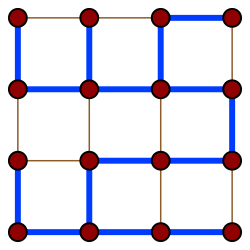
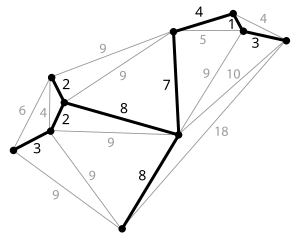
1. 신장 트리 (Spanning Tree)
무방향 그래프에서 모든 정점을 포함하며, 사이클이 없는 부분 그래프
위 그림에서 파란색으로 색칠된 부분이 신장 트리 (출처)
2. 최소 신장 트리 (Minimum Spanning Tree)
위에서 살펴본 신장 트리중에서 간선의 가중치의 합이 최소가 되는 트리
위 그림에서 검은색으로 색칠된 부분이 최소 신장 트리 (출처)
3. MST를 생성하는 알고리즘
1) Kruskal
유니온 파인드 자료구조를 활용한 MST생성
- 가중치가 최소인 간선을 선택
- 해당 간선을 연결해도 사이클이 형성되지 않을 경우에 연결
- 여기서 Union Find을 통해서 사이클 여부를 확인할 수 있음.
- 해당 간선의 목표인 정점들의 부모가 같다 -> 이미 연결 되어있다 -> 이 간선을 연결하면 사이클이 형성된다
- Union 연산에서 두 정점의 부모가 다를때만 합치기
- 여기서 Union Find을 통해서 사이클 여부를 확인할 수 있음.
int Find(int x) { if (parents[x] == x) return (x); return Find(parents[x]); } void Union(int a, int b, int& answer, int& cost) { int A = Find(a); int B = Find(b); if (A!=B) { if (A < B) parents[B] = A; else parents[A] = B; answer += cost; } }
2) Prim
임의의 정점에서 시작해 MST를 구성하는 방법
- 임의의 정점 선택
- 해당 정점(들)과 이어진 간선의 가중치중 최소 값을 가진 간선 선택
- 위에서 결정된 정점 신장 트리에 추가
- 모든 정점이 추가될 때까지 2,3 반복
#include <string> #include <vector> #include <unordered_set> #include <queue> using namespace std; struct ComaparePair { bool operator()(pair<int, int> a, pair<int, int> b) { // 누가 우선순위가 높은지 // true인 경우 b가 a보다 우선순위가 높음 return a.second > b.second; } }; int solution(int n, vector<vector<int>> costs) { int answer = 0; vector<vector<pair<int, int>>> edges(100); priority_queue<pair<int,int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, ComaparePair> pq; unordered_set<int> mst; for(int i = 0; i < costs.size(); ++i) { int from = costs[i][0]; int to = costs[i][1]; int cost = costs[i][2]; edges[from].push_back({to, cost}); edges[to].push_back({from, cost}); } pq.push({0,0}); while(mst.size() < n) { int current_node = pq.top().first; int current_cost = pq.top().second; pq.pop(); if (mst.count(current_node) != 0) continue; mst.insert(current_node); answer += current_cost; for (int i = 0; i < edges[current_node].size(); ++i) { int next_node = edges[current_node][i].first; int next_cost = edges[current_node][i].second; if (mst.count(next_node == 0)) pq.push({next_node, next_cost}); } } return answer; }