Lec3: Python Data Structure
01_특징이 있는 정보는 어떻게 저장할까
1) Data Structure 생각해보기
- 전화번호부 정보는 어떻게 저장하면 좋을까
- 은행 번호표 정보는 어떻게 처리하면 좋을까
- 서적 정보는 어떻게 관리하면 좋을까
- 창고에 쌓인 수화물의 위치를 역순으로 찾을 때
2) Python Basic Data Structure
- Stack & Queue with list
- Tuple & Set
- Dictionary
- Collection Module
3) Stack
- 나중에 넣은 Data를 먼저 Return하도록 설계된 Memory Structure
- Last In First Out (LIFO)
- Data의 Input = Push
- Data의 Output = Pop
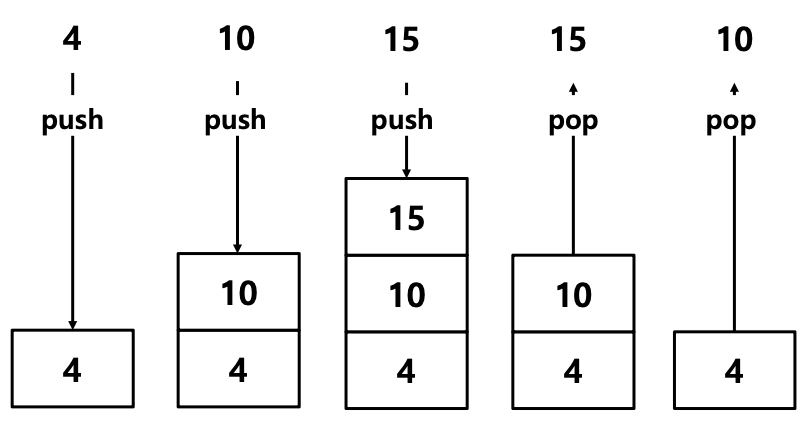
- Stack with list object
- List를 사용하여 Stack Structure를 구현 가능
- Push를 append(), Pop을 pop()을 사용
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] a.append(10) a.append(20) # a.pop() : return이 존재하면서도 a값을 변화시킨다. # a.sort() : return값이 없고 a값만 변화 # sorted(a) : return값만 있고 a값은 유지 a.pop() # 20 a.pop() # 10
- Stack Example : Stack Structure를 활용, 입력된 글자를 역순으로 출력
word = input("Input a word : ") # Input Word word_list = list(word) # String to List for i in range(len(word_list)): print(word_list.pop()) # 하나씩 빼면서 출력
4) Queue
- 먼저 넣은 Data를 먼저 Return하도록 설계된 Memory Structure
- First In First Out (FIFO)
- Stack과 반대되는 개념
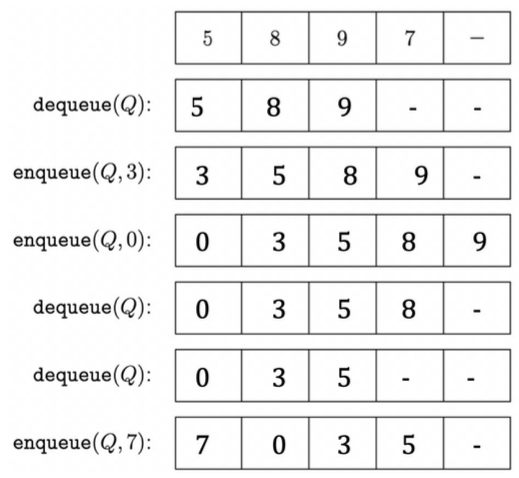
- Queue with list object
- Python은 List를 사용하여 Queue Structure를 활용
- Put을 append(), Get을 pop(0)을 사용
a = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] a.append(10) a.append(20) a.pop(0) # 1 a.pop(0) # 2
5) Tuple
- 값의 변경이 불가능한 List
- 선언 시 "[]"가 아닌 "()"를 사용
- List의 연산, Indexing, Slicing 등을 동일하게 사용
t = (1, 2, 3)
print(t + t, t * 2) # (1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3) (1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3)
len(t) # 3
t[1] = 5 # Error 발생사용하는 이유
1. Program을 작동하는 동안 변경되지 않은 Data의 저장
ex) 학번, 이름, 우편번호 등
2. Function의 Return 값 등, 사용자의 실수에 의한 Error를 사전에 방지
t = (1) # 일반정수로 인식
t = (1, ) # 값이 하나인 Tuple은 반드시 "," 를 붙여야 함6) Set
- 값을 순서없이 저장, 중복 불허 하는 자료형
- Set 객체 선언을 이용하여 객체 생성
s = set([1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]) # set 함수를 사용, 1,2,3을 set object 생성, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}도 가능
print(s) # {1, 2, 3}
s.add(1) # 한 원소 1만 추가, 중복 불허로 추가 되지 않음
print(s) # {1, 2, 3}
s.remove(1) # 1 삭제
print(s) # {2, 3}
s.update([1, 4, 5, 6, 7]) # [1, 4, 5, 6, 7] 추가
print*(s) # {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s.discard(3) # 3 삭제
