문제 - 스택2 (Silver 4)
[백준 28278] https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/28278
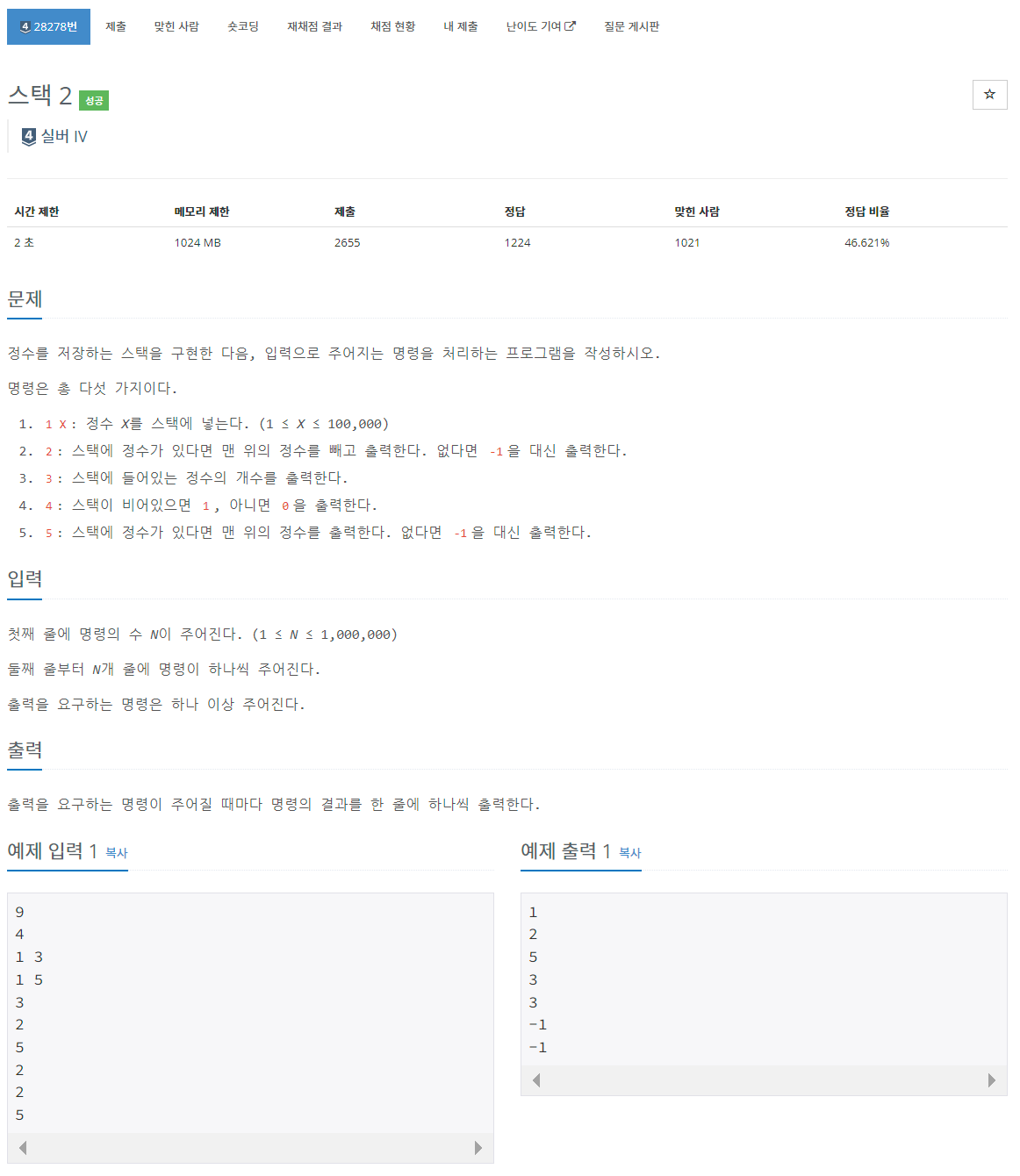
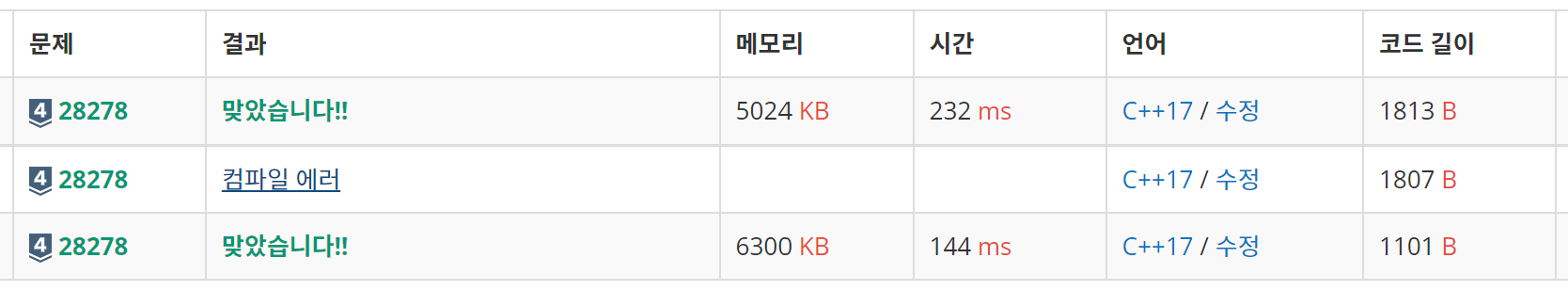
- 제일 아래가 C++ 버전, 제일 위가 C 버전이다 (중간엔 실수ㅎ)
풀이 전략
- C++ 같은 경우, Stack STL이 존재하기 때문에 Stack을 선언한 뒤, STL에 있는 명령어로 Stack에 원소를 push/pop 하면 된다.
