File 클래스 (java.io)
- 파일/디렉토리 경로를 다루는 객체, 기능 제한적.
| 메서드 | 기능 |
|---|---|
exists() | 존재 여부 확인 |
isFile() / isDirectory() | 파일/디렉토리 여부 |
mkdir() / mkdirs() | 디렉토리 생성 |
delete() | 삭제 |
renameTo(File dest) | 파일 이름 변경 or 이동 |
length() | 파일 크기 |
getName() / getPath() / getAbsolutePath() | 파일 정보 |
Files 클래스 (java.nio.file.Files)
- 파일을 직접 조작하는 유틸 클래스(static 메서드)
- 경로는 반드시 Path 타입으로 다뤄야 함 → Paths.get("경로")로 만들 수 있음
여기 눌러 참고
- 복사, 이동, 스트림 처리, 속성 조회까지 다 됨
- 실패 시 명확하게 예외 발생
- Path, WatchService, FileChannel 등과 잘 연동되고,
StandardCopyOption, LinkOption 등으로 다양한 옵션 처리 가능
| 메서드 | 기능 |
|---|---|
readAllBytes(Path) | 파일 읽기 |
write(Path, byte[]) | 파일 쓰기 |
copy(Path, Path, 옵션) | 복사 |
move(Path, Path) | 이동 |
delete(Path) | 삭제 |
createFile(Path), createDirectories(Path) | 생성 |
size(), getLastModifiedTime(), isReadable() 등 | 정보 조회 |
renameTo() vs Files.move()
| 구분 | renameTo() | Files.move() |
|---|---|---|
| 위치 | File 클래스 | Files 클래스 |
| 리턴 | 성공 여부 (true/false) | 예외 발생 방식 |
| 기능 | 이름 변경 또는 이동 | 이름 변경, 이동, 옵션 다양 |
| 신뢰성 | OS 종속적, 실패 빈도 높음 | 안정적, 예외로 문제 파악 가능 |
Files vs File 요약
| 항목 | File | Files |
|---|---|---|
| 용도 | 경로 관리 | 실제 파일 조작 |
| 기능 | 기본적인 경로 정보와 생성/삭제 | 읽기/쓰기/복사/이동 등 실무 작업 |
| 방식 | 객체 기반 | 정적 유틸리티 메서드 |
| 함께 쓰는 것 | - | Path, Paths, StandardCopyOption 등 |
✅ 자바 IO vs NIO
Files vs FileOutputStream / FileInputStream
| 항목 | Files | FileInputStream / FileOutputStream |
|---|---|---|
| 용도 | 간단하고 빠른 전체 파일 조작 | 스트림 기반의 세밀한 데이터 처리 |
| 기능 | 한 번에 파일 읽기/쓰기/복사/이동 등 | 바이트 단위로 읽고 쓰기, 스트림 연동 |
| 단순 작업 | ✅ 매우 쉬움 (readAllBytes, write) | ❌ 반복문, 버퍼 직접 처리 필요 |
| 대용량 처리 | ❌ 부적합 (메모리에 한 번에 올림) | ✅ 적합 (스트리밍 처리 가능) |
| 사용 방식 | 정적 유틸리티 (static) | 객체 기반 (입출력 스트림 생성) |
| 예외 처리 | 깔끔함 (IOException) | 비슷하지만 코드 길어짐 |
예제 코드
Files : 간단하고 빠른조작
- 단순 텍스트, 설정 파일, 작은 이미지 처리에 유리
- 코드 짧고 간편
// 전체 파일을 한 번에 읽기
byte[] data = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("a.txt"));
// 전체 파일을 한 번에 쓰기
Files.write(Paths.get("b.txt"), data);
FileInputStream / FileOutputStream :세부제어
- 대용량 파일 복사, 네트워크 전송, 스트림 필터링 등
- 데이터 조각 처리(버퍼)가 가능해서 성능 조절 가능
try (FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("a.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream("b.txt")) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int length;
while ((length = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, length);
}
}
Paths 클래스
- 문자열 경로를 Path 클래스로 바꿔주는 헬퍼클래스임 / 유틸클래스
예) Path path = Paths.get("C:/data/info.txt");
- 상대경로, 절대경로,조합경로 가능
- Paths.get(...)는 Path.of(...) 로도 대체 가능함 (Java 11+)
- Path 객체 생성용이므로 파일조작은 안됨
왜 씀? 왜 Path로 바꿔줌?
