
🙄빈 스코프란?
- ✔️스프링이 지원하는 스코프
- 싱글톤 : 기본 스코프, 스프링 컨테이너의 시작과 종료까지 유지되는 가장 넓은 범위의 스코프이다.
- 프로토타입 : 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈의 생성과 의존관계 주입까지만 관여하고 더는 관여하지 않는 매우 짧은 범위의 스코프이다.
- 웹 관련 스코프
- request : 웹 요청이 들어오고 나갈 때까지 유지되는 스코프
- session : 웹 세션이 생성되고 종료될 때까지 유지되는 스코프
- application : 웹의 서블릿 컨텍스트와 같은 범위로 유지되는 스코프
🙄프로토타입 빈
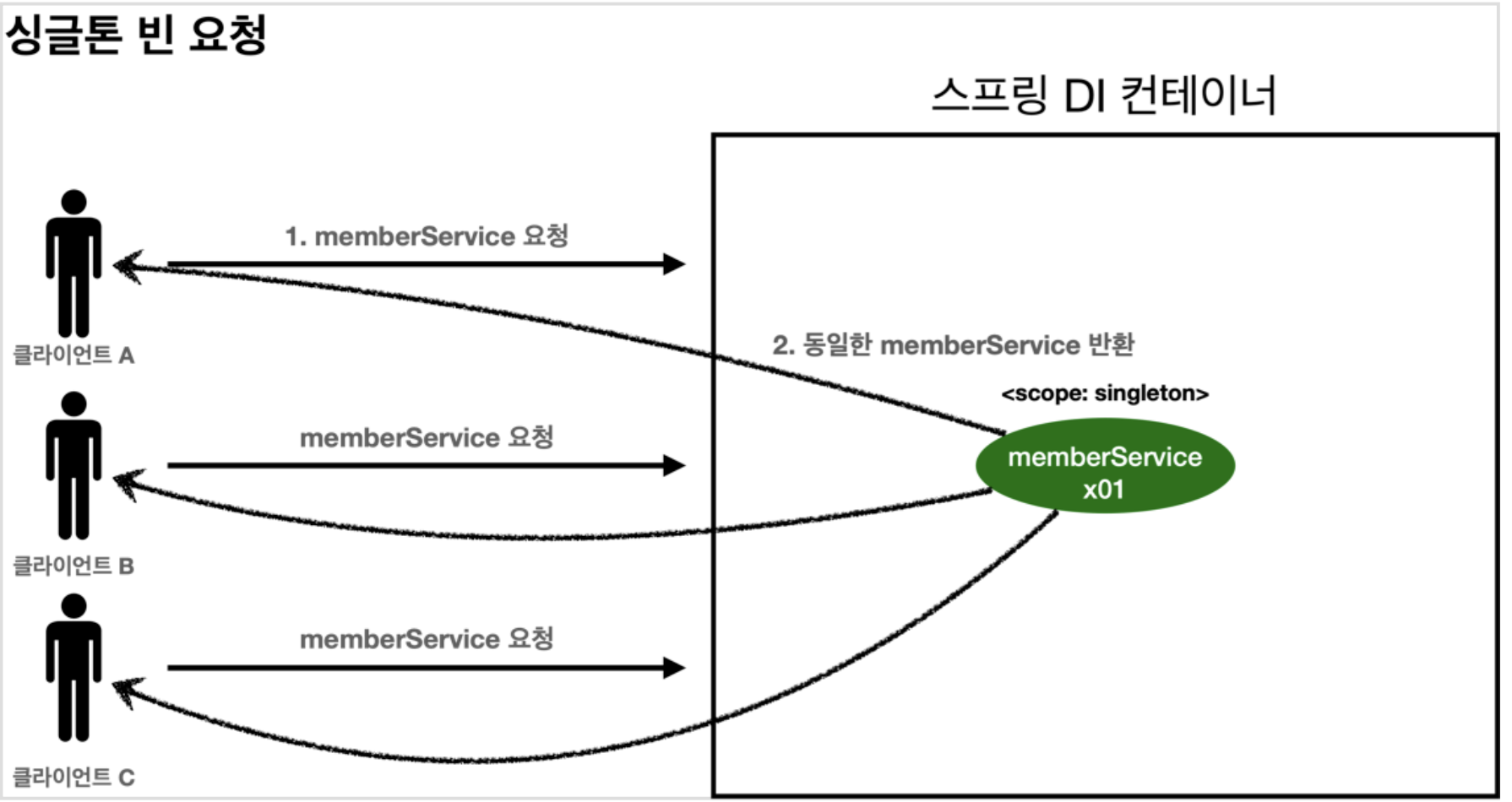
- ✔️싱글톤 특징
- 싱글톤 스코프의 빈을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 본인이 관리하는 스프링 빈을 반환한다.
- 이후에 스프링 컨테이너와 같은 요청이 와도 같은 객체 인스턴스의 스프링 빈을 반환한다.
