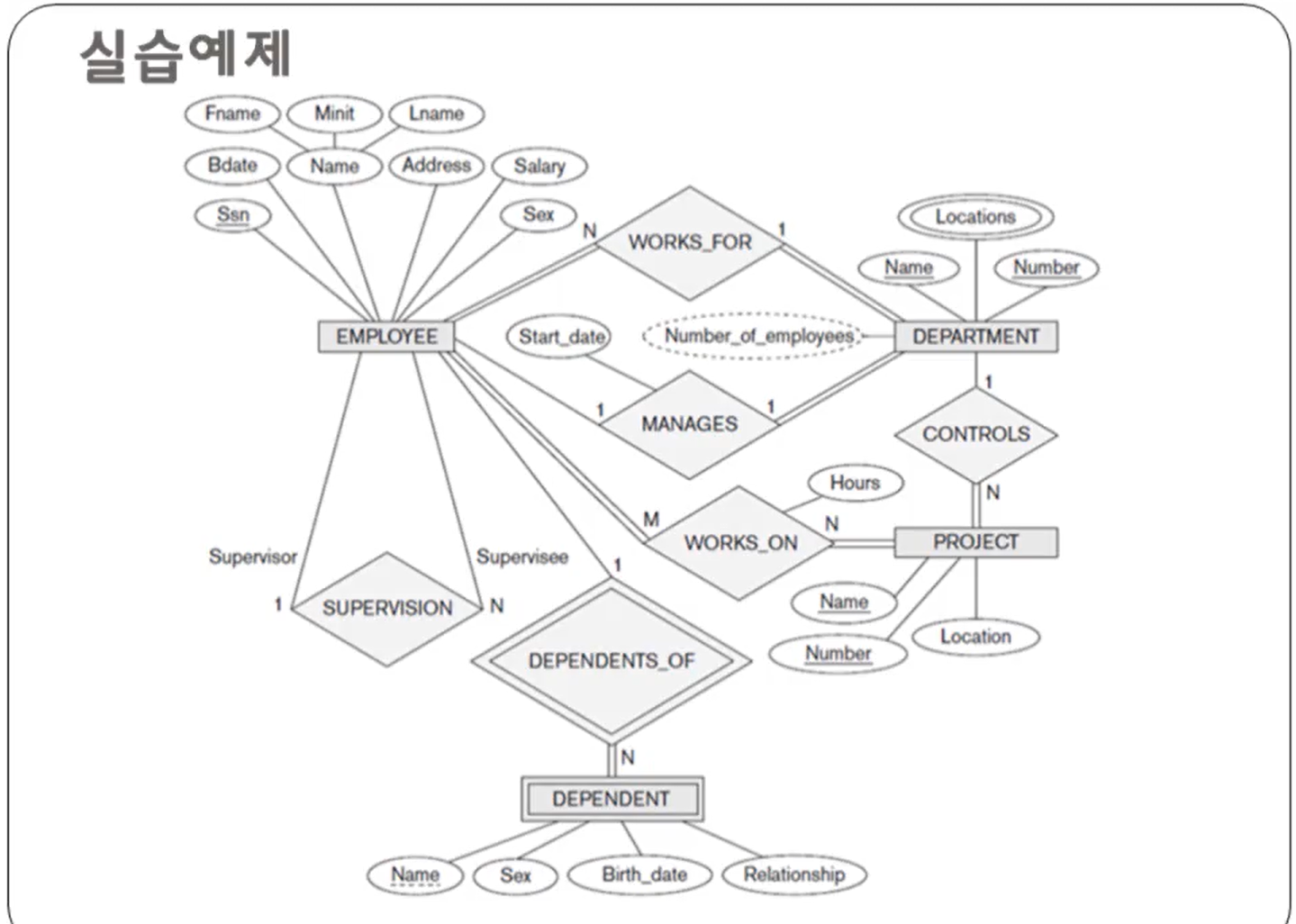
3. mySQL로 데이터베이스 구축

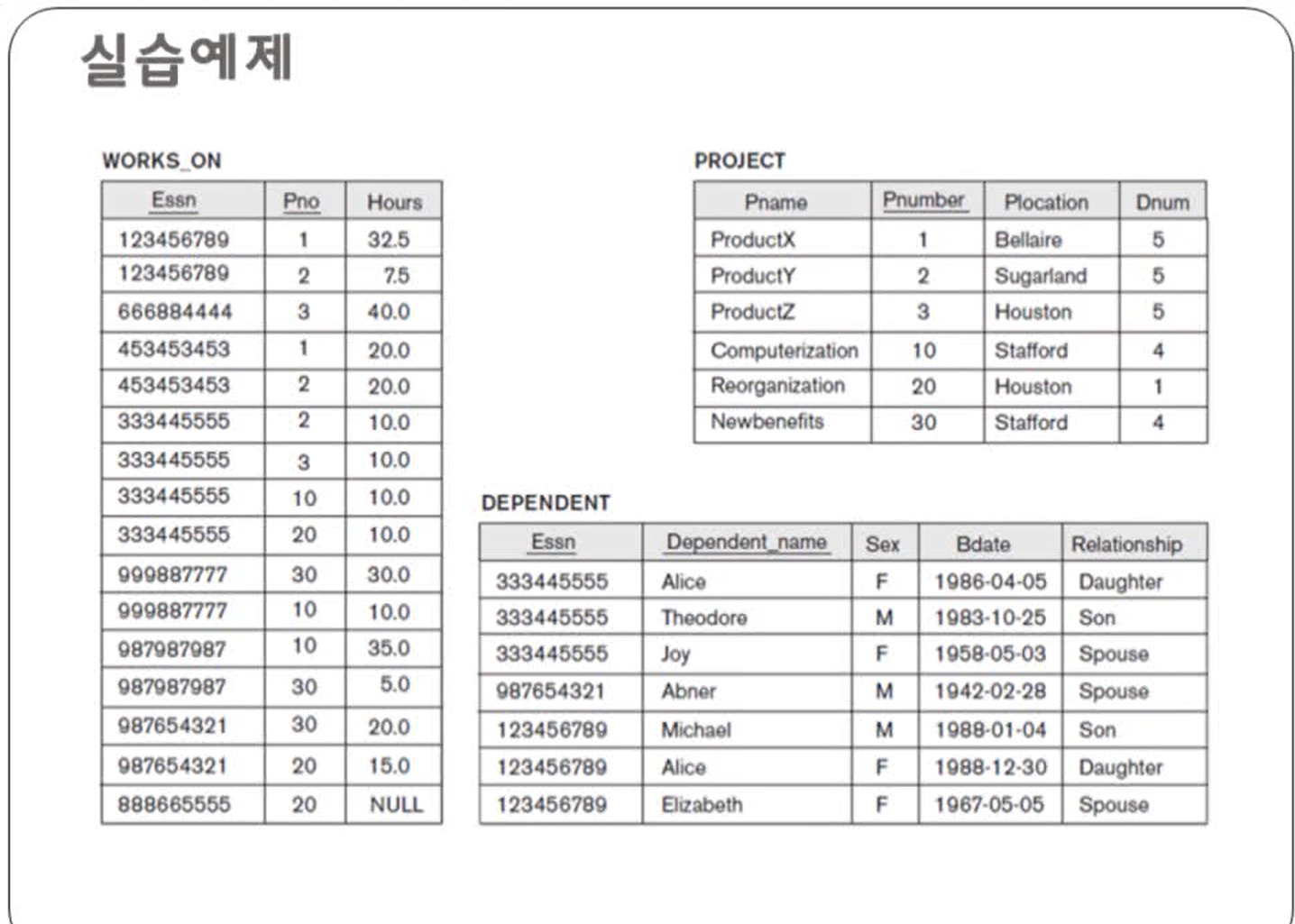
CREATE문으로 먼저 테이블 만들기
📢이전 예제와는 다르게 employee 테이블에서 department의 외래키를 참조해야 하기 때문에 오류가 발생한다. 따라서 add FOREIGN KEY들은 모두 alter table에서 진행하도록 한다.
