📌 최빈값
- 데이터에서 빈도수가 가장 많은 데이터
nums = [1,3,7,6,7,7,7,12,12,17]
indexes = [0,1,0,1,0,0,1,4,0,0,0,0,2,0,0,0,0,0,1]
-> 인덱스가 4인 7이 최빈값
💻 예제코드
강의내용
-> 강사님은 자바에서 많이 쓰는 카멜케이스를 이용하셔서 class명을 제외한 나머지만 스테이크 케이스로 바꿈
class MaxAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, nums):
self.nums = nums
self.max_num = 0
self.max_num_idx = 0
def set_max_and_index(self):
self.max_num = self.nums[0]
self.max_num_idx = 0
for i, n in enumerate(self.nums):
if self.max_num < n:
self.max_num = n
self.max_num_idx = i
def get_max_num(self):
return self.max_num
def get_max_num_idx(self):
return self.max_num_idx
nums = [1, 3, 7, 6, 7, 7, 7, 12, 12, 17]
# 인덱스 배열 생성
indexes = [0 for _ in range(max(nums) + 1)] # i 안 쓰므로 _ 로 변경
for n in nums:
indexes[n] += 1
# 최빈값 알고리즘 실행
max_algo = MaxAlgorithm(indexes)
max_algo.set_max_and_index()
max_num = max_algo.get_max_num()
max_num_idx = max_algo.get_max_num_idx()
print(f'max_num: {max_num}')
print(f'max_num_idx: {max_num_idx}')
print(f'즉, {max_num_idx}의 빈도수가 {max_num}로 가장 높다')max_num: 4