print(s) # {1, 2, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s.clear() # 모든 원소 삭제- 집합의 연산
s1 = set([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
s2 = set([3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
s1.union(s2) # s1과 s2의 합집합
# {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
s1 | s2 # {1, 2, 3 ,4, 5, 6, 7}
s1.intersection(s2) # s1과 s2의 교집합
# {3, 4, 5}
s1 & s2 # {3, 4, 5}
s1.difference(s2) # s1과 s2의 차집합
# {1, 2}
s1 - s2 # {1, 2}7) Dictionary
- Data를 저장 할 때는 구분 지을 수 있는 값을 함께 저장
ex) 주민등록 번호, 제품 모델 번호 등 - 구분을 위한 Data 고유 값을 Identifier 또는 Key라고 한다.
- Key 값을 활용하여 Data Value를 관리.
- Key와 Value를 Matching하여 Key로 Value를 검색
- 다른 언어에서는 Hash Table이라는 용어를 사용
- {Key1:Value1, Key2:Value2, Key3:Value3, ...} 형태
country_code = {} # Dictionary 생성, country_code = dict() 도 가능
country_code = {"America": 1, "Korea": 82, "China": 86, "Japan": 81}
print(country_code) # {'America': 1, 'China': 86, 'Korea': 82, 'Japan': 81}
country_code.items() # Dictionary Data 출력
# Dict_items([('America', 1), ('China', 86), ('Korea', 82), ('Japan', 81)])
print(country_code.keys()) # Key만 출력
# Dict_keys(["America", "China", "Korea", "Japan"])
country_code["German"]= 49 # Dictionary 추가
print(country_code) # {'America': 1, 'German': 49, 'China': 86, 'Korea': 82, 'Japan': 81}
country_code.values() # Dictionary Value만 출력
# dict_values([1, 49, 86, 82, 81])for k,v in country_code.items():
print("Key : ", k)
print("Value : ", v)
# Key : America
# Value : 1
# Key : Gernman
# Value : 49
# Key : China
# Value : 86
# Key : Korea
# Value : 82
# Key : Japan
# Value : 81
"Korea" in country_code.keys() # Key값에 "Korea"가 있는지 확인
# True
82 in country_code.values() # Value값에 82가 있는지 확인
# True8) Dictionary Lab: Command Analyzer
- Command = 사용자가 서버에 명령어를 입력한 명령어
어떤 사용자가 얼마나 많이 명령어를 입력했을까
import csv
def getKey(item): # 정렬을 위한 함수
return item[1]
command_data = [] # 파일 읽어오기
with open("command_data.csv", "r") as csvfile:
spamreader = csv.reader(csvfile, delimiter=',', quotechar='"')
for row in spamreader:
command_data.append(row)
command_counter = {} # Dictionary 생성, ID를 Key, 입력한 줄 수를 Value로
for data in command_data: # List Data를 Dictionary로 변경
if data[1] in command_counter.keys(): # ID가 이미 Key로 변경되었을 때
command_counter[data[1]] += 1 # 기존 출현한 ID
else:
command_counter[data[1]] = 1 # Dictionary를 List로 변경
