
launch
fun main(){
runBlocking {
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).launch {
delay(100)
throw IllegalArgumentException()
}.join()
}
}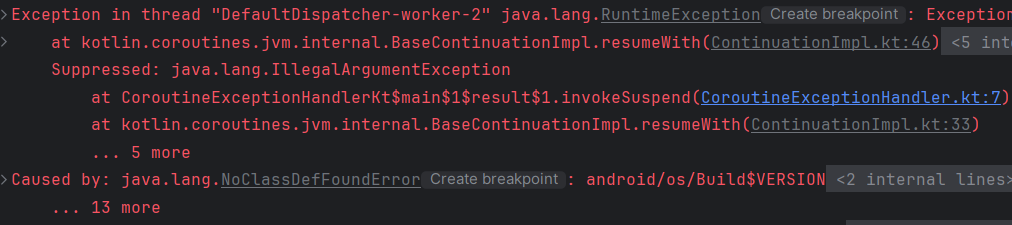
launch 내부에서 exception이 throw된 시점에 exception을 throw한다.
async
fun main() = runBlocking {
val result = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).async {
delay(100)
throw RuntimeException()
}
Thread.sleep(1000)
}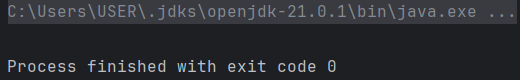
exception이 throw 되지 않는다!
async는 미래의 값을 담아놓는 Deffered를 반환한다. 위의 코드에서는 미래의 값을 필요로 하지 않기 때문에 예외를 throw 할 필요가 없다.
async + await
다음과 같이 코드를 구성하면 예외가 발생한다.
fun main(){
runBlocking {
val result = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).async {
delay(100)
throw RuntimeException()
}
result.await()
}
}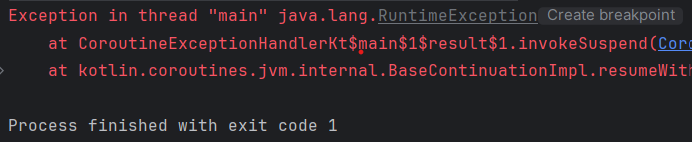
아래의 경우에서는 exception을 handling 할 수 있을까?
val exceptionHandler = CoroutineExceptionHandler { coroutineContext, throwable ->
println("exception context: $coroutineContext throwable: $throwable")
}
fun main() {
runBlocking {
val result = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default + exceptionHandler).async {
delay(100)
throw RuntimeException()
}
result.await()
}
}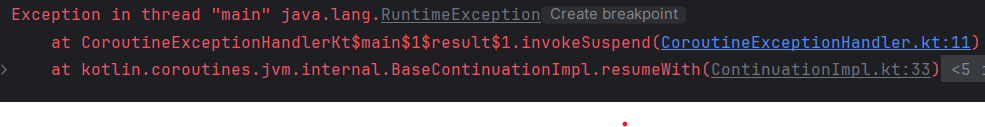
할 수 없다! 왜냐하면 await 시점에서 exception이 throw되기 때문에 exception을 handling 할 수 없다.
아래의 코드와 같이 await 시점에서 catch를 해주어야 exception을 hadling 할 수 있다.
fun main() {
runBlocking {
val result = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default + exceptionHandler).async {
delay(100)
throw RuntimeException()
}
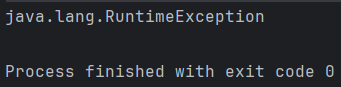
runCatching {
result.await()
}.onFailure {
println(it)
}
}
}
asnyc + join
아래의 코드에서는 exception이 throw 될 까?
fun main(){
runBlocking {
val result = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).async {
delay(100)
throw RuntimeException()
}
result.join()
}
}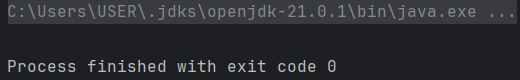
exception을 throw하지 않는다.
join의 경우에는 isCancelled(), getCancellation()을 통해 exception을 가져올 수 있다.
fun main(){
runBlocking {
val result = CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default).async {
delay(100)
throw IllegalArgumentException()
}
result.join()
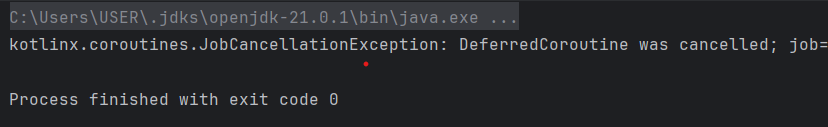
if(result.isCancelled){
println(result.getCancellationException())
}
}
}
정리
launch()는 coroutine builder 내부에서 exception이 발생하면, 즉시 상위로 에러를 전파한다.asnyc()는 exception를 바로 throw하지 않는다.await()시점에서 누적된 exception을 throw한다.join()자체로는 예외를 throw하지 않는다.isCancelled()와getCancellation()을 통해 에러 처리를 해주어야한다.