drop table if exists employee cascade;
drop table if exists department cascade;
drop table if exists dept_locations cascade;
drop table if exists works_on cascade;
drop table if exists project cascade;
drop table if exists dependent cascade;
CREATE TABLE employee (
first_name VARCHAR(50) not null,
middle_initial char(1) not null,
last_name VARCHAR(50) not null,
ssn char(10) primary key not null,
birth_date Date,
address varchar(50) not null,
sex char(1) not null, # due to check condition
salary int,
super_ssn char(10) not null,
dno int
);
create table department (
dname varchar(50) not null,
dno int primary key not null,
mgr_ssn char(10) not null,
mgr_start_date date
);
create table dept_locations (
dno int not null,
dlocation varchar(50) not null,
primary key (dno, dlocation)
);
create table works_on (
essn char(10) not null,
pno int not null,
hours float,
primary key (essn, pno)
);
create table project (
pname varchar(50) not null,
pno int primary key not null,
plocation varchar(50) not null,
dno int not null
);
create table dependent (
essn char(10) not null,
dependent_name varchar(50) not null,
sex char(1) not null,
birth_date date,
relationship varchar(50) not null,
primary key (essn, dependent_name)
);
📢GUI로 테이블을 만드는 것과 쿼리로 직접 테이블을 만드는 것은 서로 charset이 다르기 때문에 incompatible 에러가 발생하므로 주의할 것!
INSERT문으로 인스턴스 값 추가하기
📢ALTER문으로 외래키 제약조건을 먼저 추가하면 Cannot add or update a child row: a foreign key constraint fails라는 에러가 발생하는데, 이유는 외래키를 가진 employee 테이블에서 기본키를 가진 department 테이블에 값이 존재하지 않기 때문이다.
👉따라서, 제약조건을 추가하기 전에 모든 테이블에 인스턴스 값을 먼저 추가하도록 하자.
📢워크벤치 그리드 gui에서 값을 직접 넣을 때 값을 넣지 않더라도, ""로 인식을 하기 때문에 NULL이 포함된 레코드는 쿼리를 통해서 넣을 것!
ALTER문으로 제약조건 추가하기
alter table employee
add FOREIGN KEY(dno) REFERENCES department(dno),
add FOREIGN KEY(super_ssn) REFERENCES employee(ssn),
add CONSTRAINT chk_sex CHECK (sex = 'F' or sex = 'M');
alter table department
add foreign key(mgr_ssn) references employee(ssn);
alter table dept_locations
add FOREIGN KEY(dno) REFERENCES department(dno);
alter table works_on
add FOREIGN KEY(essn) REFERENCES employee(ssn),
add FOREIGN KEY(pno) REFERENCES project(pno);
alter table project
add FOREIGN KEY(dno) REFERENCES department(dno);
alter table dependent
add FOREIGN KEY(essn) REFERENCES employee(ssn),
add CONSTRAINT chk_dependent_sex CHECK (sex = 'F' or sex = 'M');4. 질의에 따른 sql 쿼리 작성하기
[질의1] Research 부서에서 일하는 모든 사원의 이름과 주소를 검색하라.
select e.first_name, e.middle_initial, e.last_name, e.address
from employee e
inner join department d
on e.dno = d.dno
where d.dname = 'Research';💡참고로 교수님은 암시적 조인을 사용했는데, 결과값은 같으므로 나의 명시적 조인을 작성하였다.
[질의2] Stafford에 위치한 모든 프로젝트에 대하여 프로젝트 번호와 관리부서 번호, 부서 관리자의 성, 주소, 생년월일을 나열하라.
자, 질의문이 상당히 복잡한데, 우선 하나의 쿼리로 먼저 작성해보자.