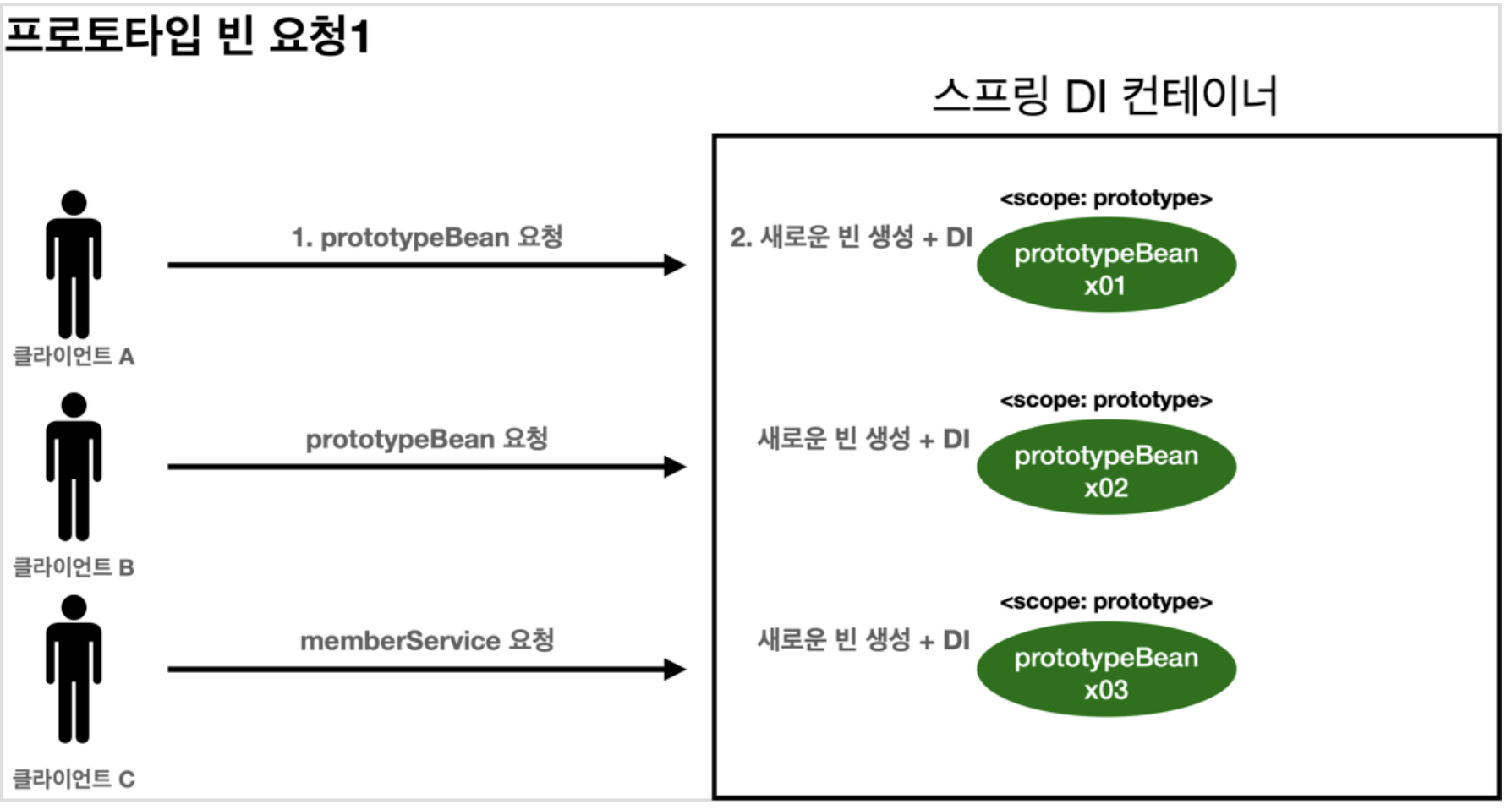
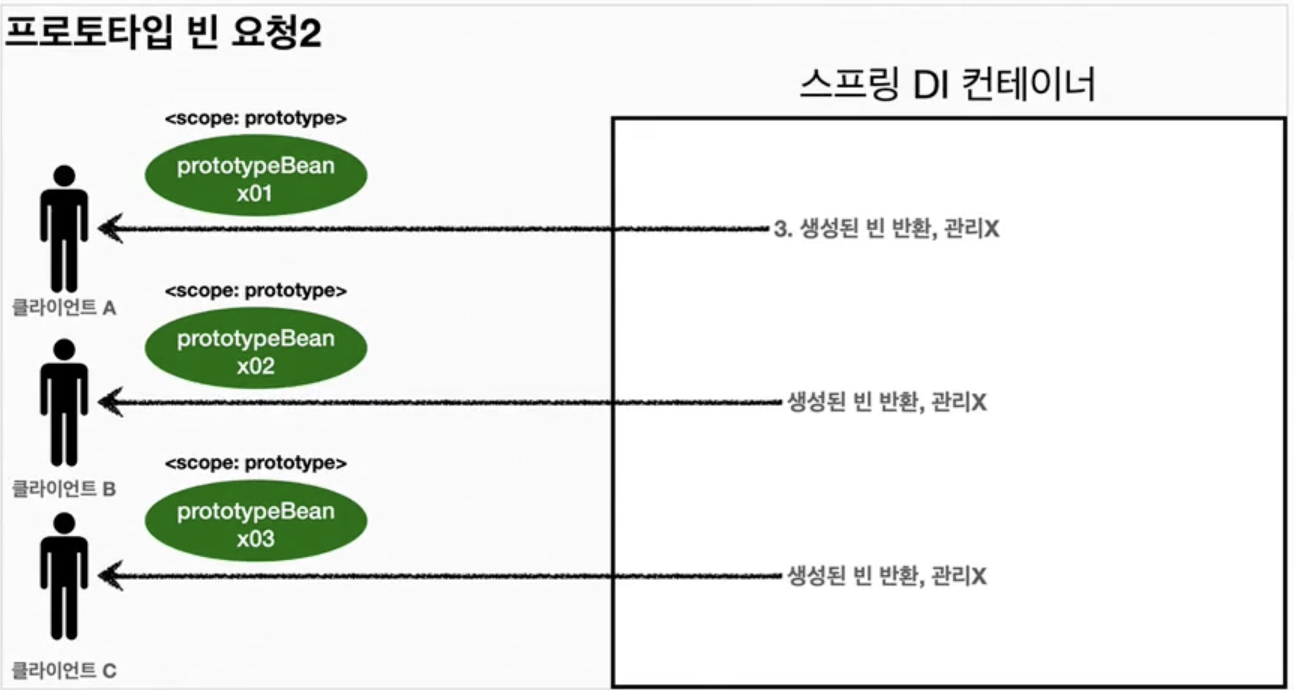
- ✔️프로토타입 특징
- 프로토타입 스코프의 빈을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 이 시점에 프로토타입 빈을 생성하고 필요한 의존관계를 주입한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 생성한 프로토타입 빈을 클라이언트에 반환한다.
