01. Strategic Management
1) Business and Operations Strategy Alignment
- Mission >> Vision(3년 계획; 계량적 목표) >> Business strategy(사업 전략) >> Operation strategy(=functional Strategy)
- Generic performance objectives 일반적인 성과 목표
: QCDPSM ; P = Productivity, S = Safety, M = Morale
2) Strategic Planning
(1) the External Environment
-
7 key issues in the external environment
-
Industry's dominant economic feature
산업의 주요한 경제적 특성- Market size and growth rate, number of buyers, supply / demand conditions
- Vertical integration 수직적 통합, economies of scale 규모의 경제 , learning and experience
- scope of rivalry 경쟁의 범위, # of rivals, product differentiation
↔ Product innovation, technological change
-
Industry attractiveness and profitability
산업 매력도 및 수익성
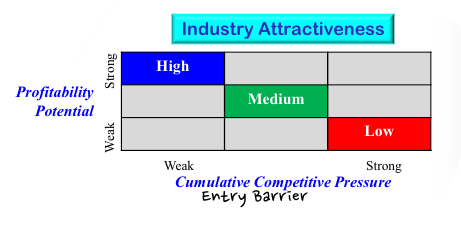
- Aggregate industry level factor 통합적 산업 수준의 요소
: growth rate, competitive pressures, risk/ uncertainty, ... - Company-specific factors 회사 특유의 요소들
: competitive position 경쟁 위치, ability to capitalize 자본력 - Competitive forces affect industry attractiveness
- High : high competition from substitute
대체품과의 높은 경쟁 - Medium
: position of most companies 대부분의 기업들 - Low
: intense supplier leverage 강력한 공급자 레버리지
- High : high competition from substitute
- Aggregate industry level factor 통합적 산업 수준의 요소
-
Forces driving changes 변화의 유도
- Internet applications, globalization
- Entry / exit of major firms, cost and efficiency
-
Market positions 시장 위치
- QCD, geographic coverage
-
KSFs for future success in the industry
산업 내에서 미래에 성공적인 성공을 위한 주요 요인- get-it-right factors, technology, manufacturing, distribution, marketing, CS
-
Strength of competitive formce 경쟁력의 강점
-
Likely strategic moves by rivals 경쟁사의 전략적 움직임 가능성
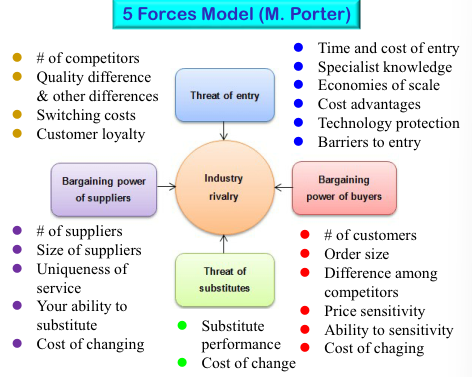
[그림 1] 마이클 포터의 5 forces model
-
(2) the Internal Environment
5 KEY issues in assessing the internal environment
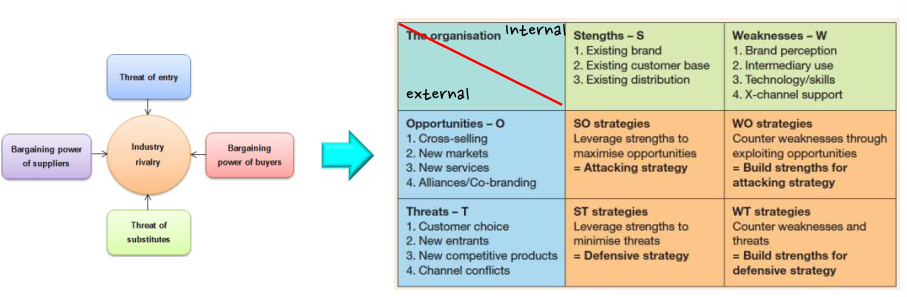
- Assessing the current strategy 현대 전략을 평가하기 (as-is analysis)
- sales and M/S growth rate, ROI trends, brand power,...
- SWOT analysis
- overall business situation → improving company strategy
- Competitiveness of price and cost 가격과 원가에서의 경쟁력
- value chain analysis, ABC accounting, benchmarking
- Strength relative to competitors 경쟁자와 비교하여 가지고 있는 강점
- selecting rating criteria
- Highest-priority issues for management 관리에 있어 가장 높은 우선순위를 가지고 있는 문제
- QCD + growth, defending enw entrants
3) Development of Competitive Strategy
Balanced plans for the followings 다음을 위한 균형 잡힌 계획
- Pleasing customers, countering rivals
- Responding to market changes
- Securing competitive advantage
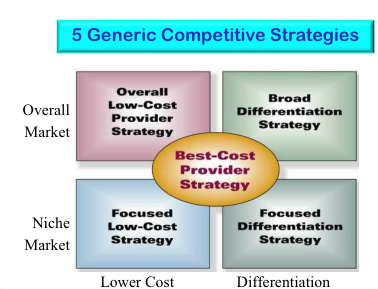
- Overall low-cost provider strategy 전반적인 저비용 공급자 전략
- Underprice competitors to increase total profits
경쟁사보다 낮은 가격으로 전체 이윤을 늘린다 - Maintain high value chain efficeincy
높은 가치 사슬 효율성을 유지한다.
