19.7 프로토타입 체인
me의 프로토타입은 프로토타입은 Person.prototype 이다.
//person 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
cosnole.log("Hi! My name is ${this.name}");
}
//person 함수에 의해 생성된 me
const me = new Person('Lee');
//me객체는 Object.prototype의 메서드인 hasOwnProperty 호출가능
console.log(me.hasOwnProperty('name')); // true
//Person.prototype의 프로토타입은 Object.prototype이다.
Object.getPrototypeOf(me) === Person.prototype; // true
Object.getPrototypeOf(Person.prototype) === Object.prototype; // true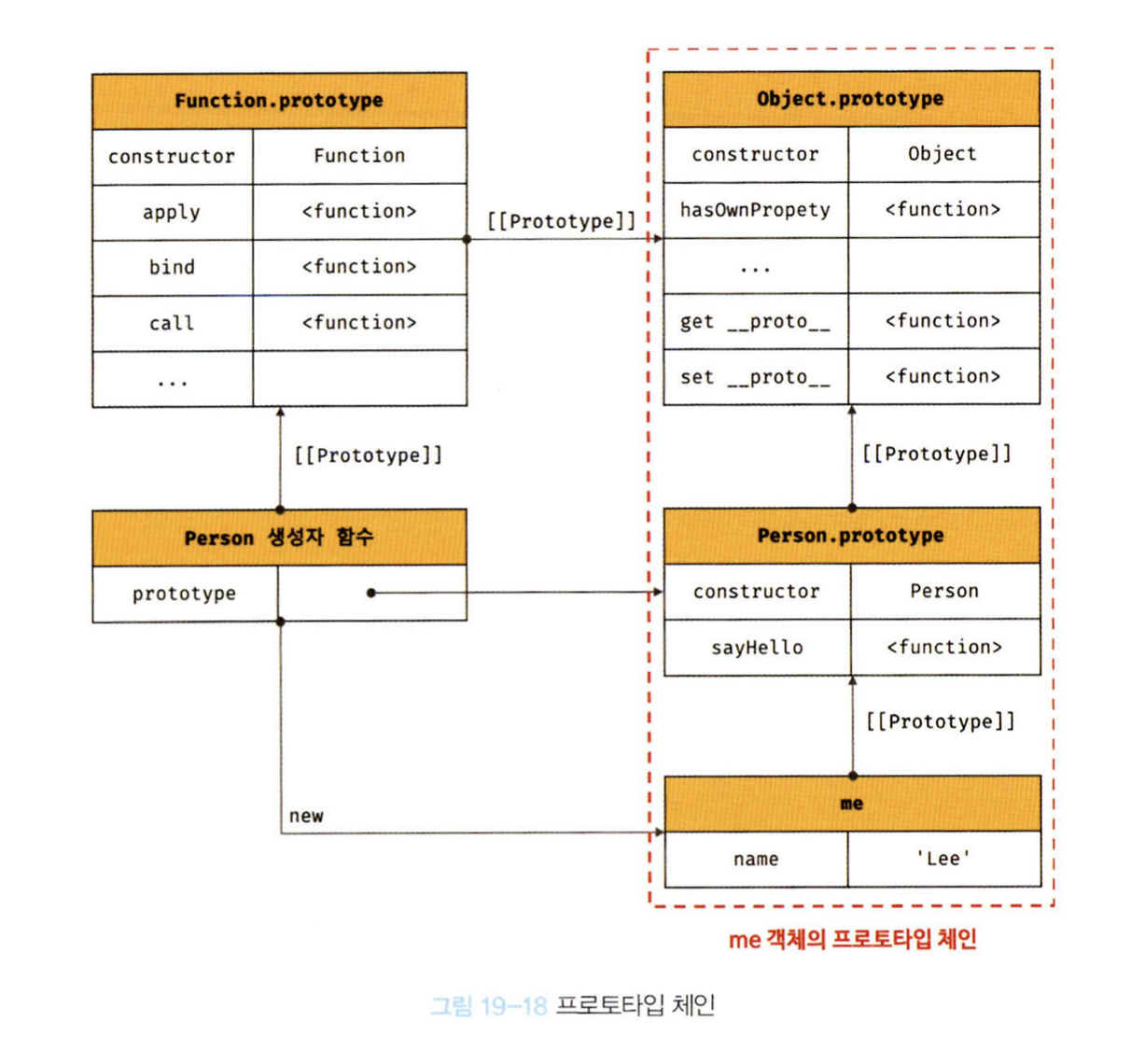
- 자바스크립트는 객체의 프로퍼티에 접근하려고 할 때 해당 객체에 접근하려는 프로퍼티가 없다면 [[Prototpe]]내부 슬롯 참조를 따라 자신의 부모 역할을 하는 프로토타입의 프로퍼티를 순차적으로 검색한다. <--이것이 바로 프로토타입 체인
- 프로토타입 체인의 최상위에 위치하는 객체(종착점)는 언제나 Object.prototype이다.