max_num_idx: 7
즉, 7의 빈도수가 4로 가장 높다
수정 코드
class MaxAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, ns):
self.nums = ns
self.max_num = None # [변경] 0 → None
self.max_num_idx = None # [변경] 0 → None
# 이유: 데이터가 음수일 수도 있기 때문에
# 0보다 작으면 최댓값 계산이 잘못될 수 있음.
# None은 "아직 값 없음"을 나타내는 파이썬식 초기화.
def set_max_and_index(self):
self.max_num = self.nums[0]
self.max_num_idx = 0
for i, n in enumerate(self.nums[1:], start=1): # [변경] enumerate(self.nums)
# 이유: 첫 원소는 이미 self.max_num에 저장했으므로,
# 두 번째 원소부터 검사 시작하면 불필요한 비교 한 번 줄일 수 있음.
if n > self.max_num:
self.max_num = n
self.max_num_idx = i
def get_max_num(self):
return self.max_num
def get_max_num_idx(self):
return self.max_num_idx
nums = [1, 3, 7, 6, 7, 7, 7, 12, 12, 17]
max_algo = MaxAlgorithm(nums)
max_algo.set_max_and_index()
print(f'max_num: {max_algo.get_max_num()}')
max_num = max_algo.get_max_num()
indexes = [0 for _ in range(max_num + 1)]
print(f'indexes len: {len(indexes)}')
for n in nums:
indexes[n] += 1