- Underprice competitors to increase total profits
- Broad differentiation strategy → Mass- customization
광범위한 차별화 정책- Buyers are attracted to intangible features of the product / service
구매자는 제품과 서비스의 비가시성의 특성들에 끌린다.
- Buyers are attracted to intangible features of the product / service
- Focused differentiation strategy 집중화된 차별화 정책
- Target customers willing to pay a premium for a product / service
제품과 서비스를 위해 프리미엄을 지불할 용의가 있는 고객에게 집중 - Niche market for specific customer segment or geographic area
특정 고객 부문 또는 지역을 위한 틈새 시장
- Target customers willing to pay a premium for a product / service
- Focused low-cost strategy
- Need to meet well-defined buyer need
구매자의 요구를 잘 정의하는 것이 필요하다
- Need to meet well-defined buyer need
- Best-cost provider strategy
- a hybrid, low-cost approach to offering a differentiated product / service
하이브리드형, 차별화된 제품과 서비슬를 낮은 가격의 접근법으로 제공한다 - Product / service significantly better than low-cost version
제품과 서비스가 단순 저가형 보다 현저히 더 낫다.
- a hybrid, low-cost approach to offering a differentiated product / service
4) Introduction
Wide range of options are available in designing MPC systems, and the choices must be governed by the company's competitive needs
MPC 시스템을 설계할 때 다양한 옵션을 사용할 수 있으며, 선택은 회사의 경쟁적 요구에 의해 관리되어야 한다.
1) Two Issues in Designing MPC systems
- Linking the design of a firm's MPC system with its corporate strategy (bs strategy) for competing in the marketplace
기업의 MPC 시스템 설계와 시장 경쟁을 위한 기업 전략(bs 전략)의 연계 - Integrating MRP and JIT in existing or new MPC systems
이미 존재하는, 혹은 새로운 MPC 시스템에서 MRP 와 JIT 의 결합
2) MPC Alternatives
MRP, MRP II, JIT, OPT (TOC), Periodic Control Systems,Finite Scheduling Systems(FAS),...
3) Three MPC Levels and Options
- MPS Options : MTO, ATO, MTS
- Detailed Material Planning options : Timephased(MRP), Bucketless, Rate Based(JIT)
- Shop-floor options, MRP(Push), TOC, JIT(Pull)
MPC Design Options
1) MPS Options
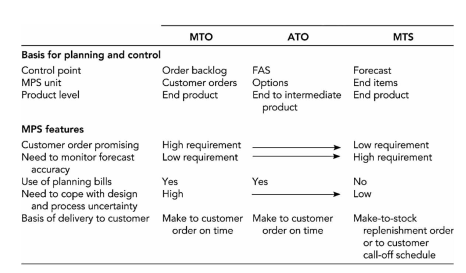
Basis for planning and control
- Control point
- MPS unit
- Product level
MPS Features- cUSTOMER ORDER PROMISING
- Need to monitor fforecast accuracy
- Use of planning bills
- Need to cope with design and process uncertainty
- Basis of delivery to customer
(1) MTO - Make to Order
- Encompass engineering design activities as well as manufacturing and supplier operations
엔지니어링 설계 활동 및 제조 및 공급업체 운영 포함 - The customer order represents the unit of control in the MPS
고객 주문이 MPS에서 관리의 단위를 나타낸다 - Planning BOM are extensively utilized to prioritize manufacturing efforts on the critical path.
계획 BOM은 임계 경로에서 제조 작업의 우선순위를 정하기 위해 광범위하게 활용
(2) ATO = Assemble to Order
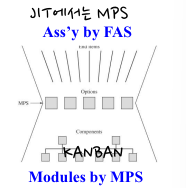
- Component inventory is held to reduce overall mfg lead time
부품 재고는 전체 생산 리드타임을 줄이기 위해 존재한다 - A key control point is the FAS
→ MPS & FAS are used for postponement - Planning BOM are based on average products and on optional feature
계획 BOM은 평균 제품과 선택적 특성의 기반으로 사용된다.
(3) MTS = Make to Stock
- Customer orders are filled from stock to provide short delivery times for standardized products
고객 주문은 표준화된 제품을 짧은 배송 시간으로 제공하기 위해 재고로 채워진다. - The type of uncertainty is forecasting errors
불확실성의 타입은 예측 에러이다.
2) Detailed Material Planning options
(1) Time phased ↔ MRP
- MRP with batch manufacturing 배치 생산과 MRP
- Based on explosion of requriements, where shop and purchase orders are created for batches
- 요구사항 전개를 기반으로 배치에 대한 상점 및 구매 주문이 생성됩니다.
