애플 공식 문서 바탕으로 정리합니다!
String Indices
: Each String value has an associated index type, String.Index, which corresponds to the position of each Character in the string.
- Use the startIndex property to access the position of the first Character of a String.
- The endIndex property is the position after the last character in a String.
- index(before:)
- index(after:)
- index(_:offsetBy:)
let greeting = "Guten Tag!"
greeting[greeting.startIndex]
// G
greeting[greeting.index(before: greeting.endIndex)]
// !
greeting[greeting.index(after: greeting.startIndex)]
// u
let index = greeting.index(greeting.startIndex, offsetBy: 7)
greeting[index]
// a- Use the indices property to access all of the indices of individual characters in a string.
for index in greeting.indices {
print("\(greeting[index]) ", terminator: "")
}
// Prints "G u t e n T a g ! "Inserting and Removing
- insert(_:at:)
- insert(contentsOf:at:)
var welcome = "hello"
welcome.insert("!", at: welcome.endIndex)
// welcome now equals "hello!"
welcome.insert(contentsOf: " there", at: welcome.index(before: welcome.endIndex))
// welcome now equals "hello there!"- remove(at:)
- removeSubrange(_:)
welcome.remove(at: welcome.index(before: welcome.endIndex))
// welcome now equals "hello there"
let range = welcome.index(welcome.endIndex, offsetBy: -6)..<welcome.endIndex
welcome.removeSubrange(range)
// welcome now equals "hello"Substrings
substring은 String과 다르게 String에 대한 작업을 수행하는 아주 짧은 시간동안만 사용한다.만약 더 길게 사용하고 싶다면 substring을 아예 새로운 String으로 만들어 줘야 한다.
let greeting = "Hello, world!"
let index = greeting.firstIndex(of: ",") ?? greeting.endIndex
let beginning = greeting[..<index]
// beginning is "Hello"
// Convert the result to a String for long-term storage.
let newString = String(beginning)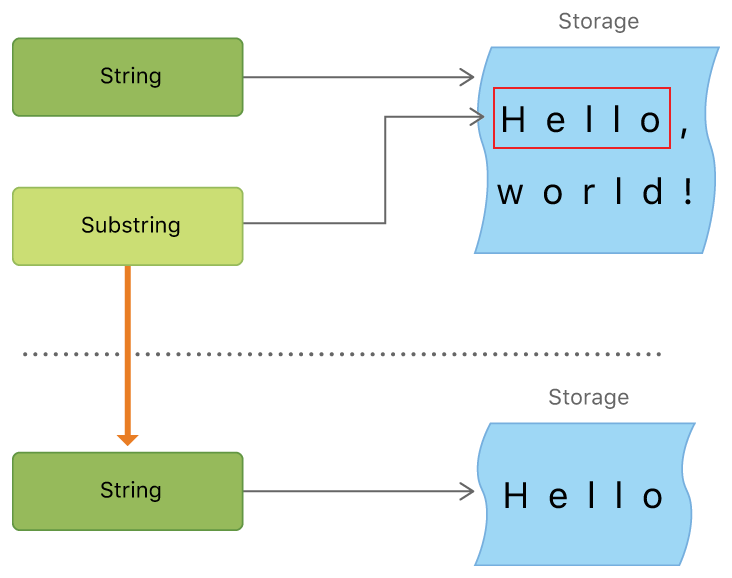
string "Hello, world!"의 "Hello"가 substring으로 가지고 있다. 이때 substring은 기존의 string의 메모리를 재사용한다.
substring이 새로운 string로 만들어주면 자체적으로 메모리를 가진다.
Prefix and Suffix Equality
: To check whether a string has a particular string prefix or suffix, call the string’s hasPrefix(:) and hasSuffix(:) methods, both of which take a single argument of type String and return a Boolean value.
let romeoAndJuliet = [
"Act 1 Scene 1: Verona, A public place",
"Act 1 Scene 2: Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 3: A room in Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 4: A street outside Capulet's mansion",
"Act 1 Scene 5: The Great Hall in Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 1: Outside Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 2: Capulet's orchard",
"Act 2 Scene 3: Outside Friar Lawrence's cell",
"Act 2 Scene 4: A street in Verona",
"Act 2 Scene 5: Capulet's mansion",
"Act 2 Scene 6: Friar Lawrence's cell"
]
var act1SceneCount = 0
for scene in romeoAndJuliet {
if scene.hasPrefix("Act 1 ") {
act1SceneCount += 1
}
}
print("There are \(act1SceneCount) scenes in Act 1")
// Prints "There are 5 scenes in Act 1"
var mansionCount = 0
var cellCount = 0
for scene in romeoAndJuliet {
if scene.hasSuffix("Capulet's mansion") {
mansionCount += 1
} else if scene.hasSuffix("Friar Lawrence's cell") {
cellCount += 1
}
}
print("\(mansionCount) mansion scenes; \(cellCount) cell scenes")
// Prints "6 mansion scenes; 2 cell scenes"