Projective Geometry and Transformations of 3D
- 에서 가 되는 것과 같이 의 특성은 의 일반화라고 할 수 있다.
- 하지만, 2개의 line이 projective plane에서는 항상 만나지만 3-space에서는 만나지 않는 것과 같이 차원확장에 의한 추가적인 특성이 나타나기도 한다.
Points in
- 3-space에서의 point 는 4-vector의 homogeneous coordinates로 표현된다. 은 points at infinity를 의미한다.
- Inhomogeneous coordinate로는 of 로 나타낼 수 있다.
Projective Transformation of Points in
- 에서의 projective transformation은 non-singular 4x4 matrix에 의한 linear transformation이다.
- 는 15 DoF로 나머지 하나는 scaling factor이다.
- 에서 mapping 된 line은 line을 유지하는 것과 마찬가지로collineation을 만족한다.
Planes in
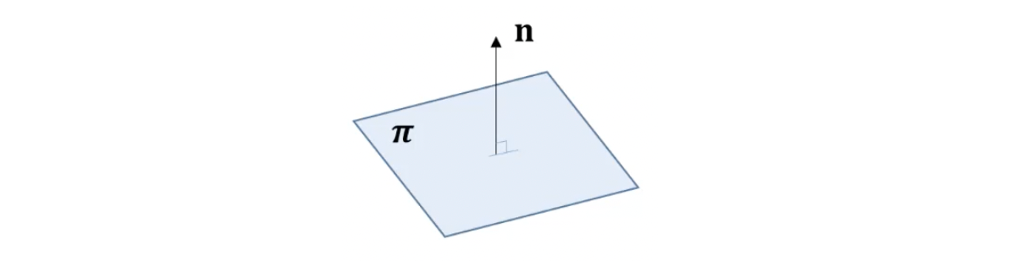
- 3-space에서의 plane은 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.
- Homogeneous coordinate에서 표현하여 라 하면 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.
or
이는 에서 line에 대한 식 과 동일하다. - Plane coefficient 세 개의 독립적인 비율 만 고려하면 되기 때문에 3 DoF이며 는 plane normal을 의미한다.
- 을 inhomogeneous로 표현하기 위해 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다. 이 식에서 은 origin으로부터 plane까지의 거리를 의미한다.
Planes in : Join and Incidence Relations
- Plane은 collinear하지 않은 세 개의 점 혹은 incident하지 않은 하나의 line과 점으로 정의할 수 있다.
- 두 개의 서로 다른 plane은 하나의 line에서 교차한다.
- 세 개의 서로 다른 plane은 하나의 point에서 교차한다.
Three Points Define a Plane
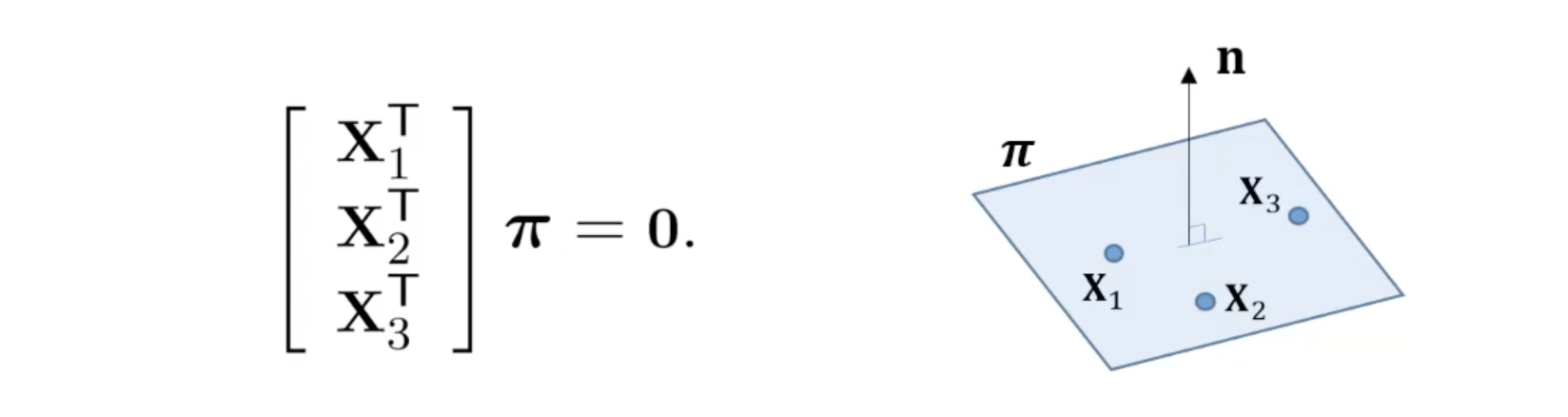
- Plane 에 incident한 세 개의 points 가 있다 가정할 때, 각 pointsms for 을 만족한다.
