
Coroutine에서 Exception이 발생한다면?
- coroutine은 exception이 발생하면 해당 coroutine을 취소하고, 해당 exception을 부모 coroutine으로 전파한다.
- exception을 전파받은 부모 coroutine은 다른 자식 coroutine들을 취소시키고 다시 부모 coroutine으로 exception을 전달한다.
- 위 과정을 최상위 coroutine까지 전달한다.
Exception을 handling하는 방법
CoroutineExceptionHandler
- coroutine내의 코드 실행 중 발생하는 exception을 처리할 수 있는 handler이다.
- 아래의 코드는 exception을 catch할 수 있을까?
suspend fun main() {
val exceptionHandler = CoroutineExceptionHandler { coroutineContext, throwable ->
println("exception context: $coroutineContext throwable: $throwable")
}
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default) .launch {
launch(exceptionHandler) {
delay(3000)
throw Throwable()
}
launch {
delay(4000)
println("im second coroutine")
}
}.join()
}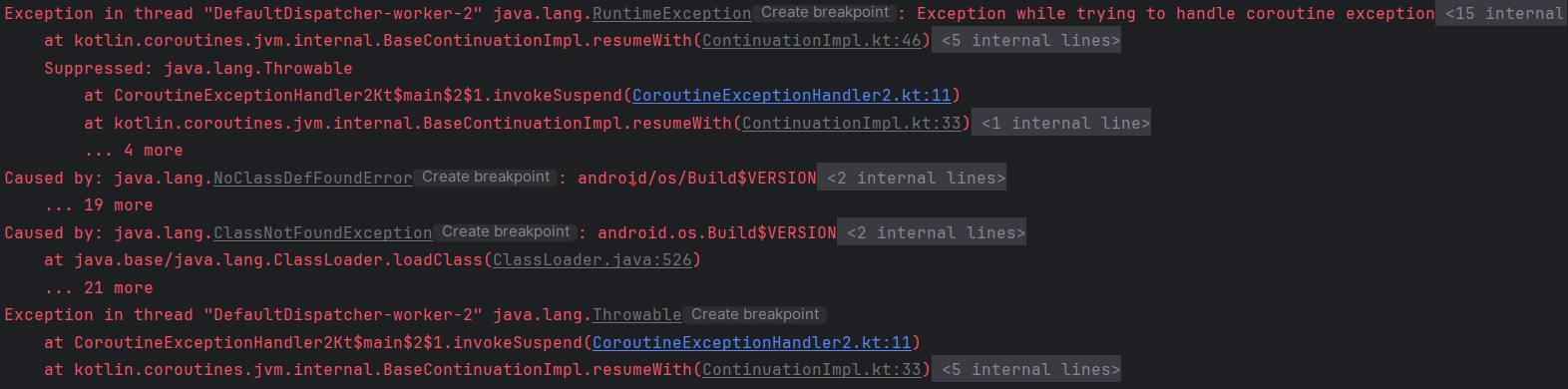
정답은 할 수 없다.이다.
위에서 언급했듯이 자식 coroutine에서 발생한 exception은 부모 coroutine으로 전파되기 때문에 exception을 catch 할 수 없다.
suspend fun main() {
val exceptionHandler = CoroutineExceptionHandler { coroutineContext, throwable ->
println("exception context: $coroutineContext throwable: $throwable")
}
CoroutineScope(Dispatchers.Default + exceptionHandler) .launch {
launch {
delay(3000)
throw Throwable()
}
launch {
delay(4000)
println("im second coroutine")
}
}.join()
}다음과 같이 부모 coroutine에 exception handler를 설정해주어야 exception을 catch 할 수 있다.

실행 결과를 보면 im second coroutine이라는 문구가 출력되지 않았다. 이유가 무엇일까?
위에서 언급했듯이 coroutine은 exception을 catch 하든 하지 않든 exception이 발생하면 다른 자식 coroutine들을 취소한다.
exception 발생 여부에 따라 다른 자식 coroutine들이 취소되지 않게 만들기 위해서는 어떻게 해야할까?
SupervisorJob
- SupervisorJob은 자식 coroutine에게 발생하는 exception을 부모로 전달시키지 않고, exception이 발생하지 않은 corotuine을 취소하지 않기 위해 사용한다.
/**
Job
**/
fun main(): Unit = runBlocking {
launch {
val supervisorJob = SupervisorJob()
launch {
delay(1000)
throw Error("Some error")
}
launch {
delay(2000)
println("Second Coroutine")
}
supervisorJob.join()
}
}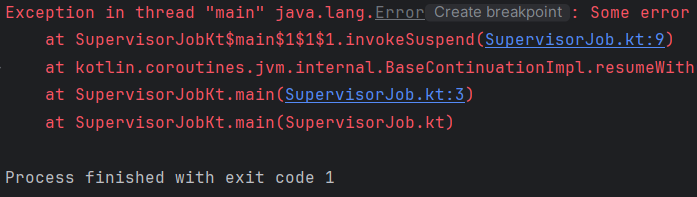
error 발생 후 Second Coroutine이 출력되지 않고 종료된다.
/**
SupervisorJob
**/
fun main(): Unit = runBlocking {
launch {
val supervisorJob = SupervisorJob()
launch(supervisorJob) {
delay(1000)
throw Error("Some error")
}
launch {
delay(2000)
println("Second Coroutine")
}
supervisorJob.join()
}
}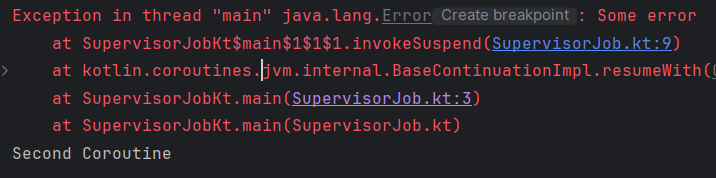
exception이 발생하더라도 다른 자식 coroutine이 취소되지 않고 Second Coroutine이 출력된다!
