📌 출처
📝 문제
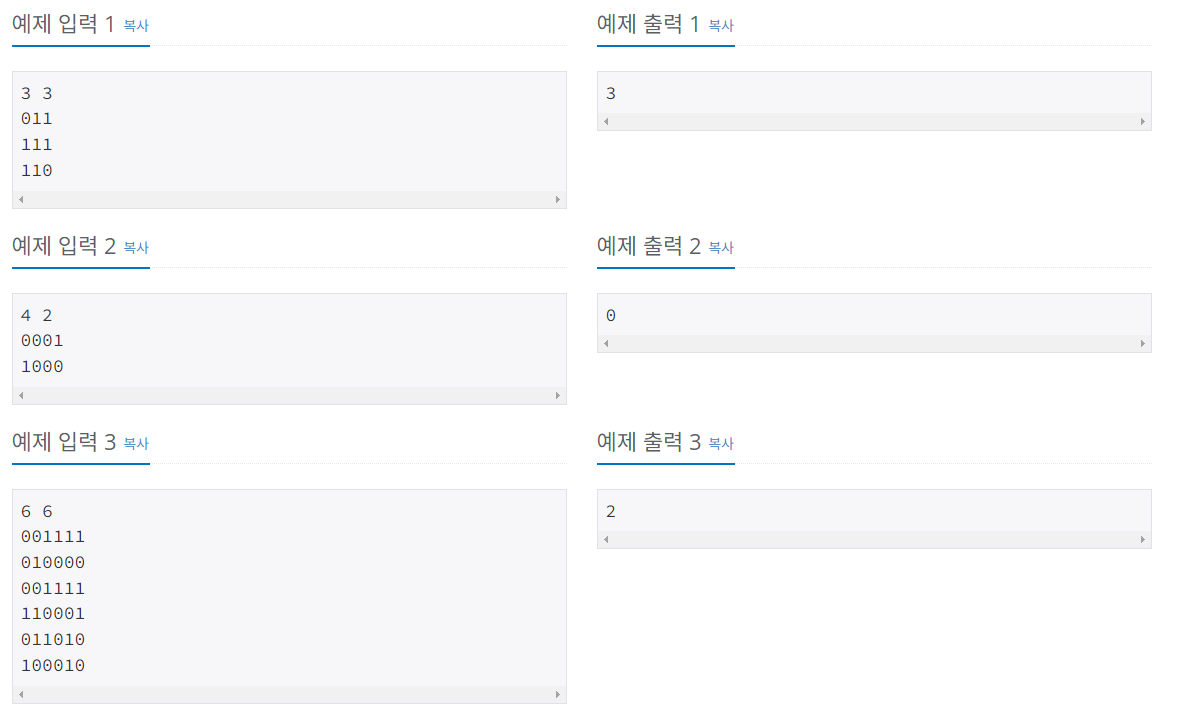
알고스팟 운영진이 모두 미로에 갇혔다. 미로는 NXM 크기이며, 총 1X1크기의 방으로 이루어져 있다. 미로는 빈 방 또는 벽으로 이루어져 있고, 빈 방은 자유롭게 다닐 수 있지만, 벽은 부수지 않으면 이동할 수 없다.
알고스팟 운영진은 여러명이지만, 항상 모두 같은 방에 있어야 한다. 즉, 여러 명이 다른 방에 있을 수는 없다. 어떤 방에서 이동할 수 있는 방은 상하좌우로 인접한 빈 방이다. 즉, 현재 운영진이 (x, y)에 있을 때, 이동할 수 있는 방은 (x+1, y), (x, y+1), (x-1, y), (x, y-1) 이다. 단, 미로의 밖으로 이동 할 수는 없다.
벽은 평소에는 이동할 수 없지만, 알고스팟의 무기 AOJ를 이용해 벽을 부수어 버릴 수 있다. 벽을 부수면, 빈 방과 동일한 방으로 변한다.
만약 이 문제가 알고스팟에 있다면, 운영진들은 궁극의 무기 sudo를 이용해 벽을 한 번에 다 없애버릴 수 있지만, 안타깝게도 이 문제는 Baekjoon Online Judge에 수록되어 있기 때문에, sudo를 사용할 수 없다.
현재 (1, 1)에 있는 알고스팟 운영진이 (N, M)으로 이동하려면 벽을 최소 몇 개 부수어야 하는지 구하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
⌨ 입력
첫째 줄에 미로의 크기를 나타내는 가로 크기 M, 세로 크기 N (1 ≤ N, M ≤ 100)이 주어진다. 다음 N개의 줄에는 미로의 상태를 나타내는 숫자 0과 1이 주어진다. 0은 빈 방을 의미하고, 1은 벽을 의미한다.
(1, 1)과 (N, M)은 항상 뚫려있다.
🖨 출력
첫째 줄에 알고스팟 운영진이 (N, M)으로 이동하기 위해 벽을 최소 몇 개 부수어야 하는지 출력한다.
💻 내 코드
1. 리스트를 사용하여 구현
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
int x;
int y;
int cnt;
Point(int x, int y, int cnt) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Point o) {
return cnt - o.cnt;
}
}
public class Main {
static int N, M;
static int[][] map;
static boolean[][] visited;
static int[] dx = new int[]{-1, 1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = new int[]{0, 0, -1, 1};
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map = new int[M][N];
visited = new boolean[M][N];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
String[] str = br.readLine().split("");
for(int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(str[j]);
}
}
int answer = bfs();
System.out.println(answer);
}
static int bfs() {
PriorityQueue<Point> queue = new PriorityQueue<>();
queue.add(new Point(0, 0, 0));
visited[0][0] = true;
int cnt = 0;
while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
Point point = queue.poll();
cnt = point.cnt;
if(point.x == M - 1 && point.y == N - 1) break;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = point.x + dx[i];
int ny = point.y + dy[i];
if(nx < 0 || nx >= M || ny < 0 || ny >= N) continue;
if(visited[nx][ny]) continue;
if(map[nx][ny] == 0) {
queue.add(new Point(nx, ny, cnt));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
if(map[nx][ny] == 1) {
queue.add(new Point(nx, ny, cnt + 1));
visited[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
✏ 설명
BFS를 사용하는 것은 맞지만 다른 문제들과의 차이점은 바로 우선순위 큐를 사용하는 것이다.
우선순위 큐를 어떻게 사용하냐면 BFS를 하면서 길을 탐색하는데 벽을 최소한으로 부순 것을 우선적으로 탐색하는 방식이다.
그래서
class Point implements Comparable<Point> {
int x;
int y;
int cnt;
Point(int x, int y, int cnt) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.cnt = cnt;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Point o) {
return cnt - o.cnt;
}
}이런식으로 Point 클래스를 생성해주었다.
Comparable을 implement해서 compareTo를 오버라이드 하는 방식은 잊지 말자.
정말 자주 쓰이는 방식이다.