(2) Rate based ↔ JIT (Line)
- Repetitive mfg, assembly lines, JIT and Other flow systems
- single level BOM is used to convert rate-based MPSs into Material plans
single level BOM 은 비율 기반 mps를 자재 계획으로 바꾸는데 이용된다 - Detailed information on WIP is not required, because of
WIP의 자세한 정보는 요구되어 지지 않는다- MPS stability, high rates of material flow, negligible WIP inventory levels, short manufacturing LT, and a relatively small variety of final products in the MPS
(3) Bucketless
- W/O using dated records, rather than buckets (or deffined time periods)
버킷(또는 정의된 기간)이 아닌 날짜 레코드를 사용한 W/O - ATO companies are shifting to bucketless systems to take advantage of the precise scheduling(APS)
ATO 기업들은 정확한 계획(APS)의 이점을 얻기 위해서 bucketless system을 채택했다.
| Time-phased | Bucketless | Rate-based | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Basis for planning and control | |||
| Control point | Shop/purchase order | planning bills | planning bills |
| Control unit | Batches+planning billes / batches | kanbans | |
| Product level | Material explosion of time-phased net requirements for product components | Material explosion of time-phased net requirements once engineering is done | Material explosion of rate-based requirements for product components |
| MPS design | ATO | MTO | MTS |
| Material planning feature | |||
| Fixed schedules | NO | NO | YES |
| Use of WIP to aid planning | high | some | low |
| Updating | Daily /Weekly | As needed | Weekly/monthly |
| Leadtime offsetting | performed | performed | None |
| lot sizing | performed | Some | None |
| Safety stock/safety lead time | considered | considered | not considered |
| container size | not considered | not considered | considered |
| Bill of material | many levels | many levels | single level |
3) Shop-floor system Options
(1) MRP ↔ Push
- Batch manufacturing operations
- W/Os are released against a schedule developed by the MRP
MRP가 개발한 일정에 따라 W/O가 출시 - Coordinate the sequencing of orders at individual work centers with order due dates
개별 작업장의 주문 순서와 주문 마감일을 조정 - Problems are highlighted through I/O analysis and shop load reports
문제는 I/O 분석과 샵 선적 리포트를 통해 강조된다
- W/Os are released against a schedule developed by the MRP
(2) JIT ↔ Pull
- Based on minimal flow times for the entire product, the emphasis is on end items
전체 제품의 최소 흐름 시간을 기준으로 최종 항목에 중점을 둔다 - Cellular mfg techniques :
detailed scheduling is a part of the basic mfg task
상세 계획은 기본적인 생산 업무의 일환이다 - The only close-out is of finished items 완제품만 마감된다
→ Back flush and phantom bill for component parts
(3) Distinction between push and pull
push와 pull의 차이점
- does any system with MRP belong to push system?
MRP가 있는 시스템은 푸시 시스템에 속합니까? - key question