->따라서 모든 객체는 Object.prototype을 상속받음. - Object.prototype의 프로토타입, 즉 [[Prototype]]의 내부슬롯 값은 null이다.
- Object.prototype까지 가서도 찾는 메서드가 존재하지 않는다면 undefined가 반환되며, 에러가 발생하지는 않는다.
me.hasOwnProperty('name');
- 우선 전역 스코프에서 me스코프를 검색한다.
- me 식별자는 전역에서 선언되었으므로 전역 스코프에서 검색된다.
- me 식벽자를 검색 후 me 객체의 프로토타입 체인에서 hasOwnProperty 메서드를 검색한다.
이처럼 스코프체인과 프로토타입 체인은 서로 연관없이 동작하는 것이 아니라 서로 협력하여 식별자와 프로퍼티를 검색하는데 사용된다.
19.8 오버라이딩과 프로퍼티 섀도잉
const Person = (function () {
// 생성자 함수
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// 프로토타입 메서드
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 생성자 함수를 반환
return Person;
}());
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 인스턴스 메서드
me.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hey! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
// 인스턴스 메서드가 호출된다. 프로토타입 메서드는 인스턴스 메서드에 의해 가려진다.
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee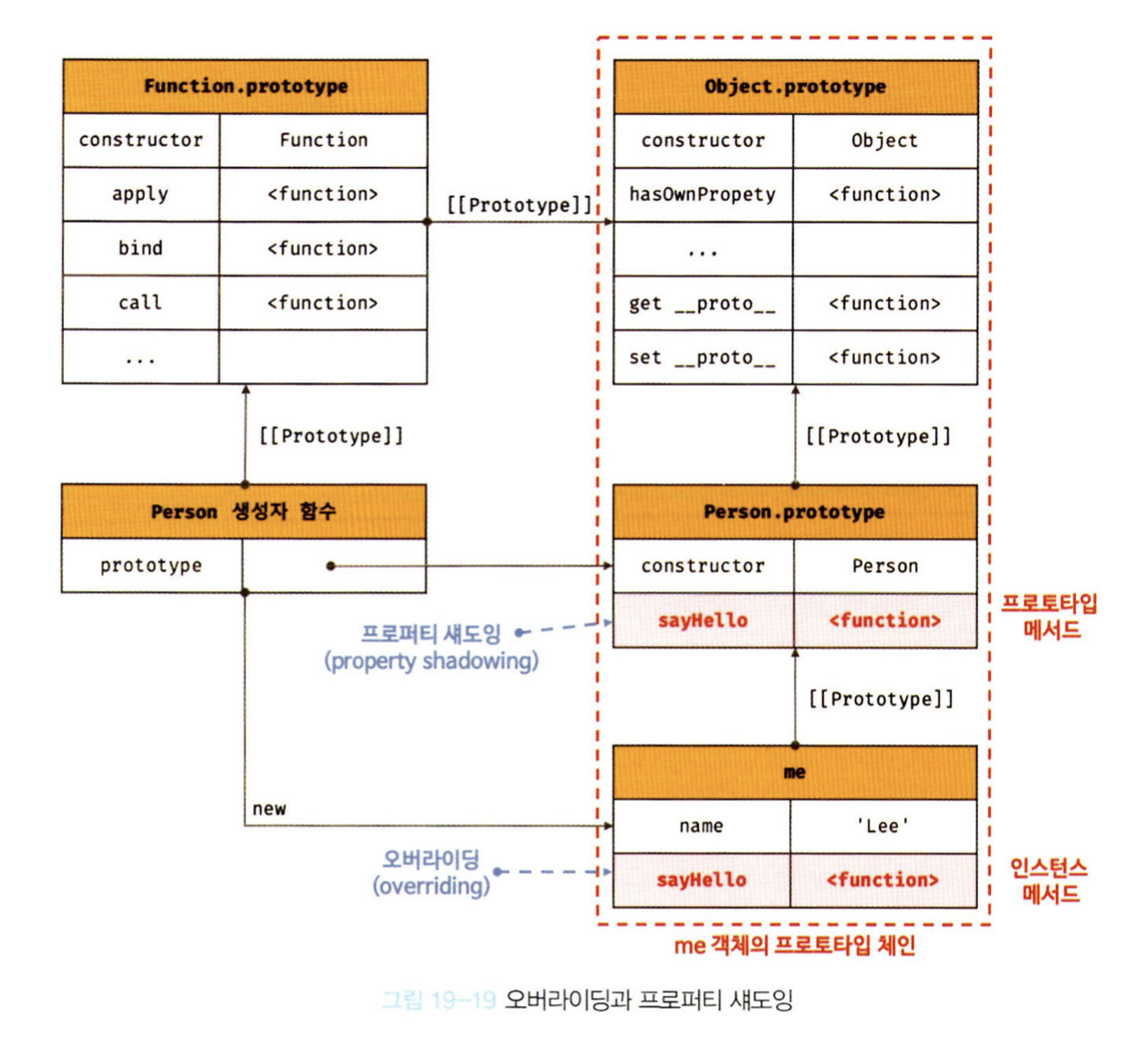
- 프로토타입이 소유한 메서드를 포함한 프로퍼티를 프로토타입 프로퍼티,