- 이후에 스프링 컨테이너에 같은 요청이 들어오면 새로운 프로토타입 빈을 생성해서 반환한다.
- 핵심은 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성하고 의존관계 주입, 초기화까지만 처리한다는 것이다. 클라이언트에 빈을 반환 후 스프링 컨테이너가 이 생성된 프로토타입 빈을 관리하지 않는다.
- 프로토타입 빈을 관리할 책임이 전적으로 클라이언트에게 있기 때문에 @PreDestroy와 같은 종료 메서드가 호출되지 않는다.
public class SingletonTest {
@Test
void singletonBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean1 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
SingletonBean singletonBean2 = ac.getBean(SingletonBean.class);
System.out.println("singletonBean1 = " + singletonBean1);
System.out.println("singletonBean2 = " + singletonBean2);
Assertions.assertThat(singletonBean1).isEqualTo(singletonBean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("singleton") // ✔️(기본) 싱글톤 빈
static class SingletonBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}
}- ✔️결과
- 초기화 / 종료 메서드 모두 호출됨
- 싱글톤이므로 반환된 객체가 모두 같다.
public class PrototypeTest {
@Test
void prototypeBeanFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
PrototypeBean bean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
PrototypeBean bean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
Assertions.assertThat(bean1).isNotSameAs(bean2);
System.out.println("bean1 = " + bean1);
System.out.println("bean2 = " + bean2);
ac.close();
}
@Scope("prototype") // ✔️프로토타입 빈
static class PrototypeBean {
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("destroy");
}
}
}- ✔️결과
- 초기화 메서드(
init)가 각각의 객체마다 호출됨 - 종료 메서드(
destroy)는 호출되지 않음- 종료는 전적으로 클라이언트의 책임
- 프로토타입이므로 각각의 객체마다 다른 값을 가진다.
- 초기화 메서드(
- ✔️정리
- 싱글톤 빈은 스프링 컨테이너 생성 시점에 초기화 메서드가 실행되지만 프로토타입 스코프의 빈은 스프링 컨테이너에서 빈을 조회할 때 생성되고 초기화 메서드도 실행된다.