whether individual work centers are allowed to utilize capacity without being driven by a specific end-item schedule?
개별 워크센터가 특정 최종 항목 일정에 따라 운영되지 않고 용량을 활용할 수 있는지 여부
→ 후공정 결정 ; Pull
(4) TOC
- Max output of key products 제품의 최대 생산량
- Bottleneck utilization 병목 활용
- Shop orders
- Large / transfer batches with large WIP / SS (lot Splitting)
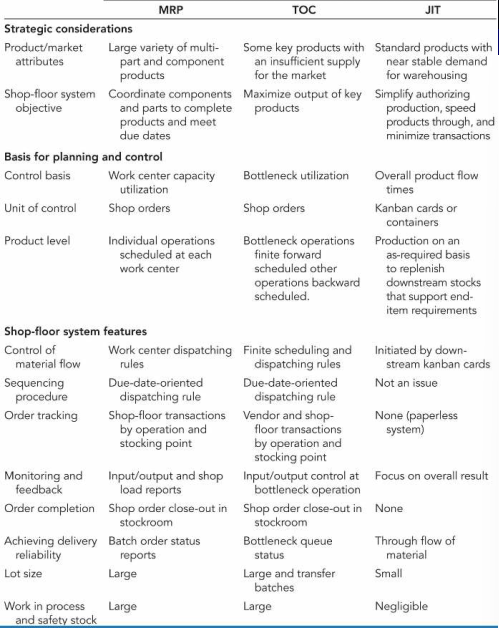
Strategic consideerations
- product / market attributes
- shop-floor system objective
Basis for planning and control- Control basis
- Unit of control
- Product level
Shop-floor system feature- control of material flow
- sequencing procedure
- order tracking
- monitoring and feedback
- order completion
- achieving delivery reliability
- lot size
- work in process and safety stock
2. Choosing the option
JIT is not always right answer JIT가 항상 옳은 정답이 되는 것은 아니다
1) Framework by Berry and Hill(1992)
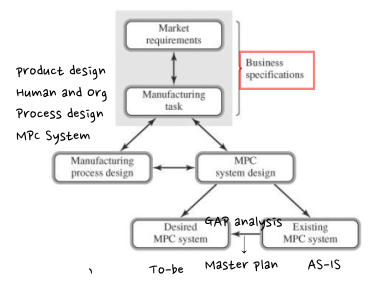
(1) Market Requirements
- Review the customers and market segments targeted by the business
사업에 의해 목표가 된 고객과 시장의 분류를 재확인한다
: products, competitors
(2) Manufacturing Task
- Should be consistent with (and that supports) the marketing stragegy
마케팅 전략과 일치해야 하며 이를 뒷받침해야 한다
→ order winner vs. order qualifiers
QCD = order qualifiers
differentiation = order winner
(3) Mfs Process Design
- Interdependency between MPC option choices and mfg process features
MPC 옵션 선택과 생산 프로세스 기능 간의 상호 의존성
; E.G : JIT + Cellular mfg + short production L/T → Rate-based detailed material planning - Simultaneous changes in marketplace requirements, mfg process, and mfg task definitions
시장 요구, 생산 프로세스, 생산 업무 정의의 동시적 변화
: E.G : Mainframe computer(MTO) → PC-type computer (MTS/ATO)
(4) MPC system design
- Resolve the differences between desirerd and existing MPC system options and features
원하는 MPC 시스템 옵션과 기존 MPC 시스템 기능 간의 차이 해결 - Consistency in the MPS, detailed material planning, and the shop-floor system
MPS에서의 일관성, 상세 자재 계획, SHOP-FLOOR 시스템
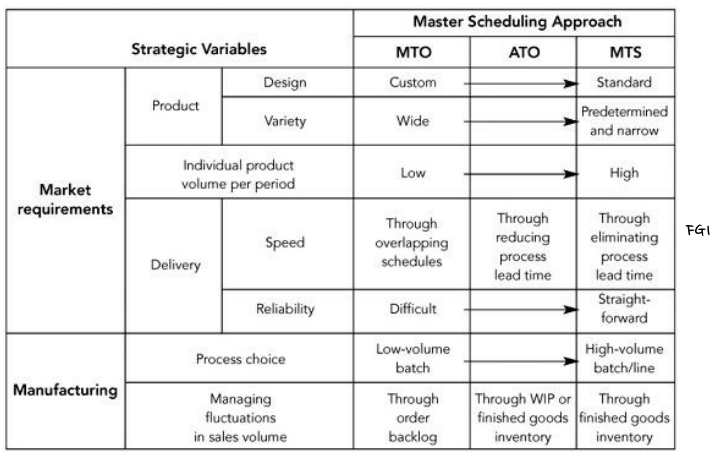
(a) MPS Options
-
MTO
- products of wide variety and custom design, involving the development of eng specs
엔지니어링 사양의 개발을 수반하는 다양한 맞춤 디자인의 제품 - low-volume mfg → how to respond to fluctuations in sales volume? 판매량 변동에 어떻게 대응할 것인가?
- products of wide variety and custom design, involving the development of eng specs
-
ATO
- an intermediate position between MTO and MTS
MTO와 MTS 사이의 위치
→ batch mfg or cellular mfg
- an intermediate position between MTO and MTS
-
MTS
- standard products in high unit volumes in narrow product variety
좁은 상품 다양성에 대량의 표준화된 제품
→ line mfg
- standard products in high unit volumes in narrow product variety
(b) Material Planning Options
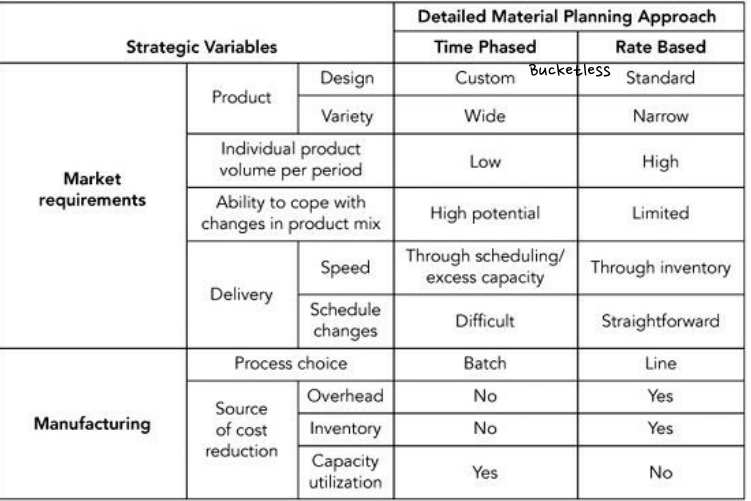