1. Stafford에 위치한 모든 프로젝트에 대하여 프로젝트 번호와 관리부서 번호: select p.pno, p,dno from project p where p.plocation = 'Stafford';
2. 부서 관리자의 성, 주소, 생년월일: 부서 관리자의 성, 주소, 생년월일은 employee 테이블에 있으니까 project 테이블과 조인을 해야겠지? 그런데, 부서 관리자는 department의 테이블에 있네?
- p.dno 외래키를 가지고 있는 project 테이블에서 department 테이블의 d.dno를 참조한다. =>
inner join department d on p.dno = d.dno - d.mgr_ssn 외래키를 갖고 있는 department 테이블에서 employee 테이블의 e.super_ssn을 참조한다 =>
inner join employee e on d.mgr_ssn = e.super_ssn
위의 과정들을 합치면 아래와 같다👇
select p.pno, p.dno, e.last_name, e.address, e.birth_date from project p
inner join department d on p.dno = d.dno # controls
inner join employee e on d.mgr_ssn = e.super_ssn # manages
where p.plocation = 'Stafford';💡참고로, 여러 개의 테이블을 조인하고 싶으면 그냥 간단하게 inner join..on을 추가하면 된다.
[질의3] 이름이 'John B.Smith'인 사원의 생년월일과 주소를 검색하라.
select birth_date, address
from employee
where first_name = 'John' and middle_initial = 'B' and last_name = 'Smith';[질의4] 주소가 'Houston, Texas'인 모든 사원의 이름을 검색하라.
select first_name, middle_initial, last_name
from employee
where address like '%Houston, TX%';- 특정 문자열을 포함할 때는
like '%str%'을 사용한다.
[질의5] 1950년대에 태어난 모든 사원의 이름을 검색하라.
select first_name, middle_initial, last_name
from employee
where birth_date between '1950-01-01' and '1959-12-31';- 특정 범위 내에서 검색하고 싶으면
between..and문법을 사용하면 된다.- 참고로 value는 number, text 그리고 date 타입이 된다.
👩🏫다른 풀이
select first_name, middle_initial, last_name
from employee
where birth_date like '195%';like '김%'와 같이 김으로 시작되는 문자열을 검색할 때 쓰는데, 195로 시작되는 텍스트만 검색하면 된다.
[질의6] 'ProductX' 프로젝트에 참여하는 모든 사원의 이름과 10%씩 올린 급여를 구하여라.
select e.first_name, e.middle_initial, e.last_name, salary * 1.1 as increased_salary
from employee e
inner join project p on e.dno = p.dno
where p.pname = 'ProductX';😓앗! project 테이블을 다시 살펴보니, dno가 5인 다른 프로젝트 이름들도 존재하기 때문에 이 쿼리는 잘못되었다.

👩🏫 올바른 풀이
select e.first_name, e.middle_initial, e.last_name, salary * 1.1 as increased_salary
from employee e
inner join works_on w on e.ssn = w.essn
inner join project p on w.pno = p.pno
where p.pname = 'ProductX';💡works_on은 연관된 개체가 다대다 관계를 가지기 때문에 따로 테이블을 생성한 것인데, E-R 관계가 잘 안보이면 ERD를 다시 볼 것!
[질의7] 급여가 30,000달러에서 40,000달러 사이에 있는 5번 부서의 모든 사원의 이름을 검색하라.
select e.first_name, e.middle_initial, e.last_name
from employee e
where e.dno = 5 and (salary >= 30000 and salary <= 40000);⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐[질의8] 부서이름과 사원 이름 및 각 사원이 근무하는 프로젝트 이름들의 리스트를 검색하는데, 부서이름 순서대로, 그리고 각 부서 내에서는 사원의 성과 이름의 알파벳 순서대로 구하라.
