자바스크립트는 명령형, 함수형, 프로토타입 기반, 객체지향 프로그래밍을 지원하는 멀티 패러다임 프로그래밍 언어이다.
19.1 객체 지향 프로그래밍
- 객체의 집합으로 프로그램을 표현하려는 프로그래밍 패러다임을 말한다.
- 다양한 속성 중에서 프로그램에서 필요한 속상만 표현하는 것을 추상화라 한다.
//이름과 주소 속성을 갖는 객체
const person={
name: 'lee',
address: 'seoul'
};
console.log(person); //{name: 'lee', address: 'seoul'}- 속성을 통해 여러 개의 값을 하나의 단위로 구상한 복합적인 자료구조를 객체라 한다.
- 객체는 상태 데이터와 동작을 하나의 논리적인 단위로 묶은 복합적인 자료구조라고 할 수 있다.
19.2 상속과 프로토타입
상속은 객체지향 프로그래밍의 핵심 개념으로, 어떤 객체의 프로퍼티 또는 메서드를 다른 객체가 상속받아 그대로 사용할 수 있는 것을 말한다.
안좋은 예제를 살펴보자
//생성자 함수
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
this.getArea = function() {
//Math.PI는 원주율을 나타내는 상수이다.
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
}
}
//반지름이 1인 인스턴스 생성
const circle1 = new Circle(1);
//반지름이 2인 인스턴스 생성
const circle2 = new Circle(2);
//Circle 생성자 함수는 인스턴스를 생성할 때마다 동일한 동작을하는 getArea메서드를 중복 생성하고 모든 인스턴스가 중복 소유한다. ---> 이것은 메모리 낭비 하나만 생성하여 모든 인스턴스가 공유해서 사용해야한다.
console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea); // false좋은 예제
// getArea 함수를 Circle 생성자 함수의 프로토타입에 추가를 한다. 이렇게 하면 circle1과 circle2는 같은 프로토타입을 공유하게 되므로 getArea 함수를 동일한 곳에서 상속받게 된다.
//console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea);은 true를 반환.
두 객체가 동일한 함수를 참조하고 있기 때문이다.
function Circle(radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
Circle.prototype.getArea = function () {
return Math.PI * this.radius ** 2;
};
const circle1 = new Circle(1);
const circle2 = new Circle(2);
console.log(circle1.getArea === circle2.getArea); // true19.3 프로타입 객체
- 프로타입 객체란 객체 간 상속을 구현하기 위해 사용된다.
- 프로토타입은 어떤 객체의 상위 객체 역할을 하는 객체로서 다른객체에 공유 프로퍼티(메서드 포함)를 제공한다.
- 모든 객체는 [[Prototype]]이라는 내부 슬롯을 가지며, 이 내부 슬롯의 값은 프로토타입의 참조(null일 수도 있음)다.
- 객체가 생성될 때 객체 생성 방식에 따라 프로토타입이 결정되고 [[Prototype]]에 저장된다.
- 모든 객체는 하나의 프로토타입을 갖는다.
- 모든 프로토타입은 생성자 함수와 연결되어 있다.
19.3.1 proto 접근자 프로퍼티
- 모든 객체는 proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 자신의 프로토타입, 즉 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯에 간접적으로 접근할 수 있다.
- 크롬에서 출력해보니 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 보이지 않고 바로 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯을 출력해줌.

그림의 빨간 박스로 표시된 것이 person 객체의 프로토타입인 object.prototype이다.
proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 person 객체의 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯이 가리키는 객체인 object.prototype에 접근한 결과를 브라우저가 콘솔에 표시한 것이다.
모든 객체는 proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 프로토타입을 가리키는 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯에 접근할 수 있다.
proto는 접근자 프로퍼티이다.
proto접근자 프로퍼티를 통해 프로토타입에 접근하는 이유
- 상호 참조에 의해 프로토타입 체인이 생성되는 것을 방지하기 위해서다.
const parent = {};
const child = {};
//child의 프로토티입을 parent로 설정
child.__proto__ = parent;
//parent 프로토티입을 child 설정
parent.__proto__ = child; // TypeError: Cyclic __proto__ value- 프로퍼티 검색 방향이 한쪽 방향으로만 흘러가야 한다.