- Time-phased
- appropriate for custom products in wide variety and low volume
넓은 다양성과 낮은 생산량을 가지는 개별화 제품에 적절 - Needs relatively high overhead and WIP due to the planning staff and extensive transaction
계획 직원과 광범위한 트랜잭션으로 인해 상대적으로 높은 간접비 및 WIP 필요
- appropriate for custom products in wide variety and low volume
- Rate-based
- a narrow range of standard / stable product design produced in high volume
좁은 다양성의 표준화 / 안정된 제품 디자인 (대량생산)
- a narrow range of standard / stable product design produced in high volume
(c) Shop floor System options
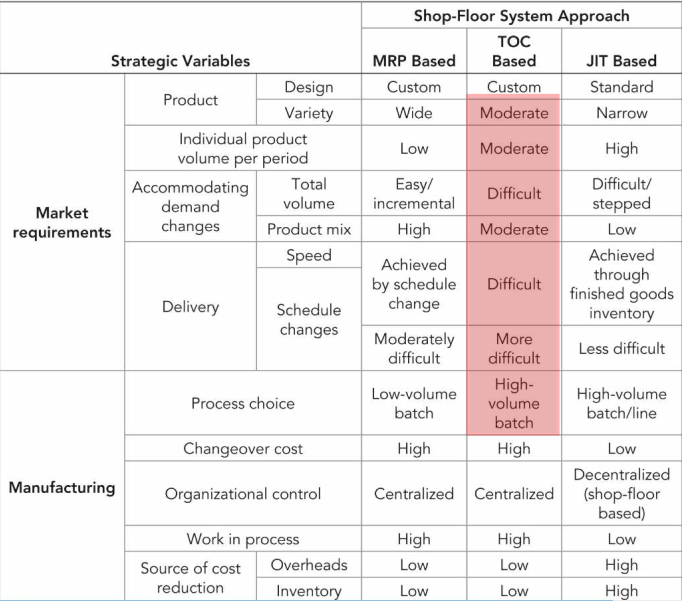
| MRP | JIT |
|---|---|
| a wide variety of custom products is produced in low unit volume 넓은 다양성과 낮은 생산량을 가지는 개별화 제품에 적절 | standard products produced in limited variety and high volume 좁은 다양성의 표준화 / 안정된 제품 디자인 (대량생산) |
3. The Choices in Practice
1) Moog, Inc., Space Products Division
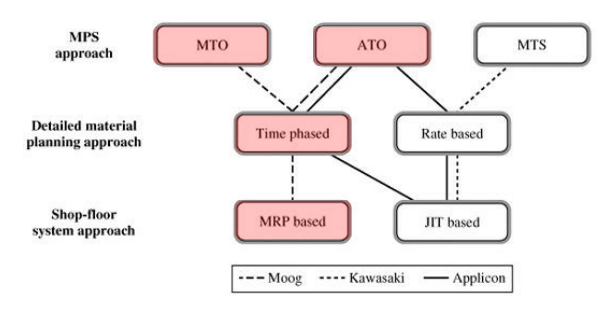
| Market requirements | High quality hydraulic systems of advanced design 고급 설계의 고품질 유압 시스템 → low volume, custom design |
|---|---|
| Mfg task | broad range of equipment / employee capabilities 광범위한 도구 / 고용 수용력 → L/T, Delivery reliability |
| Mfg process and MPC system | MTO+ATO,Time-phased, MRP-Based SFC |
2) Kawasaki, USA
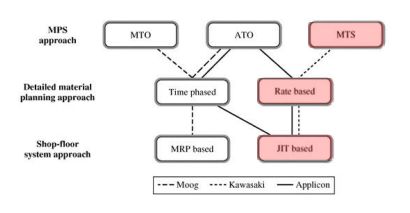
- Market requirements
- 100 different end-items → seasonal demand, high volume
- Mfg task
- low-cost mfg, short seetup times and small production batches for JIT
- 3 month frozen MPS, SMED
- Mfg process and MPC system
- MTS, Rate based (with a planning BOM), JIT based SFC
3) Applicon
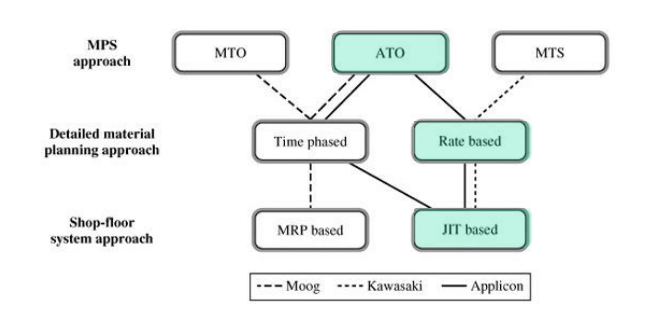
- Market requirements
- CAD/CAM system manufacturer for the elctronics / mechanical design → Custom design
- Mfg task
- high quality products with options in small volumes at low cost in short LT → cells, JIT
- Mfg process and MPC system
- (Before) MTS, Time, MRP → (after) ATO, Rate, JIT
- 5 mfg cells for cellular mfg
- Batch manufacturing General-purpose equipment Functional plant layout 4-5 month mfg L/T
- Straight-line flows of material Mfg cells dedicated to particular product families Short setup times Short mfg L/T (1 wk)
- The company plans using forecast info in the MPS, but builds product only to customer orders using a FAS
MPS에서 예측 정보를 사용할 계획이지만 FAS를 사용하여 고객의 주문에 대해서만 제품을 구축 - Only 2 inventory transactions are recorded – from suppliers into the stock bins, and out of stock bins as finished products are shipped from the plant
공급업체에서 재고 보관함으로 들어오는 재고 거래와 공장에서 완제품이 배송되는 재고 보관함으로 인한 재고 부족 거래 2건만 기록됨
4. Integrating MRP and JIT
JIT needs to achieve much closer integration in MPC systems between customer and suppliers
JIT는 고객과 공급업체 간의 MPC 시스템에서 훨씬 더 긴밀한 통합을 달성해야 한다.