🤔SQL 강의록에서는 '각~', '별~'은 group by로 처리하라고 했는데, 교수님은 다음과 같은 쿼리를 작성하였다.
select d.dname, e.first_name, e.last_name, p.pname
from department d
inner join employee e on d.dno = e.dno
inner join works_on w on e.ssn = w.essn
inner join project p on w.pno = p.pno
order by d.dname, e.last_name, e.first_name;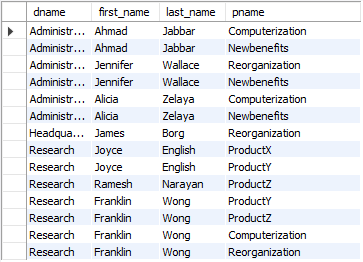
😓이 문제를 어렵게 생각한 이유는, 먼저 테이블(개체 및 관계)를 생각하지 않고 '각~'이라는 키워드에 꽂혀서 그룹핑을 먼저 생각했기 때문이다.
⚙️ 해결 과정
-
해당 속성이 있는 테이블들을 모두 찾기:
부서 이름이 있는 부서 테이블, 사원 이름이 있는 사원 테이블, 사원이 근무하는 근무 테이블, 그리고 프로젝트 이름 이 있는 프로젝트 테이블을 먼저 찾아내야 한다.
from department d, employee e, works_on w, project p -
테이블이 여러 개가 있기 때문에 ERD를 다시 보고 관계가 있는 외래키를 찾아서 테이블끼리 조인을 한다.
inner join employee e on d.dno = e.dno- Department와 Employee 간의 works_for 관계(외래키는 dno)
inner join works_on w on e.ssn = w.essn- Employee와 Works_on 간의 관계(외래키는 ssn이고, Employee와 Project는 다대다 관계라 별도의 릴레이션인 Works_on을 통해서 접근해야함)
inner join project p on w.pno = p.pno- Works_on과 Project 간의 관계(외래키는 pno)
💡테이블이 N개라면, 당연히 조인 연산자는 (N-1)개가 필요
📝또한, group by는 같은 값을 가진 row끼리 하나의 그룹으로 뭉쳐주는 키워드이기 때문에 이 데이터들을 묶어서 어디에 활용할 것인가를 생각해야 한다.(e.g. 집계함수: COUNT(), AVG(), SUM(), MIN(), MAX())
[질의9] 상사가 없는 모든 사원의 이름을 검색하라.
select first_name, middle_initial, last_name
from employee
where super_ssn is null;⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐[질의10] 평균봉급이 가장 높은 부서 번호를 검색하라.
1. 부서별 평균봉급을 먼저 검색하기 위해서 먼저 dno를 그룹핑한다.
select avg(salary), dno
from employee
group by dno;💡select절에 avg()와 같은 집계함수를 사용했기 때문에 salary 속성은 group by에 추가하지 않아도 된다.
- 1에서 가장 높은 부서 번호를 검색하기 위해 max()를 사용해야 하는데 max(avg())와 같이 사용할 수 없어서 하위 쿼리를 작성한다.
select avg(salary), dno
from employee
where salary = (select max(salary) from employee)
group by dno;😣다시 생각해보니, salary 속성에서 가장 높은 값이 55000이기 때문에 where절은 잘못되었다. 따라서 모범 답안에 맞춰서 교정하도록 한다.
- 심지어, 질의문에서는 "평균봉급이 가장 높은 부서 번호를 검색하라."라고 되어있는데 쓸데없이 salary 속성도 검색하였다.
👩🏫 올바른 풀이
select dno
from employee
group by dno having avg(salary) >= all (
select avg(salary)
from employee
group by dno
);🤔group by를 통해서 최댓값을 리턴하려면 어떻게 해야할까?
💡ALL: 부속 질의문의 결과 값 모두와 비교한 결과가 참이면 검색 조건을 만족(비교 연산자와 함께 사용)
이 키워드를 이용해서 위의 복잡한 쿼리를 풀어보면 다음과 같다:
- 외부쿼리:
select dno, avg(salary)
from employee
group by dno;결과값: {1: 55000, 4: 31000, 5: 33250}
👉편의를 위해 딕셔너리 형태로 작성하였음.
- 서브쿼리:
select avg(salary)
from employee
group by dno;결과값: [55000, 31000, 33250] 마찬가지로 동일하다.