- Point들이 선형 독립일 때 3x4 matrix 는 rank 3을 가진다.
- Point들에 의해 정의되는 plane 는 1차원 (right) null-space로 유일하게 정의된다.
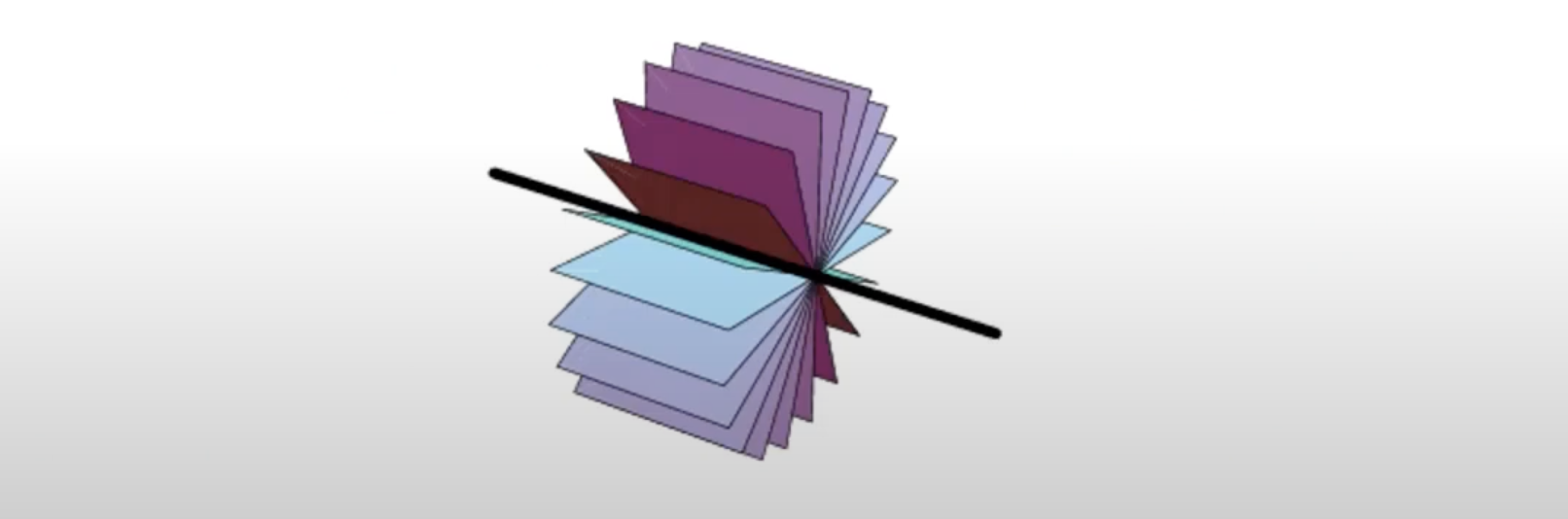
-Matrix 의 rank가 2라면 null-space가 2차원이며 이는 points가 collinear하고 그 point들의 line을 축으로 아주 많은 plane들이 만들어질 수 있음을 의미한다.
Three Planes Define a Point
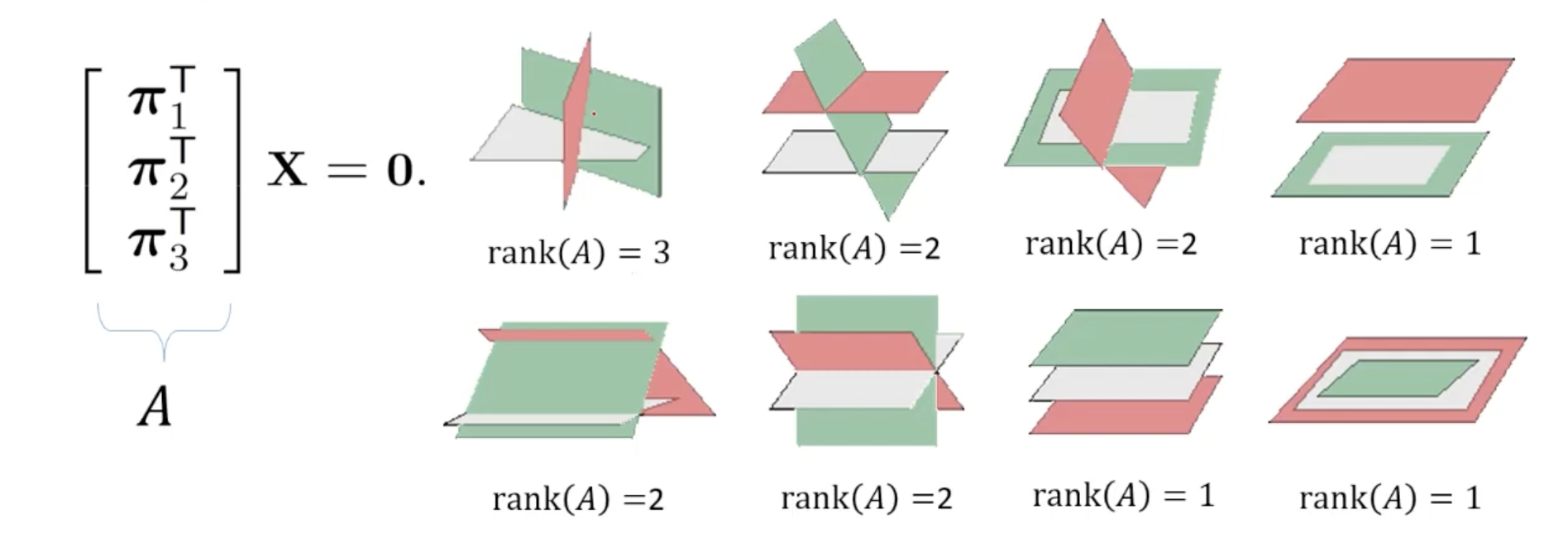
- 세 개의 plane의 교차점은 3x4 matrix의 (right) null-space로 계산된다.
