98일차 시작.... (tensorflow)
tensorflow Graph 영역 함수tensorflow unique value 추출tensorflow 관계 연산tensorflow 논리 연산tensorflow 모듈 Importtensorflow 변수 내부값 변경tensorflow 변수 선언tensorflow 상수 - 데이터 타입 변환tensorflow 상수 - 산술 연산tensorflow 상수 선언tensorflow 설치tensorflow 원-핫 백터 원본 데이터로 복구tensorflow 원-핫 인코딩tensorflow 조건 메소드tensorflow 차원 변경tensorflow 차원 축소tensorflow 차원 확대tensorflow 타입 변환tensorflow란?
[교육] Python DL
목록 보기
1/16

📊 tensorflow
📌 tensorflow란?
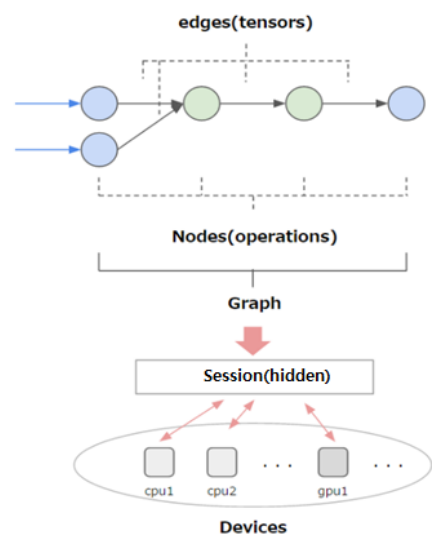
- 정의
- Array(tensor)를 특정 학습 알고리즘에 흘려보내는 것(flow)
- 아래 그림과 같이 설계도(Graph)를 만들어 tensor를 흘려보내 실행시킨다.
📌 tensorflow 설치
- 설치 방법
1) anaconda prompt 실행
2) pip install --upgrade pip
3) pip install tensorflow
4) pip install --upgrade tensorflow
📊 tensorflow 기초
📌 tensorflow 모듈 Import
- 라이브러리 Import
import tensorflow as tfimport tensorflow as tf
📌 tensorflow 상수 선언
- 상수 선언
- tf.constant(스칼라 or 백터 or 매트릭스)# 0-dim tensor 선언 print(tf.constant(1), type(tf.constant(1))) # tf.Tensor(1, shape=(), dtype=int32) <class 'tensorflow.python.framework.ops.EagerTensor'> # 1-dim tensor 선언 print(tf.constant([1])) # tf.Tensor([1], shape=(1,), dtype=int32) # 2-dim tensor 선언 print(tf.constant([[1]])) # tf.Tensor([[1]], shape=(1, 1), dtype=int32)
📌 tensorflow 상수 - 산술 연산
- 산술 연산
- tf.add(tensor, tensor)a = tf.constant([1, 2]) b = tf.constant([3, 4]) c = a + b print(c) # tf.Tensor([4 6], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) c = tf.add(a, b) print(c) # tf.Tensor([4 6], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) d = tf.constant([[3]]) # (1, 1) 2-dim tensor e = c + d print(e) # tf.Tensor([[7 9]], shape=(1, 2), dtype=int32)
📌 tensorflow 상수 - 데이터 타입 변환
- 데이터 타입 변환
print(tf.convert_to_tensor(7, dtype=tf.float32)) print(tf.constant(7, dtype=tf.float32)) print(tf.cast(7, dtype=tf.float32)) print(tf.constant(7.0)) # tf.Tensor(7.0, shape=(), dtype=float32)
📌 tensorflow 타입 변환
1. tensor type으로 변환
import numpy as np arr = np.array([1, 2]) print(arr, type(arr)) # [1 2] <class 'numpy.ndarray'> # [ tensor로 변환 ] tf_arr = tf.constant(arr) print(tf_arr) # tf.Tensor([1 2], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) tf_arr = tf.add(arr, 5) print(tf_arr) # tf.Tensor([6 7], shape=(2,), dtype=int32)
2. numpy type으로 변환
# [ numpy로 변환 ] print(tf_arr.numpy()) # 강제 변환 # [6 7] print(np.add(tf_arr, 1)) # 자동 변환 # [7 8]
📌 tensorflow 변수 선언
- 변수 선언
- tf.Variable(스칼라 or 백터 or 매트릭스)f = tf.Variable(1.0) v = tf.Variable(tf.ones((2,))) m = tf.Variable(tf.ones((2, 1))) print(f) print(v) print(m) # <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=() dtype=float32, numpy=1.0> # <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2,) dtype=float32, numpy=array([1., 1.], dtype=float32)> # <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(2, 1) dtype=float32, numpy= # array([[1.], # [1.]], dtype=float32)>
📌 tensorflow 변수 내부값 변경
- 변수 내부값 변경
- tf.assign(스칼라 or 백터 or 매트릭스)
- 변수 내부값의 차원에 맞게 변경# 0-dim tensor 변수값 변경 v1 = tf.Variable(1) v1.assign(10) print(v1) # <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=() dtype=int32, numpy=10> # 1-dim tensor 변수값 변경 v2 = tf.Variable(tf.ones((1,))) v2.assign([10]) print(v2) # <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(1,) dtype=float32, numpy=array([10.], dtype=float32)> # 2-dim tensor 변수값 변경 v3 = tf.Variable(tf.ones((1, 2))) v3.assign([[20, 30]]) print(v3) # <tf.Variable 'Variable:0' shape=(1, 2) dtype=float32, numpy=array([[20., 30.]], dtype=float32)>
