94일차 시작.... (앙상블 기법)
랜덤 포레스트 실습랜덤 포레스트란?레이블 인코딩 작업 [레이블 인코딩]배깅(Bagging)이란?배깅과 부스팅의 공통점과 차이점부스팅(boosting)이란?앙상블 기법 실습앙상블 기법이란?원-핫 인코딩 작업 [레이블 인코딩]특성 중요도 추출
[교육] Python ML
목록 보기
9/17

📊 앙상블 기법
📌 앙상블 기법이란?
- 정의
- 개별적인 여러 모델들을 모아 종합적으로 취합 후, 최종 분류 결과를 출력하는 기법
- 종류
- voting : 직접투표, 간접투표
- bagging
- boosting
📌 앙상블 기법 실습
- 실습할 앙상블 모델
LogisticRegression + DecisionTree + KNN
1. 라이브러리 Import
import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.datasets import load_breast_cancer from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split # 모델 from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier # 정확도 평가 지표 from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
2. 데이터 준비
# 2. 데이터 준비 breast = load_breast_cancer() data = pd.DataFrame(breast.data, columns=breast.feature_names) print(data.head(3)) # mean radius mean texture ... worst symmetry worst fractal dimension # 0 17.99 10.38 ... 0.4601 0.11890 # 1 20.57 17.77 ... 0.2750 0.08902 # 2 19.69 21.25 ... 0.3613 0.08758
3. 학습, 테스트 데이터 분리
x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(breast.data, breast.target, test_size=0.3, random_state=1) print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape) # (398, 30) (171, 30) print(set(y_train)) # {0, 1}
4. 앙상블 모델에 사용할 개별 모델 준비
# 4. Ensemble 모델(VotingClassifier) logi_model = LogisticRegression() dt_model = DecisionTreeClassifier() knn_model = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
5. Ensemble 모델(VotingClassifier)
- estimators 속성 : 모델 지정
- voting 속성 : 투표 방법 지정
- hard voting : 다수결의 원칙으로 많이 표를 갖는 모델이 승리
- soft voting : 분류모델들의 분류 예측 확률값을 이용해 가장 높은 확률을 갖는 클래스를 예측함ensemble = VotingClassifier( estimators=[('LR', logi_model), ('DT', dt_model), ('knn', knn_model)], voting='soft' )
6. 개별 모델 학습 및 평가
classifiers = [logi_model, dt_model, knn_model] for classifier in classifiers: # 개별 모델 학습 classifier.fit(x_train, y_train) # 개별 모델 예측 y_pred = classifier.predict(x_test) # 개별 모델 이름 class_name = classifier.__class__.__name__ # 개별 모델 정확도 출력 print(f'{class_name} 모델 정확도 : ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred).round(3)) # LogisticRegression 모델 정확도 : 0.924 # DecisionTreeClassifier 모델 정확도 : 0.953 # KNeighborsClassifier 모델 정확도 : 0.924
7. 앙상블 모델 학습 및 평가
ensemble.fit(x_train, y_train) y_en_pred = ensemble.predict(x_test) print('앙상블 모델 정확도 : ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_en_pred).round(3)) # 앙상블 모델 정확도 : 0.959
📊 앙상블 - Bagging, Boosting
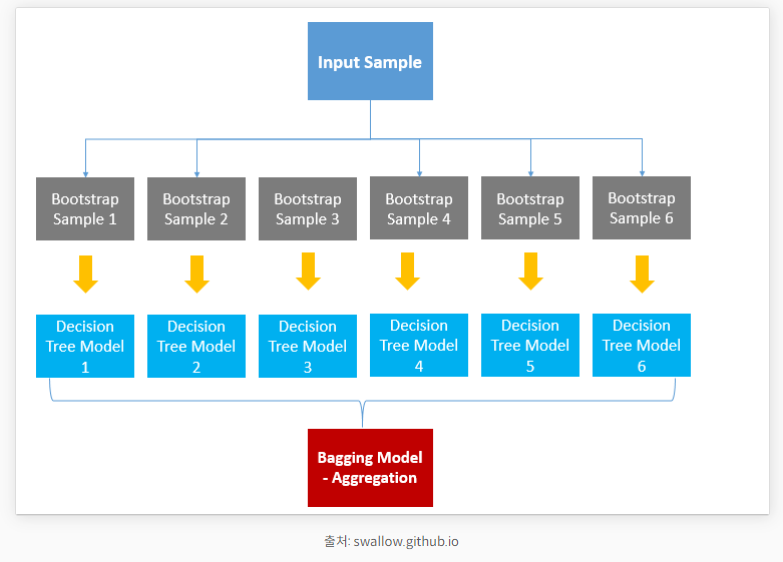
📌 배깅(Bagging)이란?
