Quick Sort 알고리즘이란?
Quick sort란, 임의의 무작위 배열을 sorting하는 함수의 일종으로, comparison을 기반으로 제작되었다.
시간 복잡도는 comparison을 기반으로 한 함수의 최소인 O(n logn)이다. (one average)
Input : array of n numbers, unsorted
Output : same numbers, sorted in increasing order
Quick Sort 함수는 크게 2개로 나눌 수 있다.
- Partitioning O(n)
- Quick Sort recursive
1은 선택한 pivot을 기준으로 나누는 것이고, 2는 1을 이용하여 재귀 함수를 작동시키는 것이다.
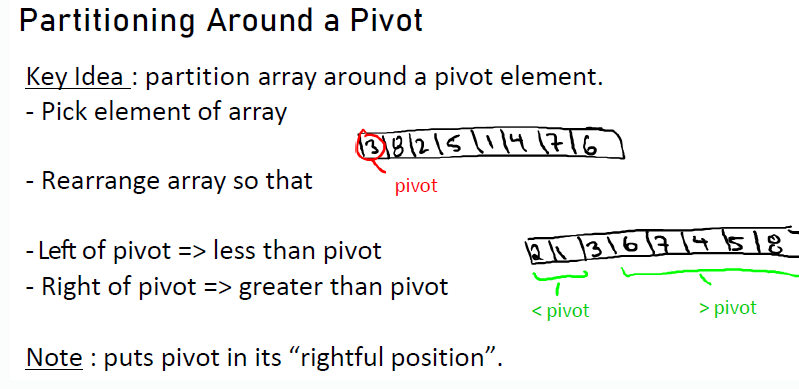
Partitioning 예시
Partition이 적절히 되었다면 다음과 같이 될 것이다. p는 pivot이다.
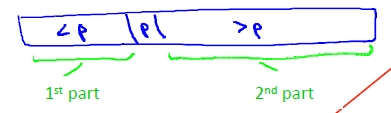
이 과정을 좌, 우에 적용하여 recursive하게 작동시킨다.
Running time
최악의 경우, Running time은 θ(n^2)가 될 것이다. 그 이유는, 이미 정렬된 함수의 경우 한 element마다 매번 recursive가 작동되어
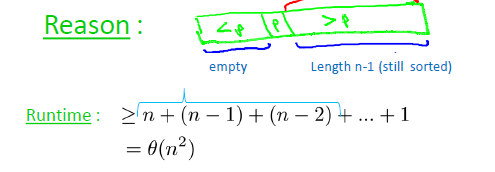
다음과 같은 결과가 나타난다.
이상적인 결과는, pivot이 median이 선택되어 θ(nlogn)의 작동이 되는 것이다.
median인 경우는 T(n) <= 2T(n/2) + θ(n)으로 Master's method에 의해 θ(nlogn)이 될 것이다.
위의 과정들을 보면, pivot을 고르는 것이 실행 시간에 매우 큰 영향을 주는 것을 알 수 있다.
Pivot 선택 과정은 보통 처음 원소를 pivot으로, 혹은 맨 끝 원소를 pivot으로 하는 것이다. 사실 이는 실행 시간을 거의 운에 맡겼다 할 수 있다. 이를 보완하기 위해 Median of three라는 방법이 있다.
Median of three란, 처음 원소, 마지막 원소, 그리고 중간 원소 중 중간값을 pivot으로 하는 것이다. 그러면 기존의 방식보다는 같거나 더 빨라질 것이다.
여기서 속도를 더 높이려면, 세 원소 중 중간값을 택하고, 세 원소를 각 자리에서 순서에 맡게 정렬하는 것이다. 그러면 후에 partition할 때, 적어도 세 원소는 이미 partition된 상태이기에 Recursive 단계의 깊이를 낮출 수 있다.