📌 tensorflow Graph 영역 함수
- Graph 영역 함수
- @tf.function : auto graph 기능이 적용된 함수(tf.Graph + tf.Session이 적용)w = tf.Variable(tf.ones((1,))) b = tf.Variable(tf.ones((1,))) w.assign([2]) b.assign([3]) @tf.function def func1(x): return w * x + b out_a1 = func1([2]) print('out_a1 : ', out_a1) # out_a1 : tf.Tensor([7.], shape=(1,), dtype=float32)
📌 tensorflow 조건 메소드
- 조건 메소드
- tf.cond(조건, True, False)
- tf.case([(tf.관계연산메소드, True)], default=False)print(tf.cond(x > y, lambda:tf.add(x, y), lambda:123)) f1 = lambda:tf.constant(123) f2 = lambda:tf.constant(0) print(tf.case([(tf.greater(x, y), f1)], default=f2))
📌 tensorflow 관계 연산
- 관계 연산
- tf.equal(인자1, 인자2) : 동등 비교
- tf.not_equal(인자1, 인자2) : 비동등 비교
- tf.greater(인자1, 인자2) : 왼쪽 인자가 더 큰지 비교
- tf.greater_equal(인자1, 인자2) : 왼쪽 인자가 더 큰거나 같은지 비교
- tf.less(인자1, 인자2) : 왼쪽 인자가 더 작은지 비교
- tf.less_equal(인자1, 인자2) : 왼쪽 인자가 더 작거나 같은지 비교print(tf.equal(1, 2).numpy()) # False print(tf.not_equal(1, 2).numpy()) # True print(tf.greater(1, 2).numpy()) # False print(tf.greater_equal(1, 2).numpy()) # False print(tf.less(1, 2).numpy()) # True
📌 tensorflow 논리 연산
- 논리 연산
- tf.logical_and(인자1, 인자2) : and 연산
- tf.logical_or(인자1, 인자2) : or 연산
- tf.logical_not(인자1) : not 연산print(tf.logical_and(True, False).numpy()) # False print(tf.logical_or(True, False).numpy()) # True print(tf.logical_not(False).numpy()) # True
📌 tensorflow unique value 추출
- unique value 추출
- tf.unique(인자값)aa = tf.constant([1, 2, 2, 2, 3]) val, idx = tf.unique(aa) print(val.numpy()) print(idx.numpy()) # [1 2 3] # [0 1 1 1 2]
📌 tensorflow 차원 축소
- 차원 축소
- tf.reduce_mean(인자값)
- tf.squeeze(인자값)arr = [[1,2], [3,4]] print(tf.reduce_mean(arr).numpy()) # 전체 평균 print(tf.reduce_mean(arr, axis=0).numpy()) # 열 평균 print(tf.reduce_mean(arr, axis=1).numpy()) # 행 평균 # 2 # [2 3] # [1 3] aa = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4]]) print(aa.shape) # (4, 1) bb = tf.squeeze(aa) print(bb.shape) # (4,)
📌 tensorflow 차원 변경
- 차원 변경
- tf.reshape(인자값, shape=변경할 형태)t = np.array([[[1,2,3], [4,5,6], [7,8,9], [10,11,12]]]) print(t.shape) # (1, 4, 3) print(tf.reshape(t, shape=(2,6))) print(tf.reshape(t, shape=(-1,6))) print(tf.reshape(t, shape=(2,-1))) # tf.Tensor( # [[ 1 2 3 4 5 6] # [ 7 8 9 10 11 12]], shape=(2, 6), dtype=int32)
📌 tensorflow 차원 확대
- 차원 확대
- tf.expand_dims(인자값, 차원 확대할 축 지정)tarr = tf.constant([[1,2,3], [4,5,6]]) print(tf.shape(tarr)) # tf.Tensor([2 3], shape=(2,), dtype=int32) sbs1 = tf.expand_dims(tarr, 0) # 첫번째 차원을 추가 print(tf.shape(sbs1).numpy()) # (1, 2, 3) sbs2 = tf.expand_dims(tarr, 1) # 두번째 차원을 추가 print(tf.shape(sbs2).numpy()) # (2, 1, 3) sbs3 = tf.expand_dims(tarr, 2) # 세번째 차원을 추가 print(tf.shape(sbs3).numpy()) # (2, 3, 1)
📌 tensorflow 원-핫 인코딩
- 원-핫 인코딩
- tf.one_hot(인자값, depth=분리할 카테고리 개수)print(tf.one_hot([0, 1, 2, 3], depth=4)) # tf.Tensor( # [[1. 0. 0. 0.] # [0. 1. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 1. 0.] # [0. 0. 0. 1.]], shape=(4, 4), dtype=float32)
📌 tensorflow 원-핫 백터 원본 데이터로 복구
- 원-핫 백터 원복
- tf.argmax(tf.one_hot(인자값, depth=분리할 카테고리 개수))print(tf.argmax(tf.one_hot([0, 1, 2, 3], depth=4))) # tf.Tensor([0 1 2 3], shape=(4,), dtype=int64)