- 정의
- 배깅은 샘플을 여러 번 뽑아(Bootstrap) 각 모델을 학습시켜 결과물을 집계(Aggregration)하는 방법입니다
- Bagging = Bootstrap Aggregation
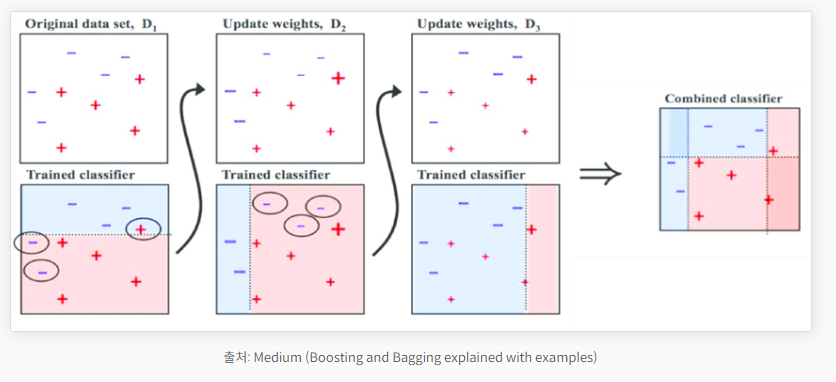
📌 부스팅(boosting)이란?
- 정의
- 부스팅은 가중치를 활용하여 약 분류기를 강 분류기로 만드는 방법
- 처음 모델이 예측을 하면 그 예측 결과에 따라 데이터에 가중치가 부여되고, 부여된 가중치가 다음 모델에 영향을 준다.
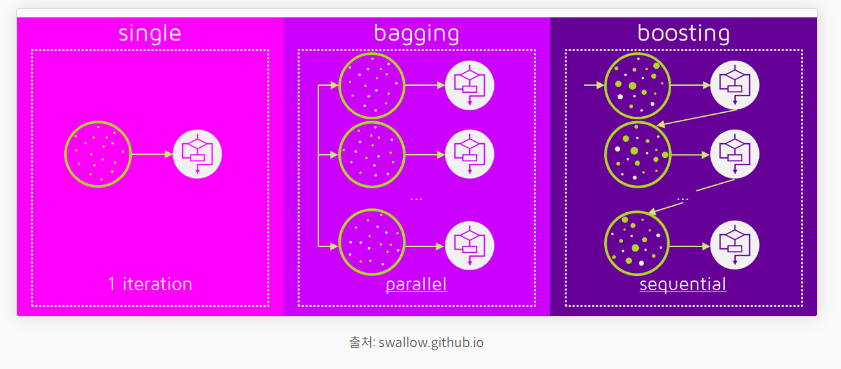
📌 배깅과 부스팅의 공통점과 차이점
- 차이점
- 배깅(bagging) : 병렬 처리
- 부스팅(boosting) : 직렬 처리
- 특징
- 배깅(bagging)의 예시 : 렌덤포레스트 모델
→ [ 밸런스 기반 ]- 부스팅(boosting)의 예시 : XGboost 모델
→ [ 성능 기반 ]
- 공통점
- 두 기법 모두 여러 개의 모델을 사용하기 때문에 과적합을 주의해야 한다.
📊 랜덤 포레스트
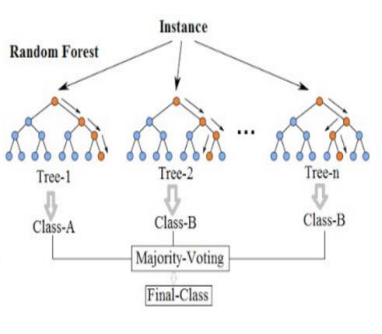
📌 랜덤 포레스트란?
- 정의
- Random Forest는 ensemble(앙상블) Machine Learning 모델이다.
