4학년 1학기에 Information Security 수업을 듣고, 정리한 내용이다.
Computer security concepts
Key Security Concepts
1. Confidentiality
- Preserving authorized restrictions on information access and disclosure, including means for protecting personal privacy and proprietary(독점적인) information
- 정보가 기밀로 유지되어야 하며, 인증되지 않은 어떤 개인에게도 정보의 열람은 엄격하게 규제되어야 함
2. Integrity
- Guarding against improper information modification or destruction
- 부적절한 정보의 수정을 막는 것 → 데이터는 원본 그대로 지켜져야 함
3. Availability
- Ensuring timely and reliable access to and use of information
- 인증된 사용자가 정보를 확인하고 싶을 때 언제나 정보가 접근가능 해야 함
4. Authenticity
- Verifying: User who they are, Data is from trusted source
- Confidence in the validity of a transmission, a message, or message originator
- 개인이 자신을 인증하는 것에 대한 증명
5. Accountability
- Traceability of entities to find possible security breaches
- Must keep records of their activities to permite later forensic anlysis
- (ex) log information, 예를 들어 해커가 어떻게 접근했는지 알 수 있어야 함
Levels of Impact by the Loss of Security Properties
- 한 프로퍼티가 damage에 의해 영향을 받았을 때, degree of impact에 의해 level을 classify 가능
- Low(easily cover possible) → Moderate → High(very critical damage)
Computer Security Challenges
- Attackers only need to find a single weakness, the developer needs to find all weaknesses
- Users and system managers tend to not see the benefits of security until a failure occurs
- Thought of as an impediment to efficient and user-friendly operation
- Security requires regular and constant monitoring
- Is often an afterthought to be incorporated into a system after the design is complete
- IT system은 먼저 design 된 다음 security를 고려하는 경우가 많다. Security고려는 design 단계에 포함해야 한다.
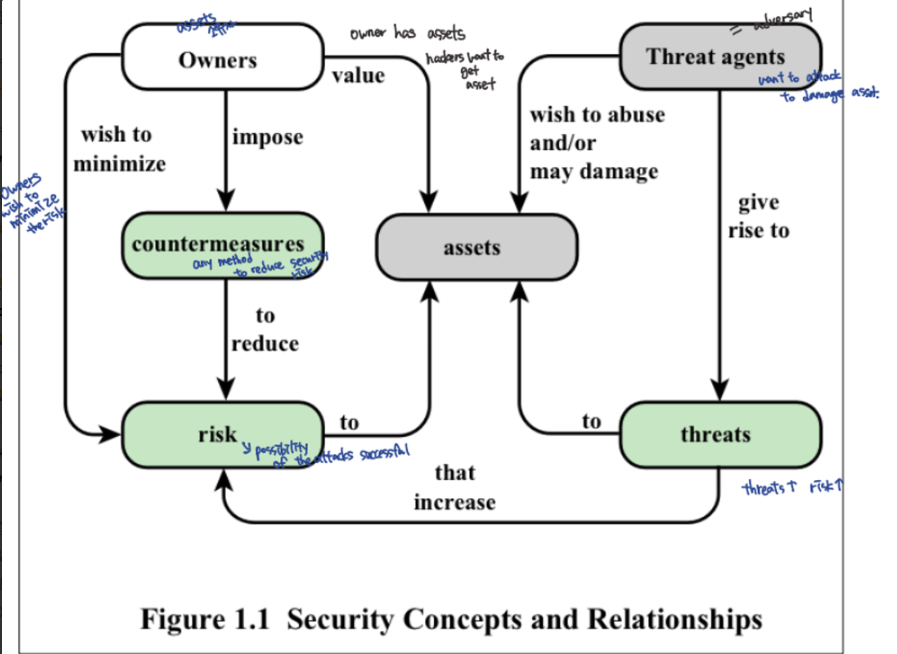
Computer Security Concepts and Relationships
Adversary(=threat agent): An entity that attacks, or is a threat to, a systemAttack: An assault on system security that derives from an intelligent threatCountermeasure: An action, device, procedure, or technique that reduces a threat by eliminating or preventing it, by minimizing the harm it can cause, or by discovering and reporting it so that corrective action can be taken- means used to deal with security attacks
- Goal: to minimize residual level of risk to the assets
- Problem: residual vulnerabilities may remain, May itself introduce new vulnerabilities
Risk: Probability that a particular threat will exploit a particular vulnerability with a particular harmful resultAsset: The thing which should be protected- Hardware, Software, Data, Communication facilities and networks
Threats, Assets, Attacks
Vulnerabilities, Threats, and Attacks
- Categories of vulnerabilities
- Corrupted (loss of integrity)
- Leaky (loss of confidentiality)
- Unavailable or very slow (loss of availability)
- Threats
- Capable of exploiting vulnerabilities
- Represent potential security harm to an asset
- Attacks (threats carried out)
- Passive/Active
- Passive Attack
- Attempts to learn or make use of information from the system but does not affect system resources
- Eavesdropping on, or monitoring of, transmissions
- Goal of attacker is to obtain information that is being transmitted
- Two types:
- release of message contents
- traffic analysis
- Active Attack
- Attempts to alter system resources or affect their operation
- Involve some modification of the data stream or the creation of a false stream
- Four categories
- Replay
- Masquerade
- Modification of messages
- Denial of service
- Passive Attack
- Insider/Outsider
- Passive/Active
Threat Consequences and Attacks
1. Unauthorized Disclosure
- A circumstance or event whereby an entity gains unauthorized access to data 무단으로 데이터에 접근하여 데이터가 의도하지 않은 대상에게 노출되는 상황
- Threat Action
- Exposure(노출)
- Exposing sensitive data to unauthorized entity
- Interception(가로채기)
- Accessing sensitive data traveling between authorized source and destination
- Inference(추론)
- Indirectly accessing sensitive data by either reasoning from characteristics or byproducts of communication
- Intrusion(침입)
- An unauthorized entity gains an access to sensitive data by circumventing(우회적인) a systems’s security protections
- Exposure(노출)
2. Deception(속임수)
- A circumstance or event that may result in an authorized(권한이 있는) entity receiving false data and believing it to be true
- Threat Action
- Masquerade(가장)
- Attacks with posing as an authorized entity.(권한이 있는 엔티티로 가장하여 공격)
- ex) Phishing, Spoofing
- Falsification(위조)
- False data deceives an authorized entity.