dictlist = []
for key, value in command_counter.items():
temp = [key,value]
dictlist.append(temp)
sorted_dict = sorted(dictlist, key=getKey, reverse=True) # List를 입력 줄 수로 정렬
print(sorted_dict[:100]) # List의 상위 100개값만 출력[['bookworm', 8500], ['elsa', 7500], ['fillmore', 7394], ['francis', 5978], ['anton_ego', 5819], ['queen_grimhilde', 5000], ['kristoff', 4934], ['brent_mustangburger', 4838], ['emperor_zurg', 4470], ['tarzan', 4193], ['stitch', 3742], ['marlon_the_alligator', 3203], ['faline', 3115], ['meg', 3098], ['fear', 2968], ['roo', 2782], ['claire_wheeler', 2777], ['don_carlton', 2773], ['guido', 2541], ['flynn_rider', 1996], ['mama_odie', 1883], ['darla_sherman', 1861], ['tiger_lily', 1846], ['chick_hicks', 1678], ['louis_the_alligator', 1374], ['the_dodo', 1364], ['ray_the_firefly', 998], ['tigger', 884], ['jane_porter', 852], ['al_mcwhiggin', 777], ['tinker_bell', 696], ['peter_pig', 500], ['rocket_raccoon', 473], ['charlotte_la_bouff', 472], ['peter_pan', 463], ['auto', 458], ['kocoum', 438], ['prince_naveen', 425], ['flik', 424], ['dory', 410], ['bo_peep', 407], ['captain_hook', 403], ['aladdin', 402], ['chatter_telephone', 372], ['django', 371], ['charlie', 363], ['bomb_voyage', 337], ['riley_anderson', 330], ['flo', 324], ['finn_mcmissile', 319], ['nani_pelekai', 319], ['pocahontas', 312], ['chum', 311], ['bing_bong', 311], ['disgust', 305], ['anna', 304], ['boo', 304], ['fa_zhou', 299], ['francesco_bernoulli', 292], ['bambi', 275], ['prince_hans', 275], ['aurora', 267], ['duke_of_weselton', 264], ['bumblebee', 260], ['joy', 258], ['dolly', 254], ['flora', 247], ['fred', 244], ['brock_pearson', 242], ['dim', 240], ['eve', 239], ['white_rabbit', 237], ['mungo', 237], ['crush', 231], ['pascal', 224], ['carrie_williams', 223], ['rapunzel', 219], ['merryweather', 219], ['wendy_darling', 218], ['roger_rabbit', 211], ['collette_tatou', 206], ['cheshire_cat', 200], ['eudora', 191], ['lilo_pelekai', 190], ['mulan', 188], ['coral', 186], ['maximus', 172], ['emile', 168], ['tiana', 167], ['auguste_gusteau', 153], ['darrell_cartrip', 146], ['sadness', 133], ['nakoma', 133], ['chunk', 126], ['alice', 123], ['the_magic_mirror', 116], ['snow_white', 115], ['splunk_teamlab', 115], ['thor', 98], ['fritz', 94]]9) Collections