- 프로토타입 빈을 2번 조회했으므로 완전히 다른 스프링 빈이 생성되고 초기화도 2번 실행된다.
- 싱글톤 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 관리하기 때문에 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때까지 빈의 종료 메서드가 실행되지만 프로토타입 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 생성과 의존관계 주입 그리고 초기화까지만 관여하고 더는 관리하지 않는다.
- 프로토타입 빈은 스프링 컨테이너가 종료될 때
@PreDestroy와 같은 종료 메서드가 호출되지않는다.
🙄프로토타입 스코프 - 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용시 문제점
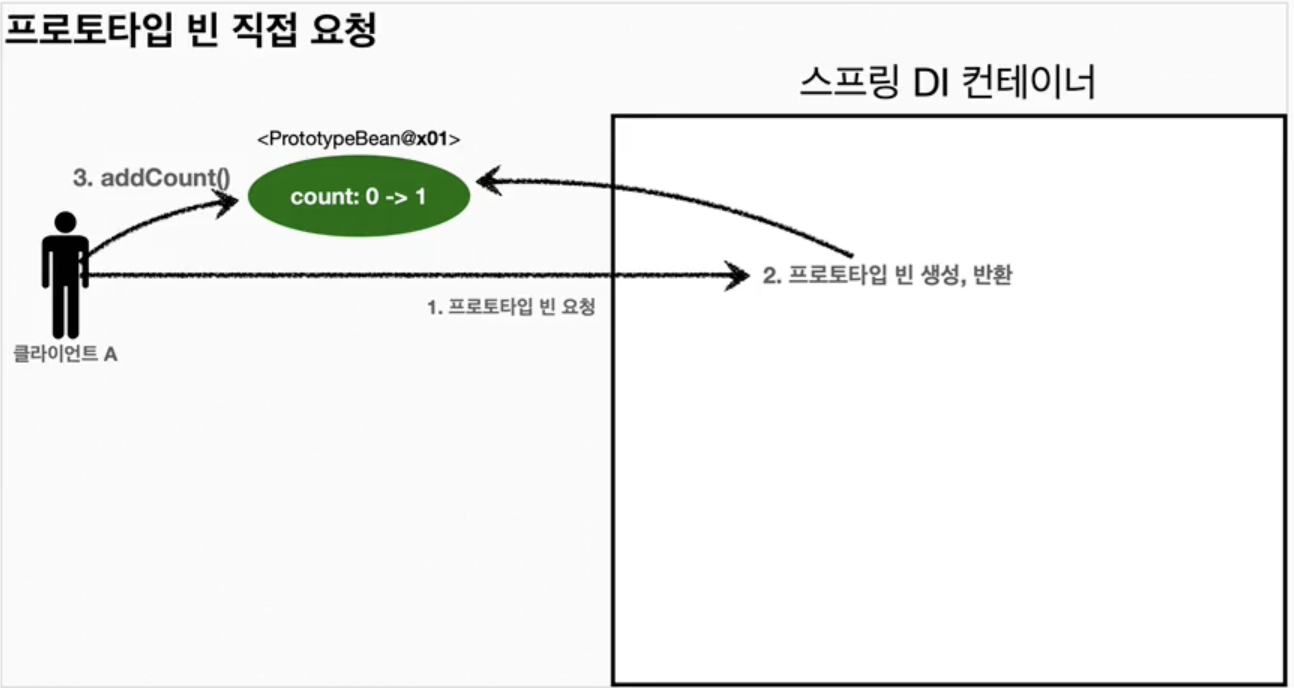
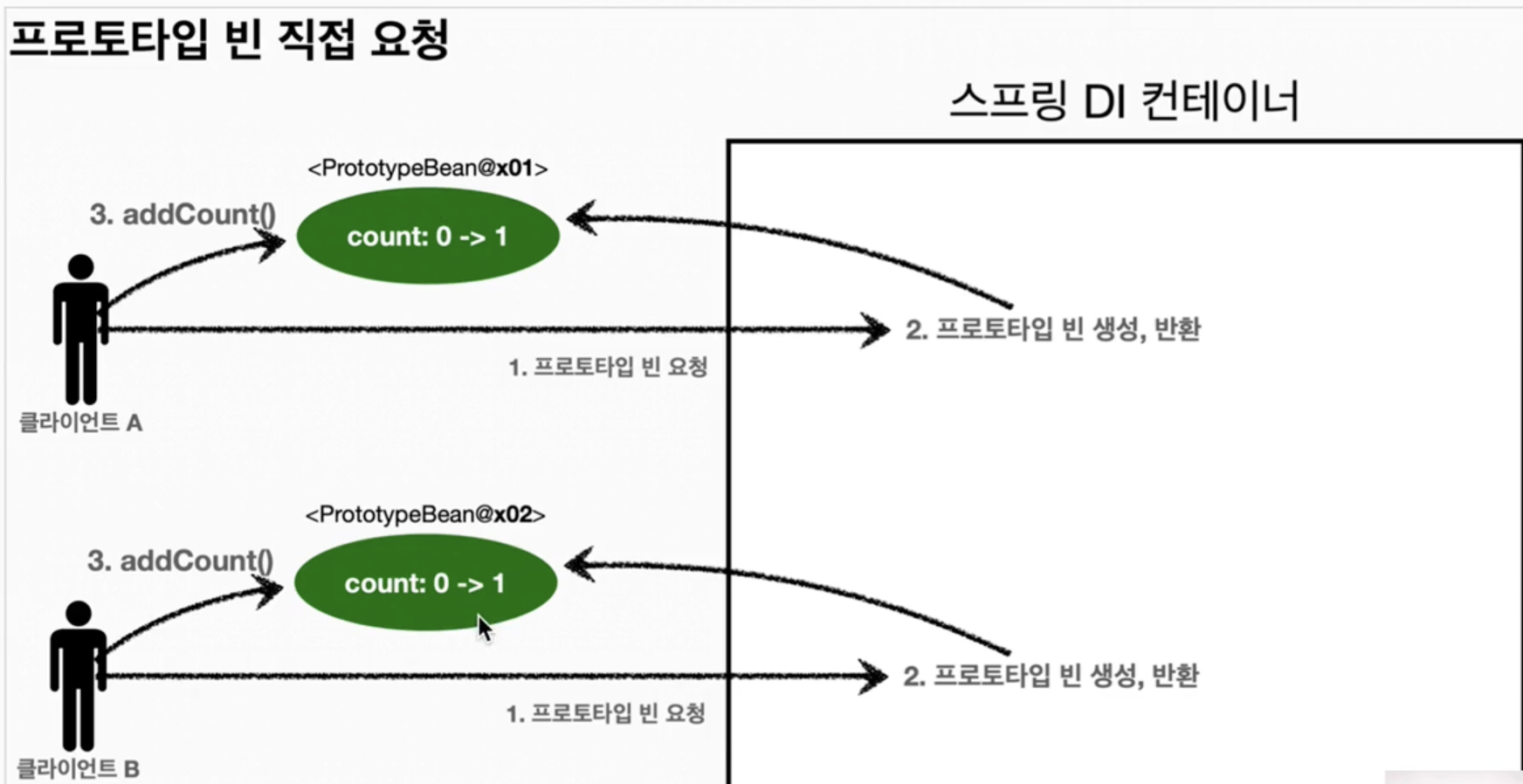
- ✔️과정1
- 클라이언트A는 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성해서 반환한다.
- 빈을 반환한 시점에서 count값은 0이다.
- 클라이언트A가 빈에 대해 addCount()를 호출하면 count값은 1이 된다.
- ✔️과정2
- 클라이언트B는 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다.
- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성해서 반환한다.
- 빈을 반환한 시점에서 count값은 0이다.
- 클라이언트A가 빈에 대해 addCount()를 호출하면 count값은 1이 된다.
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest1 {
@Test
void prototypeFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
PrototypeBean bean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println(bean1.getCount());
bean1.addCount();
Assertions.assertThat(bean1.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
PrototypeBean bean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println(bean2.getCount());
bean2.addCount();
Assertions.assertThat(bean2.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean destroy");
}
}
}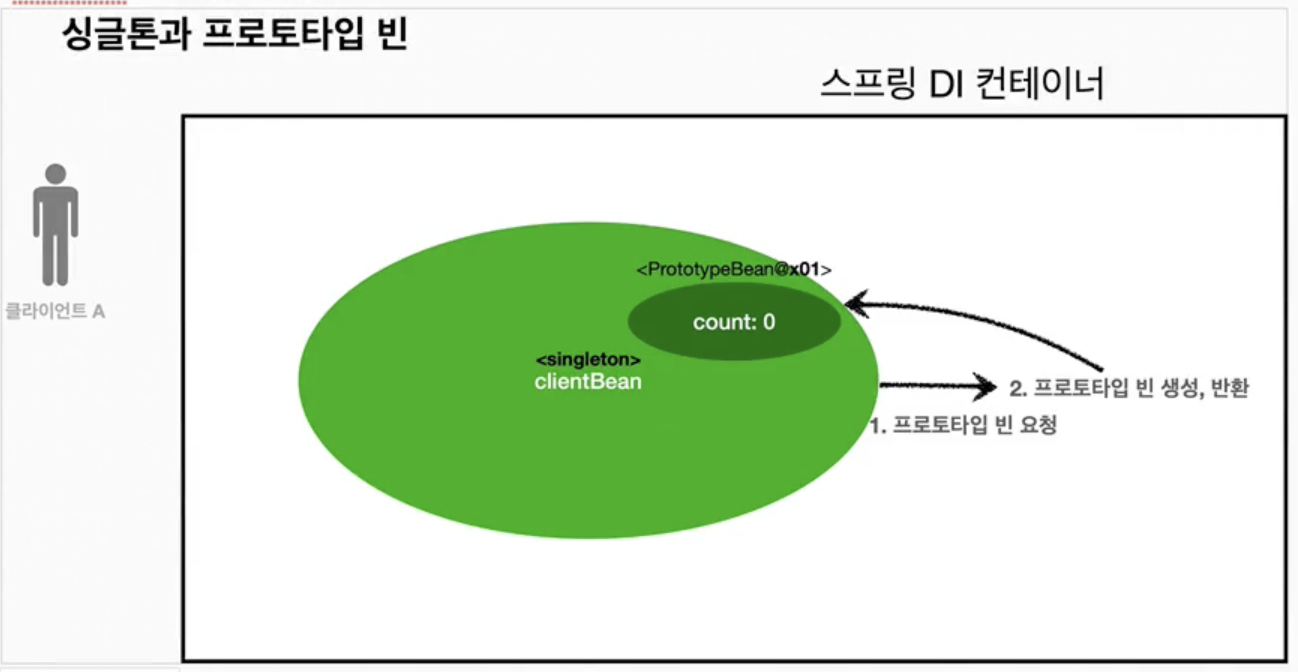
- ✔️과정1
clientBean은 싱글톤이므로 스프링 컨테이너 생성 시점에 함께 생성되고 의존관계도 함께 주입된다.clientBean은 의존관계 주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 프로토타입 빈을 요청한다.- 스프링 컨테이너는 프로토타입 빈을 생성해서
clientBean에 반환한다. 프로토타입 빈의 count 필드 값은 0이다.