Parametrized Points on a Plane
- Plane 상의 points 는 로 나타낼 수 있다. 이 4x3 matrix로 4x1의 각 column vector를 라 할 때 는 linear combination 라 할 수 있다.
- 이 때 은 plane 내의 모든 sub-space를 정의한다.
- 4x3 matrix 의 columns는 의 rank 3 null-space를 만든다.
- 이며 는 0이 아닐 때 은 유일하지 않으며 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.

Lines in
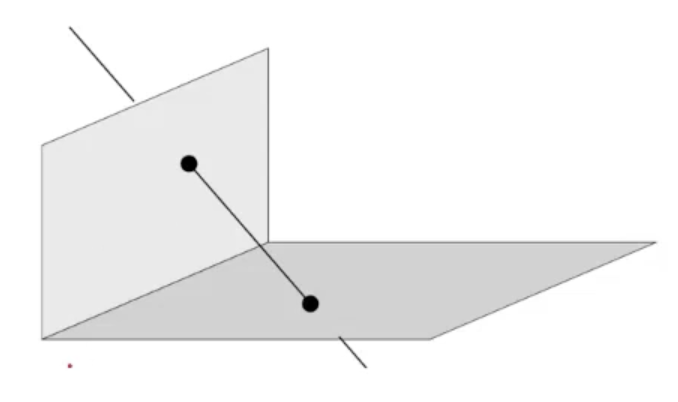
- Line은 두 points의 조합 혹은 두 planes의 교차점으로 정의된다.
- 3-space에서 line은 두 plane의 두 개의 교차점으로 나타낼 수 있으며 각 교차점은 2DoF()이므로 line은 4DoF를 가진다.
- 3-space의 line을 homogeneous 5-vector로 나타내는 것은 어색하기 때문에 2개의 대안으로 나타낸다.
Lines in : Null-Space and Span Representation
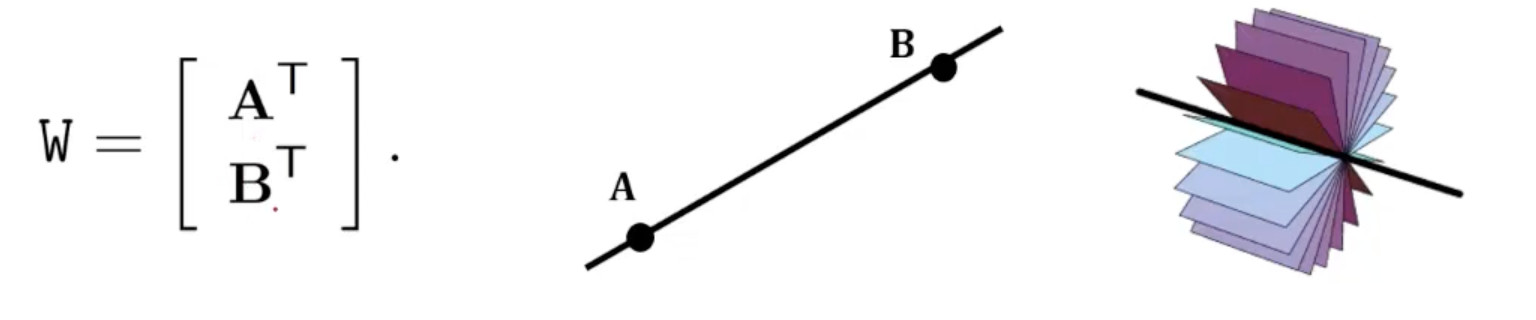
- 가 두 non-coincident space의 points라고 가정하자.