print(f'indexes: {indexes}')💻 실습코드
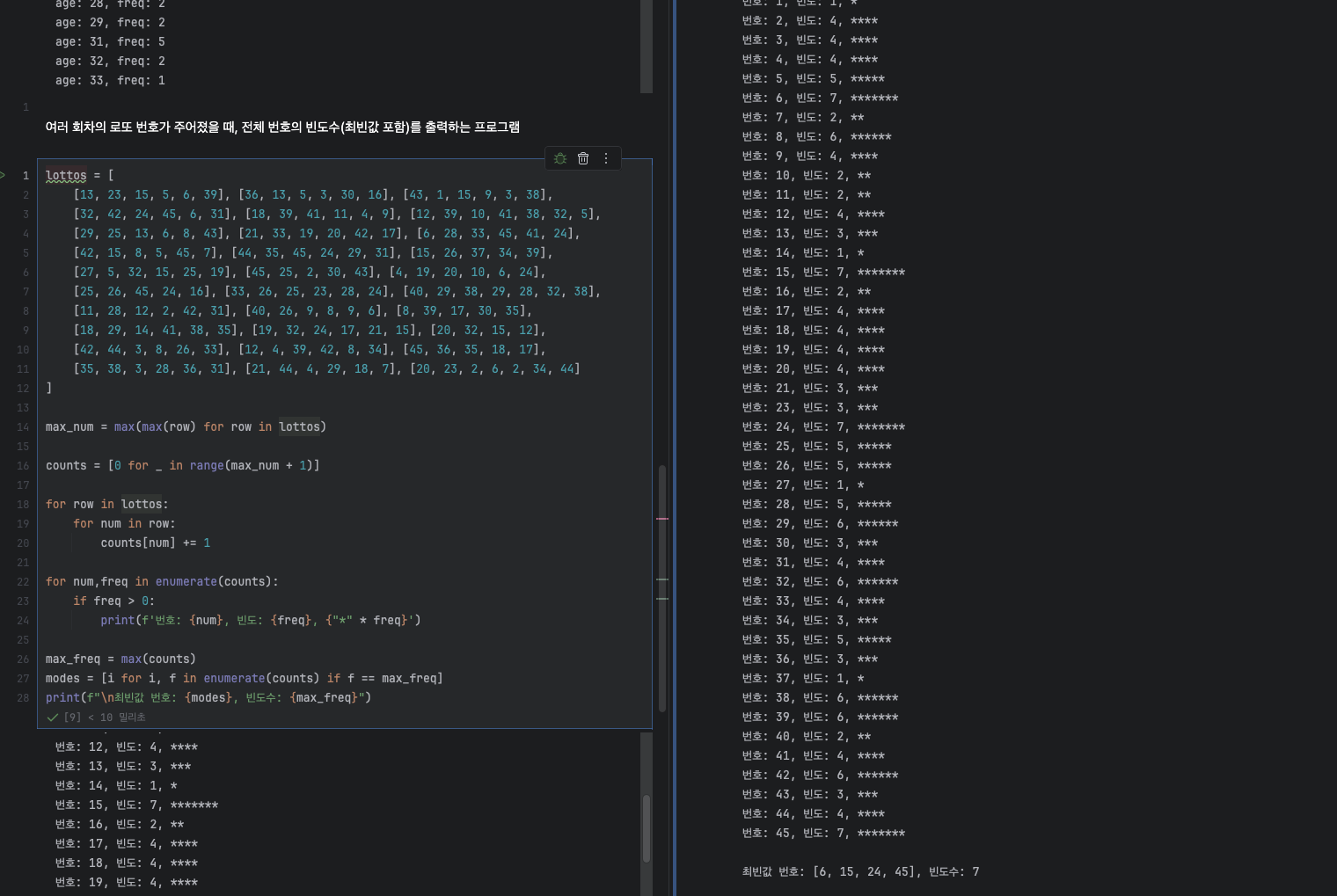
여러 회차의 로또 번호가 주어졌을 때, 전체 번호의 빈도수(최빈값 포함)를 출력하는 프로그램
lottos = [
[13, 23, 15, 5, 6, 39], [36, 13, 5, 3, 30, 16], [43, 1, 15, 9, 3, 38],
[32, 42, 24, 45, 6, 31], [18, 39, 41, 11, 4, 9], [12, 39, 10, 41, 38, 32, 5],
[29, 25, 13, 6, 8, 43], [21, 33, 19, 20, 42, 17], [6, 28, 33, 45, 41, 24],
[42, 15, 8, 5, 45, 7], [44, 35, 45, 24, 29, 31], [15, 26, 37, 34, 39],
[27, 5, 32, 15, 25, 19], [45, 25, 2, 30, 43], [4, 19, 20, 10, 6, 24],
[25, 26, 45, 24, 16], [33, 26, 25, 23, 28, 24], [40, 29, 38, 29, 28, 32, 38],
[11, 28, 12, 2, 42, 31], [40, 26, 9, 8, 9, 6], [8, 39, 17, 30, 35],
[18, 29, 14, 41, 38, 35], [19, 32, 24, 17, 21, 15], [20, 32, 15, 12],
[42, 44, 3, 8, 26, 33], [12, 4, 39, 42, 8, 34], [45, 36, 35, 18, 17],
[35, 38, 3, 28, 36, 31], [21, 44, 4, 29, 18, 7], [20, 23, 2, 6, 2, 34, 44]
]
max_num = max(max(row) for row in lottos)
counts = [0 for _ in range(max_num + 1)]
for row in lottos:
for num in row:
counts[num] += 1