- ex) 거래 기록 조작, 위조된 문서
- Repudiation(부인)
- An entity deceives another by falsely denying responsibility
for an act(한 엔티티가 특정 행위에 대한 책임을 거짓으로 부인하는 것) - ex) 전자 메일이나 문서에 대한 작성자가 자신이 해당 문서를 작성하지 않았다고 부인하는 경우
- An entity deceives another by falsely denying responsibility
- Masquerade(가장)
3. Disruption(중단)
- A circumstance or event that interrupts or prevents the correct operation(작동)of a system services and functions
- Threat Action
- Incapacitation(무력화)
- Prevents or interrupts system operation by disabling(비활성화) a system component
- Corruption(손상)
- Undesirably(원치 않게) alter system operation by adversely(불리하게) modifying system functions or data
- 소프트웨어 코드 악의적인 수정, 설정 변경 등
- Obstruction(방해)
- A threat action that interrupts delivery of system services by hindering(방해하다) system operation
- ex) 네트워크 트래픽의 과부하, DoS공격
- Incapacitation(무력화)
4. Usurpation(착취)
- A circumstance or event that results in control of system services or functions by unauthorized entity 시스템 서비스나 기능의 제어권이 권한이 없는 엔티티에 의해 획득되는 상황이나 사건
- Threat Action
- Misappropriation(불법 사용)
- An entity assumes unauthorized logical or physical control of a system resource
- 공격자가 비밀번호를 도용하여 시스템에 무단 접근하는 등
- Misuse(오용)
- Causes a system component to perform a function or service that is detrimental(해로운) to system security
- 정상적인 프로세스를 중단시키거나, 불법적인 데이터 처리를 수행하는 등
- Misappropriation(불법 사용)
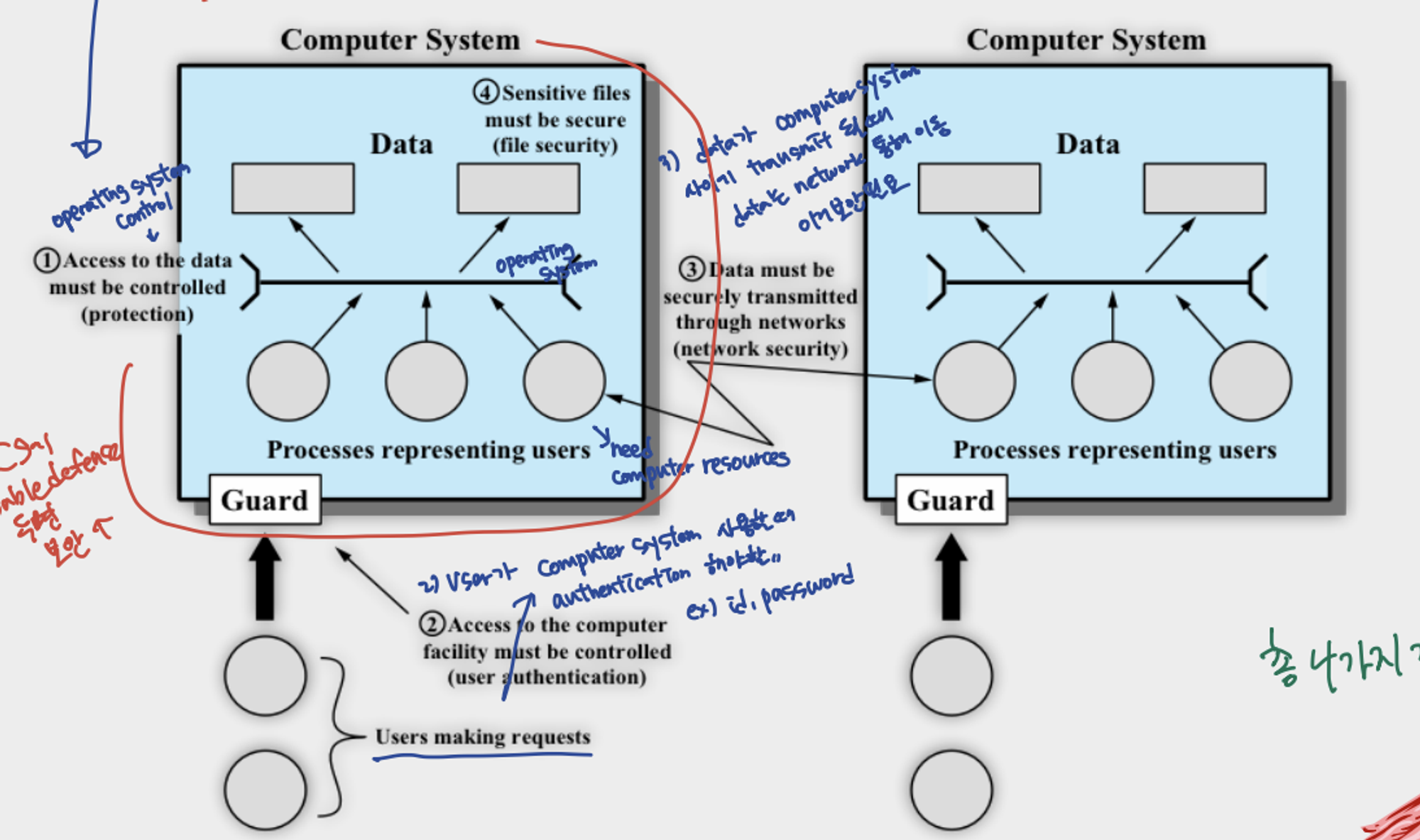
Scope of Computer Security
- 앱이 시작될 때, Process need computer resources → operating system have to do protection access to the data resouces inside of computer system from processes
- When user makes request for computer system, have to perform user authentication, which access to the computer facility must be controlled
- Network security: Data must be securely transmitted through networks