- 반면에 C 같은 경우, STL이 존재하지 않기 때문에 일일히 명령어를 작성해야 한다.
참고
스택
한 쪽 끝에서만 데이터를 넣었다 뺐다 할 수 있는 자료구조로, LIFO (Last In First Out) 형태의 선형 자료구조이다.
DFS (Depth First Search) [깊이 우선 탐색], 백트래킹에 활용됨 (후입선출이 재귀 알고리즘과 유사)

스택 STL
- 선언
#include <stack> stack<int> stack;
- 기본 함수
- push
-> 스택의 제일 위에 요소 추가stack.push(element);
- pop
-> 스택에서 제일 위에 있는 요소 제거stack.pop();
- top
-> 스택의 최 상단 요소 반환stack.top();
- size
-> 스택에 있는 요소의 개수를 확인할 때 사용stack.size();
- empty
-> 스택 내부가 비어있는지 확인할 때 사용stack.empty();
소스 코드
1. C
c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct StackRecord *Stack;
struct StackRecord{
int Capacity;
int Top;
int* array;
};
Stack CreateStack(int maxElement){
Stack S=(Stack)malloc(sizeof(struct StackRecord));
if(S==NULL){
exit(1);
}
S->array=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*maxElement);
if(S->array==NULL){
exit(1);
}
S->Capacity=maxElement;
S->Top=-1;
return S;
}
int IsEmpty(Stack S){
return S->Top==-1;
}
int IsFull(Stack S){
return S->Top==S->Capacity-1;
}
void Push(int x, Stack S){
if(IsFull(S)){
return;
}
S->array[++S->Top]=x;
// ++가 앞에 있어야 다음 위치에 요소가 array로 들어가게 된다
}
void Pop(Stack S){
if(IsEmpty(S)){
printf("-1\n");
}else{
printf("%d\n",S->array[S->Top]);
S->Top--;
// 제일 위에 있는 요소를 출력한 뒤 제거해야 제거한 요소가 출력된다
}
}
int Top(Stack S){
if(IsEmpty(S)){
return -1;
}
return S->array[S->Top];
}
int main(){
int x,order;
scanf("%d",&x);
Stack stack=CreateStack(x);
for(int i=0;i<x;i++){
scanf("%d",&order);
switch(order){
case 1:
int element;
scanf("%d",&element);
Push(element,stack);
break;
case 2:
Pop(stack);
break;
case 3:
printf("%d\n",stack->Top+1);
// 아무것도 없을 때가 -1이기 때문에
break;
case 4:
if(IsEmpty(stack)){
printf("1\n");
}else{
printf("0\n");
}
break;
case 5:
if(!IsEmpty(stack)){
printf("%d\n",Top(stack));
}else{
printf("-1\n");
}
break;
}
}
free(stack->array);
free(stack);
return 0;
}2. C++
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <stack>
using namespace std;
int main(void){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
int N;
cin>>N;
stack<int> S;
int order;
while(N--){
cin>>order;
switch(order){
case 1:
int num;
cin>>num;
S.push(num);
break;
case 2:
if(!S.empty()){
cout<<S.top()<<'\n';
S.pop();
// 빼낸 요소를 출력해야 하기 때문에 pop이 나중에 선언되어야 한다.
}else{
cout<<-1<<'\n';
}
break;
case 3:
cout<<S.size()<<'\n';
break;
case 4:
if(!S.empty()){
cout<<0<<'\n';
}else{
cout<<1<<'\n';
}
break;
case 5:
if(!S.empty()){
cout<<S.top()<<'\n';
}else{
cout<<-1<<'\n';
}
break;
}
}
return 0;
}결과
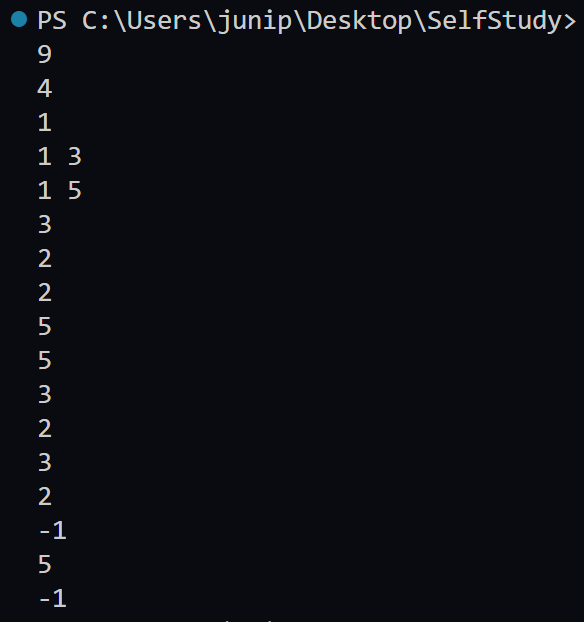
결론
- C++ 컨테이너를 사용하면 지~~ㄴ짜 편하다
- C로 하게 되면 동적할당, 함수 선언 등등 신경써야할게 너무 많다..
일례로 처음에 C로 동적할당을 할 때, (int*)를 안쓰고 malloc을 했다가 (void*)로 자동으로 선언이 되면서 컴파일에러가 떴었다