구현
// set compare number as global variable
int cmp_first=0;
int cmp_end=0;
int cmp_median=0;
int cmp_random=0;
// find pivot function, returns location of pivot in array
int find_pivot(int *arr, int pivot, int l, int r)
{
int i;
// from l to r, interval that I want to know
for(i=l; i<=r; i++)
{
// if same
if(arr[i]==pivot)
{
// return location
return i;
}
}
return 0;
}
// partition function, use pivot, can use when there is duplicate variable
// return compare number
int partition(int pivot, int *arr, int l, int r)
{
int cmp=0;
int i = l+1, j;
int tmp;
for(j=l+1; j<=r; j++)
{
cmp+=1;
// if small
if(arr[j]<pivot)
{
// swap
tmp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[i];
arr[i] = tmp;
i+=1;
}
// if same or big, just do nothing
}
// swap
tmp = arr[i-1];
arr[i-1] = arr[l];
arr[l] = tmp;
// return compare number
return cmp;
}
// use first variable of array as pivot
void quickA_first(int *arr, int len, int l, int r)
{
// if length of array == 1 return
if(len==1)
{
return;
}
//set pivot as first variable
int pivot = arr[l];
// add compare number
cmp_first+=partition(pivot, arr, l, r);
// find location of pivot to manage small case
int p = find_pivot(arr, pivot, l, r);
// if pivot is left most, just do right side
if(p==l)
{
quickA_first(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
// if pivot is right most, just do left side
else if(p==r)
{
quickA_first(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
return;
}
// if pivot is in middle, do both side
else
{
quickA_first(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
quickA_first(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
return;
}
// almost same as quickA_first, so I will write comment in different seciton
// use last variable of array as pivot
void quickA_end(int *arr, int len, int l, int r)
{
if(len==1)
{
return;
}
// set pivot as last one
int pivot = arr[r];
// for simplicity, I used same algorithm as quickA_start
// so just change first and last pivot, then first one became pivot, and do same algorithm as quickA_first
int tmp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[r];
arr[r] = tmp;
cmp_end+=partition(pivot, arr, l, r);
int p = find_pivot(arr, pivot, l, r);
if(p==l)
{
quickA_end(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
else if(p==r)
{
quickA_end(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
return;
}
else
{
quickA_end(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
quickA_end(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
return;
}
// almost same as quickA_first, so I will write comment in different seciton
// use random variable of array as pivot, do 10 times in performance and divide for average number
void quickA_random(int *arr, int len, int l, int r)
{
if(len==1)
{
return;
}
// choose random variable as pivot
int random = rand()%len + l;
int pivot = arr[random];
// swap with first element to use first_element algorithm
int tmp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[random];
arr[random] = tmp;
cmp_random+=partition(pivot, arr, l, r);
int p = find_pivot(arr, pivot, l, r);
if(p==l)
{
quickA_random(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
else if(p==r)
{
quickA_random(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
return;
}
else
{
quickA_random(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
quickA_random(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
return;
}
// almost same as quickA_first, so I will write comment in different seciton
// use median variable of array as pivot, to choose median variable, use 3 element and compare each other
void quickA_median(int *arr, int len, int l, int r)
{
if(len==1)
{
return;
}
// finding median
int median;
// in assignment paper, find middle varaible like this
if(len%2==0)
{
median = arr[l+len/2-1];
}
else
{
median = arr[l+(len-1)/2];
}
int pivot;
// set each variable for convenience
int a = arr[l];
int b = median;
int c = arr[r];
// find median by comparing
if (a > b)
{
if (b > c)
{
pivot = b;
}
else
{
if (a > c)
{
pivot = c;
}
else
{
pivot = a;
}
}
}
else
{
if (a > c)
{
pivot = a;
}
else
{
if (b > c)
{
pivot = c;
}
else
{
pivot = b;
}
}
}
// find pivot
int max_position = find_pivot(arr, pivot, l, r);
// if median is just first element, we don't need to swap
if(max_position!=l)
{
int tmp = arr[l];
arr[l] = arr[max_position];
arr[max_position] = tmp;
}
cmp_median+=partition(pivot, arr, l, r);
int p = find_pivot(arr, pivot, l, r);
if(p==l)
{
quickA_median(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
else if(p==r)
{
quickA_median(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
return;
}
else
{
quickA_median(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
quickA_median(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
return;
}위 함수들은 기본적인 Quick Sort를 first element로 만들고 변형한 것이다. 비교 횟수를 보기 위해 출력란에 cmp를 출력한다. 이를 위해 전역 변수인 cmp_*를 설정했다.