- 이 두 포인트를 연결하는 Linedms 2x4 matrix로 나타낼 수 있으며 이는 6DoF로 overparameterized 되어있다.
- 의 span은 line 상에서 수많은 point들인 가 된다.
- 의 2차원 right null space의 span은 line을 축으로 하는 수많은 plane들이 된다.
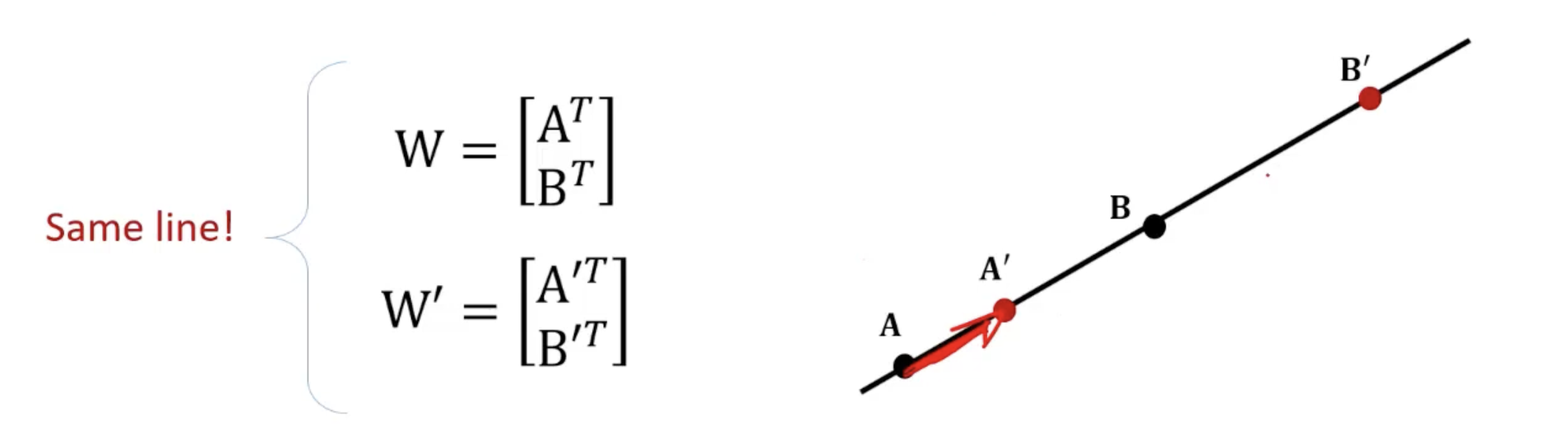
- Line 상의 다른 points 는 와 동일한 span을 가지는 matrix 를 만든다.
- 따라서, representation의 정의는 특정 point들에 독립적이다.
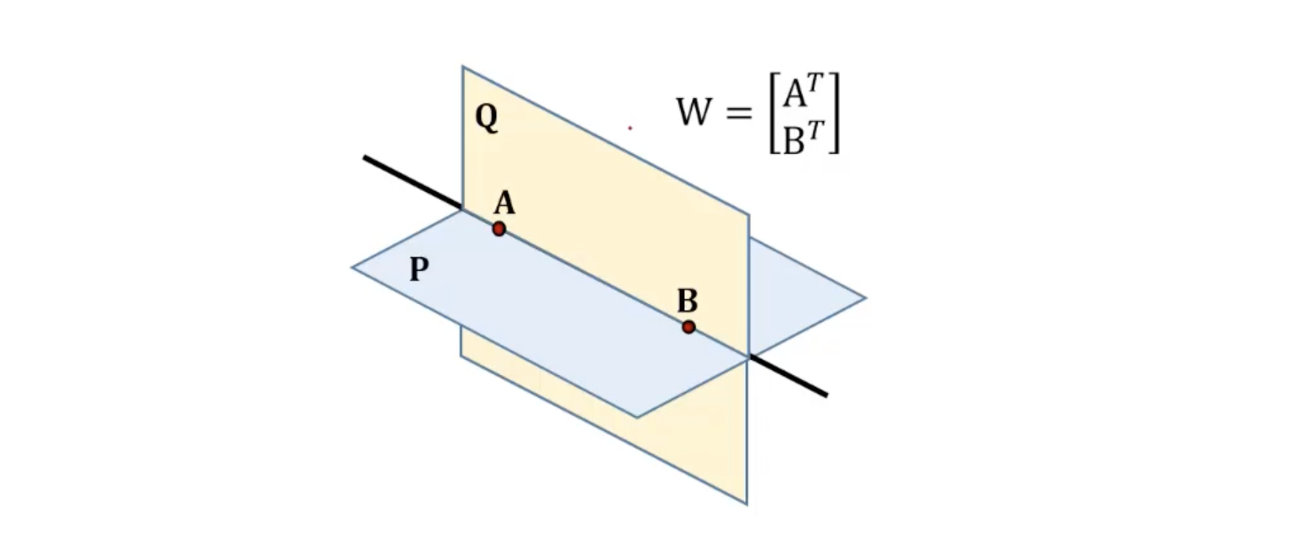
- 가 null-space의 basis라 가정할 때, 이고 그 결과 이 된다.