- ✔️과정2
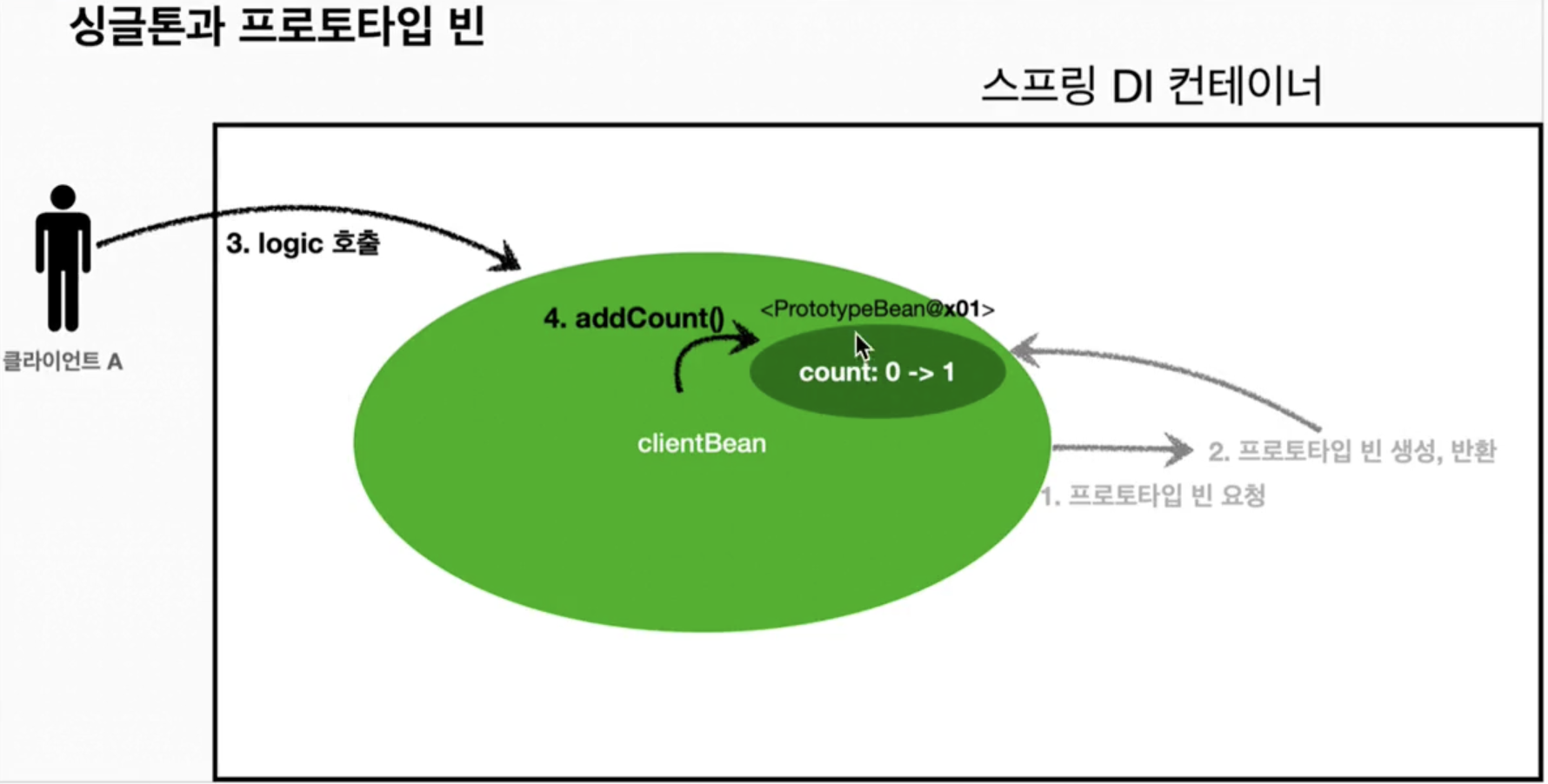
- 클라이언트A는
clientBean을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 받는다. 싱글톤이므로 항상 같은clientBean이 반환된다. - 클라이언트A가 logic을 호출한다.
clientBean은 프로토타입의 addCount()를 호출해서 프로토타입 빈의 count 필드 값을 증가시킨다. 따라서 count 필드 값은 1이다.