이번에는 Quick Sort의 속도를 개선했다.
// same with quickA_median, but make length minimum as 3
void quickB(int *arr, int len, int l, int r)
{
if(len==1)
{
return;
}
// if len ==2, just compare and swap
if(len==2)
{
if(arr[l]>arr[r])
{
int temp2 = arr[l];
arr[l]=arr[r];
arr[r]=temp2;
}
return;
}
// if len==3, compare and swap
if(len==3)
{
int a1 = arr[l];
int b1 = arr[l+1];
int c1 = arr[r];
if (a1 > b1)
{
if (b1 > c1)
{
int temp3 = arr[l];
arr[l]=arr[r];
arr[r]=temp3;
return;
}
else
{
if (a1 > c1)
{
int temp4 = arr[l];
int temp5 = arr[l+1];
arr[l+1]=arr[r];
arr[l]=temp5;
arr[r]=temp4;
return;
}
else
{
int temp6 = arr[l];
arr[l]=arr[l+1];
arr[l+1]=temp6;
return;
}
}
}
else
{
if (a1 > c1)
{
int temp7 = arr[l];
int temp8 = arr[l+1];
arr[l]=arr[r];
arr[l+1]=temp7;
arr[r]=temp8;
return;
}
else
{
if (b1 > c1)
{
int temp9 = arr[r];
arr[r]=arr[l+1];
arr[l+1]=temp9;
return;
}
else
{
return;
}
}
}
return;
}
// same with quickA_median function
int median;
int median_position;
if(len%2==0)
{
median = arr[l+len/2-1];
median_position = l+len/2-1;
}
else
{
median = arr[l+(len-1)/2];
median_position = l+(len-1)/2;
}
int pivot;
int a = arr[l];
int b = median;
int c = arr[r];
if (a > b)
{
if (b > c)
{
pivot = b;
arr[l]=c;
arr[median_position]=b;
arr[r]=a;
}
else
{
if (a > c)
{
pivot = c;
arr[l]=b;
arr[median_position]=c;
arr[r]=a;
}
else
{
pivot = a;
arr[median_position]=a;
arr[l]=b;
}
}
}
else
{
if (a > c)
{
pivot = a;
arr[l]=c;
arr[median_position]=a;
arr[r]=b;
}
else
{
if (b > c)
{
pivot = c;
arr[median_position]=c;
arr[r]=b;
}
else
{
pivot = b;
}
}
}
// so l, median, r are already sorted
// arr[l]<median, so we just need to swap l+1 element and median
int tmp = arr[l+1];
arr[l+1] = arr[median_position];
arr[median_position] = tmp;
// first and last one are already partitioned
partition(pivot, arr, l+1, r-1);
int p = find_pivot(arr, pivot, l+1, r-1);
// do recursive
if(p==l+1)
{
quickB(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
else if(p==r-1)
{
quickB(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
return;
}
else
{
quickB(arr, p-l, l, p-1);
quickB(arr, r-p, p+1, r);
return;
}
return;
}기존의 quickA_median에서 len==3을 최소 case로 처리하고, 앞서 언급했듯이 partition의 깊이를 얕게 만들었다. c언어는 내장 qsort() 함수가 있다. 내가 만든 Quick Sort와 1000만 줄짜리 input2.txt를 비교하면 속도는 다음과 같다.
~$ ./quickB mine < input2.txt > out1
It took 1.051 seconds
~$ ./quickB crt < input2.txt > out2
It took 1.053 seconds
quickB mine, crt는 argv로 옵션을 추가한 것이다. mine이 내가 만든 Quick Sort, crt가 내장 qsort()이다. 결과는 내가 0.002초로 빨랐다.
물론 거의 차이 안 나는 것 같지만, 실제로는 웬만한 input의 경우 출력하면 보통 0.000초가 뜬다. (.3f) 즉, 0.002초는 상당한 차이라는 것이다.
+) argv 처리 방법
argv는 strcmp로 처리해야 한다.
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
~
if(strcmp(argv[1], "mine")==0)
~
}이런 식으로 strcmp를 사용하면 된다. 물론 <string.h>를 include 해줘야 한다.