- 서로가 자신의 프로토타입이 되는 순환 참주 프로토타입 체인을 만들려고 하기에 에러를 발생시킨다. --> 무한루프에 빠짐
- 따라서 아무 체크 없이 무조건적으로 프로토타입을 교체할 수 없도록 proto 접근자 프로퍼티 를 통해 프로토타입에 접근하고 교체하도록 구현되어 있다.
proto접근자 프로퍼티를 코드내에서 직접 사용하는 것은 권장하지 않는다.
- 모든 객체가 proto 접근자 프로퍼티를 사용할 수 있는 것은 아니다.
- 직접 상속을 통해 Object.prototype 을 상속받지 않는 객체를 생성할 수도 있다.
// 프로토타입 체인의 종점이라서 Object.__proto__ 를 상속받을 수 없음.
const obj = Object.create(null);
// obj는 Object.__proto__ 를 상속받을 수 없음.
console.log(obj.__proto__); // undefined
//따라서 __proto__보다 Object.getPrototypeOf 메서드를 사용하는 편이 좋다.
console.log(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj)); // null19.3.2 함수 객체의 prototype 프로퍼티
- 함수 객체만이 소유하는 prototype 프로퍼티는 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스의 프로토타입을 가리킨다.
- non-constructor 인 화살표 함수와 ES6 메서드 축약 표현으로 정의한 메서드는 prototype 프로퍼티 소유하지 않으며, 프로토타입도 생성하지 않는다.
// 화살표 함수는 non-constructor 이다.
const Person = (name) => {
this.name = name;
};
//non-constructor는 prototype 프로퍼티를 소유하지 않는다.
console.log(Person.hasOwnProperty('prototype')); // false
//non-constructor는 프로토타입을 생성하지 않는다.
console.log(Person.prototype); // undefined
// es6의 메서드 축약표현으로 정의한 메서드는 non-constructor이다.
const obj = {
foo() {}
};
//non-constructor는 prototype 프로퍼티를 소유하지 않는다.
console.log(obj.foo.hasOwnProperty('prototype')); // false
//non-constructor는 프로토타입을 생성하지 않는다.
console.log(obj.foo.prototype); // undefined생성자 함수로 객체를 생성한 후 proto접근자 프로퍼티와 prototype프로퍼티로 프로토타입 객체에 접근해보자.
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const me = new Person('chanmi');
// 동일한 프로토타입을 가리킨다.
console.log(Person.prototype === me.__proto__); // true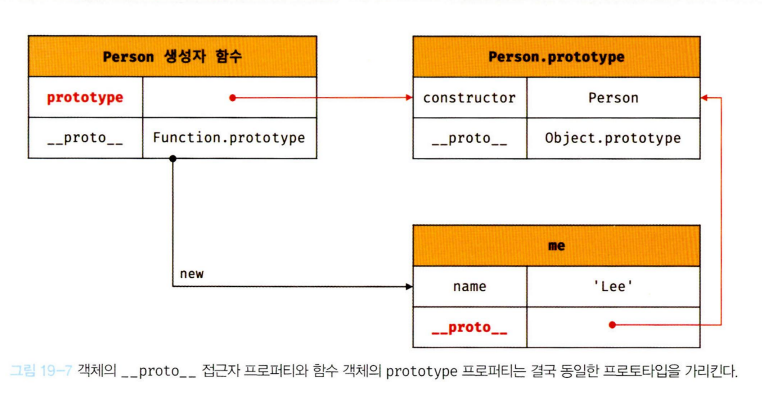
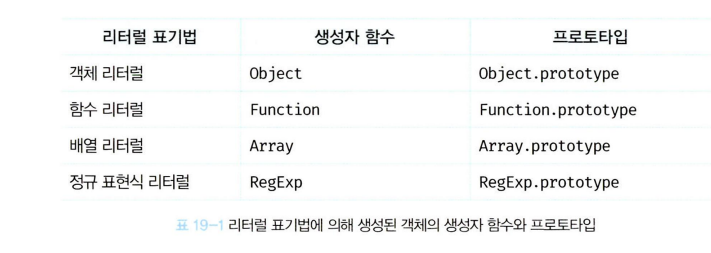
19.4 리터럴 표기법에 의해 생성된 객체의 생성자 함수와 프로토타입
19.5 프로토타입의 생성 시점
- 프로토타입은 생성자 함수가 생성되는 시점에 더불어 생성된다.
