알아두면 좋은 개념
- 이진트리 : 각 노드가 최대 두 개의 자식을 갖는 트리 즉 자식이 없거나 한 개 이거나 두 개만을 갖는다.
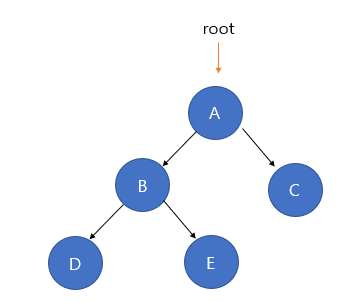
트리의 순회는 알고리즘 파트에 정리해뒀다.
- 완전 이진트리 : 마지막 레벨을 제외하고 모든 레벨이 완전히 채워져 있는 트리이다. 노드는 왼쪽 자식 노드부터 채워져야한다.
힙(Heap)
- 우선순위 큐를 구현하는 밑받침이 되는 자료구조로 완전 이진 트리의 형태를 지닌다.
- 최대 힙 : 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 크거나 같은 완전 이진트리.
- 최소 힙 : 부모 노드의 키 값이 자식 노드의 키 값보다 작거나 같은 완전 이진트리.
힙(Heap)의 구현
- 힙을 저장하는 표준적인 자료구조는 배열이다.
- 구현의 편의성을 위해 첫 번째 인덱스인 0은 사용하지 않는다.
- 특정 위치의 노드 번호는 새로운 노드가 추가되어도 변하지 않는다.
- 힙에서의 부모 노드와 자식 노드의 관계는 다음과 같다.
- 왼쪽 자식의 인덱스 = 부모의 인덱스 * 2
- 오른쪽 자식의 인덱스 = 부모의 인덱스 * 2 + 1
- 부모의 인덱스 = 자식의 인덱스 / 2
- js로 치면
Math.floor(i/2)
위 사항을 고려하여 구현된 기능
class Heap {
constructor() {
// 배열 형태의 heap
// 첫 번째 인덱스(0번 인덱스)는 null 값을 넣어뒀다.
this.heap = [ null ];
}
}삽입
- 힙에 새로운 요소가 들어오면 새로운 노드를 힙의 마지막 노드에 삽입한다.
- 새로운 노드를 부모 노드들과 교환해서 힙의 성질을 만족 시킨다.
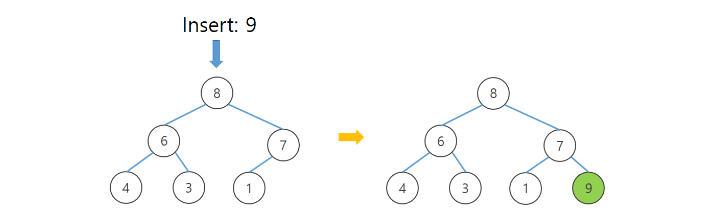
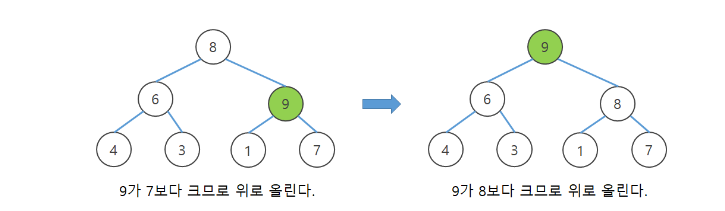
...
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
let cur = this.heap.length-1; // 마지막 요소
let parent = Math.floor(cur / 2); // 삽입된 노드의 부모의 부모요소
// 추가한 값보다 부모 노드의 값이 더 큰 값이 나올 때 까지 root를 향해 Swap해간다.
while(cur > 1 && this.heap[parent] < this.heap[cur]) {
[this.heap[parent], this.heap[cur]] = [this.heap[cur], this.heap[parent]];
cur = parent;
parent = Math.floor(cur / 2);
}
}삭제
- 루트 노드를 삭제한다.
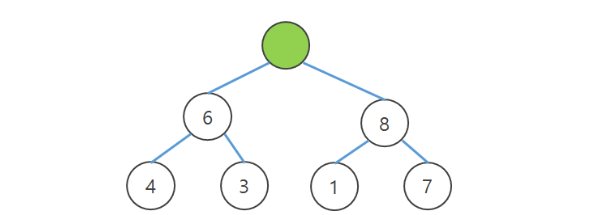
- 루트에 가장 큰 수가 오도록 swap한다.
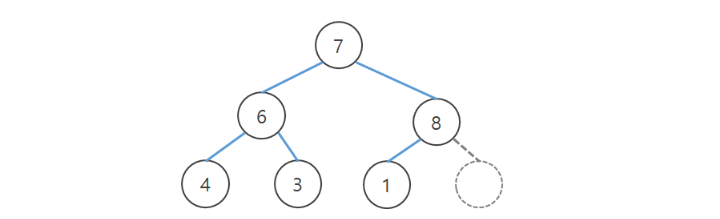
- 마지막 노드의 값을 루트 노드에 넣는다.