- Files 클래스는 문자열이 아니라 Path 객체가 필요함
// 예시 코드
Path path = Paths.get("data/test.txt"); // 문자열 → Path
Files.exists(path); // 존재 확인
Files.readAllBytes(path); // 파일 내용 읽기
Path 클래스
- 파일이나 디렉토리의 경로 정보를 표현하는 객체 / 경로조작 기능제공
- 생성방식 : Paths.get("경로") or Path.of("경로")
- 문자열 ㄴㄴ 경로를 논리적으로 다룸
- 경로 결합, 절대 경로 변환, 상대 경로 ㄱㄴ
Path vs File
| 구분 | File | Path |
|---|---|---|
| 도입 시점 | 오래됨 (Java 1.0) | Java 7부터 |
| 설계 목적 | 경로 + 파일 정보 | 경로 자체에 집중 |
| 조작 기능 | 제한적 (복사/이동 없음) | 풍부 (resolve, normalize, relativize) |
| API 연동 | java.io | java.nio.file (Files 등과 함께 사용) |
기존IO File 클래스를 활용했다면
TODO : Files 유틸클래스를 활용해서 빠르고 간결하게 바이너리파일을 읽고 써보기로 함
- 기존 임의로 만든 FileUtil 클래스의 중복 체크 로직은 사용해야됨 파일 조회 후 write 시 이름중복해주는 메서드는 없기때문
- 스케쥴러 클래스 수정 부분
-
저장할 파일데이터를 byte[] 로 가져오기
byte[] filesdata = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filePath).resolve(file.getName()));
---> .resolve: 하위 파일명까지 붙여줘야됨 또는 Paths.get() 인자 두개 넣기 file.getName()
요렇게 :byte[] filesdata = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filePath,file.getName())); -
insert 후 파일을 성공경로로 이동시킴 origin -> target
두 Path는 파일명까지 포함해야함
Path originPath = Paths.get(file.getPath());
Path targetPath = Paths.get(succsessDir.getPath() , file.getName());
Files.move(originPath,targetPath); -
다운로드 메서드의 try catch 문 중 try 내부의
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(target)주석처리 후 try{ 내부에
Files.write(Paths.get(target.getPath()),vo.getFileData());써줌
target 은 다운로드 경로에 같은이름의 파일이있는지 체크하는 로직 후 File 로 리턴받은 값이다.
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0/3 * * * ?") // 3분 주기
public void uploadBinaryFile() throws Exception {
//File 객체를 이용해서 파일이 존재하는지, 읽기 가능한지, 바이트로 읽을지 등을 처리
File dir = new File(filePath); // 경로 담는 객체
File succsessDir = new File(filePath + "/succsess"); //성공시 디렉토리
File failDir = new File(filePath + "/fail"); //실패시 디렉토리
if(!dir.isDirectory() || !dir.exists()) return;
File[] files =dir.listFiles(); // 파일 리스트 가져옴
if(files !=null){
for(File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
try{
// TO DO : NIO 방식
// Files 유틸 사용 (빠르게 읽고쓰기 가능) .resolve - 하위 파일명 붙여줘야됨 또는 Paths.get() 인자 두개 넣기 file.getName()
byte[] filesdata = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get(filePath).resolve(file.getName()));
byte[] data = FileUtil.readFileToByteArray(file);
log.info("처리중 파일 : " + file.getName());
FileVO vo = new FileVO();
// 시퀀스 받아오기
vo.setFileId(fileService.getFileId());
vo.setFileName(file.getName());
vo.setFileType("application/octet-stream"); // 파일의 MIME 타입지정 - 바이너리파일이라는뜻
// vo.setFileData(data); //IO
vo.setFileData(filesdata); // NIO
fileService.insertBinaryFile(vo);
/* 완료된파일 이동시키기
File dest = new File(file.getParent() + "/processed/" + file.getName());
file.renameTo(dest);
*/
/* 저장 완료 후 파일 이동시킴 -- 사용자 유틸클래스
if(FileUtil.moveFile(file, succsessDir)) log.info("파일이동 성공" + file.getName());
else log.info("파일이동 실패" + file.getName());
*/
// NIO 방식 (originPath 는 파일명포함한 경로) 해서 targetPath(성공경로+현재파일명)으로 넘긴다.