19.5.1 사용자 정의 생성자 함수와 프로토타입 생성 시점
- 내부 메서드 [[Construct]] 를 갖는 함수 객체, 즉 일반 함수(함수 선언문, 표현식)로 정의한 함수 객체는 new 연산자와 함께 생성자 함수로서 호출할 수 있다.
- constructor는 함수 정의가 평가되어 함수 객체를 생성하는 시점에 프로토타입도 더불어 생성된다.
- 사용자 정의 생성자 함수는 자신이 평가되어 함수 객체로 생성되는 시점에 프로토타입도 더불어 생성되며, 생성된 프로토타입의 프로토타입은 언제나 Object.prototype 이다.
// constructor 가 평가되어 함수 객체 생성 시점에 프로토타입도 더불어 생성됨.
console.log(Person.prototype); // {constructor: f}
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}- 생성자 함수로서 호출할 수 없는 함수. 즉 non-constructor는 프로토타입이 생성되지 않는다.
19.5.2 빌트인 생성자 함수와 프로토타입 생성 시점
(빌트인 생성자란 JavaScript에 내장된 기본 생성자 함수)
- 빌트인 생성자 함수도 일반 함수와 마찬가지로 빌트인 생성자 함수가 생성되는 시점에 프로토타입이 생성된다.
- 모든 빌트인 생성자 함수는 전역 객체가 생성되는 시점에 생성된다.
- 생성자 함수 또는 리터럴 표기법으로 객체를 생성하면 프로토타입은 생성된 객체의 [[Prototype]] 내부 슬롯에 할당된다.
19.6 객체 생성 방식과 프로토타입의 결정
- 객체의 프로토타입은 추상 연산 OrdinaryObjectCreate 에 전달되는 인수에 의해 결정된다. 이 인수는 객체가 생성되는 시점에 객체 생성 방식에 의해 결정된다.
19.6.1 객체 리터럴에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
- JS 엔진이 객체 리터럴을 평가하여 객체를 생성할 때 OrdinaryObjectCreate 를 호출한다. 이때 전달되는 프로토타입은 Object.prototype 이다. 즉, 생성되는 객체의 프로토타입은 Object.prototype 이다.
//obj가 객체 리터를을 통해 생성되었고 이 객체 리터럴은 내장된 object 생성자 함수에 의해 생성되었다.
const obj = { x: 1 };
console.log(obj.constructor === Object); // true
//obj가 x 라는 속성을 가지고 있음
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty('x')); // true19.6.2 Object 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
- Object 생성자 함수를 호출하면 객체 리터럴과 마찬가지로 OrdinaryObjectCreate 를 호출된다. 이때 전달되는 프로토타입은 Object.prototype 이다.
- 객체 리터럴과의 차이는 프로퍼티를 추가하는 방식이다. 객체 리터럴은 리터럴 내부에 프로퍼티를 추가하지만 Object 생성자 함수 방식은 일단 빈 객체를 생성한 이후 프로퍼티를 추가한다.
//obj 객체는 object 생성자 함수에 의해 생성되었다. constructor 프로퍼티는 object를 가르킨다.
//obj 역시 x 라는 속성을 가지고 있음
const obj = new Object();
obj.x = 1;
console.log(obj.constructor === Object); // true
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty('x')); // true19.6.3 생성자 함수에 의해 생성된 객체의 프로토타입
- new 연산자와 함께 생성자 함수를 호출하여 인스턴스를 생성하면 다른 객체 생성 방식과 마찬가지로 OrdinaryObjectCreate 를 호출된다. 이때 전달되는 프로토타입은 생성자 함수의 prototype 프로퍼티에 바인딩 되어있는 객체다.
- Object 생성자 함수와 더불어 생성된 프로토타입 Object.prototype 은 다양한 빌트인 메서드를 가지고 있지만 사용자 정의 생성자 함수로 생성된 프로토타입의 프로퍼티는 constructor 뿐이다.
// Person 생성자 함수 정의
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
//sayHello 메서드를 Person의 프로토타입에 추가
Person.prototype.sayHello = function() {
console.log(`hi my name is ${this.name}`);
}
//me 라는 객체를 Person 생성자 함수를 통해 만들고
const me = new Person('PPP');
//sayHello 메서드를 호출!
me.sayHello(); // hi my name is PPP