오늘은 Pwnable.kr의 lotto 문제를 풀어보려한다🔥
바로 SSH로 접속하여, 바이너리를 실행했다!  ? 뭐지.. input password가 뒤늦게 출력된다.
? 뭐지.. input password가 뒤늦게 출력된다.
바로 C코드부터 살펴보자.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#define PW_LEN 10
#define XORKEY 1
// https://modoocode.com/36
void xor(char* s, int len){
int i;
for(i=0; i<len; i++){
s[i] ^= XORKEY; // s[i] = s[i] ^ 1
}
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
int fd;
if(fd=open("/home/mistake/password",O_RDONLY,0400) < 0){
printf("can't open password %d\n", fd);
return 0;
}
printf("do not bruteforce...\n");
sleep(time(0)%20);
char pw_buf[PW_LEN+1];
int len;
if(!(len=read(fd,pw_buf,PW_LEN) > 0)){
printf("read error\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}
char pw_buf2[PW_LEN+1];
printf("input password : ");
scanf("%10s", pw_buf2);
xor(pw_buf2, 10);
if(!strncmp(pw_buf, pw_buf2, PW_LEN)){
printf("Password OK\n");
system("/bin/cat flag\n");
}
else{
printf("Wrong Password\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}c코드는 위와 같이 짧다.
우선 main함수부터 살펴보자.
- main()
int main(int argc, char* argv[]){
int fd;
if(fd=open("/home/mistake/password",O_RDONLY,0400) < 0){
printf("can't open password %d\n", fd);
return 0;
}
printf("do not bruteforce...\n");
sleep(time(0)%20);
char pw_buf[PW_LEN+1];
int len;
if(!(len=read(fd,pw_buf,PW_LEN) > 0)){
printf("read error\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}
char pw_buf2[PW_LEN+1];
printf("input password : ");
scanf("%10s", pw_buf2);
xor(pw_buf2, 10);
if(!strncmp(pw_buf, pw_buf2, PW_LEN)){
printf("Password OK\n");
system("/bin/cat flag\n");
}
else{
printf("Wrong Password\n");
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}우선 /home/mistake 경로에 있는 password 파일을 읽기 전용으로 오픈한다.
if(fd=open("/home/mistake/password", O_RDONLY, 0400) < 0){ }중요한 부분은 바로 IF문의 조건이다! (문제 HINT → "operator priority")
💡 연산자 우선순위
연산자 우선순위를 보면, <(괄호)가 =(대입 연산자)보다 우선순위가 높다!
즉, open( ) < 0 부분을 먼저 수행하면 결과가 0이 되고, fd에는 0이 들어가게 된다!!!
이제 다시 fd=0이 들어간다는 것을 생각하고, main 함수의 코드를 살펴보자.
printf("do not bruteforce...\n");
sleep(time(0)%20);
char pw_buf[PW_LEN+1];
int len;
if(!(len=read(fd,pw_buf,PW_LEN) > 0)){
printf("read error\n");
close(fd);
return 0;
}그러면 이제 IF문의 조건문은 아래와 같이 바뀌게 된다.
if(!(len=read(fd=0, pw_buf, PW_LEN=10) >0)){ }즉, 아래에서 비교할 pw_buf라는 변수에 사용자의 입력값을 10bytes만큼 받는 것이다!
따라서 사용자의 입력값 1과 사용자의 입력값2가 같은지 비교하게 되는 것이다.. 다만 사용자의 입력값2는 xor 함수를 거친다.
사용자의 입력값2는 차례대로 하나씩 1과 XOR해서 나온 값이 다시 담기게 된다.
 5 ^ 1 = 4이다... 즉, 4를 10번 넣고 두 번째 입력값으로 5를 10번 넣어주면 pw_buf와 pw_buf2가 같을 것이다!
5 ^ 1 = 4이다... 즉, 4를 10번 넣고 두 번째 입력값으로 5를 10번 넣어주면 pw_buf와 pw_buf2가 같을 것이다!
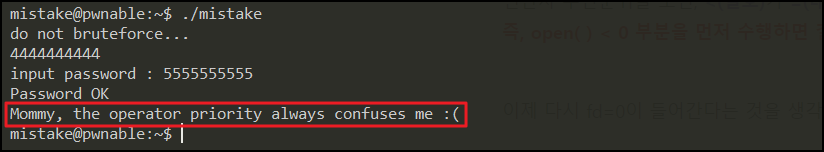 🚩 획득!
🚩 획득!
이번 문제는 풀다가 생각보다 안보여서, 다른 블로그를 슬쩍 봤다....
※ 참고
👉 연산자 우선순위 : http://www.tcpschool.com/codingmath/priority
👉 Blog.. Write up : https://dokhakdubini.tistory.com/202