- 여러 개의 DecisionTree 사용
- 각 DecisionTree가 전체 데이터를 사용하는 것이 아닌 데이터 일부만 사용함 (Bagging)
- 각 트리가 분류한 결과에서 가장 많이 득표한 결과를 최종 분류 결과로 선택 (Ensemble Voting)
📌 랜덤 포레스트 실습
- 1. 라이브러리 Import
import pandas as pd import numpy as np # 레이블 인코딩 작업 : 라벨링 + 원-핫 인코딩 from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder, OneHotEncoder from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
- 2. 데이터 준비
# 타이타닉 데이터세트 사용 df = pd.read_csv("../testdata/titanic_data.csv") print(df.head(3)) # PassengerId Survived Pclass ... Fare Cabin Embarked # 0 1 0 3 ... 7.2500 NaN S # 1 2 1 1 ... 71.2833 C85 C # 2 3 1 3 ... 7.9250 NaN S
- 3. 결측치 확인
print(df.info()) # RangeIndex: 891 entries, 0 to 890 # # Column Non-Null Count Dtype # --- ------ -------------- ----- # 0 PassengerId 891 non-null int64 # 1 Survived 891 non-null int64 # 2 Pclass 891 non-null int64 # 3 Name 891 non-null object # 4 Sex 891 non-null object # 5 Age 714 non-null float64 # 6 SibSp 891 non-null int64 # 7 Parch 891 non-null int64 # 8 Ticket 891 non-null object # 9 Fare 891 non-null float64 # 10 Cabin 204 non-null object # 11 Embarked 889 non-null object print(df.isnull().sum()) # PassengerId 0 # Survived 0 # Pclass 0 # Name 0 # Sex 0 # Age 177 # SibSp 0 # Parch 0 # Ticket 0 # Fare 0 # Cabin 687 # Embarked 2
- 3-1. 결측치 제거 후 사용 칼럼 추출
df = df.dropna(subset=['Pclass', 'Sex', 'Age']) df = df.loc[:, ['Pclass', 'Sex', 'Age']] print(df.info()) # Int64Index: 714 entries, 0 to 890 # # Column Non-Null Count Dtype # --- ------ -------------- ----- # 0 Pclass 714 non-null int64 # 1 Sex 714 non-null object # 2 Age 714 non-null float64
- 4-1. 레이블 인코딩 작업 [레이블 인코딩]
- ⭐ LabelEncoder 모듈 : Number 라벨링# 1) 레이블 라벨링 작업 encoder = LabelEncoder() df['Sex'] = encoder.fit_transform(df['Sex']) print(df.head(2)) # Pclass Sex Age # 0 3 1 22.0 # 1 1 0 38.0
- 4-2. 원-핫 인코딩 작업 [레이블 인코딩]
- ⭐ OneHotEncoder 모듈 : 범주형 데이터 값을 0과 1을 사용하여 표현onehot = OneHotEncoder() print(onehot.fit_transform(df[['Pclass']]).toarray()) # [[0. 0. 1.] # [1. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 1.] # ... # [1. 0. 0.] # [1. 0. 0.] # [0. 0. 1.]] df_onehot = pd.DataFrame(onehot.fit_transform(df[['Pclass']]).toarray()) df_onehot.columns = ['f_class', 's_class', 't_class'] df = pd.concat([df, df_onehot], axis=1) print(df.head(2)) # Pclass Sex Age Survived f_class s_class t_class # 0 3.0 1.0 22.0 0.0 0.0 0.0 1.0 # 1 1.0 0.0 38.0 1.0 1.0 0.0 0.0
- 5. 학습, 테스트 데이터 분리
df_x = df.drop(['Survived'], axis=1) df_y = df['Survived'] x_train, x_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(df_x, df_y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1) print(x_train.shape, x_test.shape, y_train.shape, y_test.shape) # (602, 6) (259, 6) (602,) (259,)
- 6. 랜덤 포레스트 모델
model = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=500, criterion='entropy') model.fit(x_train, y_train)
- 7. 예측값, 실제값 비교
y_pred = model.predict(x_test) print('실제값 : ', np.array(y_test[:3])) print('예측값 : ', y_pred[:3]) # 실제값 : [1. 0. 0.] # 예측값 : [0. 0. 0.]
- 8. 성능 평가
print('acc : ', accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)) # acc : 0.783625730994152
- 9. 교차 검증
cross_val = cross_val_score(model, df_x, df_y, cv=5) print(cross_val) print(np.mean(cross_val)) # [0.74561404 0.79824561 0.81415929 0.78761062 0.79646018] # 0.7884179475236764
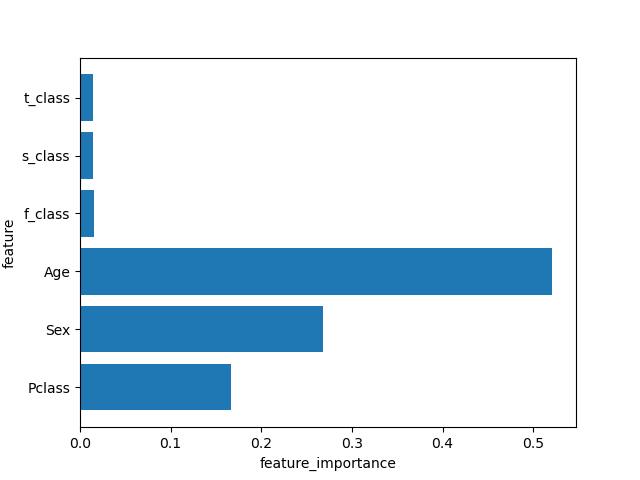
- 10. 특성 중요도 추출
print('특정(변수) 중요도 : ', model.feature_importances_) # 특정(변수) 중요도 : [0.16178083 0.26556737 0.52703405 0.01613185 0.01424291 0.01524298] def plot_importance(model): n_features = df_x.shape[1] plt.barh(np.arange(n_features), model.feature_importances_) plt.yticks(np.arange(n_features), df_x.columns) plt.xlabel('feature_importance') plt.ylabel('feature') plt.show() plot_importance(model)