- File security: Sensitive files must be secure
Fundamental security design principles
Economy of mechanism(경제성의 원칙)
- every security mechanism should be efficient and intuitive because if it is inefficient, then affect the performance underlying the target system to protect
- 보안 메커니즘은 효율적이고 직관적이어야 함. 복잡, 비효율적인 보안 메커니즘은 시스템의 성능을 저하시킬 수 있으며, 이로 인해 보호하고자 하는 대상 시스템의 목적에 영향을 줄 수 있음
Fail-safe defaults(실패 안전 기본값)
- bad situation → should accept any output
- 안전하지 않은 상황이 발생하면 → 시스템은 기본적으로 안전한 상태로 돌아가거나, 최소한의 권한만을 부여해야 함
Complete mediation(완전 중재)
- every access to resources should be checked by based security
- 시스템의 모든 리소스 접근은 반드시 보안 검사를 거쳐야 함
Open design(개방형 설계)
- design should be opened public
- 보안 시스템의 설계와 구현은 공개적이어야 함
Separation of privilege(권한의 분리)
- 단일 권한에 의존하는 것이 아니라 다양한 권한의 조합을 통해 보안을 강화해야 함
Least privilege(최소 권한)
- in order to do some task, need to give user less privilege possible so that hacker can do as small thing
- 특정 작업을 수행하기 위해 필요한 최소한의 권한만을 사용자에게 부여하여, 공격자가 시스템을 악용할 수 있는 범위를 최소화
Least common mechanism(최소 공통 메커니즘)
- security module has less code as possible
- 보안 메커니즘은 가능한 최소한의 코드로 구성되어야 함. 공통적으로 사용하는 메커니즘이 많을수록 공격 가능한 범위가 넓어짐
Psychological acceptability(심리적 수용성)
- anny security module should be psychologically acceptable
- 사용자가 쉽게 이해하고 사용할 수 있어야 함
Isolation
- important asset should be seperate from public resource
- multi user system user cannot access other user resource
Encapsulation
- 캡슐화를 통해 데이터와 기능의 노출을 최소화
Modularity
- 보안 메커니즘은 독립적인 모듈로 설계되어야 하며, 각 모듈은 단일 기능에 초점을 맞춰야 함
Layering
- defense should be layered
- 각 계층은 시스템을 보호하기 위한 추가적인 장벽을 제공하며, 한 계층의 보안이 뚫려도 다른 계층이 시스템을 보호할 수 있음
Least astonishment
- user interface should be always respond astonish to the user
- 사용자 인터페이스는 사용자가 예상하는 방식으로 항상 반응해야 하며, 이 원칙은 사용자 인터페이스가 사용자에게 익숙하고 예측 가능해야 함을 의미함