...
pop() {
const max = this.heap[1]; // 배열 첫 원소를 비워두므로 root는 heap[1]에 항상 위치한다.
if (this.heap.length <= 2) this.heap = [null];
else this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
// 배열 마지막 원소를 root 위치에 먼저 배치하는 과정이다.
// if-else로 분기되는 이유는 추후 heap이 비었는지 아닌지 확인하기 위해 size 체크 함수를 만들때 -1을 통해 0을 만들어주기 때문.
let curIdx = 1;
let leftIdx = curIdx * 2;
let rightIdx = curIdx * 2 + 1;
// 왼쪽 자식이 없다면 오른쪽 자식도 없는 것(완전 이진 트리)
if (!this.heap[leftIdx]) return max;
// 오른쪽 자식은 없고 왼쪽 자식만 있는 경우
if (!this.heap[rightIdx]) {
// 왼쪽 자식이 부모보다 크다면 swap
if (this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[curIdx]) {
[this.heap[leftIdx], this.heap[curIdx]] = [this.heap[curIdx], this.heap[leftIdx]];
}
return max;
}
// 위 두번의 경우에서 걸러지지 않았다면 왼쪽, 오른쪽 자식이 다 있는 것.
while (
this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[curIdx] ||
this.heap[rightIdx] > this.heap[curIdx]
) {
// 왼쪽 과 오른쪽 중 큰 값의 인덱스
const maxIdx = this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[rightIdx] ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
[this.heap[maxIdx], this.heap[curIdx]] = [this.heap[curIdx], this.heap[maxIdx]];
curIdx = maxIdx;
leftIdx = curIdx * 2;
rightIdx = curIdx * 2 + 1;
}
return max;
}
전체 코드
- 다른 부가적인 기능을 추가한 전체 코드
- 최대 힙
class MaxHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [null];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length - 1;
}
getMax() {
return this.heap[1] ? this.heap[1] : null;
}
swap(a, b) {
[this.heap[a], this.heap[b]] = [this.heap[b], this.heap[a]];
}
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
let curidx = this.heap.length - 1;
let parentidx = Math.floor(curidx / 2);
while (curidx > 1 && this.heap[parentidx] < this.heap[curidx]) {
[this.heap[parentidx], this.heap[curidx]] = [
this.heap[curidx],
this.heap[parentidx],
];
curidx = parentidx;
parentidx = Math.floor(curidx / 2);
}
}
pop() {
const max = this.heap[1];
if (this.heap.length <= 2) this.heap = [null];
else this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
let curIdx = 1;
let leftIdx = curIdx * 2;
let rightIdx = curIdx * 2 + 1;
if (!this.heap[leftIdx]) return max;
if (!this.heap[rightIdx]) {
if (this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[curIdx]) {
[this.heap[leftIdx], this.heap[curIdx]] = [
this.heap[curIdx],
this.heap[leftIdx],
];
}
return max;
}
while (
this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[curIdx] ||
this.heap[rightIdx] > this.heap[curIdx]
) {
const maxIdx =
this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[rightIdx] ? leftIdx : rightIdx;
[this.heap[maxIdx], this.heap[curIdx]] = [
this.heap[curIdx],
this.heap[maxIdx],
];
curIdx = maxIdx;
leftIdx = curIdx * 2;
rightIdx = curIdx * 2 + 1;
}
return max;
}
}
- 최소 힙
class MinHeap {
constructor() {
this.heap = [ null ];
}
size() {
return this.heap.length - 1;
}
getMin() {
return this.heap[1] ? this.heap[1] : null;
}
swap(a, b) {
[ this.heap[a], this.heap[b] ] = [ this.heap[b], this.heap[a] ];
}
insert(value) {
this.heap.push(value);
let curIdx = this.heap.length - 1;
let parIdx = (curIdx / 2) >> 0;
while(curIdx > 1 && this.heap[parIdx] > this.heap[curIdx]) {
this.swap(parIdx, curIdx)
curIdx = parIdx;
parIdx = (curIdx / 2) >> 0;
}
}
pop() {
const min = this.heap[1];
if(this.heap.length <= 2) this.heap = [ null ];
else this.heap[1] = this.heap.pop();
let curIdx = 1;
let leftIdx = curIdx * 2;
let rightIdx = curIdx * 2 + 1;
if(!this.heap[leftIdx]) return min;
if(!this.heap[rightIdx]) {
if(this.heap[leftIdx] < this.heap[curIdx]) {
this.swap(leftIdx, curIdx);
}
return min;
}
while(this.heap[leftIdx] < this.heap[curIdx] || this.heap[rightIdx] < this.heap[curIdx]) {
const minIdx = this.heap[leftIdx] > this.heap[rightIdx] ? rightIdx : leftIdx;
this.swap(minIdx, curIdx);
curIdx = minIdx;
leftIdx = curIdx * 2;
rightIdx = curIdx * 2 + 1;
}
return min;
}
}- 부모 노드의 요소가 자식 노드의 요소보다 작게 설정된다.