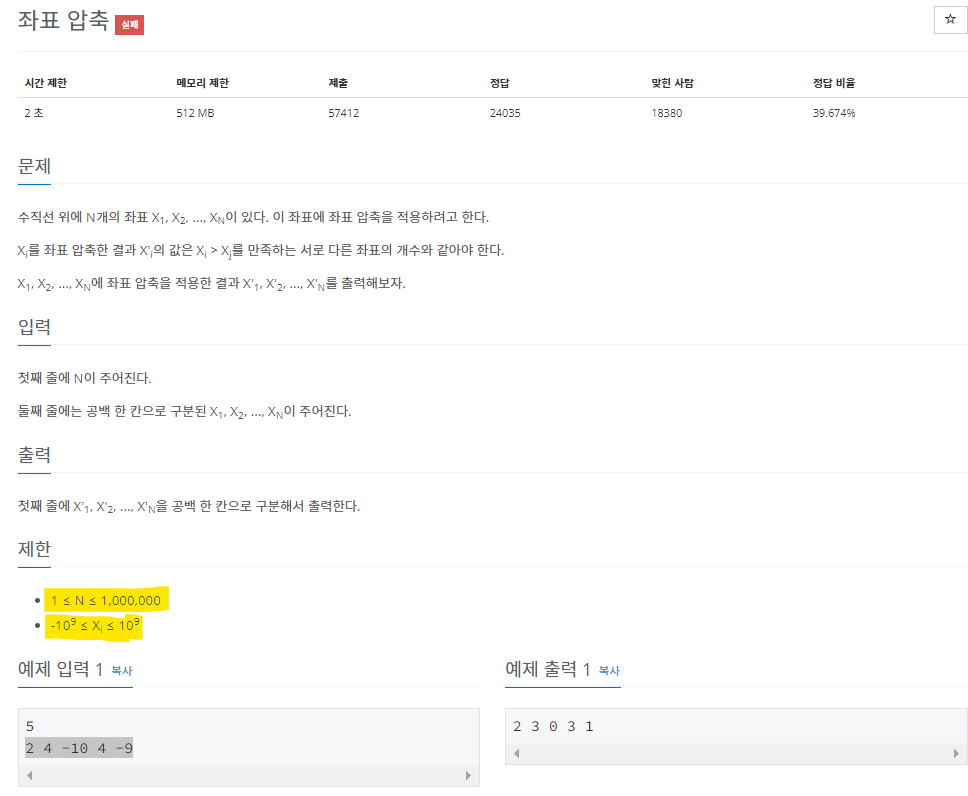
(노란색 형광펜:들어오는 수의 범위는 중요하므로 꼭 내가 표현하고자 하는 자료형의 범위를 넘어서지는 않은지 꼭 확인하자.)
이 문제는 나보다 작은 것의 개수를 구하는 것이다.
그래서 중복을 제거한 뒤 나열하면
그 값의 인덱스가 그 값보다 작은 것의 개수가 된다.
예를 들어
2 4 -10 4 -9 -> 중복을 제거하여 나열 -> -10 -9 2 4
따라서 -10보다 작은거 0개이므로 index 0
-9보다 작은거 1개이므로 index 1
이런식으로 하려고 했다.
- 중복을 제거하고 크기 순으로 나열된 TreeMap에 키값으로 값들을 넣는다
- Key 값들을 set에 옮기는 map.keySet()함수를 이용하고 이를 다루기 쉽게 list에 저장
- 구하고자 하는 값들을 list의 indexOf를 통해서 넣고 검색하여 index 번호를 반환하려는 계획었으나
하면서도 너무 비효율적이라는 생각은 했다.
시간초과가 나왔다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
//중복을 제거 및 크기 순 나열을 위해 TreeMap에 저장
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
//진짜 들어온 값들을 저장
int[] arr = new int[N];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
map.put(a,1);
arr[i]=a;
}
// 중복이 없고 크기 순으로 나열된 key 값들을 뽑기
Set<Integer> keyset = map.keySet();
Iterator it = keyset.iterator();
//set을 효율적으로 이용하기 위해 list에 넣기
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while(it.hasNext()){
list.add((Integer)it.next());
}
//list의 인덱스가 찾고자 하는 정답
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
bw.write(Integer.toString(list.indexOf(arr[i]))+" ");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}풀이를 보니까 문제를 잘 접근을 했지만 중간에 더 효율적으로 할 수 있는 방법이 존재했다.
- 중복을 제거하고 크기 순으로 나열된
TreeMap에 키값으로 값들을 넣는다
2. Key 값들을 set에 옮기는 map.keySet()함수를 이용하고 이를 다루기 쉽게 list에 저장
3. 구하고자 하는 값들을 list의 indexOf를 통해서 넣고 검색하여 index 번호를 반환하려는 계획었으나
TreeMap이 아니라 그냥 HashMap을 이용하는 것이었다.
- 그냥 array와 정렬된 sorted_array를 만들어준다.
- sorted_array의 값들을 인덱스 순서대로 HashMap에 넣어주되, 값으로 rank를 넣어주는 것이다. rank는 하나씩 증가한다. 단, sorted_array에 중복된 값이 꺼내질 경우에는 무시해야 한다.
이 과정으로 진행된다.
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
int N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
int[] arr = new int[N];
int[] sorted_arr = new int[N];
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()," ");
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
int a = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
arr[i]=sorted_arr[i]=a;
}
Arrays.sort(sorted_arr);
Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int rank=0;
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
map.put(sorted_arr[i],rank);
if(i<=N-2 &&sorted_arr[i]!=sorted_arr[i+1]) {
rank++;
}
}
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
bw.write(Integer.toString(map.get(arr[i]))+" ");
}
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
}HashMap에 키 값들으 크기 순으로 저장하고 그 키에 대한 값으로 rank를 넣어주자
중복된 값에 대해서 들어오지 못하도록 아래와 같은 풀이도 가능하다.
if(!rankingMap.containsKey(v)) {
rankingMap.put(v, rank);
rank++;
}