- 클라이언트A는
- ✔️과정3
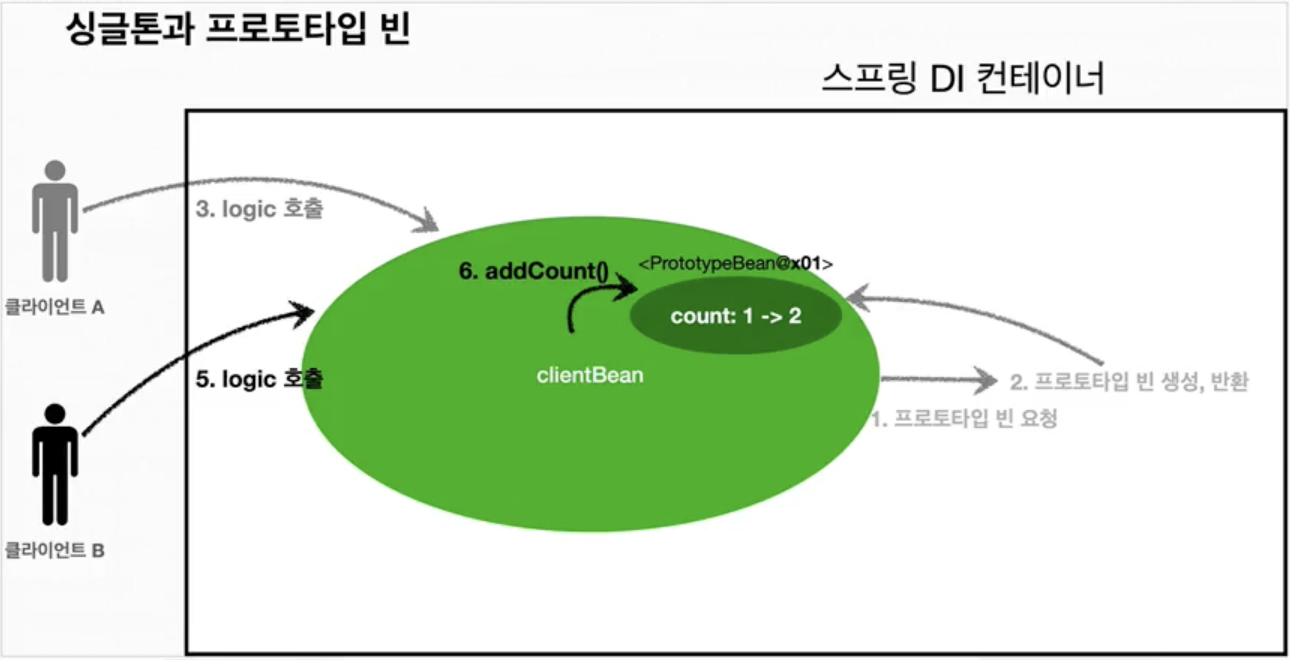
- 클라이언트B가
clientBean을 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 받는다. 싱글톤이므로 항상 같은clientBean이 반환된다. - ✔️
clientBean내부에 있는 프로토타입 빈은 이미 과거에 주입이 끝난 빈이다. 주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 프로토타입 빈이 새로 생성이 된 것이지 사용할 때마다 새로 생성되는 것이 아니다. - 클라이언트B가 logic을 호출한다.
clientBean은 프로토타입의 addCount()를 호출해서 프로토타입 빈의 count를 증가한다. 원래 필드 값이 1이므로 증가해서 2가 된다.
- 클라이언트B가
public class SingletonWithPrototypeTest1 {
@Test
void prototypeFind() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class);
PrototypeBean bean1 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println(bean1.getCount());
bean1.addCount();
Assertions.assertThat(bean1.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
PrototypeBean bean2 = ac.getBean(PrototypeBean.class);
System.out.println(bean2.getCount());
bean2.addCount();
Assertions.assertThat(bean2.getCount()).isEqualTo(1);
}
@Test
void singletonClientUsePrototype() {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(PrototypeBean.class, ClientBean.class);
ClientBean bean1 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count1 = bean1.logic();
Assertions.assertThat(count1).isEqualTo(1);
ClientBean bean2 = ac.getBean(ClientBean.class);
int count2 = bean2.logic();
Assertions.assertThat(count2).isEqualTo(2);
}
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
// ✔️싱글톤 클라이언트 빈 내부에 프로토타입 빈 의존관계 자동 주입
// ✔️요청이 들어올 때마다 새로 생성되는 것이 아니다.
private final PrototypeBean prototypeBean;
@Autowired
ClientBean(PrototypeBean prototypeBean) {
this.prototypeBean = prototypeBean;
}
public int logic() {
prototypeBean.addCount();
int count = prototypeBean.getCount();
return count;
}
}
@Scope("prototype")
static class PrototypeBean {
private int count = 0;
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void addCount() {
count++;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean init");
}
@PreDestroy
public void destroy() {
System.out.println("PrototypeBean destroy");
}
}
}🙄프로토타입 스코프 - 싱글톤 빈과 함께 사용시 Provider로 문제 해결
- ✔️ObjectFactory, ObjectProvider
- 지정한 빈을 스프링 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는 DL 서비스를 제공하는 것이 바로
ObjectProvider이다. - 과거에는
ObjectFactory가 있었으나 여기에 편의 기능을 추가한 것이 바로ObjectProvider이다.
- 지정한 빈을 스프링 컨테이너에서 대신 찾아주는 DL 서비스를 제공하는 것이 바로
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
// ✔️ 주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 빈을 새로 생성한 것
@Autowired
private ObjectProvider<PrototypeBean> prototypeBean;
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean object = prototypeBean.getObject();
object.addCount();
int count = object.getCount();
return count;
}
}- ✔️정리
- 과정3에서
clientBean내부에 있는 프로토타입 빈은 이미 과거에 주입이 끝난 빈이다. 프로토타입 빈의 경우 스프링 컨테이너가 생성 후 의존관계 주입, 그리고 반환까지의 사이클을 거치게 되면 관리를 하지 않는다. 주입 시점에 스프링 컨테이너에 요청해서 빈이 새로 생성이 된 것이지 사용할 때마다 새로 생성되지 않는다. 이를 해결하기 위해서ObjectProvider를 사용한다. prototypeBean.getObject()를 통해 항상 새로운 프로토타입 빈이 생성되도록 할 수 있다.