- 따라서, 는 를 포함하는 plane이 되며 또한 두 points를 포함하는 또 다른 plane이다.
- 가 모두 planes 상에 있기 때문에 로 정의되는 line은 plane intersection이 된다.
- Line을 축으로 삼는 수많은 plane들이 span 로 주어진다.
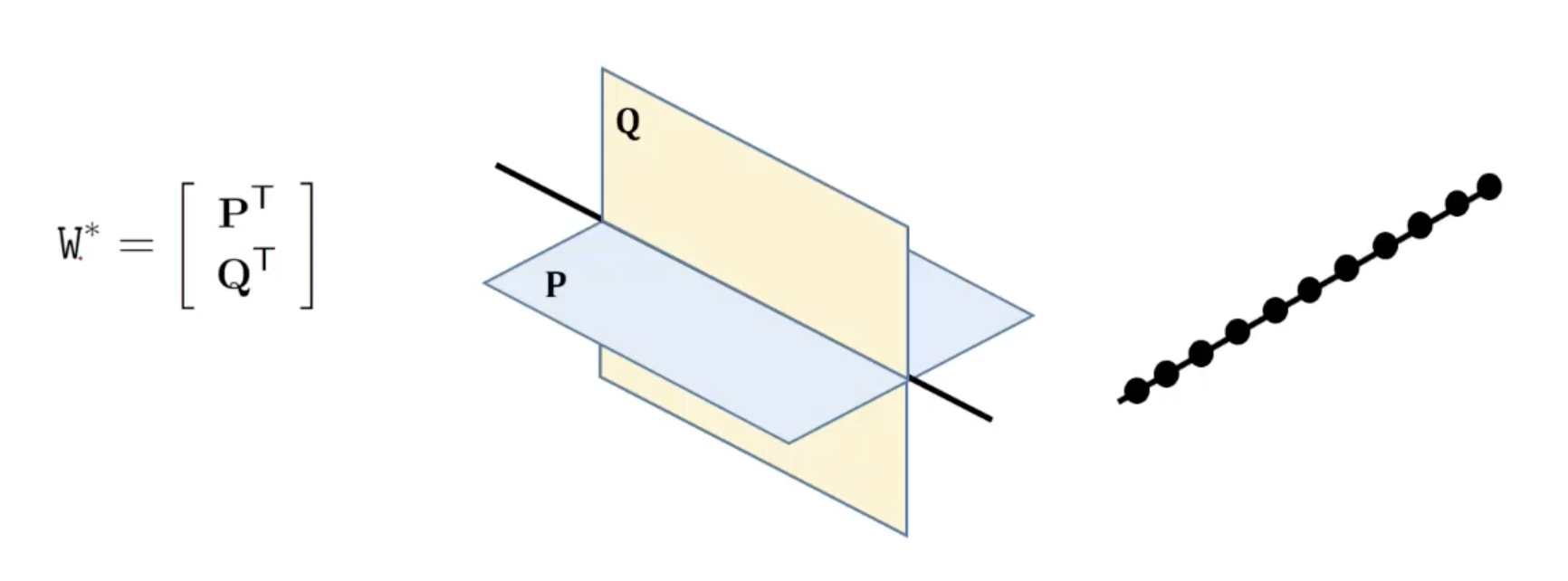
- Line의 dual representation은 두 plane 로 구성되는 2x4 matrix 의 span으로 표현된다.
- 의 span은 로 표현되는 수많은 plane들이고 의 2차원 null space는 line 상의 수많은 point들이므로 두 representation은 다음 식으로 연관시킬 수 있다.