- List, Tuple, Dictionary에 대한 Python Built-in 확장 자료 구조(Module)
- 편리함, 실행 효율성 제공
- 아래의 Module이 존재
from collections import deque
from collections import Counter
from collections import OrderedDict
from collections import defaultdict
from collections import namedtuple10) Deque
- Stack & Queue를 지원하는 Module
- List에 비해 효율적이고 빠른 자료 저장 방식을 지원
from collections import deque
deque_list = deque()
for i in range(5):
deque_list.append(i)
print(deque_list)
deque_list.appendleft(10)
print(deque_list)
# deque([0, 1, 2, 3, 4])
# deque([10, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4])- Rotate, Reverse 등 Linked List의 특성을 지원
- 기존 List 형태의 함수를 모두 지원
deque_list.rotate(2)
print(deque_list)
deque_list.rotate(2)
print(deque_list)
print(deque(reversed(deque_list)))
deque_list.extend([5, 6, 7])
print(deque_list)
deque_list.extendleft([5, 6, 7])
print(deque_list)
# deque([3, 4, 10, 0, 1, 2])
# deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 0])
# deque([0, 10, 4, 3, 2, 1])
# deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 0, 5, 6, 7])
# deque([7, 6, 5, 1, 2, 3, 4, 10, 0, 5, 6, 7])- Deque와 기존 List 비교
# < Deque >
from collections import deque
import time
start_time = time.clock()
deque_list = deque()
# Stack
for i in range(10000):
for i in range(10000):
deque_list.append(i)
deque_list.pop()
print(time.clock() - start_time, "seconds")
# 3.6ms
# < General List >
import time
start_time = time.clock()
just_list = []
for i in range(10000):
for i in range(10000):
just_list.append(i)
just_list.pop()
print(time.clock() - start_time, "seconds")
# 1.04ms11) OrderedDict
- Dictionary와 달리, Data를 입력한 순서대로 Dict를 Return
- 그러나 Dict도 Python 3.6부터 입력한 순서를 보장하여 출력
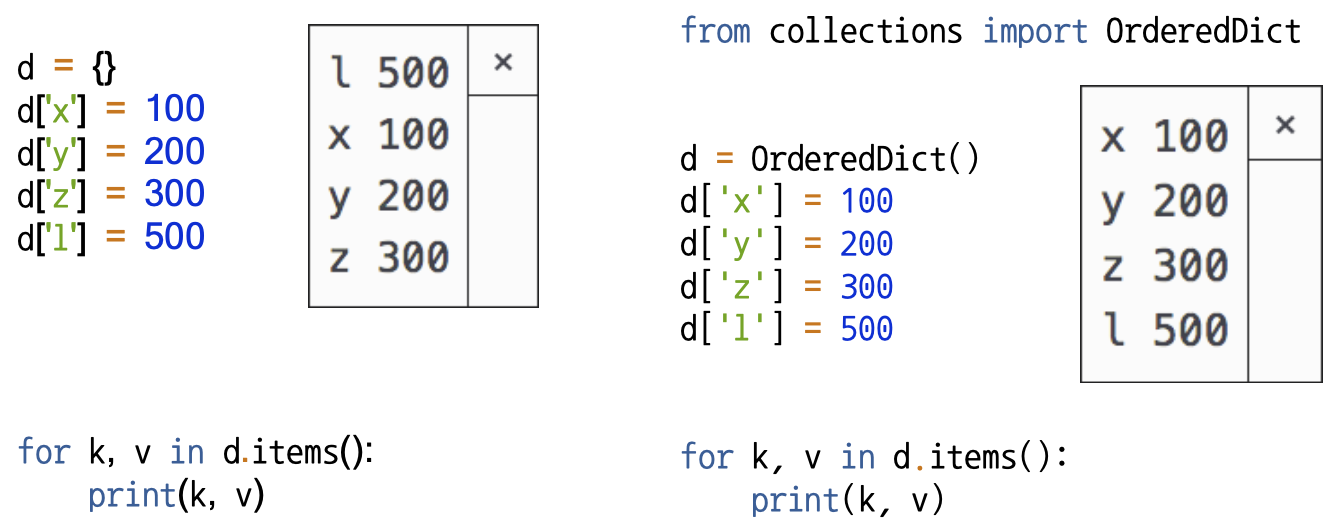
- Dict Type의 값을, Value 또는 Key 값으로 정렬할 때 사용 가능

12) DefaultDict
- Dict Type의 값에 Default 값을 지정, 신규값 생성 시 사용하는 방법
from collections import defaultdict
d = defaultdict(object) # Default Dictionary를 생성
d = defaultdict(lambda: 0) # Default 값을 0으로 설정
print(d["first"]) # 0- 하나의 지문에 각 단어들이 몇 개나 있는지 세기
- Text-Mining 접근법 : Vector Space Model
text = """A press release is the quickest and easiest way to get free publicity.
If well written, a press release can result in multiple published articles about your firm and its products.