그런데, ALL 키워드를 다시 한번 보면 서브쿼리의 결과 값 모두와 비교한 결과가 참일 때만 검색 조건을 만족한다고 하였다.
외부 쿼리값이 55000인 경우:
55000 ≥ 55000 → 참
55000 ≥ 31000 → 참
55000 ≥ 33250 → 참
→ 조건을 모두 만족한다.
반면 외부 쿼리값이 31000이나 33250인 경우는,
31000나 33250은 내부 쿼리값인 55000과 비교했을 때 거짓이 되어 검색 조건을 만족하지 않는다.
📝따라서, 최종적으로 avg(salary)의 최댓값인 55000을 가진 dno를 검색한다.
[질의11] 'Research' 부서에 근무하는 모든 사원의 급여의 합, 최고 급여, 최소 급여, 평균 급여를 구하라.
SELECT sum(salary) AS total_salary, max(salary) AS max_salary, min(salary) AS min_salary, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employee e
INNER JOIN department d ON e.dno = d.dno
WHERE d.dname = 'Research';[질의12] 'Research' 부서에서 근무하는 총 사원수를 검색하라.
SELECT count(*) AS num_of_employee FROM employee e
INNER JOIN department d ON e.dno = d.dno
WHERE d.dname = 'Research';💡테이블의 "모든 행"을 카운트하기 때문에 중복 여부 상관 x
[질의13] 각 부서에 대해서 부서번호, 부서에 속한 사원들의 수, 각 부서에 속한 사원들의 평균 급여를 구하라.
select dno, count(*) as num_of_employee, avg(salary) as avg_salary
from employee
group by dno;[질의14] 두 명 이상의 사원이 근무하는 각 프로젝트에 대해서 프로젝트 번호, 프로젝트 이름, 프로젝트에서 근무하는 사원의 수를 검색하라.
⚙️ 해결 과정
- 먼저, 두 명 이상의 사원이 근무하는 프로젝트를 알아내기 위해 group by를 사용하여 pno를 먼저 검색한다.
select pno, count(*) as num_of_employee
from works_on
group by pno having num_of_employee >= 2;=> {1: 2, 2: 3, 3: 2, 10: 3, 20: 3, 30: 3} # {pno: num_of_employee}
-
프로젝트 번호, 프로젝트 이름, (프로젝트에서 근무하는 사원의 수)를 검색:
select p.pno, p.pname from project p -
위의 works_on 테이블과 project 테이블을 조인한다.
select w.pno, p.pname, count(*) as num_of_employee
from works_on w
inner join project p on w.pno = p.pno
group by pno having num_of_employee >= 2;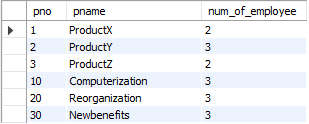
💡주 테이블을 works_on으로 했기 때문에 count(*)는 works_on의 행을 대상으로 집계한다.
👩🏫 교수님이 작성한 쿼리
select p.pno, p.pname, count(*) as num_emp
from employee e, works_on w, project p
where w.essn=e.ssn and p.pno = w.pno
group by p.pno, p.pname
having count(*) >= 2🤖employee 테이블과의 조인이 필요한 이유:
향후 확장성을 위해 나중에 쿼리에 employee의 추가 정보를 포함하거나, 특정 조건(예: 부서, 근속기간 등)을 필터링할 필요가 생길 때, 이미 employee 테이블과 조인되어 있으면 쿼리 수정이 용이합니다.
⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐[질의15] 2명 이상의 사원이 근무하는 각 부서에 대해서 부서 번호, 부서이름과 40,000달러가 넘는 급여를 받는 사원의 수를 검색하라.