Path originPath = Paths.get(file.getPath());
Path targetPath = Paths.get(succsessDir.getPath() , file.getName());
try {
Files.move(originPath,targetPath);
log.info("업로드성공 파일 이동" + file.getName());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("파일이동실패" ,e);
// TODO: handle exception
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
// if(FileUtil.moveFile(file, failDir)) log.info("업로드실패로인한 파일 실패경로 이동" + file.getName());
log.info("업로드실패로인한 파일 실패경로 이동" + file.getName());
}
}
}
}
}
@Scheduled(cron = "0 0/5 * * * ?") // 5분 주기
public void downLoadBinaryFile() throws Exception {
List<FileVO> files = fileService.selectBinaryFile();
if(files !=null){
for(FileVO vo : files){
File target = FileUtil.getFileDupChk(new File(downloadPath), vo.getFileName());
/* IO
File target = new File(downloadPath,vo.getFileName());
try(FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(target)) {
fos.write(vo.getFileData());
*/
// NIO
try{
Files.write(Paths.get(target.getPath()),vo.getFileData());
log.info("다운로드 완료"+target.getAbsolutePath()); //
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.info("다운로드 실패"+ vo.getFileName());
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
}아래는 db 저장(업로드) / 파일이동 / db 조회 바이너리파일 로컬 다운로드
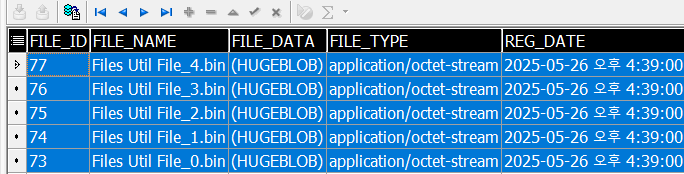
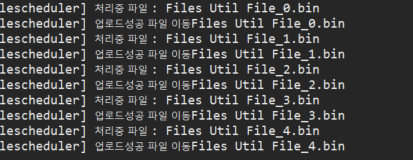
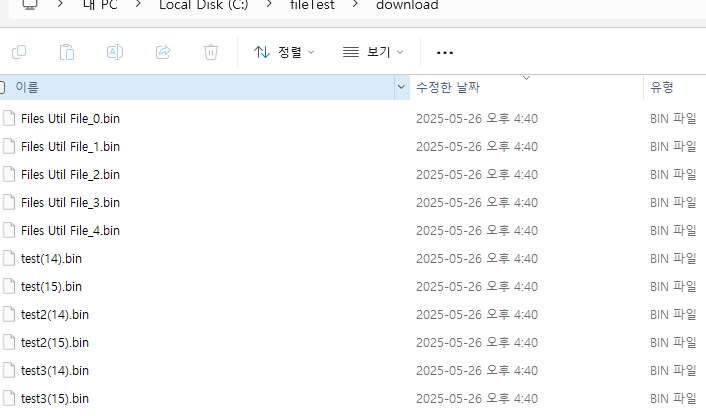
Files.move(originPath,targetPath);
db저장 후 파일이동하면서 계속 파일경로 에러는 나는데 insert 가 쳐지니까
롤백이 안되어서
try {
Files.move(originPath,targetPath);
log.info("업로드성공 파일 이동" + file.getName());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("파일이동실패" ,e);
// TODO: handle exception
}클래스에 @Tracnsactional 어노테이션달아도 Exception 을 던져줘야 rollback됨
rollbackFor = Exception.class) 어노테이션 수정
-> 안됨。。ㅋ
service 단에 넘겨야될듯
서비스로직 수정
@Override
public void insertBinaryFile(FileVO vo, File file) throws Exception {
fileMapper.insertBinaryFile(vo);
try {
Path originPath = Paths.get(file.getPath(),"ddsdfsd");
Path targetPath = Paths.get("C:/fileTest/upload/succsess",file.getName());
Files.move(originPath,targetPath);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException("파일이동실패로인한 업로드실패",e);
}
}Path originPath = Paths.get(file.getPath(),"ddsdfsd");
이부분은 억지로 exception 날리기위한 경로를 잘못 입력함
올바른 코드는 Path originPath = Paths.get(file.getPath());
- tracntion설정 xml 가서 포인트컷 포함되는지 확인해줘야됨 또는 tx-driven 태그 확인
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" rollback-for="Exception"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="requiredTx" expression="execution(* 패키지 .*Impl.*(..))
|| execution(* 패지지.*Impl.*(..))"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="requiredTx" />
</aop:config>- 서비스 클래스에 어노테이션
@Service
@Transactional - 예외가 RuntimeException 이어야 Rollback 됨
기본적으로 RuntimeException (또는 그 하위)만 rollback 트리거 됨.