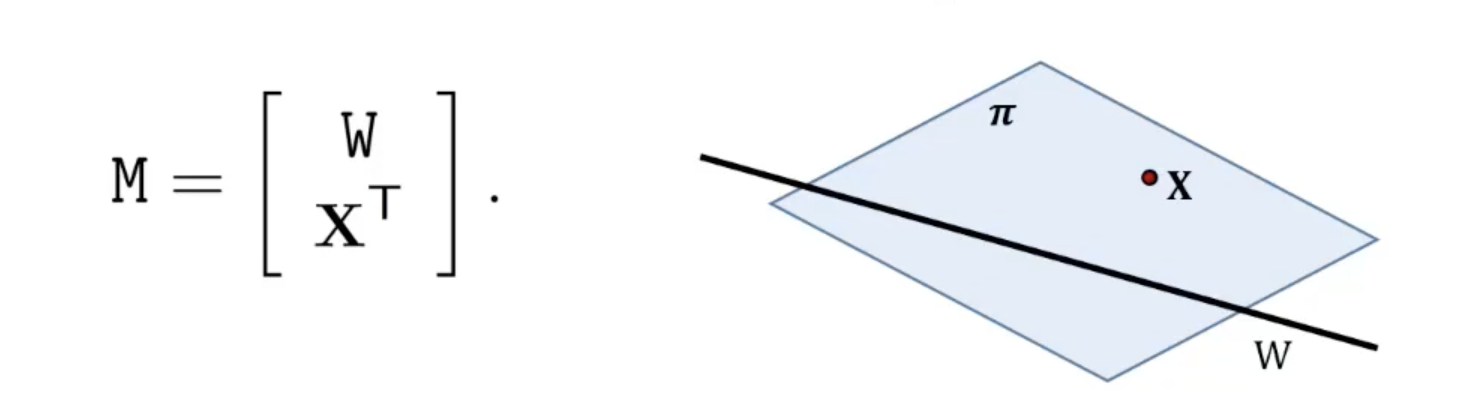
- Point 와 line 의 join으로 정의되는 plane 는 의 null space로부터 얻어진다.
- 의 null space가 2차원이라면 는 위에 있으며 그렇지 않으면 이다.
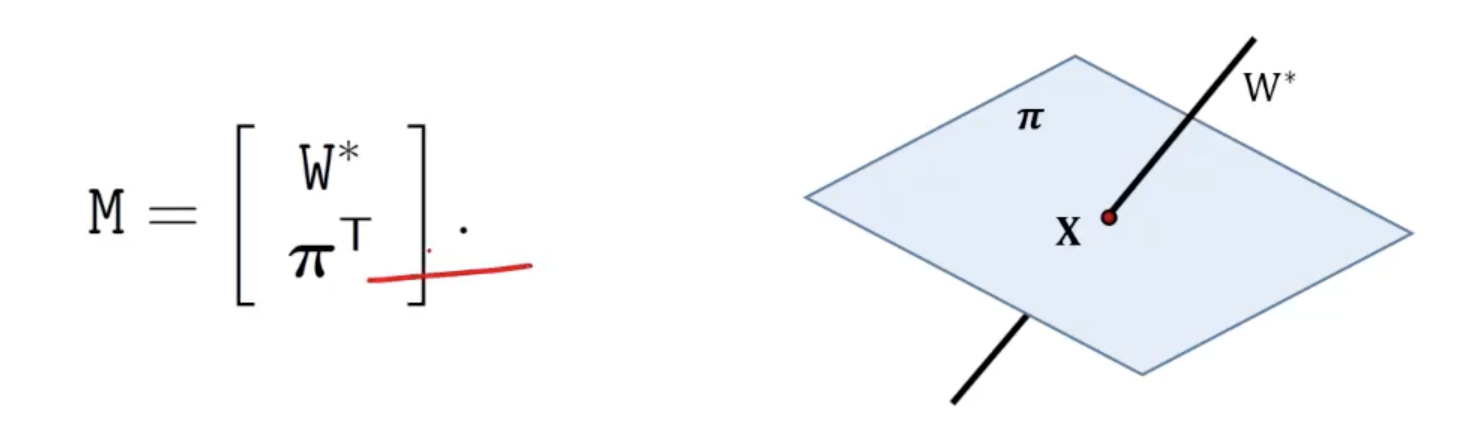
- Line 와 plane 의 교차점으로 정의되는 point 는 의 null space로부터 얻어진다.
- 의 null space가 2차원이라면 line 는 상에 있으며 그렇지 않으면 이다.