for num,freq in enumerate(counts):
if freq > 0:
print(f'번호: {num}, 빈도: {freq}, {"*" * freq}')
max_freq = max(counts)
modes = [i for i, f in enumerate(counts) if f == max_freq]
print(f"\n최빈값 번호: {modes}, 빈도수: {max_freq}")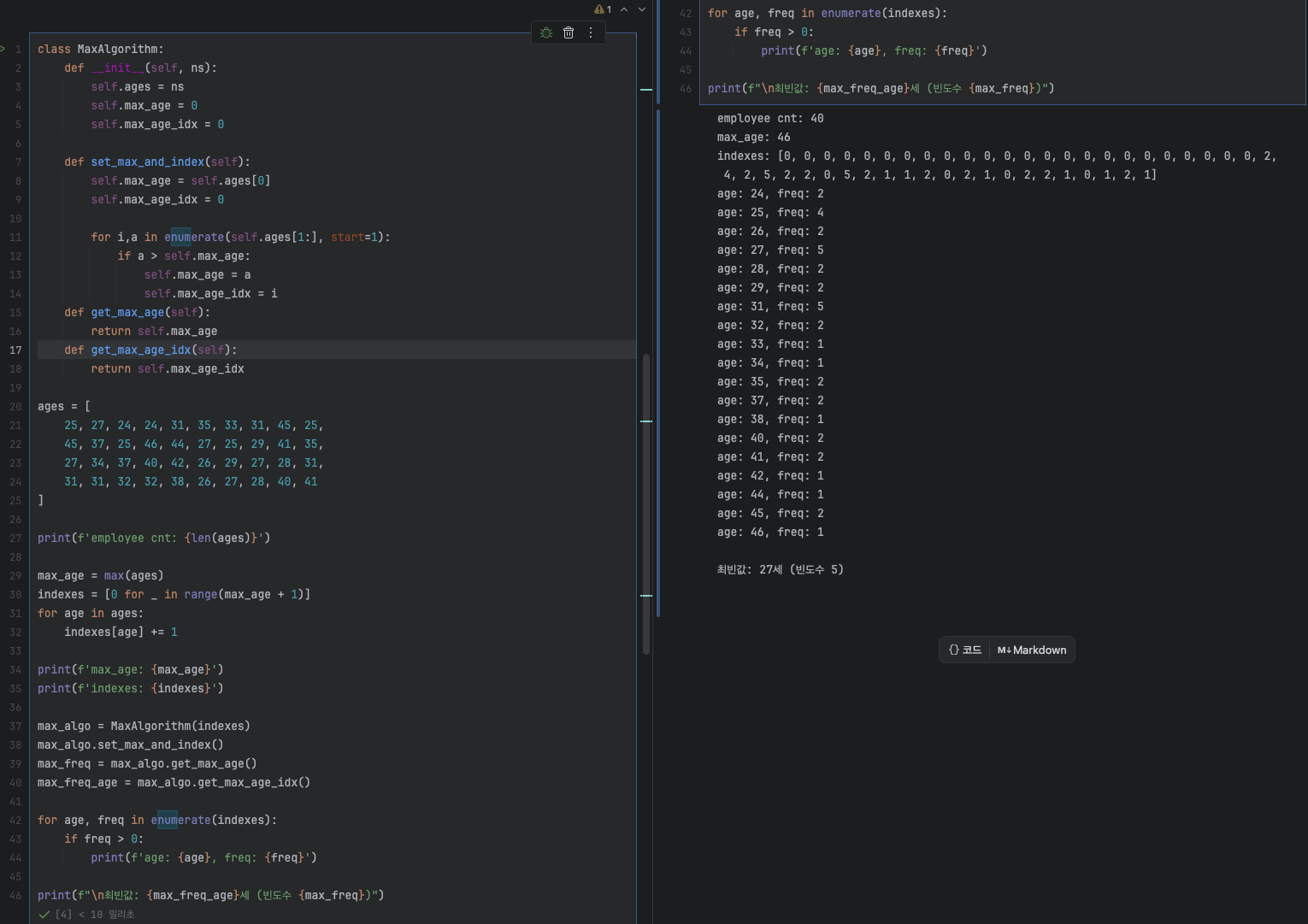
📌 근삿값
- 특정 값(참값)에 가장 가까운 값을 근삿값이라고
합니다
예시:
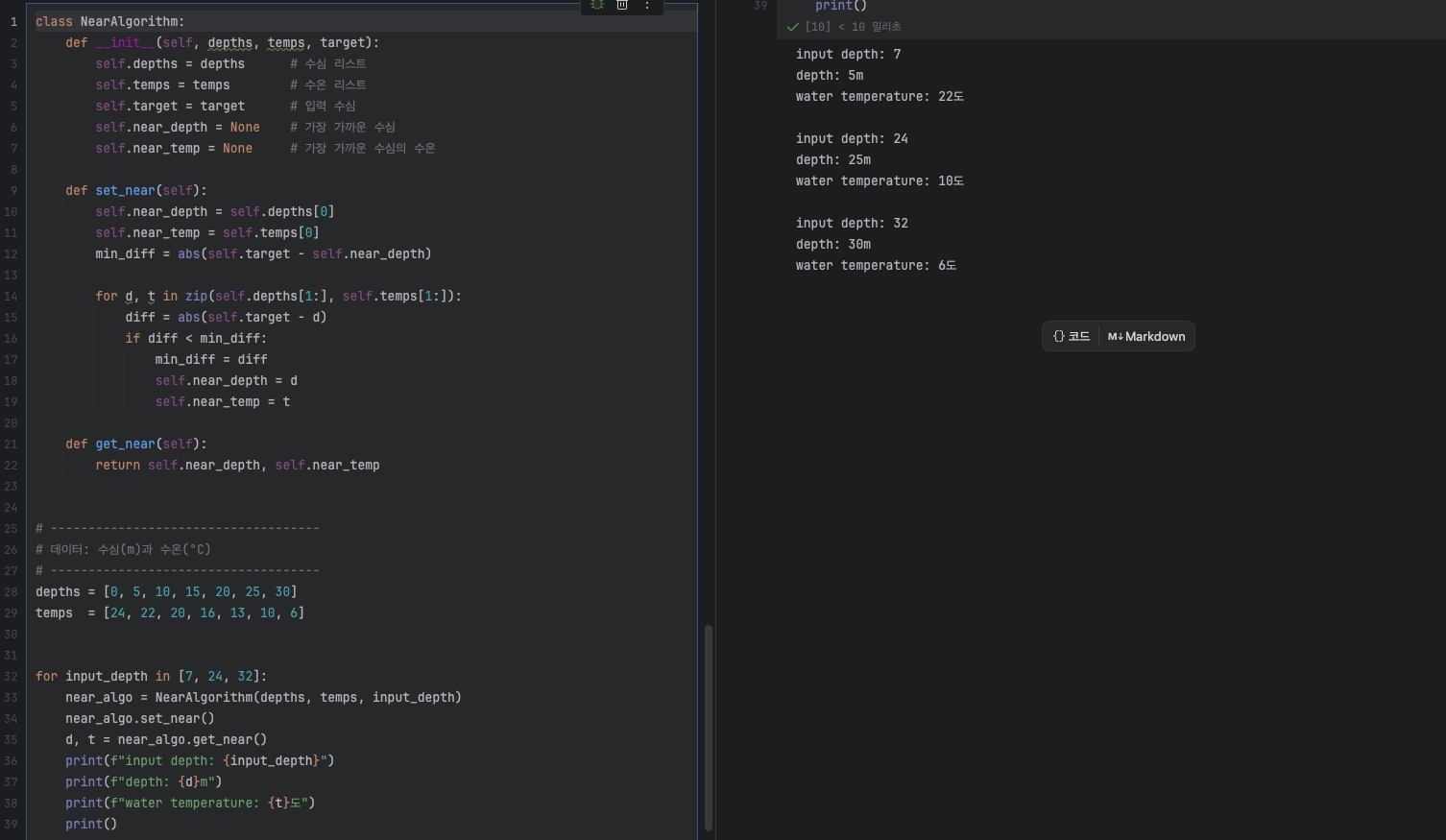
nums = [7, 43, 14, 44, 6, 26, 24, 3, 25, 47, 2, 32, 27, 38, 18, 17, 33, 29, 28, 0]
input number = 11
→ 11과 가장 가까운 값은 14 (차이=3)📌 실습: 시험 점수 → 학점 매기기
근삿값 알고리즘을 이용해 입력 점수를 학점으로 변환하는
프로그램
- 95 근삿값 → A학점
- 85 근삿값 → B학점
- 75 근삿값 → C학점
- 65 근삿값 → D학점
- 55 근삿값 → F학점
🧑💻 코드
class NearAlgorithm:
def __init__(self, values, target):
self.values = values
self.target = target
self.near_value = None
self.min_diff = None
def set_near(self):
self.near_value = self.values[0]
self.min_diff = abs(self.target - self.near_value)
for v in self.values[1:]:
diff = abs(self.target - v)
if diff < self.min_diff:
self.min_diff = diff
self.near_value = v
def get_near(self):