And that can mean new prospects contacting you asking you to sell to them. ....""".lower().split()
print(text)['a', 'press', 'release', 'is', 'the', 'quickest', 'and', 'easiest', 'way', 'to', 'get', 'free', 'publicity.', 'if', 'well', 'written,', 'a', 'press', 'release', 'can', 'result', 'in', 'multiple', 'published', 'articles', 'about', 'your', 'firm', 'and', 'its', 'products.', 'and', 'that', 'can', 'mean', 'new', 'prospects', 'contacting', 'you', 'asking', 'you', 'to', 'sell', 'to', 'them.', '....']from collections import OrderedDict
word_count = defaultdict(lambda: 0) # Default 값을 0으로 설정
for word in text:
word_count[word] += 1
for i, v in OrderedDict(sorted(word_count.items(), key=lambda t: t[1], reverse=True)).items():
print(i, v)and 3
to 3
a 2
press 2
release 2
can 2
you 2
is 1
the 1
quickest 1
easiest 1
way 1
get 1
free 1
publicity. 1
if 1
well 1
written, 1
result 1
in 1
multiple 1
published 1
articles 1
about 1
your 1
...
asking 1
sell 1
them. 1
.... 113) Counter
- Sequence type의 Data Element들의 갯수를 Dict 형태로 변환
from collections import Counter
c = Counter() # a new, empty counter
c = Counter('gallahed') # a mew counter from an iterable
print(c)
# Counter({'a': 3, 'l': 2, 'g': 1, 'd': 1, 'h':1})c = Counter({'red': 4, 'blue': 2}) # a new counter from a mapping
print(c)
print(list(c.elements()))
# Counter({'red': 4, 'blue': 2})
# ['red', 'red', 'red', 'red', 'blue', 'blue']
c = Counter(cats=4, dogs=8)
print(c)
print(list(c.elements()))
# Counter({'dogs': 8, 'cats': 4})
# ['cats', 'cats', 'cats', 'cats', 'dogs', 'dogs', 'dogs', 'dogs', 'dogs', 'dogs', 'dogs', 'dogs']- Set의 연산들을 지원
c = Counter(a=4, b=2, c=0, d=-2)
d = Counter(a=1, b=2, c=3, d=4)
c.subtract(d) # c - d
print(c)
# Counter({'a': 3, 'b': 0, 'c': -3, 'd': -6})
print(c + d)
# Counter({'a': 4, 'b': 2})
print(c & d)
# Counter({'a': 1})
print(c | d)
# Counter({'d': 4, 'a': 3, 'c': 3, 'b': 2})- Word Counter의 기능도 손쉽게 제공
text = """A press release is the quickest and easiest way to get free publicity.
If well written, a press release can result in multiple published articles about your firm and its products.
And that can mean new prospects contacting you asking you to sell to them. ....""".lower().split()
print(Counter(text))
print(Counter(text)["a"])Counter({'and': 3, 'to': 3, 'a': 2, 'press': 2, 'release': 2, 'can': 2, 'you': 2, 'is': 1, 'the': 1, 'quickest': 1, 'easiest': 1, 'way': 1, 'get': 1, 'free': 1, 'publicity.': 1, 'if': 1, 'well': 1, 'written,': 1, 'result': 1, 'in': 1, 'multiple': 1, 'published': 1, 'articles': 1, 'about': 1, 'your': 1, 'firm': 1, 'its': 1, 'products.': 1, 'that': 1, 'mean': 1, 'new': 1, 'prospects': 1, 'contacting': 1, 'asking': 1, 'sell': 1, 'them.': 1, '....': 1})
214) NamedTuple
- Tuple 형태로 Data 구조체를 저장하는 방법
- 저장되는 Data의 Variable을 사전에 지정해서 저장
from collections import namedtuple
Point = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])
p = Point(11, y=22)
print(p[0] + p[1])
x, y = p
print(x, y)
print(p.x + p.y)
print(Point(x=11, y=22))33
11 22
33
Point(x=11, y=22)from collections import namedtuple
import csv
f = open("users.csv", "r")
next(f)
reader = csv.reader(f)
student_list = []
for row in reader:
student_list.append(row)
print(row)
coloumns = ["user_id", "integration_id", "login_id", "password", "first_name",
"last_name", "full_name", "sortable_name", "short_name",
"email", "status"]
Student = namedtuple('Student', " ".join(coloumns))
student_namedtupe_list = []
for row in student_list:
student = Student(*row)
student_namedtupe_list.append(student)
print(student_namedtupe_list)
print(student_namedtupe_list[0].full_name)