Lines in $\mathbb{P}^3: Plucker Line Coordinates
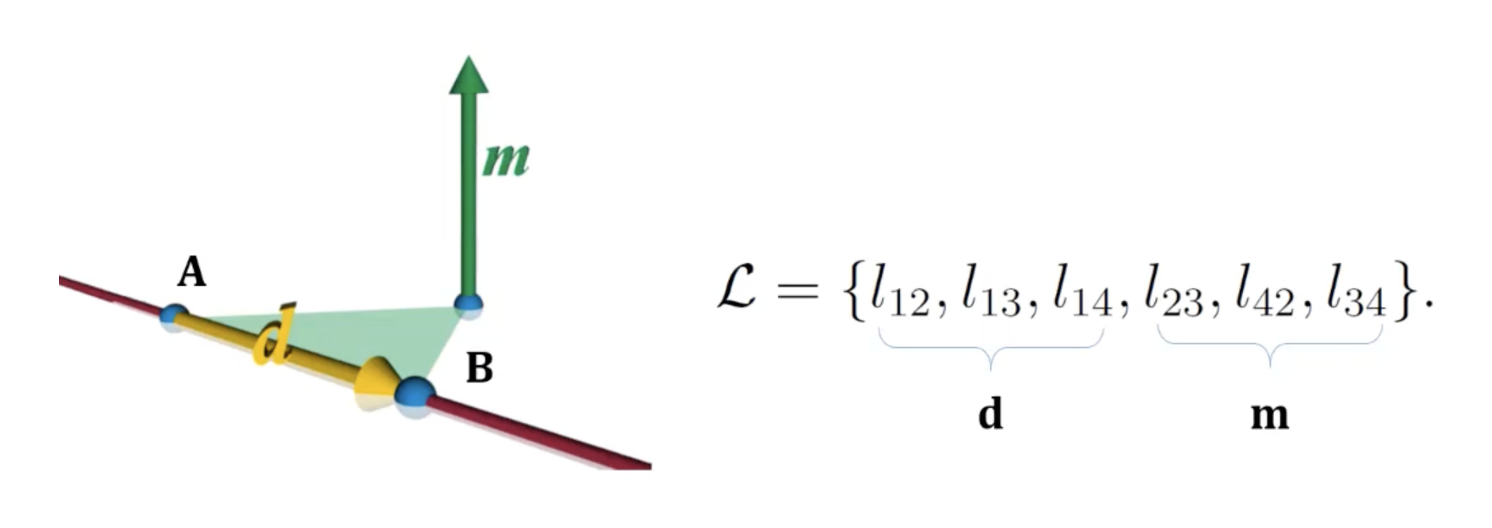
-
Plucker line coordinates는 0이 아닌 6개의 값으로 구성된 벡터로 첫 3개의 elements는 와 사이의 direction vector, 뒤 3개의 elements는 의 moment vector이다.
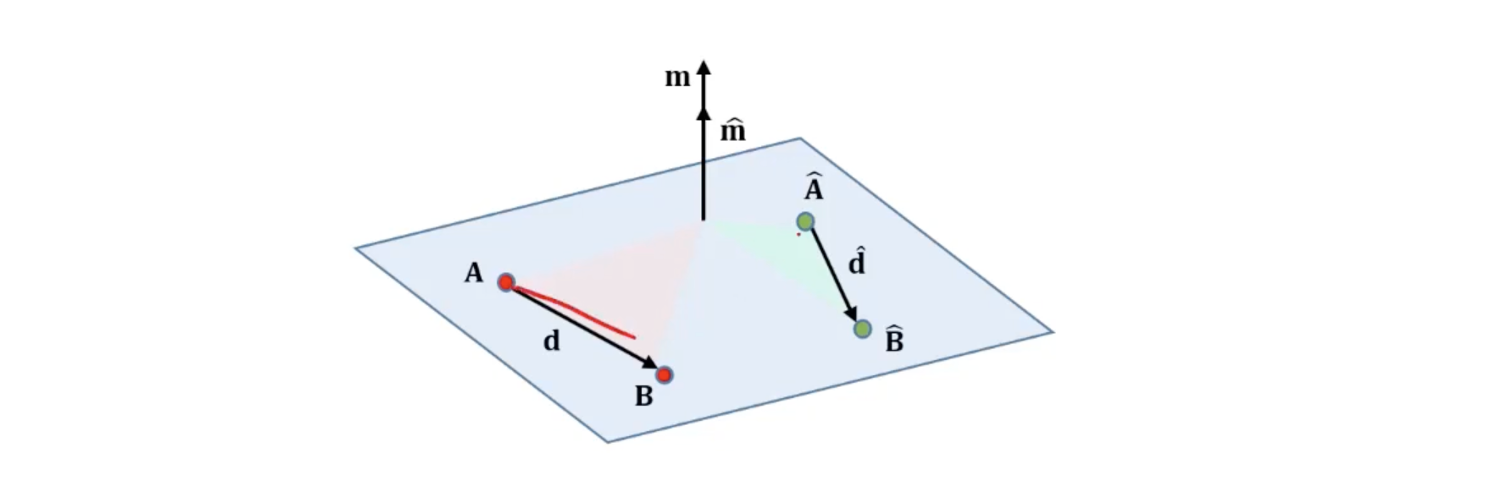
-
두 line 이 각각 points 와 의 join이라고 가정하자.
-
Lines는 4개의 points가 동일한 평면에 존재할 때만 교차하며 필요충분 조건은 다음과 같다.