1) Case: TelTech
- Telecom equipment manufacturer & turn-key system implementer for telephone systems operators
전화 시스템 운영자를 위한 통신 장비 제조업체 및 턴키 시스템 구현자 - Lengthy processes for order processing : 10 ~ 20 days from order decision to MPS
주문 처리에 걸리는 긴 프로세스 : 주문 결정부터 MPS까지 10~20일 소요- 2 ~ 3 days in the customer :
two excutive signatures on the order documnet
2-3일 동안 고객:
주문서 상의 두 개의 서명 - 1 ~ 2 days from the marketing to the factory
- More delays for determining the detailed spec of the system
시스템의 상세 사양을 결정하기 위해 더 많은 delay
→ configuration management
- 2 ~ 3 days in the customer :
- Improvement
- online MPC system to support product configuration management
제품 형성 관리를 지원하기 위한 온라인 MPC 시스템 - Configuration of an order take place before the order was issued
주문이 발행되기 전에 주문 구성이 수행됩니다.
- online MPC system to support product configuration management
2) Supply Relationships
(1) Level of Supply Relationships
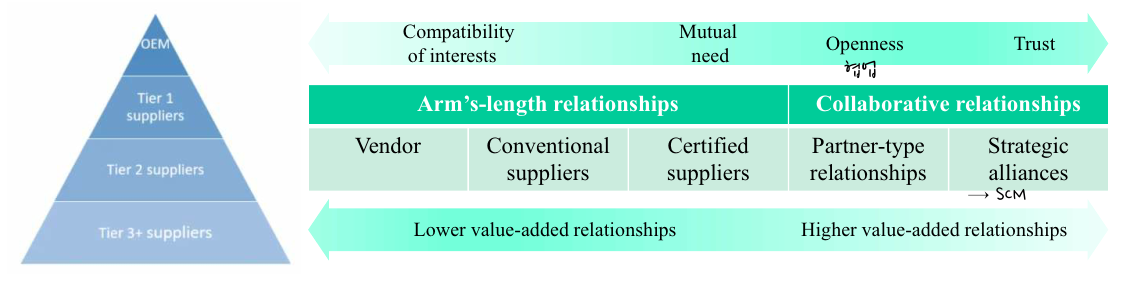
Oem, Tier 1 Suppliers, Tier 2 suppliers, Tier 3 suppliers
Lower value - added relationships = Arm's length relationships
- Compatibility of interest
- Vendor, Conventional suppliers
- Mutual need
- Certified suppliers
Higher value-added relationships = collaborative relationships- Openness = 협력 = Partner type relationships
- Trust = Strategic alliances
(2) Manufacturing Capacity
- In House mfg = Direct
- Competency 편하다, new capacity, tooling, capacity utilization, workforce stability
- Supplier
- Qualtiy, lead time reliability, specilized knowledge 노하우를 가져올 수 있다, design assistance and confidentiality
(3) Cost Analysis : Make or Buy Decision
자작 대 외주
- Make cost
- materials, labor, inventory carrying, overhead, capital, production mgmt
- Buy cost
- purchase price, transportation, receiving / inspection, purchasing transaction and mgmt
- 사온다 ← 입찰 (경쟁) ↔ VMI (single)
(4) Supply Risk and Profit Impact Model
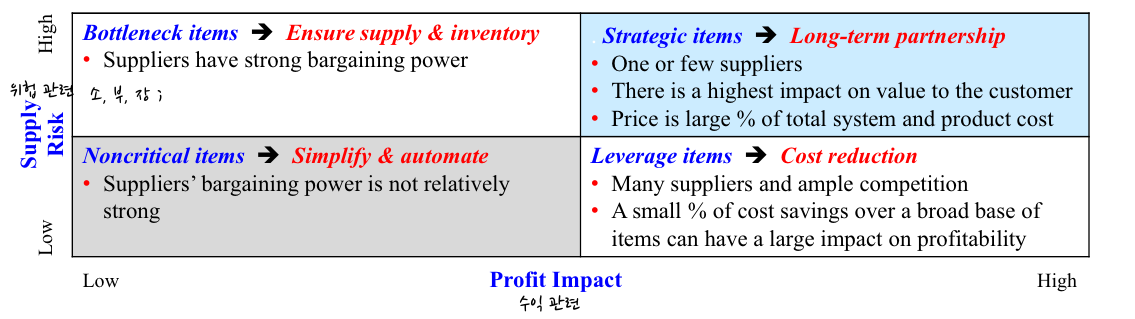
- Bottleneck items → Ensure supply and inventory
- High supply risk and low profit impact
- Suppliers have strong bargaining power
- Strategic items → Long term partnership
- High supply risk and High profit impact
- One or few suppliers
- There is a highest impact on value to the customer
고객이 느끼는 가치에 가장 많은 영향을 준다 - Price is large % of total system and product cost
가격은 전체 시스템과 제품 가격의 많은 비중을 차지한다.
