이 내용은 'Learning JavaScript Data Structures and Algorithms'(로이아니 그로네르 저, 이일웅 역) 책의 내용을 제 생각과 함께 정리한 글입니다.
틀린 내용 혹은 수정이 필요한 내용이 있다면 말씀해주시면 감사하겠습니다.
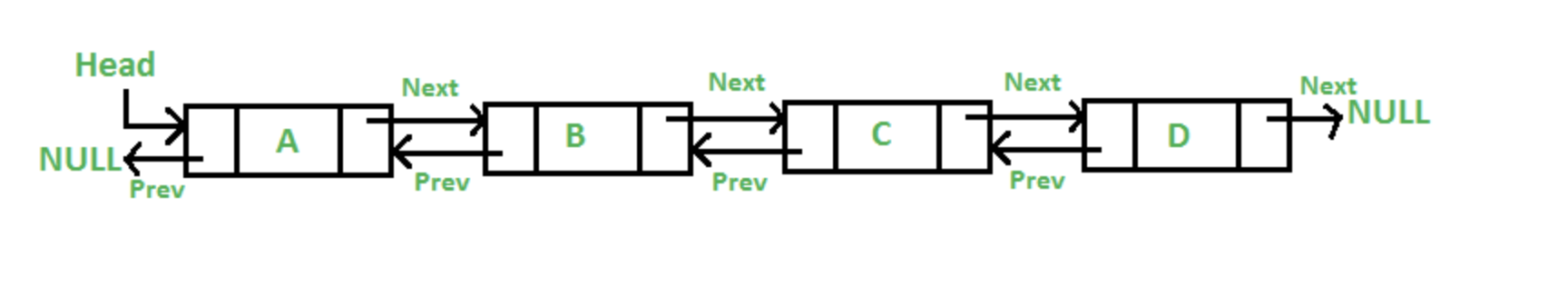
- 이중 연결 리스트(Doubly Linked List)는 다음 노드와 이전 노드, 2개의 연결정보를 이중으로 가지고 있다.
function DoublyLinkedList() {
const Node = function (element) {
this.element = element;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null; // New
};
let length = 0;
let head = null;
let tail = null; // New
// 메소드는 여기 아래에 기술
}-
이전의 Singly Linked List와의 차이점은 위 코드 주석의 New부분을 보면 알 수 있을 것이다.
-
Doubly Linked List는 처음에서 끝, 끝에서 처음, 양방향으로 리스트 순회가 가능하다.
-
Singly Linked List는 순회 시 원소를 찾지 못한다면 다시 맨 처음으로 돌아가야 했었다. 바로 이런 점에서 Doubly Linked List의 강점이 부각된다.
삽입
this.insert = function (position, element) {
// 범위 외의 값인지 체크한다.
if (position >= 0 && position <= length) {
let node = new Node(element);
let current = head;
let previous = undefined;
let index = 0;
// 처음 부분에 원소를 추가할 때
if (position === 0) {
if (!head) {
// 리스트가 비어있는 경우
head = node;
tail = node;
} else {
node.next = current;
current.prev = node; // 이전 원소에 대한 포인터 세팅만 추가됨
}
}
// 맨 끝에 원소를 추가할 때
else if (position === length) {
current = tail;
node.prev = current;
tail = node;
}
// 임의의 위치에 원소를 삽입하는 경우
else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
node.next = current;
previous.next = node;
current.prev = node;
node.prev = previous;
}
} else return false;
};원소 삭제
this.remove = function (element) {
if (position > -1 && position < length) {
let current = head; // current는 삭제할 원소를 의미한다
let previous = undefined;
let index = 0;
// 첫 번째 원소 삭제
if (position === 0) {
head = current.next;
// 원소가 하나뿐이라면 tail을 업데이트한다.
if (length === 1) tail = null;
else head.prev = null;
}
// 마지막 원소 삭제
else if (position === length - 1) {
current = tail;
tail = current.prev;
tail.next = null;
}
// 임의의 위치의 원소 삭제
else {
while (index++ < position) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
previous.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = previous;
}
} else {
return null;
}
};배열과 달리 다른 원소를 이동하지 않고도 원소를 쉽게 추가/삭제할 수 있다는 Linked List만의 강점을 살펴봤다. 따라서, 많은 원소를 추가/삭제해야 할 경우, 배열보다는 연결 리스트가 더 어울리는 자료구조라고 할 수 있다.
