stack
슬라이스로 충분히 스택이 구현이 가능하기에 Golang 표준 라이브러리에서는 따로 지원하지않는다
아래는 구현한 스택이다
package eval
// Eval returns the evaluation result of the given expr.
import (
"strconv"
"strings"
)
// The expression can have +, -, *, /, (, ) operators and
// decimal integers. Operators and operands should be
func Eval(expr string) int {
var ops []string
var nums []int
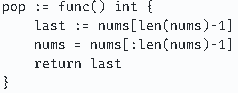
pop := func() int {
last := nums[len(nums)-1]
nums = nums[:len(nums)-1]
return last
}
reduce := func(higher string) {
for len(ops) > 0 {
op := ops[len(ops)-1]
if strings.Index(higher, op) < 0 {
// 목록에 없는 연산자이므로 종료
return
}
ops = ops[:len(ops)-1]
if op == "(" {
// 괄호를 제거하였으므로 종료
return
}
b, a := pop(), pop()
switch op {
case "+":
nums = append(nums, a+b)
case "-":
nums = append(nums, a-b)
case "*":
nums = append(nums, a*b)
case "/":
nums = append(nums, a/b)
}
}
}
for _, token := range strings.Split(expr, " ") {
switch token {
case "(":
ops = append(ops, token)
case "+", "-":
// 덧셈과 뺄셈 이상의 우선순위를 가진 사칙연산 적용
reduce("+-*/")
ops = append(ops, token)
case "*", "/":
// 곱셈과 나눗셈 이상의 우선순위를 가진 것은 둘 뿐
reduce("*/")
ops = append(ops, token)
case ")":
// 닫는 괄호는 여는 괄호까지 계산을 하고 제거
reduce("+-*/(")
default:
num, _ := strconv.Atoi(token)
nums = append(nums, num)
}
}
reduce("+-*/")
return nums[0]
}pop()은 숫자 스택에서 숫자를 꺼내는 함수이다

reduce()는 연산의 결과값을 num에 추가하는 함수이다

이후 동작과정

map
map은 해시테이블로 구현된다
그래서 순서가 없는 대신 key-value쌍으로 이루어져 key를 이용해 value를 O(1) 시간복잡도로 가져올 수 있다.
맵을 담는 변수는
var m map[keyType]valueType로 만드는데
이는 "빈 맵으로 취급되어" 맵을 담을 수는 있지만 사용은 불가능하다
맵을 생성하려면
m := make(map[keyType]valueType)
m := map[keyType]valueType{}
맵을 읽을 때 2개의 변수로 받으면
value, ok := m[key]
값, 존재여부(T,F)로 받을 수 있다.
맵을 사용하는 방법은 보통
func count(s string, codeCount map[rune]int) {
for _, r := range s {
codeCount[r]++
}codeCount[r]로 value를 저장하고 ++로 key를 하나씩 올리는 방법으로 사용한다