- Noncritical items → simplify and automate
- low supply risk and low profit impact
- Supplier's bargaining power is not relatively strong
- leverage items → cost reduction
- low supply risk and high profit impact
- many suppliers and ample competition
많은 공급자와 적절한 경쟁자가 있다 - A small % of cost savings over a broad base of items can have a large impact on profitability
광범위한 품목에 비해 적은 %의 비용 절감은 수익성에 큰 영향을 미칠 수 있다
(5) Strategic Sourcing
- Objectives
- reliable source, quality, flexibility and responsiveness, cost reduction
- Activities
- analyze spend patterns→access leverage → establish / maintain relationships
(6) Tactical Buying → Noncritical + leverage item
- ample supplier competition, buyer's leverage advantage, standard specs and reliable quality
- risk criteria : price, service, qualtiy, tech, market trends
(7) financial viability of suppliers : ratio analysis
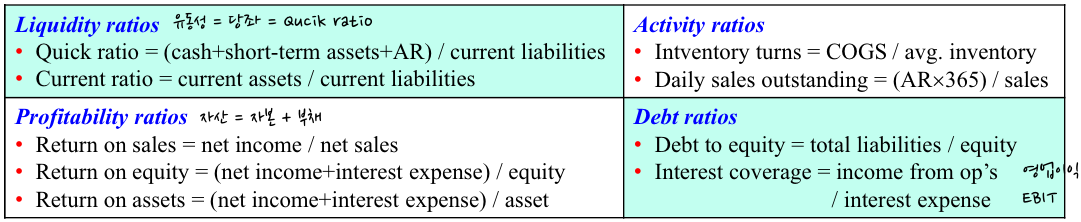
- Liquidity ration 유동성 = 당좌 = Quick ratio
- quick ratio = (cash+shrt term assets + AR) / current liabilities
- Current ratio = current assets / current liabilities
- Activity ratios
- inventory turns = COGS / avg. inventory
- Daily sales outstanding = (AR * 365) / sales
- Profitability ratio 자산 = 자본 + 부채
- Return on sales = net income / net sales
- Return on equity = (net income+interest expense) / equity
- Return on assets = (net income + interest expense) / asset
- Debt ratios
- debt to equity = total liabilities / equity
- interest coverage = income from op's / interest expense
- 영업이익 EBIT ↔ 경상 이익
(8) collaborative relationships
- Strategic alliances : development of linked and common processes with joint investments
전략적 제휴: 공동 투자와 연계되고 공통적인 프로세스 개발- Technical and operational partnering
- Ibm ↔ Intel + MS
- manufacturer distributor integration : scm
- 3pl : fedex, dhl, amazon (유연함)
- retailer - supplier partnerships:
CPFR, ECR ( Efficient Consumer Response)
→ QR for the apparel industry / SPA (Special Store retailer private Label apprel) brand
- Technical and operational partnering
- Supplier partnerships : similar to strategic alliance but
- less clear strategic goal than strategic alliance, coordinated (not common) process
전략적 제휴보다 덜 명확한 전략적 목표, 조정된(일반적이지 않은) 프로세스 - partner type relationship
- goal
- product development, operational integration, quality management, flexibility, access to markets, management of investment risk
- less clear strategic goal than strategic alliance, coordinated (not common) process
(9) supply alternatives and techniques
- sourcing : sole, single, and multiple sourcing
- sole supplier = the only supplier ↔ single supplier = one of many possible suppliers
- supplier managed inventory
- consignment inventory 위탁 재고, VMI, on site representation
- VMI vs consignment
: visibility to the supplier, role and planning and replenishment
(10) manufacturing with suppliers ← time to market
- cross functional teams to select suppliers 공급자를 선택하기 위한 다기능 팀
- supplier performance evaluation, supplier certification,, new product development
공급업체 성과 평가, 공급업체 인증, 신제품 개발 - concurrent engineering 동시 공학
: cross functional team with customers and suppliers
공급업체와 고객을 포함한 다기능 팀
- supplier performance evaluation, supplier certification,, new product development
- Advantages of supplier involvement 협력업체를 참여시킬 때의 장점
- sharing of tech and design information, reduced time and resources
기술과 디자인 정보의 공유, 줄어든 시간과 자원 - simplified and standardized product design, easier to manufacture or assemble
단순화되고 표준화된 제품 설계, 제조 또는 조립이 용이함 - fewer engineering design changes and quality problems
공학 디자인 변경과 품질 문제의 감소
- sharing of tech and design information, reduced time and resources
- Disadvantage
- core competency 를 유지못할 수 있다 → 상호 부담
3) Supply Performance and Relationship management
(1) specification of quality requirements
- supplier selection with the appropriate type of contract
적절한 유형의 계약과 함께 공급업체 선정- deffine the supply quality system, numerical quality / reliability requirements for lots
- Trend toward single sourcing
- simplified transaction, access to supplier assistance
← SCM
- simplified transaction, access to supplier assistance
(2) supplier capability assessment
- Product design
- detailed definiation and specs of product requirement : FMECA
- Manufacturing processes
- history data, process capabiltiy analysis quality survey
- failure mode, effects and criticality analysis 고장 및 영향 분석
→ reliability eng 신뢰성 공학
(3) sc quality planning and control ← collaboration and partnerships
- plannning
- customer/supplier team activities, value engineering, reduction of TCO & quality costs
- control
- supplier certification, supplier quality rating 공급업체 인증, 공급업체 품질 등급
← Reduce supplier base to those qualified 공급업체 기반을 적격 업체로 축소
- supplier certification, supplier quality rating 공급업체 인증, 공급업체 품질 등급
- supplier classes
- A(no inspection w/ supplier data) >> B (no inspection) >> C (optional sampling) >> D (sampling) >> E (100% inspection)
(4) sc quality improvement
- Cross-functional quality improvement teams, management leadership, …
- Methods: market survey, Pareto analysis, QFD & House of Quality, CE (DFM, DFA, DFL), …
- DFM = Design for manufacture
4) Purchasing and SCM
(1) Overview of purchasing
- Purchasing approaches
- P/O, blanket orders 포괄 주문, lean, consignment inventory, VMI
- types of contract
- buy-back, revenue-sharing, pay-back, cost-sharing, pricing, capacity reservation
- global sourcing
- cost and non-cost advantages, SCM challenges, importance of strategic sourcing
(2) relationships with SCM
- TCO (Total cost ownership)
- costs from acquisition to usage and end-of-life
구입에서 사용 및 사용 종료까지의 비용
- costs from acquisition to usage and end-of-life
- parnership goals and benefits
- L/T reduction, better demand visibility, faster time-to-market, …
L/T 절감, 수요 파악 능력 향상, 출시 기간 단축 등
- L/T reduction, better demand visibility, faster time-to-market, …
- supplier and customer training
- product design, quality requirements, delivery processes, …
- role of engineering
- new product/process design, engineering change, supplier input to mfg.