⚙️ 해결 과정
- 근무하는 두명 이상의 사원을 먼저 검색한다.
select w.essn, count(*) as num_of_employee
from works_on w
group by w.essn having num_of_employee >= 2;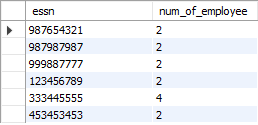
- 부서 번호, 부서 이름, 40,000달러가 넘는 급여를 받는 사원을 검색
select e.dno, d.dname, ssn
from employee e
inner join department d on e.dno = d.dno
where salary > 40000;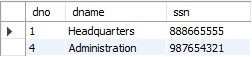

급여가 40000 달러 초과인 사람만 조회했으므로 검색 결과가 참이다.
- 위의 2가지를 짬뽕시킨다.
select e.dno, d.dname, e.salary, count(*) as num_of_employee
from employee e
inner join department d on e.dno = d.dno
inner join works_on w on e.ssn = w.essn
group by w.essn having num_of_employee >= 2 and e.salary > 40000;
😫앗! 위의 employee 테이블에 따르면 2명 이상 근무하는 부서 중 40000달러를 초과한 사람은 43000달러를 받는 1명만 나와야되는데 결과값이 다르다!!
🤔왜 이런 결과가 발생한걸까?
이유는 간단하다. "근무하는"이라는 문장에 꽂혀서 관계를 생각하지 않고 질의문과 ERD를 꼼꼼하게 보지 않았기 때문이다. 질의문을 다시 한번 살펴보자.🔎
2명 이상의 사원이 근무하는 각 부서에 대해서 부서 번호, 부서이름과 40,000달러가 넘는 급여를 받는 사원의 수를 검색하라.
employee 테이블: 부서 번호(department의 외래키), 급여
department 테이블: 부서이름
📢 자! 어디에 works_on 테이블을 가져오라는 단서가 있었지? 질의문을 꼼꼼하게 볼 것!
👩🏫 올바른 풀이
select e.dno, d.dname, count(*) as num_emp_over_40000
from employee e, department d
where e.salary > 40000 and e.dno = d.dno and e.dno in (
select e.dno
from employee e
group by e.dno having count(*) >= 2
)
group by e.dno, d.dname;위의 모범 답안 쿼리 도출 과정도 상당히 복잡하기 때문에, 역시 나눠서 생각해보자.
- 2명 이상의 사원이 근무하는 각 부서에 대해 검색
select e.dno, count(*) as num_emp
from employee e
group by e.dno having num_emp >= 2;- 부서이름과 40000달러가 넘는 급여를 받는 부서를 검색
select d.dname, e.dno
from department d
inner join employee e on d.dno = e.dno
where e.salary > 40000;위의 2가지 과정을 종합하면,
👩외부 쿼리: 부서별로 부서 번호와 부서 이름, 그리고 40,000달러가 넘는 급여를 받는 사원의 수를 구하되,
👶서브 쿼리: 부서 전체의 사원 수가 2명 이상인 부서만 선택
select e.dno, d.dname, count(*) as num_emp_over_40000
from employee e
inner join department d on e.dno = d.dno
where e.salary > 40000 and e.dno in (
select e.dno
from employee e
group by e.dno
having count(*) >= 2
)
group by e.dno, d.dname;🔖IN 연산자(다중 행 부속 질의문에 사용): 부속 질의문의 결과 값 중 일치하는 것이 있으면 검색 조건이 참
💡참고로, ONLY_FULL_GROUP_BY 모드가 활성화되어 있으면, SELECT 문에 있는 모든 열은 집계 함수가 되거나 GROUP BY 절에 나타나야 한다.
- 위의 쿼리는 department 테이블의 dno가 기본키 역할을 해서d.dname을 유일하게 결정하기 때문에 사실상 GROUP BY절에 d.dname을 작성하지 않아도 되지만 안전장치를 걸어두자.
📚참고 자료
🔗between 문법: https://www.w3schools.com/mysql/mysql_between.asp
🔗group by 사용 이유 및 오류 해결법: https://kimsyoung.tistory.com/entry/GROUP-BY%E4%B8%8B-%EC%98%A4%EB%A5%98%EB%AC%B8-%ED%95%B4%EA%B2%B0%ED%95%98%EA%B8%B0?category=822739
