OVERVIEW: 구글에서 진행한 코세라 강의가 있는 것을 보고 학생용으로 한번 강의를 들어봤는데, 꽤 들을만했던 것 같다. 다만. Interaction Design Foundation 이 조금 더 나은 강의같다는 생각이 들었다. 아무래도 Coursera는 개발 베이스라서 그런 것 같다.
WEEK 1 요약
Introduction to Course 1: Foundations of User Experience Design
The user experience is how a person, the user, feels about interacting with or experiencing a product.
A product is a good, service, or feature
A good ux must be
- usable - making something easier to use (eg.ketchup bottle)
- equitable- your designs are usable for everyone (disable or what)
- enjoyable - positive connection. (상품에 평점을 남길 수 있는 서비스 같은거)
- useful - solve problems (지도 앱 가은 경우 사용자의 위치를 추적할 수 있어야한다)
ux 디자이너가 갖춰야할 능력
Empathy- The ability to understand someone else's feelings or thoughts in a situation
Roles
- interation designers- focus on designing the experience of a product and how it functions.
- visual desingers- focus on how the product or technology looks
- motions designers- move through a product. and transition
- graphic designers
- ux designers- focus on how users interact with a product
- ux researchers- conduct studies or interviews that help us learn how people use a product
- ux writers - think about how to make the language within a product clearer help define a brand's voice and personality
- production designers-make sure first and final designs match in the finished product materials and that the assets are ready to be handed off to the engineering team
- ux engineers- translate the design's intent into a functioning experience
- ux project manager - ensure clear and timely communication, so that the process of building a useful prodeuct moves smoothly from start to finissh
- Conversation designer - google assistant , siri or response systems like customer sevice systems you can talk to. develop 'persona' or personality of the voice. as well as the flow and dialog of the interaction
Product development life cycle
The process used to take a product from an idea to reality
Stage
- Brainstorm - an active discovery stage that's all about generating ideas about the user and potential needs or challenges the user might have
- Define - using the insights from the brainstorm stage and starting to narrow the focus who what what feature
- Design- implementing insights into new design (storyboard, wireframe(outline), prototypes)
- Test - evaluating the product based on users
- Launch - sharing listing in googe stor, app store
Design for a good user experience/ Characteristics of good user experience
doors with poor ux- norman door
- Usable - design, structure and purpose of the product is clear and easy to use.
- Equitable(공정한) -
💡
idea
내가 열심히 참여하겠다는 의지를 서베이 몽키로 받는다
Roles of ux researchers
- Research - understand audiences and learn about their backgrounds demographics motivations painpoints emotions and life goals.
- Wireframe - outline and a sketch of a design
- Prototype early model.
- information architecture categories and
확인해보면 좋을 것 같은 링크들
/
https://www.nngroup.com/articles/
https://xd.adobe.com/ideas/?sdid=61PM7WSH&mv=social&mv2=ownsoc-org
WEEK 2 요약
User
any person who uses a product
End user
the specific audience a UX designer creates something for 사실적인 타깃 유저라고 생각하면 되나?
eg. 완구회사에서 유저는 부모 자식 포함/ 앤드 유저는 자식들
User experience : how a person, the user, feels about interacting with, or experiencing a product
User centered design puts the user front-and-center
Prioritize the user
iterative quality of the user-centered design process.
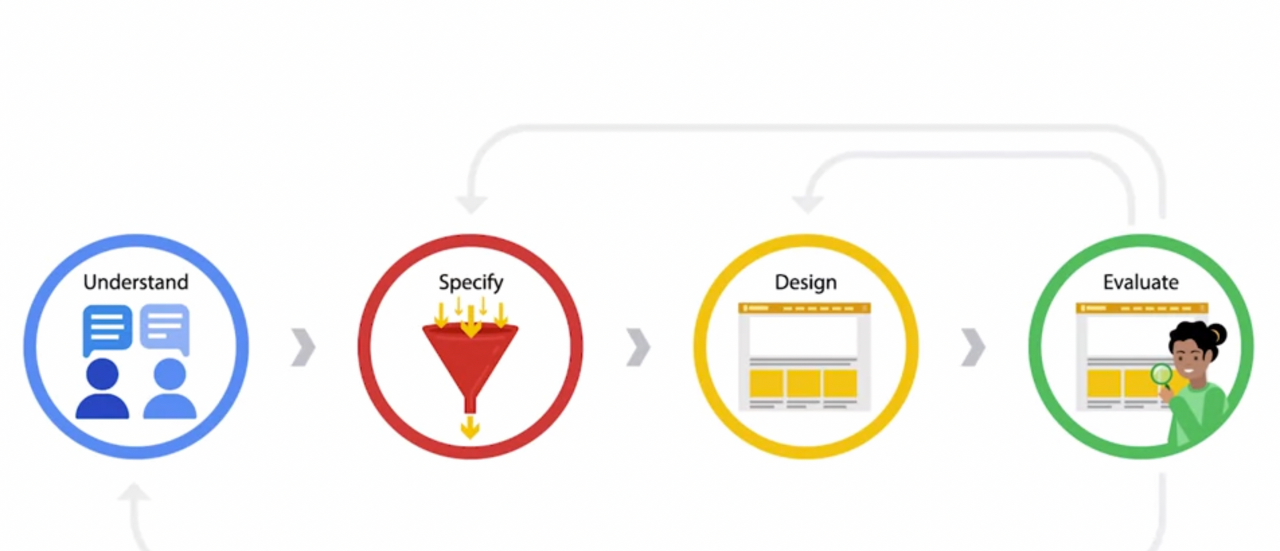
'as you go down the task iteration is key'
Iteration : doing something again, by building on previous versions and making tweaks
---