- 과정3에서
- ✔️JSR-330 Provider
- JSR-330 자바 표준을 사용하는 방법
@Scope("singleton")
static class ClientBean {
@Autowired
private Provider<PrototypeBean> prototypeBean;
public int logic() {
PrototypeBean object = prototypeBean.get();
object.addCount();
int count = object.getCount();
return count;
}
}- ✔️정리
- 별도의 라이브러리를 필요로 하며
get()메서드 하나로 기능이 매우 단순하다. - 자바 표준이므로 스프링이 아닌 다른 컨테이너에서도 사용할 수 있다.
- 별도의 라이브러리를 필요로 하며
- ✔️전체 정리
- 프로토타입 빈은 언제 사용을 할까
- 매번 사용할 때마다 의존관계 주입이 완료된 새로운 객체가 필요하면 사용하면 된다.
🙄웹 스코프
웹 환경에서만 동작
웹 스코프는 프로토타입과 다르게 스프링이 해당 스코프의 종료 시점까지 관리하므로 종료 메서드가 호출된다.
- ✔️웹 스코프의 종류
- request : HTTP 요청 하나가 들어오고 나갈 때까지 유지되는 스코프, 각각의 HTTP 요청마다 별도의 빈 인스턴스가 생성되고 관리된다.
- session : HTTP session과 동일한 생명주기를 가지는 스코프
- application : 서블릿 컨텍스트와 동일한 생명주기를 가지는 스코프
- websocket : 웹 소켓과 동일한 생명주기를 가지는 스코프
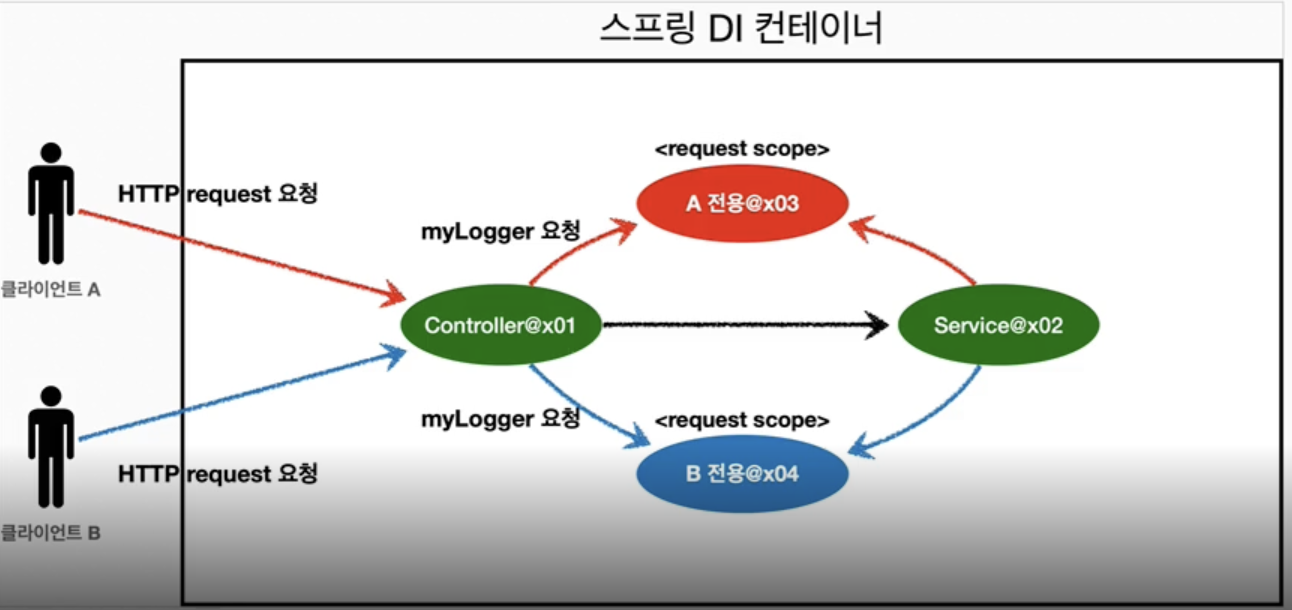
🙄request 스코프 예제
✔️MyLogger 클래스
@Component
@Scope(value = "request")
public class MyLogger {
private String uuid;
private String requestURL;
public void log(String message) {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "]" + "[" + requestURL + "]" + message);
}
public void setRequestURL(String requestURL) {
this.requestURL = requestURL;
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean create: " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean close: " + this);
}
}- ✔️정리
@Scope(value = "request")를 사용해서 request 스코프로 지정- 이 빈은 HTTP 요청 당 하나씩 생성되고 HTTP 요청이 끝나는 시점에 소멸된다.
- 이 빈이 생성되는 시점에 @PostConstruct 초기화 메서드를 사용해서 uuid를 랜덤하게 생성 후 저장한다. 이 빈은 HTTP 요청 당 하나씩 생성되므로 uuid를 저장해두면 다른 HTTP 요청과 구분할 수 있다.
- 이 빈이 소멸되는 시점에 @PreDestroy 종료 메서드를 사용해서 종료 메시지를 남긴다.
- 빈이 생성되는 시점에 requestURL은 모르므로 외부에서 setter로 입력받는다.