인스턴스가 소유한 프로퍼티를 인스턴스 프로퍼티라고한다. - 프로토타입 프로퍼티와 같은 이름의 프로퍼티를 인스턴스에 추가하면
프로토타입 체인을 따라 프로토타입 프로퍼티를 검색하여 프로토타입 프로퍼티를 덮어쓰는 것이 아니라
인스턴스 프로퍼티로 추가한다. - 인스턴스 메서드 sayHello는 프로토타입 메서드 sayHello를 오버라이딩했고 프로토타입 메서드 sayHello는 가려진다. 상속 관계에 의해 프로퍼티가 가려지는 현상을 프로퍼티 새도잉이라 한다.
- 오버라이딩이란? 상위 클래스가가지고 있는 메서드를 하위 클래스가 재정의하여 사용하는 방식
- 오버로딩? 함수의 이름은 동일하지만 매개변수의 타입 또는 개수가 다른 메서드를 구현하고
매개변수에 의해 메서드를 구별하여 호출하는 방식이다.
프로퍼티를 삭제하는 경우도 마찬가지이다.
//인스턴스 메서드를 삭제한다.
delete me.sayHello;
//인스턴스에서는 sayHello 메서드가 없으므로 프로토타입 메서드가 호출된다.
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee
// 프로토타입 체인을 통해 프로토타입 메서드가 삭제되지 않는다.
delete me.sayHello;
// 프로토타입 메서드가 호출된다.
me.sayHello();// Hi! My name is Lee
// 프로토타입 메서드 변경
Person.prototype.sayHello = function () {
console.log(`Hey! My name is ${this.name}`);
};
me.sayHello(); // Hey! My name is Lee
// 프로토타입 메서드 삭제
delete Person.prototype.sayHello;
me.sayHello(); // TypeError: me.sayHello is not a function- 프로퍼티를 삭제하는 경우에도 마찬가지로 인스턴스 메서드를 삭제하면 삭제되고 프로토타입 메서드가 호출된다.