return self.near_value
# 기준 학점 점수
grade_points = [95, 85, 75, 65, 55]
grades = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'F']
# 입력 점수
score = 87
# 근삿값 실행
near_algo = NearAlgorithm(grade_points, score)
near_algo.set_near()
near_point = near_algo.get_near()
# 학점 매핑
grade = grades[grade_points.index(near_point)]
print(f"입력 점수: {score}, 근삿값: {near_point}, 학점: {grade}")입력 점수: 87, 근삿값: 85, 학점: B
📌 평균
- 여러 수나 양의 중간값을 갖는 수를 평균이라고
한다
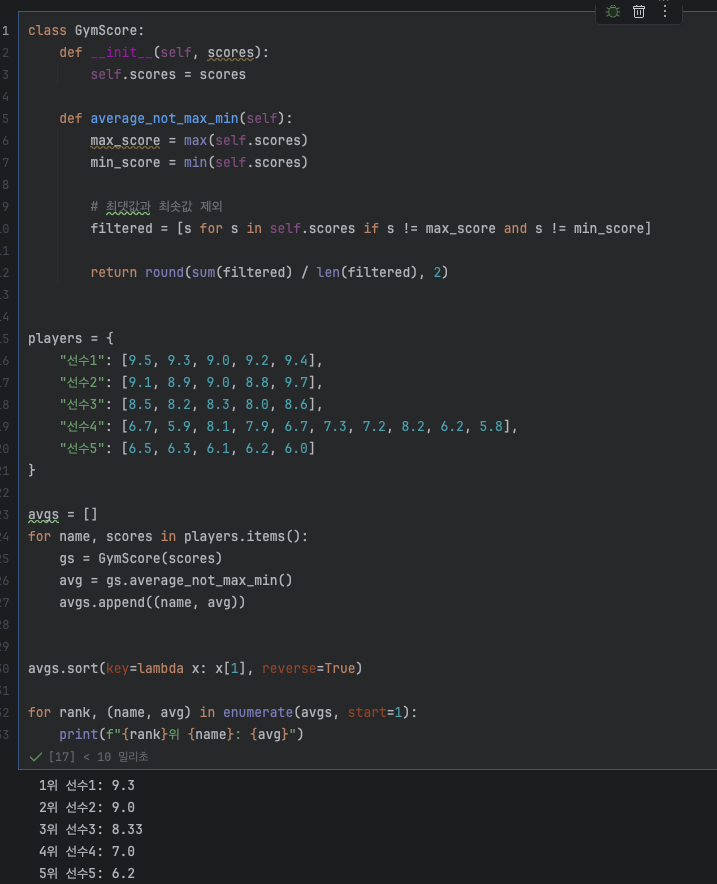
📌 실습: 체조 선수 점수 평균 & 순위 정하기
다음 점수의 평균을 구하고 순위를 정하는 프로그램
🧑💻 코드
scores = [
[9.12, 8.95, 8.39, 7.90, 7.88], # 선수1
[9.10, 8.92, 8.35, 7.85, 7.80], # 선수2
[9.05, 8.70, 8.20, 7.95, 7.85], # 선수3
]
# 평균 계산
averages = []
for i, row in enumerate(scores):
avg = sum(row) / len(row)
averages.append((i+1, avg))
# 평균 내림차순 정렬
averages.sort(key=lambda x: x[1], reverse=True)
# 결과 출력
for rank, (player, avg) in enumerate(averages, start=1):
print(f"{rank}위 선수{player}: 평균 {avg:.2f}")1위 선수1: 평균 8.85
2위 선수2: 평균 8.68
3위 선수3: 평균 8.55