framework : creates the basic structure that focuses and supports the problem you're trying to solve
TWO TYPES OF FRAMEWORK
five elements of UX design : steps a designer takes to turn an idea into a working product
- 나머지는 다 기획, 구상이라고 보면 되고 Surface 가 실질적으로 사용자가 보게 될 화면이다

Design Thinking : a way to create solutions that address a real user problem and are functional and affordable
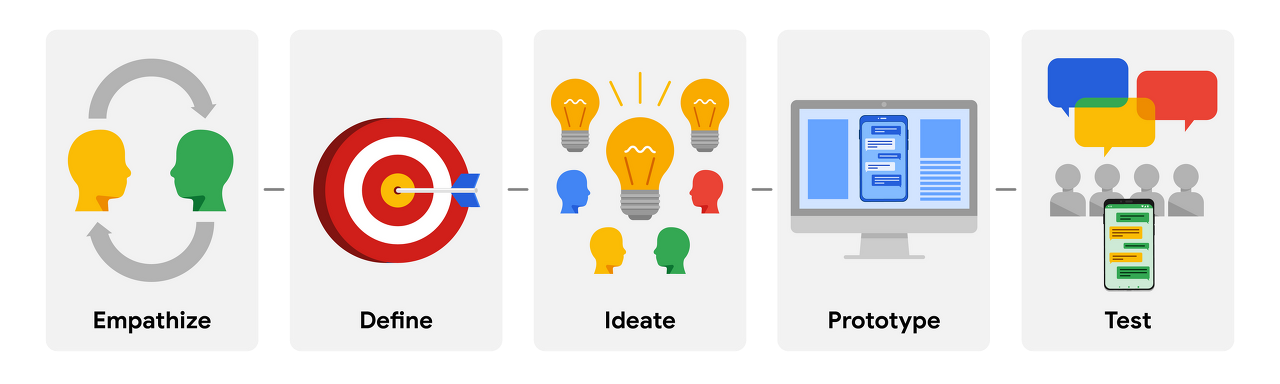
what users really feel : survey, interview to learn who the end user is
define: find the problem
prototype : scale down version
Design for Next Billion Users (NBU)
앞으로 앱을 사용할 next billion users.
Challenges
- Cost
- Connectivity
- Digital Literacy
- Literacy
Design for different platforms
Responsive web design : allows a website to change automatically depending on the size of the device
The four C's
Consistency
Continuity-노트북이랑 핸드폰은 조금 다를지라도 같은 기능을 담고 있음을 알 수 있어야한다
Context - 흐름이 좋아야함. 메일을 확인했다면 노트북에서 확인했을 때도 확인한 것으로 인식할 수 있어야한다
Complementary-
Universal design, Inclusive design and equity focused design
- Universal design- one size fits all
- Inclusive design - solve for one, extend to many (accessablity (+a11y) - 특정사람을 위한것. 또한 포함이다)
- Equity focused design - designing for groups that have been historically underrepresented or ignored when building product
- Equality : providing the same amount of opportunity and support
- Equity : providing different levels of opportunity and support for each person in order to achieve fair outcomes*social model of disability : defines a disability as being caused by the way society is organized or how porducts are designed, rather than a person's ability or difference (갑자기 깁스를 하거나, 콘서트 끝나고 잠시 귀가 위잉하는사람) 도 고려해야한다!!

*social model of disability : defines a disability as being caused by the way society is organized or how porducts are designed, rather than a person's ability or difference (갑자기 깁스를 하거나, 콘서트 끝나고 잠시 귀가 위잉하는사람) 도 고려해야한다!
WEEK 3 요약
Design Sprints
time bound process with face
solve a critical design challenge through designing, prototyping and testing ideas with users
benefits
- save time
- create a path to bring a product to market
- prioritize the user
- test product before launch
Phases of Sprints
Understand
Ideate
coming up with ideas
Decide
decide the solution
Prototype
confirm test users
Test
prototype to the test, user feedback, interviews
before bringing market
Benefits of design sprints
- It's all about the user
- Value every person in the room(from intern to experienced..)
- Best ideas rise to the top
- TIme to focus
- Lower risks
- Versatile schedule
Plan design sprints
- User research
- Call in the experts
- Find the right space
- Gather supplies
- Establish sprint rules
- Plan introductions
- Post-sprint planning
Sprint brief
a document that you share with all your attendees to help them prepare for the sprint
Design sprint retrospectives
\= a collaborative critique of the team's design sprint
The goal of a retrospective is to make sure everyone who took part in the sprint has the chance to give feedback and think about opportunities for improvement
The key questions to ask during a retrospective are:
- What went well?
- What can be improved?
Questions you might ask during this part of the retrospective include:
- What went wrong that caught you off guard?
- Which problems came up the most often?
- When do you think we experienced the biggest challenge as a team?
Then, examine the sprint’s outcome or final product, and ask questions like:
- Did the team overestimate or underestimate the work required to complete the design?
- Did an external factor derail your productivity?
- And most importantly, does the final design actually solve the user problem?
