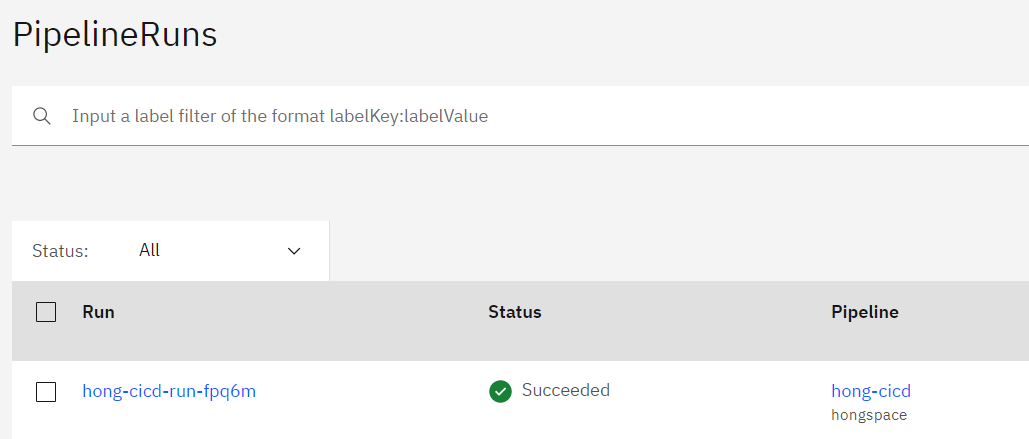
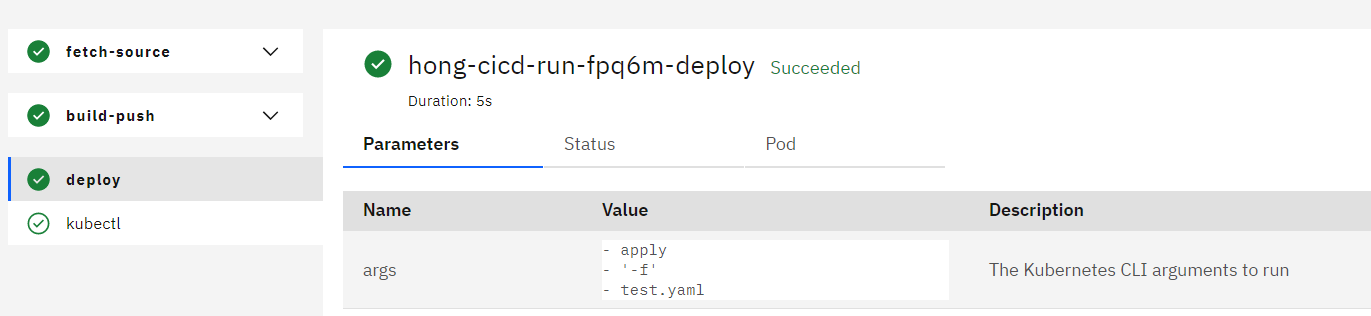
Deploy 확인
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 tektontest]$ k get deploy -n hongspace
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
tektontestpod 3/3 3 3 9s
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 tektontest]$ k get pod -n hongspace | grep tektontestpo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
tektontestpod-c5ff89b8c-7bbw8 1/1 Running 0 25s
tektontestpod-c5ff89b8c-f7s54 1/1 Running 0 25s
tektontestpod-c5ff89b8c-jcf5v 1/1 Running 0 25s
- Kubernetes Cluster에 잘 배포되었는지 확인하자. 잘 배포되었다
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 tektontest]$ k describe pod -n hongspace tektontestpod-c5ff89b8c-7bbw8
Name: tektontestpod-c5ff89b8c-7bbw8
Namespace: hongspace
Priority: 0
Service Account: default
Node: ****************************
Start Time: Thu, 27 Apr 2023 06:06:45 +0000
Labels: app=hong