- 하위 객체를 통한 프로토타입 프로퍼티 변경 및 삭제는 허용되지 않는다.
즉 하위 객체를 통한 프로토타입의 get 엑세스는 허용되나, set은 허용되지 않는다. - 프로토타입 프로퍼티를 변경 및 삭제 하려면 하위 객체를 통해 프로토타입 체인으로 접근할 게 아니라 프로토타입으로 직접 접근해야한다.
19.9 프로토타입의 교체
프로토타입은 임의의 다른 객체로 변경가능하다.
부모 객체인 프로토타입을 동적으로 변경할 수 있다는 의미이다.
19.9.1 생성자 함수에 의한 프로타입의 교체
const Person = (function () {
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
// ① 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티를 통해 프로토타입을 교체
Person.prototype = {
sayHello() {
console.log(`Hi! My name is ${this.name}`);
}
};
return Person;
}());
const me = new Person('Lee');
// 생성자 함수의 constructor와 연결 끊김
console.log(me.constructor === Person); // false
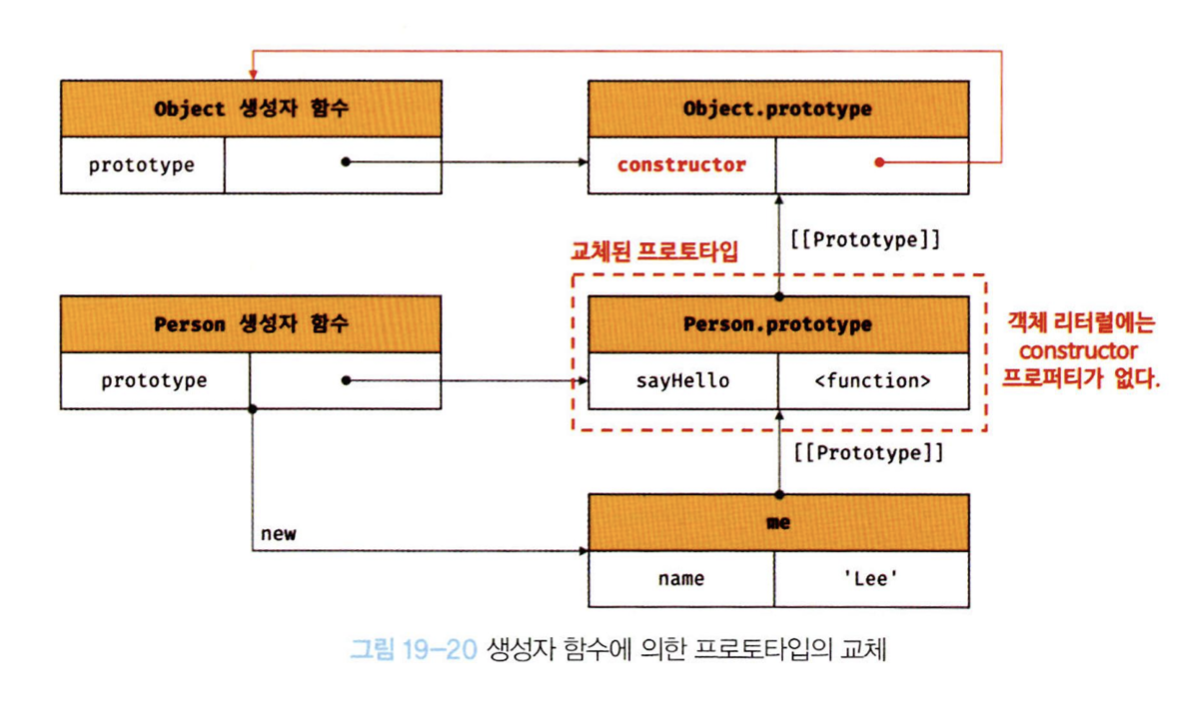
console.log(me.constructor === Object); // ture① 에서 Person.prototype에 객체 리터럴을 할당.
이것은 Person 생성자 함수가 생성할 객체의 프로토타입을 객체 리터럴로 교체한 것이다.
프로토타입으로 교체한 객체 리터럴에는 constructor 프로퍼티가 없다.