(proof) 가 동일 평면에 존재할 때 의 direction vector와 의 moment vector는 수직 관계를 가진다.
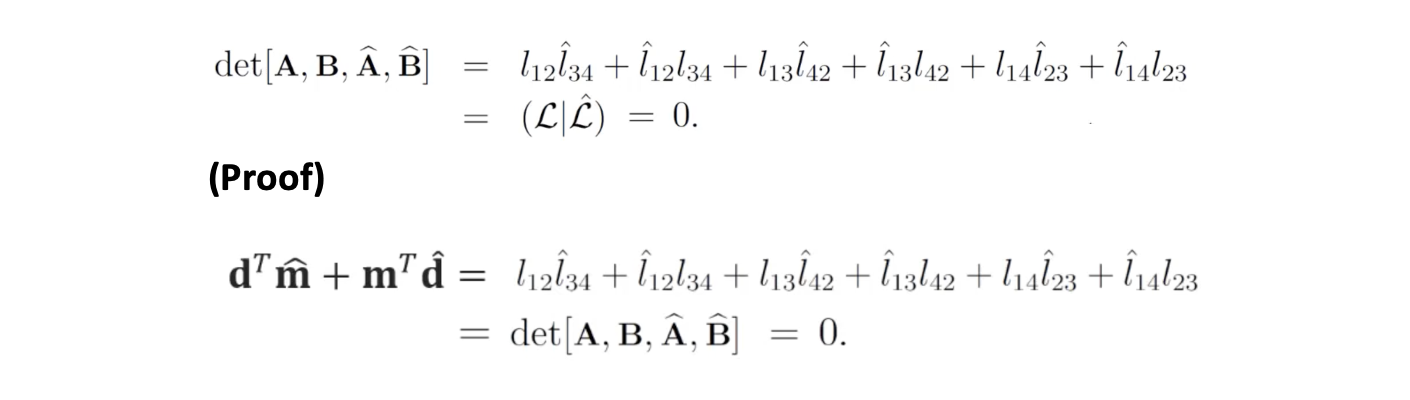
-
동일하게, 두 lines 이 각각 planes 와 의 교차선이라 할 때 lines가 교차한다면 다음 조건을 만족한다.
-
두 planes 의 교차선이 이고 이 두 points 의 join이라면 lines가 교차할때 다음을 만족한다.
Quadrics and Dual Quadrics
- Quadric은 에서 다음 식에 의해 정의되는 surface이다. 는 4x4 matrix이다.
- Quadric의 많은 특성들은 conics의 특성과 직결된다.
- Quadric은 4x4 symmetric matrix로 scale을 제외한 9DoF를 가진다.
- 9개의 point들에 의해 quadric이 정의된다.
- Matrix 가 singular라면 quadric은 더 적은 point들로 정의된다.
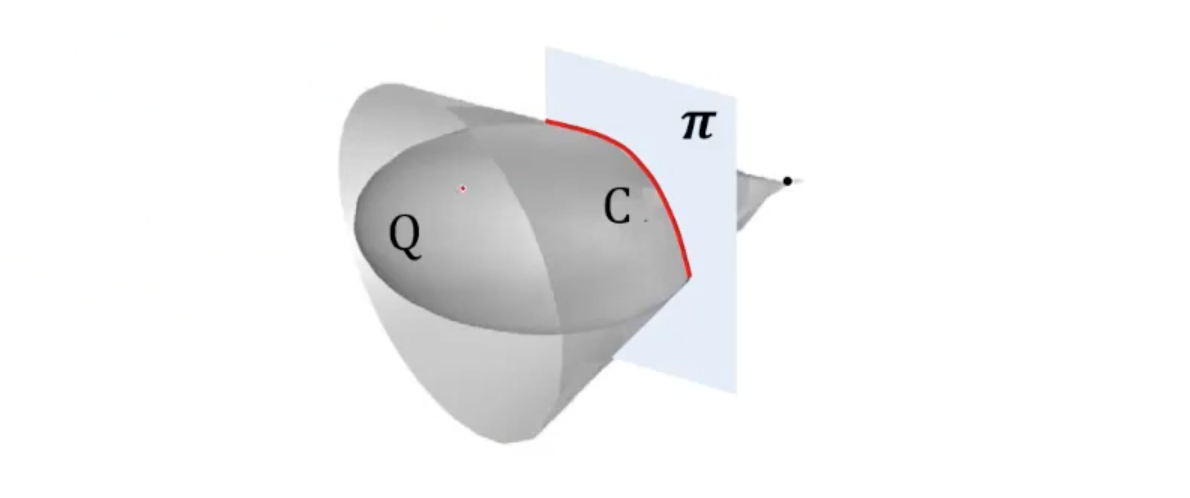
- Plane 와 quadric 의 intersection은 conic 이다.