- SRM system
- automated procure-to-pay business processes, supplier evaluation, info exchange, …
-delivery approaches - QR, 3PL, cross-docking, delivery to point-of-use and point-of-fit, VMI
- automated procure-to-pay business processes, supplier evaluation, info exchange, …
- supplier rating system
- quatitative measure 정량적 기법
- certification, quality, delivery, cost, cooperation, quantity accuracy, …
- lean oriented measures
- L/T, on-time delivery, lot size, space requirements, …
- quatitative measure 정량적 기법
5) Distribution planning
(1) distribution network planning
- Types of distribution channels
- complex, exclusive/selective, direct/internal, …
- network configuration
- customer locations ↔ distribution networks ↔ physical components
- inventory locations and transportation modes → BOD = Bill of distribution
(2) DRP & LRRP
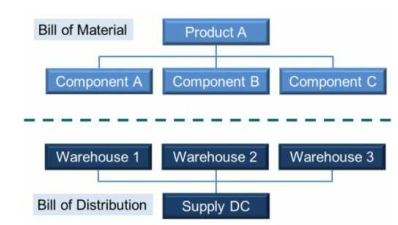
- key issues of DRP = Distribution requirements planning
- when, where and how much distribution inventory is needed?
언제, 어디서, 그리고 얼마만큼 운송 재고가 필요한가?
(RCCP 에 대응) - When resources are nessasary for timely delivery and storage?
적절한 운송 및 보관에 따른 적절한 자재 필요 시기
- when, where and how much distribution inventory is needed?
- DRP approaches
- push vs. pull
- DRP logic
- time-phased order logic, BOD, MPS implosion
← similar to MRP
- time-phased order logic, BOD, MPS implosion
- LRRP = Logistic Resource Requests Planning
- SOP-level resource planning for logistics
(3) Measuring performance
categories: service, flow response, operating variance reduction, minimum inventories, …
5. CPIM
when manufacturing lead times excessed customer requirements and products can be constructed from modular compoents, which master production scheduling approach is most likely to employed?
I. Make to order
II. Assemble to order
III. Make to stock
IV. Engineer to order
answer : II
From lowest to highest, rank the master production shceduling approaches according to the need to monitor forecast accuracy.
I. assemble to order, make to stock, maker to order
II. maker to order, make to stock, assemble to order
III. make to stock, assemble to order, maker to order
IV. maker to order, assemble to order, make to stock
answer : IV
Which of the following is true?
I. A key objective under material requirement planning (MRP) is to use each work center's capacity effectively
II. A key objective under JIT is to minimize flow times
III. JIT systems are best suited to situations where demand is relatively constant
answer : I, II, III
Which shop floor control system is most likely to be appropriate when a variety of custom products is being manufactured?
I. Time phased planning
II. rate based planning
III. Either is appropriate
IV. Neither is appropriate
answer : I
Which of the following are used to support the integration of MRP and JIT systems?
I. Phantom bills of materials
II. Planninng bills of material
III. capacity bills
answer : I ; II = ATO, III = RCCP
DRP accomplishes wich of the following?
I. Extends manufacturing planning and control (MPC) visibility
II. Summarizes detailed field information
III. Analyze potential warehouse location
answer : I, ii

Your article on strategy and MPC system design provides a comprehensive overview of crucial concepts in the field. The strategic approach and the breakdown of MPC system components offer valuable insights for anyone delving into this complex domain. If you're interested in exploring the application of strategy in software development contracts, this guide on time and materials contracts might provide additional context: https://www.cleveroad.com/blog/time-and-materials-contract-in-outsourcing-all-you-need-to-know/.