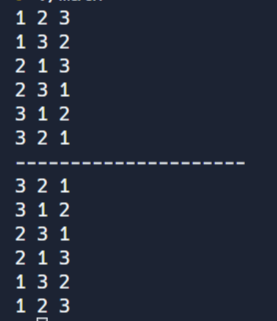
오름차순으로 순열 뽑기 : next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end());
내림차순으로 순열 뽑기 : prev_permutation(v.begin(), v.end());
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void printV(vector<int> &v) {
for(int i = 0; i < v.size(); i++) {
cout << v[i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
int a[3] = { 1, 2, 3 };
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 0 ; i < 3; i++) v.push_back(a[i]);
do {
printV(v);
// 1, 2, 3 부터 오름차순으로 순열을 뽑습니다.
}while(next_permutation(v.begin(), v.end()));
cout << "--------------------- " << "\n";
v.clear();
for(int i = 2; i >= 0; i--) v.push_back(a[i]);
do {
printV(v);
// 3, 2, 1부터 내림차순으로 순열을 뽑습니다.
}while(prev_permutation(v.begin(), v.end()));
return 0;
}
2. 조합의 구현
(1) 재귀 함수 이용하기
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
int n = 5, k = 3, a[5] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
using namespace std;
void print(vector<int> b) {
for(int i : b) cout << i << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
void combi(int start, vector<int> b) {
if(b.size() == k) {
print(b);
return;
}
for(int i = start+1; i < n; i++) {
b.push_back(i);
combi(i, b);
b.pop_back();
}
return;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> b;
combi(-1, b);
return 0;
}3. 소수판별 - 에라토스테네스의 체
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
bool check(int n) {
if(n <= 1) return 0;
if(n == 2) return 1;
if(n%2 == 0) return 0;
for(int i = 2; i*i <= n; i++) {
if(n%i == 0) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
if(check(i)) {
cout << i << " 는 소수입니다. \n";
}
}
return 0;
}2. 코딩테스트에 나오는 필수로직
1) lower_bound과 upper_bound
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> v;
int a[5] = { 1, 2, 2, 2, 3 };
for(int i = 0 ; i < 5; i++) v.push_back(a[i]);
int x = 2;
int c = (int)(upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x)-(lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x)));
int f = (int)(lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x) - v.begin());
int t = (int)(upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x) - v.begin());
int f2 = *lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
int t2 = *upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), x);
cout << x << "의 갯수 : " << c << ", 시작되는 점 : "
<< f << ", 끝나는 점 : " << t << "\n";
cout << "lower_bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : " << f2 <<
", upper_bound가 시작되는 점의 값 : " << t2 << "\n";
}#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// upper_bound : 어떤 값의 "이상이 되는 위치" 반환
// lower_bound : 그 값이 시작되기 전의 위치 반환
// 시간 복잡도 : O(nlogn)
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 2; i <= 5; i++) v.push_back(i);
v.push_back(7);
// v = { 2, 3, 4, 5, 7 }
cout << upper_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 6) - v.begin() << "\n"; //7의 위치: 4
cout << lower_bound(v.begin(), v.end(), 6) - v.begin() << "\n"; //5의 위치 : 4
return 0;
}2) 시계방향 회전과 반시계방향 회전, rotate()
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//시계방향, 반시계방향 회전 rotate()함수
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 1; i < 10; i++) v.push_back(i);
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
//rotate(v.begin(), v.begin()+1, v.end());
// 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 앞으로 갈땐 이렇게
rotate(v.begin(), v.begin()+ v.size()-1, v.end());
// 9 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 뒤로 갈떈 이렇게
for(vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it!=v.end(); it++) {
cout << ' ' << *it;
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;`
3) 배열 중 가장 큰 요소를 출력하는 함수, max_element()
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// max_element() :: 배열 중 가장 큰 요소를 출력하는 함수
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> v = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9,10};
cout << *max_element(v.begin(), v.end());
return 0;
}4) 진법 변환
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL); cout.tie(NULL);
vector<int> v;
int n = 100;
int b = 2;
while(n > 1) {
v.push_back(n % b);
n /= b;
}
if(n == 1) v.push_back(1);
reverse(v.begin(), v.end());
for(int a : v) {
if(a>=10) cout << char(a+55);
else cout << a;
}
}