✔️LogDemoController
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogDemoController {
private final LogDemoService logDemoService;
private final MyLogger myLogger;
@RequestMapping("/log-demo")
@ResponseBody
public String logDemo(HttpServletRequest request) {
String requestURI = request.getRequestURL().toString();
myLogger.setRequestURL(requestURI);
myLogger.log("controller test!");
logDemoService.logic("testId");
return "ok";
}
}✔️LogDemoService
@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogDemoService {
private final MyLogger myLogger;
public void logic(String testId) {
myLogger.log("service Id = " + testId);
}
}실행 결과
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ScopeNotActiveException: Error creating bean with name 'myLogger': Scope 'request' is not active for the current thread; consider defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:385) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.getBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:200) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.config.DependencyDescriptor.resolveCandidate(DependencyDescriptor.java:254) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.doResolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1443) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory.resolveDependency(DefaultListableBeanFactory.java:1353) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver.resolveAutowiredArgument(ConstructorResolver.java:904) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ConstructorResolver.createArgumentArray(ConstructorResolver.java:782) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
... 33 common frames omitted
Caused by: java.lang.IllegalStateException: No thread-bound request found: Are you referring to request attributes outside of an actual web request, or processing a request outside of the originally receiving thread? If you are actually operating within a web request and still receive this message, your code is probably running outside of DispatcherServlet: In this case, use RequestContextListener or RequestContextFilter to expose the current request.
at org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes(RequestContextHolder.java:131) ~[spring-web-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.web.context.request.AbstractRequestAttributesScope.get(AbstractRequestAttributesScope.java:42) ~[spring-web-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
at org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory.doGetBean(AbstractBeanFactory.java:373) ~[spring-beans-6.1.8.jar:6.1.8]
... 39 common frames omitted스프링 애플리케이션을 실행하는 시점에 싱글톤 빈은 생성해서 의존관계 주입이 가능하지만 request 스코프 빈은 아직 생성되지 않는다. 이 빈은 실제 고객으로부터의 요청이 와야 생성되는 것이다. 실제 고객으로부터의 요청이 올 때 생성되게끔 해야 하므로 위에서 공부했던 싱글톤 빈 내의 프로토타입 빈 사용 때 사용했었던 Provider를 활용할 수 있다.
🙄스코프와 Provider
@Controller
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogDemoController {
private final LogDemoService logDemoService;
private final ObjectProvider<MyLogger> myLoggerObjectProvider;
@RequestMapping("/log-demo")
@ResponseBody
public String logDemo(HttpServletRequest request) {
String requestURL = request.getRequestURL().toString();
MyLogger myLogger = myLoggerObjectProvider.getObject();
myLogger.setRequestURL(requestURL);
myLogger.log("controller test!");
logDemoService.logic("testId");
return "ok";
}
}@Service
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class LogDemoService {
private final ObjectProvider<MyLogger> myLoggerObjectProvider;
public void logic(String testId) {
MyLogger myLogger = myLoggerObjectProvider.getObject();
myLogger.log("service Id = " + testId);
}
}실행 결과
[41ab9237-a2ff-4060-94fe-41cea2d8b382] request scope bean create: hello.core.common.MyLogger@11f3fc9e
[41ab9237-a2ff-4060-94fe-41cea2d8b382][http://localhost:8080/log-demo]controller test!
[41ab9237-a2ff-4060-94fe-41cea2d8b382][http://localhost:8080/log-demo]service Id = testId
[41ab9237-a2ff-4060-94fe-41cea2d8b382] request scope bean close: hello.core.common.MyLogger@11f3fc9e🙄스코프와 프록시
@Component
// ✔️프록시 방식 적용 → 적용 대상이 인터페이스가 아닌 클래스면 TARGET_CLASS 선택
// ✔️프록시 방식 적용 → 적용 대상이 인터페이스면 INTERFACE를 선택
@Scope(value = "request", proxyMode = ScopedProxyMode.TARGET_CLASS)
public class MyLogger {
private String uuid;
private String requestURL;
public void setRequestURL(String requestURL) {
this.requestURL = requestURL;
}
public void log(String message) {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "]" + "[" + requestURL + "]" + message);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
uuid = UUID.randomUUID().toString();
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean create: " + this);
}
@PreDestroy
public void close() {
System.out.println("[" + uuid + "] request scope bean close: " + this);
}
}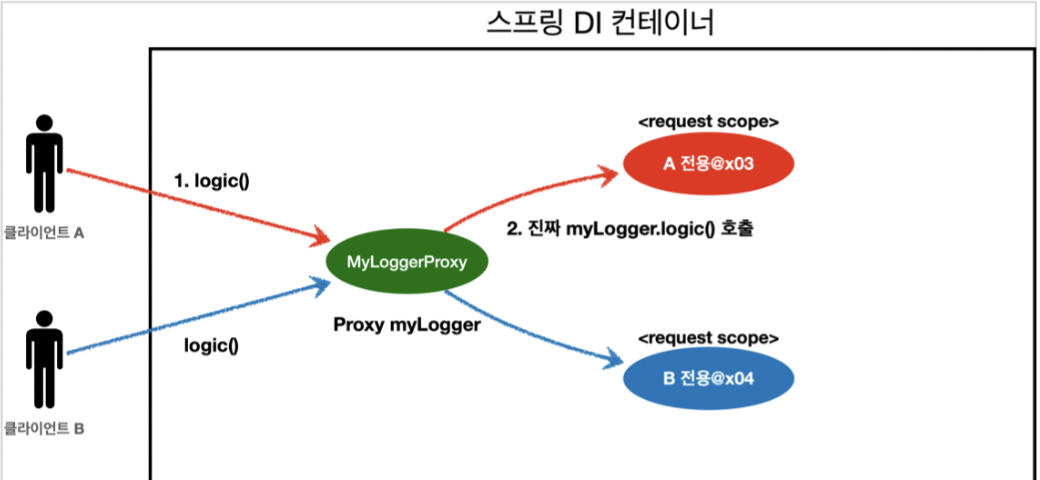
- ✔️정리
- MyLogger 클래스의 가짜 프록시 클래스를 만들어두고 HTTP request와 상관없이 가짜 프록시 클래스를 다른 빈에 미리 주입할 수 있다.
- CGLIB라는 라이브러리로 클래스를 상속받은 가짜 프록시 객체를 만들어서 주입한다.
- 가짜 프록시 객체는 내부에 진짜 MyLogger를 찾는 방법을 알고 있다
- 가짜 프록시 객체는 request 스코프의 진짜
myLogger.logic()를 호출한다 - 가짜 프록시 객체는 원본 클래스를 상속 받아 만들어졌기 때문에 이 객체를 사용하는 클라이언트 입장에서 사실 원본인지 아닌지도 모르게 동일하게 사용할 수 있다.