pod-template-hash=c5ff89b8c
Annotations: <none>
Status: Running
IP: ************
IPs:
IP: ********************
Controlled By: ReplicaSet/tektontestpod-c5ff89b8c
Containers:
hongcontainer:
Container ID: containerd://******************************
Image: lijahong/tektontest:1.0
Image ID: docker.io/lijahong/tektontest@sha256:*************************
Port: 80/TCP
Host Port: 0/TCP
State: Running
Started: Thu, 27 Apr 2023 06:06:46 +0000
Ready: True
- Pod의 상세 정보를 확인하자. Build 한 Image를 이용해 배포되었으며, 잘 동작하는 것을 확인할 수 있다
LoadBalancer 접속
[ec2-user@ip-100-0-1-19 tektontest]$ k get svc -n hongspace
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
svc-lb-hong LoadBalancer 10.100.91.61 a*************************.ap-northeast-2.elb.amazonaws.com 80:32637/TCP 3m7s
- 우리는 LoadBalancer Type Service를 배포했으므로, 자동으로 AWS 상에 LB가 생성된다
- 주소를 확인하자
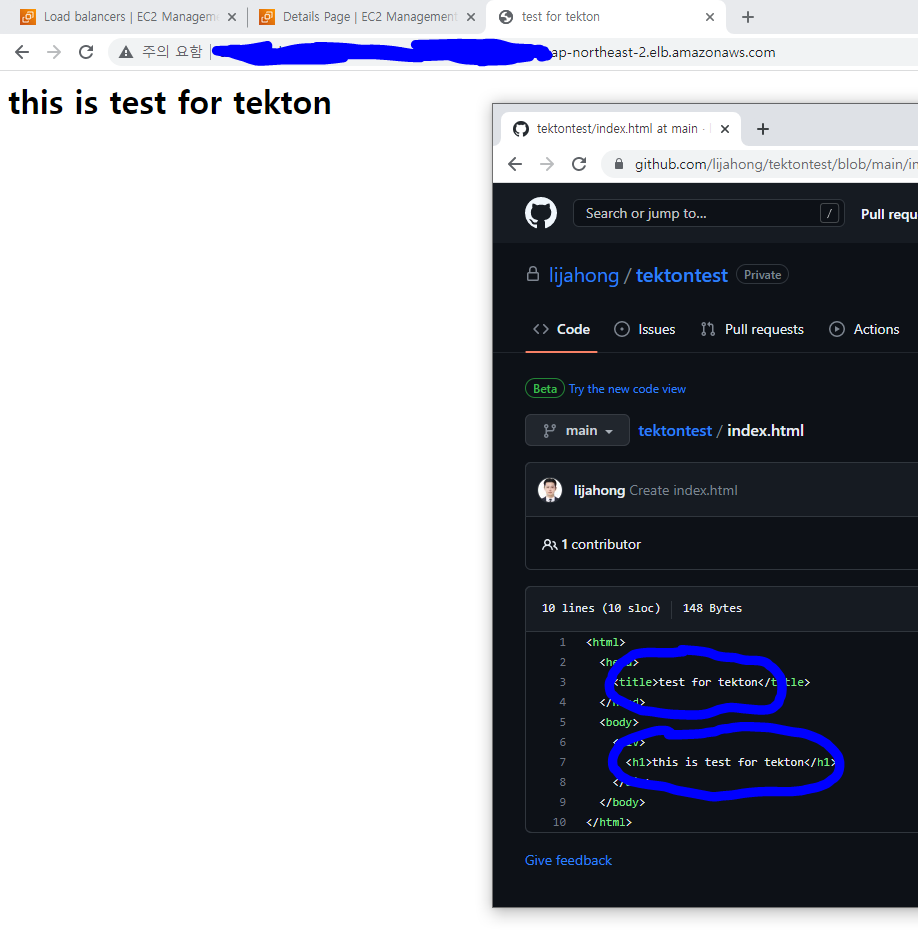
- 잘 접속된다! 설정한 내용대로 Image가 잘 Build 되었으며, 해당 Image를 이용하여 Pod가 잘 배포되었다