(constructor 프로퍼티는 자바스크립트 엔진이 프로토타입을 생성할 때 암묵적으로 추가한 프로퍼티이다.
따라서 me객체의 생성자 함수를 검색하면 Person이 아닌 Object가 나온다.
19.9.2 인스턴스에 의한 프로타입의 교체
- 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 다른 임의 객체를 바인딩 하는것은 미래에 생성할 인스턴스의 프로토타입을 교체하는 것이다.
- proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 프로토타입을 교체하는 것은 이미 생성된 객체의 프로토타입을 교체하는 것이다.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const me = new Person('chanmi');
//프로토타입으로 교체할 객체
const parent = {
sayHello() {
console.log(`hi my name is ${this.name}`);
}
};
// 1. me 객체를 프로토타입을 parent객체로 교체
Object.setPrototypeOf(me, parent);
// 2. 1번과 동일하게 동작
me.__proto__ = parent;
me.sayHello(); // hi my name is chanmi19.10 instanceof 연산자
- 우변의 생성자 함수의 prototype에 바인딩된 객체가 좌변의 객체의 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재하면 true, 아니면 false로 평가된다.
- 생성자 함수의 prototype에 바인딩된 객체가 프로토타입 체인 상에 존재하는지 확인한다.
- constructor 프로퍼티와 생성자 함수 간의 연결이 파괴되어도 instanceof 는 영향을 받지 않는다.
19.11 직접상속
19.11.1 Object.create에 의한 직접 상속
- Object.create 는 명시적으로 프로토타입을 지정하여 새로운 객체를 생성한다.
장점 - new 연산자 없이 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
- 프로토타입 지정하면서 객체를 생성할 수 있다.
- 객체 리터럴에 의해 생성된 객체도 상속 받을 수 있다.
19.11.2 객체 리터럴 내부에서 proto 에 의한 직접 상속
- ES6에서는 객체 리터럴 내부에서 proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 사용하여 직접 상속을 구현할 수 있다.
const myProto = { x: 10 };
//객체 리터럴에 의해 객체를 생성하면서 프로토타입을 직접 상속받을 수 있다.
const obj = {
y: 20,
// 직접 상속
// obj -> myProto -> Object.prototype -> null
__proto__: myProto
};
console.log(obj.x, obj.y); // 10 20
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj) === myProto) // true19.12 정적 프로퍼티/메서드
- 정적(static) 프로퍼티/메서드는 생성자 함수로 인스턴스를 생성하지 않아도 참조/호출 할 수 있는 프로퍼티/메서드를 말한다.
19.13 프로퍼티 존재 확인
19.13.1 in연산자
in연산자는 객체 내에 특정 프로퍼티가 존재하는지 여부를 확인한다.
key in object
const person = {
name: 'lee',
address: 'seoul'
};
//person 객체에 name프로퍼티가 존재한다.
console.log('name' in person); // true
//person 객체에 address프로퍼티가 존재한다.
console.log('address' in person); // true
console.log('age' in person); // false
// 객체가 상속받은 모든 프로토타입의 프로퍼티를 확인함.
// toString은 Object.prototype의 메서드임.
console.log('toString' in person); // truein연산자 대신 ES6에 도입된 Reflect.has 메서드 사용
// Reflect.has 메서드 사용
const person = { name: 'lee' };
console.log(Reflect.has(person, 'name')); // trueObject.prototype.hasOwnProperty 메서드
- Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty 메서드를 사용해도 객체에 특정 프로퍼티가 존재하는지 확인할 수 있다.
19.14 프로퍼티 열거
19.14.1 for...in문
객체의 모든 프로퍼티를 순회하며 열거하려면 for...in문을 사용한다.
사용법: for (변수선언문 in 객체) { ... }
- 배열에는 for in문을 사용하지 말고 for 문, for of 문, forEach 메서드 사용을 권장한다.
19.14.2 Object.keys/values/entries 메서드
- 객체 자신의 고유 프로퍼티만 열거하기 위해서는 for in문 보다는 Object.keys/values/entries 메서드 사용을 권장한다.
